San Joaquin Valley
| San Joaquin Valley | |
|---|---|
 San Joaquin Valley | |
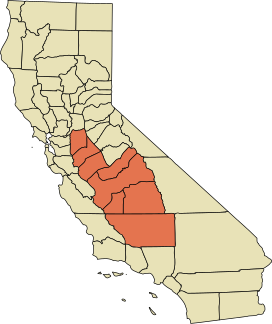 A map of the counties encompassing the San Joaquin Valley ecoregion | |
| Naming | |
| Native name | Spanish: Valle de San Joaquín |
| Geography | |
| Location | California, United States |
| Population centers | Stockton, Tulare, Porterville, Modesto, Turlock, Merced, Fresno, Visalia, Bakersfield, Clovis and Madera. |
| Borders on | Sierra Nevada (east), Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta (north), Coast Range, San Francisco Bay (west), Tehachapi Mountains (south) |
| Coordinates | 36°37′44″N 120°11′06″W / 36.62889°N 120.18500°WCoordinates: 36°37′44″N 120°11′06″W / 36.62889°N 120.18500°W |
| Traversed by | Interstate 5, State Route 99 |
| Rivers | San Joaquin River |
The San Joaquin Valley (/ˌsæn hwɑːˈkiːn/ SAN whah-KEEN) is the area of the Central Valley of the U.S. state of California that lies south of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and is drained by the San Joaquin River. It comprises seven counties of Northern and one of Southern California, including, in the north, all of San Joaquin and Kings counties, most of Stanislaus, Merced, and Fresno counties, and parts of Madera and Tulare counties, along with a majority of Kern County, in Southern California.[1] Although the valley is predominantly rural, it does contain urban centers such as Fresno, Bakersfield, Stockton, Modesto, Tulare, Visalia, and Merced.
The San Joaquin Valley was originally inhabited by the Yokuts and Miwok peoples. The first European to enter the valley was Pedro Fages in 1772.[2]
Geography[]

This section does not cite any sources. (April 2021) |
The San Joaquin Valley extends from the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta in the north to the Tehachapi Mountains in the south, and from the various California coastal ranges (from the Diablo Range in the north to the Temblor Range in the south) in the west to the Sierra Nevada in the east. Unlike the Sacramento Valley, the river system for which the San Joaquin Valley is named does not extend very far along the valley. Most of the valley south of Fresno, instead, drains into Tulare Lake, which no longer exists continuously due to diversion of its sources. The valley's primary river is the San Joaquin, which drains north through about half of the valley into the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta. The Kings and Kern Rivers are in the southern endorheic basin of the valley, all of which have been largely diverted for agricultural uses and are mostly dry in their lower reaches.
Geological history[]
The San Joaquin Valley began to form about 66 million years ago during the early Paleocene era. Broad fluctuations in the sea level caused various areas of the valley to be flooded with ocean water for the next 60 million years. About 5 million years ago, the marine outlets began to close due to uplift of the coastal ranges and the deposition of sediment in the valley. Starting 2 million years ago, a series of glacial episodes periodically caused much of the valley to become a fresh water lake. Lake Corcoran was the last widespread lake to fill the valley about 700,000 years ago. At the beginning of the Holocene there were three major lakes remaining in the southern part of the Valley, Tulare Lake, Buena Vista Lake and Kern Lake. In the late 19th and in the 20th century, agricultural diversion of the Kern River eventually dried out these lakes. Today, only a fragment of Buena Vista Lake remains as two small lakes Lake Webb and Lake Evans in a portion of the former Buena Vista Lakebed.
Climate[]
The San Joaquin Valley has extremely hot, dry summers and pleasantly mild winters characterized by dense tule fog. Its rainy season normally runs from November through April. The valley experienced a severe drought from 2011 to 2017.
In August 2015, the Director of the California Department of Water Resources stated, "Because of increased pumping, groundwater levels are reaching record lows—up to 100 feet lower than previous records."[3] Research from NASA shows that parts of the San Joaquin Valley sank as much as 8 inches (0.20 m) in a four-month period, and land near Corcoran sank 13 inches (0.33 m) in 8 months. The sinking has destroyed thousands of groundwater well casings and has the potential to damage aqueducts, roads, bridges, and flood-control structures. In the long term, the subsidence caused by extracting groundwater could irreversibly reduce the underground aquifer's water storage capacity, although immediate and short term needs are given higher priority and sense of urgency than long term sustainability.[3][4]
The National Weather Service Forecast Office for the San Joaquin Valley is located in Hanford and includes a Doppler weather radar. Weather forecasts and climatological information for the San Joaquin Valley are available from its official website.[5]
Demographics[]
The total population of the eight counties comprising the San Joaquin Valley at the time of the 2011-2015 American Community Survey 5-year Estimates by United States Census Bureau reported a population of 4,080,509.[6] The racial composition of San Joaquin Valley was 2,775,074 (68.0%) White, 2,048,280 (50.2%) Hispanic or Latino, 310,557 (7.6%) Asian, 193,694 (4.7%) Black or African American, 40,911 (1.0%) American Indian and Alaska Native, and 13,000 (0.32%) Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander.[6]
The educational attainment of high school graduate or higher is 72.7%.[6]
Agriculture[]

The San Joaquin Valley produces the majority of the 12.8% of the United States' agricultural production (as measured by dollar value) that comes from California.[7] Grapes—table, raisin, wines, cotton, nuts (especially almonds and pistachios), citrus, and vegetables. Walnuts, oranges, peaches, garlic, tangerines, tomatoes, kiwis, hay, alfalfa and numerous other crops have been harvested with great success. Certain places are identified quite strongly with a given crop: Stockton produces the majority of the domestic asparagus consumed in the United States, and Fresno County is the largest producer of raisins.
Cattle and sheep ranching are also vitally important to the valley's economy. During the late 19th century and early 20th century, the Miller & Lux corporation built an agricultural monopoly centered around cattle. The corporation can be characterized as a precursor to corporate farming transforming the yeoman farmer into wage workers. The success of the business can be attributed to founder Henry Miller's direct management style which is reflected in his detailed correspondences to his subordinates.[8] During recent years, dairy farming has greatly expanded in importance. As areas such as Chino and Corona have become absorbed into the suburban sprawl of Los Angeles, many dairy farmers have cashed out and moved their herds to Kings, Tulare, and Kern counties.
Between 1990 and 2004, 28,092 hectares (70,231 acres) of agricultural land was lost to urban development in the San Joaquin Valley.[9] Although there have been some token efforts at confronting the problems of (sub)urban sprawl, the politically conservative climate of the Valley generally prefers traditional suburban sprawl type of growth such as low density housing and strip malls anchored by so-called big box stores and opposes measures such as "Smart Growth", "Transit Oriented Development", "High Density Housing", and increased public transit such as light and commuter rail. By August 2014, a three-year drought was prompting changes to the agriculture industry in the valley. Farmers began using complex irrigation systems and using treated waste water to feed crops, while many were switching from farming cotton to other commodities, chief among them, almonds.[10]
Petroleum[]


California has long been one of the nation's most important oil-producing states, and the San Joaquin Valley has long since eclipsed the Los Angeles Basin as the state's primary oil production region. Scattered oil wells on small oil fields are found throughout the region, and several enormous extraction facilities – most notably near Lost Hills and Taft, including the enormous Midway-Sunset Oil Field, the third-largest oil field in the United States – are veritable forests of pumps.
Shell operated a major refinery in Bakersfield; it was sold in 2005 to Flying J, a Salt Lake-based firm that operates truck stops and refineries. Flying J's bankruptcy in 2009 resulted in the refinery being shut down.[11]
The oil and gas fields in Kern County are receiving increased attention since the July 2009 announcement by Occidental Petroleum of significant discovery of oil and gas reserves[12] Even prior to this discovery the region retains more oil reserves than any other part of California. Of California fields outside of the San Joaquin Valley, only the Wilmington Oil Field in Los Angeles County has untapped reserves greater than 100,000,000 barrels (16,000,000 m3), while six fields in the San Joaquin Valley (Midway-Sunset, Kern River, South Belridge, Elk Hills, Cymric, and Lost Hills) each have reserves exceeding 100,000,000 barrels (16,000,000 m3) of oil.[13]
Culture[]
The San Joaquin Valley has been a major influence in American country, soul, nu metal, R&B, and hip hop music particularly through the Bakersfield Sound, the Doowop Era, and the Bakersfield Rap Scene, also referred to as Central California Hip Hop, Central Valley Hip Hop, or Central California Rap, which are all subgenres of Gangsta rap, Bass-Rap, West Coast G-funk, and West Coast Hip hop which are all different styles of West Coast Rap.[14] The Valley has been the home to many country, nu metal, and doo-wop musicians and singers, such as Buck Owens, Merle Haggard, Billy Mize, Korn, Red Simpson, Dennis Payne, The Maddox Brothers and Rose, The Paradons, The Colts, and the Sons of the San Joaquin.[15] The San Joaquin Valley is also home to many Indie Hip Hop labels, R&B singers, Jazz & Funk musicians, and Hip Hop artist such as: Fashawn, Killa Tay, The Def Dames, Cali Agents, Planet Asia.[16] The Valley also has a strong literary tradition, heavy in poetry, producing many famous poets such as Sherley Anne Williams, and Gary Soto, current U.S. Poet Laureate Juan Felipe Herrera, and David St. John.[17] An MFA Creative Writing program started by former US Poet Laureate Philip Levine, resides at Fresno State, continuing to cultivate the region's literary talent.
Other major industries and employers[]
The isolation and vastness of the San Joaquin Valley, as well as its poverty and need for jobs, have led the state to build numerous prisons in the area. The most notable of these is Corcoran, whose inmates have included Charles Manson and Juan Corona. Other correctional facilities in the valley are at Avenal, Chowchilla, Tracy, Delano, Coalinga, and Wasco.
The only significant military base in the region is Naval Air Station Lemoore, a vast air base located 25 kilometres (16 mi) WSW of Hanford. Unlike many of California's other military installations, NAS Lemoore's operational importance has increased in the 1990s and 2000s. The other, Castle Air Force Base, located near Atwater was closed during the Base Realignment and Closure of the 1990s. Although both are in Kern County, Edwards Air Force Base and China Lake Naval Air Weapons Station are located in the High Desert area of that county.
Poverty[]
The United States Census Bureau issued a report entitled the American Community Survey in 2007, which found that six San Joaquin Valley counties had the highest percentage of residents living below the federal poverty line in 2006 of any counties in California. The report also revealed that the same six counties were among the 52 counties with the highest poverty rate in the United States.[18] The median income for a household in the valley was $46,713.[6] The poverty rate for individuals below the poverty level is 23.7%.[6]
Ethnic and cultural groups[]
Latinos/Hispanics, Chicanos and Mexicans[]

Currently, the Latino and Mexican descendants are large percentage of the demographics in the San Joaquin Valley. Since not long after the onset of the bracero program during World War II, all but a minor percentage of the farmworkers in the region have been of Mexican ancestry. Ethnic and economic friction between Mexican-Americans and the valley's predominantly white farming elite manifested itself most notably during the 1960s and 1970s, when the United Farm Workers, led by César Chávez, went on numerous strikes and called for boycotts of table grapes. The UFW generated enormous sympathy throughout the United States, even managing to terminate several agricultural mechanization projects at the United States Department of Agriculture. However, from the 1970s onward, landlords and large corporations have also hired undocumented immigrants. This has allowed them to increase their profits due to low overhead on wages.
European and Asian groups[]
The San Joaquin Valley has—by California standards—an unusually large number of European, Middle Eastern, and Asian ethnicities in the heritage of its citizens. These communities are often quite large and, relative to Americans immigration patterns, quite eclectic: for example, there are more Azorean Portuguese in the San Joaquin Valley than in the Azores. Many groups are found in majorities in specific cities, and hardly anywhere else in the region. For example, Assyrians are concentrated in Turlock, Dutch in Ripon, Sikhs in Stockton and Livingston, and Croats[19] in Delano. Kingsburg is famous for its distinctly Swedish air, having been founded by immigrants from that country. Ethnic groups found in a broader area are Portuguese, Armenians, Basques, and the "Okies" who migrated to California from the Midwest and South. Since the early 1970s East Indians of predominantly Punjabi, Gujrati and Southern India have settled in the valley communities. Most recently large numbers of Pakistanis have settled in Modesto and Lodi. In addition, the late 1970s and 80s saw an influx of immigrants from Indochina following the War in Vietnam. These immigrants, the majority of whom are Hmong, Thai, Laotian, Cambodian, and Vietnamese, have settled in the communities of Stockton, Modesto, Merced, and Fresno.
The Filipino American population is concentrated in Delano and Lathrop. Filipinos have a strong history in Stockton. Filipino organizations in Stockton are reflected in various commercial buildings identified as Filipino. Filipinos fought for the U.S. against Japan in WWII, in exchange for favorable immigration status. Stockton has been an adjunct to the San Francisco Bay Area, which was a major military production and transit area during WWII. Filipino emigration to Stockton followed.
These cultures are often the result of established ethnic communities and groups of immigrants coming to the United States at once. This is in part due to the founding of religious communes in the San Joaquin Valley: for example, the first permanent Sikh Gurdwara was founded in Stockton in 1915.
African Americans[]
Colonel Allensworth State Historic Park marks the location of the only California town to be founded, financed and governed by African Americans. The small farming community was founded in 1908 by Lt. Colonel Allen Allensworth, Professor William Payne, William Peck, a minister, John W. Palmer, a miner, and Harry A. Mitchell, a real estate agent, dedicated to improving the economic and social status of African Americans. Uncontrollable circumstances, including a drop in the area's water table, resulted in the town's demise. The "Allensworth Historic District" is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The park is in Allensworth, California, an unincorporated area in Tulare County.
Okies and Arkies[]
The Depression-era migrants to the San Joaquin Valley from the South and Midwest are one of the more well-known groups in the Central Valley, in large part due to the popularity of John Steinbeck's novel The Grapes of Wrath and the Henry Fonda movie made from it. By 1910, agriculture in the southern Great Plains had become nearly unviable due to soil erosion and poor rainfall. Much of the rural population of states such as Kansas, Texas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas left at this time, selling their land and moving to Chicago, Kansas City, Detroit, and fast-growing Los Angeles. Those who remained experienced continuing deterioration of conditions, which reached their nadir during the drought that began in the late 1920s and created the infamous Dust Bowl. (Small cotton farmers in states such as Mississippi and Alabama suffered similar problems from the first major infestation of the boll weevil.) When the onset of the Great Depression created a national banking crisis, family farmers—usually heavily in debt—often had their mortgages foreclosed by banks desperate to shore up their balance sheets. In response, many farmers loaded their families and portable possessions into their automobiles and drove west.
Taking Route 66 to Barstow or Los Angeles and crossing the Tehachapi or Tejon passes, they began new lives as fruit and vegetable pickers on truck farms in the San Joaquin Valley. Having gone from the relative independence of homesteading to a condition that was essentially peasantry, many of them lived in squalid agricultural camps and were deeply unhappy with their economic plight; domestic disputes, crime, and suicide were rampant, and occasional riots broke out. New Deal measures alleviated some of these problems, albeit belatedly: by the time that The Grapes of Wrath drew public attention to the Okies' plight, many of them had already left the valley. Those who didn't were gradually assimilated into California culture and society where many of them and their descendants became noted artists, tradesmen, educators, legislators and professional business people, and their influence remains strong in many parts of the Valley today, especially in the south near Bakersfield.
Many of the Okies and Arkies left the San Joaquin Valley during World War II, most of them going to Los Angeles, San Francisco and San Diego to work in war-related industries. Many of those who stayed ended up in Bakersfield and Oildale, as the southern San Joaquin Valley became an important area of oil production after major Southern California oil fields such as Signal Hill began to dry up. Country music legends Buck Owens and Merle Haggard came out of Bakersfield's honky-tonk scene and created a hard-driving sound that is still deeply associated with the city.
Recent changes[]
The California real estate boom that began in the late 1990s has significantly changed the San Joaquin Valley. Once distinctly and fiercely independent of Los Angeles and San Francisco, the area has seen increasing exurban development as the cost of living forces young families and small businesses further and further away from the coastal urban cores. Stockton, Modesto, Tracy (as well as the nearby unincorporated community of Mountain House), Manteca, and Los Banos are increasingly dominated by commuters to San Francisco and Silicon Valley, and the small farming towns to the south are finding themselves in the Bay Area's orbit as well. Bakersfield, traditionally a boom-bust oil town once described by urban scholar Joel Kotkin as an "American Abu Dhabi," has seen a massive influx of former Los Angeles business owners and commuters, to the extent that gated communities containing million-dollar homes are going up on the city's outskirts. Wal-Mart, IKEA, Target, Amazon, CVS Pharmacy, Restoration Hardware, and other various large shipping firms have built huge distribution centers both in the southern end of the valley and northern part of the valley because of quick access to major interstates and low local wages. Further integration with the rest of the state is likely to continue for the foreseeable future.
Educational institutions[]

- University of California, Merced, Merced
- California State University, Bakersfield, Bakersfield
- California State University, Fresno, Fresno
- California State University, Stanislaus, Turlock
- Fresno Pacific University, Fresno
- University of the Pacific, Stockton
- Humphreys College, Stockton
- Bakersfield College, Bakersfield
- Clovis Community College, Clovis
- Cerro Coso Community College, Kern County and surrounding areas
- College of the Sequoias, Visalia
- Fresno City College, Fresno
- Madera Community College, Madera
- Merced College, Merced
- Modesto Junior College, Modesto
- Porterville College, Porterville
- Reedley College, Reedley
- A.T. Still University, Porterville
- San Joaquin College of Law, Clovis
- San Joaquin Delta College, Stockton
- Taft College, Taft
- West Hills College Coalinga, Coalinga
- West Hills College Lemoore, Lemoore
Transportation[]
Roads[]

Interstate 5 (I-5) and State Route 99 (SR 99) each run along for almost the entire length of the San Joaquin Valley. I-5 runs in the western part of the valley, bypassing the major population centers (including Fresno, currently the largest U.S. city without an Interstate highway), while SR 99 runs through them. Both highways then merge at the southern end of valley en route to Los Angeles. When the Interstate Highway System was created in the 1950s, the decision was made to build I-5 as an entirely then-new freeway bypass instead of upgrading the then-existing U.S. 99. Since then, state and federal representatives have pushed to convert SR 99 to an Interstate, although this cannot occur until all of the portions of SR 99 between I-5 and the U.S. 50 junction in Sacramento are upgraded to Interstate standards.
State Route 58 (SR 58), which is a freeway in Bakersfield and along most of its route until its terminus in Barstow, is an extremely important and very heavily traveled route for truckers from the valley and the Bay Area who want to cross the Sierra Nevada and leave California (by way of Interstate 15 or Interstate 40) without having to climb Donner Pass or brave the traffic congestion of Los Angeles. Proposals have also been made to designate this highway as a western extension of I-40 once the entirety of the route between Mojave and Barstow has been upgraded to a freeway. This would provide an Interstate connection for Bakersfield, currently the second-largest U.S. city without an Interstate. The most recent additions to this system are State Routes 168 and 180. Route 168 begins in Fresno on Route 180 linking to Huntington Lake in the mountains through Clovis and many smaller communities. This route is part of the California Freeway and Expressway System[2] and is eligible for the State Scenic Highway System[3]. State Route 180 is a state highway which runs through the heart of the San Joaquin Valley from Mendota through Fresno to Kings Canyon National Park. A short piece near the eastern end, through the Grant Grove section of Kings Canyon National Park, is not state-maintained. The part east of unbuilt State Route 65 near Minkler is eligible for the State Scenic Highway System; the road east of Dunlap is the Kings Canyon Scenic Byway, a Forest Service Byway.
Other important highways in the valley include State Route 46 (SR 46) and State Route 41 (SR 41), which respectively link the California Central Coast with Bakersfield and Fresno; State Route 33 (SR 33), which runs south to north along the valley's western rim and provides a connection to Ventura and Santa Barbara over the Santa Ynez Mountains; and State Route 152 (SR 152), an important commuter route linking Silicon Valley with its fast-growing exurbs such as Los Banos.
Rail[]
Amtrak provides rail service through the San Joaquin Valley by way of the San Joaquin service, between Bakersfield, Stockton and either Sacramento or Oakland (Amtrak service does not continue south of Bakersfield, as the Union Pacific Railroad does not currently allow the San Joaquin trains to run on the highly congested rail route over Tehachapi Pass, which is the only route between Bakersfield and Los Angeles, so passengers heading south of Bakersfield must take the bus connection to their final destinations). The Coast Starlight, on extremely rare circumstances, passes through the San Joaquin Valley when detours are required due to trackwork on its normal trackage, but does not make any stops.
Pollution[]
Air Pollution[]
Hemmed in by mountains and rarely having strong winds to disperse smog, the San Joaquin Valley has long suffered from some of the United States' worst air pollution. This pollution, exacerbated by stagnant weather, comes mainly from diesel and gasoline fueled vehicles and agricultural operations.[20] Ammonium nitrate, which forms from the combination of vehicle nitrogen oxides (NOx) and ammonia gas contained in cow manure and urine, "accounts for more than half of the region’s PM2.5 on the area’s most polluted days."[20]
Population growth has caused the San Joaquin Valley to rank with Los Angeles and Houston in most measures of air pollution.[21] Only the Inland Empire region east of Los Angeles has worse overall air quality, and the San Joaquin Valley led the nation in 2004 in the number of days with quantities of ozone considered unhealthy by the Environmental Protection Agency.[21] The San Joaquin Valley has been deemed an "extreme non-attainment zone" by the Environmental Protection Agency, meaning residents are exposed to air quality that is confirmed to be hazardous to human health.[22]

Water Pollution[]
Less water is used for irrigation than in the early 20th century due to Federal restrictions on shallow water irrigation. This results in seasonal run-off in wetter winters concentrated with fertilizer and contaminants from the air. Such run-off poses a biohazard without water treatment in the agricultural ditches themselves. Lack of such irrigation is also an economic burden as it restricts food production capability in the valley. In areas of endorheic evaporation of seasonal watercourses and of the water table in the flatter and closing parts of the valley, soil salination results where the upper layers of soil are impermeable. Fertility and economic viability of potentially highly fertile tracts such as the Tulare lake bed has been lost in order to provide a federal law solution to high Southern California water demand. Land owners in such areas may be able to farm again if water is piped from the far north of the state, however one of the main deterrents to this is that without advanced run-off treatment apparatus this would worsen the quality of the ground water in the valley.
Nitrates in Groundwater[]
San Joaquin Valley, within the Central Valley of California, is made up of eight counties that are well known for agriculture.[23] Overuse of nitrogen fertilizers and irrigated agriculture is common, and according to Thomas Harter, the Chair for Water Resources Management and Policy at UC Davis, “more than 80 pounds of nitrogen per acre per year may leach into groundwater beneath irrigated lands, usually as nitrates”.[24] Between the 1950s and 1980s, when nitrogen fertilizer use grew sixfold, nitrate concentrations in groundwater increased 2.5 times.[25] Fertilizer runoffs contributes roughly 90% of all nitrate inputs to the alluvial groundwater system. Within agriculture, the two major factors are High-Intensity Crop Production and Large Dairy Herds.[26] Because these communities are cut off from larger water distribution, they are dependent on wells,[27] making groundwater a source of drinking water for 90% of San Joaquin Valley's residents.[28]
High-intensity crop production[]
Within the past century, farmers have been increasing their production to meet high demand. To increase output and efficiency, farmers have increased the amount of fertilizers used, including nitrates. Because only a fraction of the nitrogen in fertilizers is efficiently used to help produce crops, this has led to a greater concentration of nitrates and phosphates in the waters, causing eutrophication and contamination of possible drinking water.[29]
Large dairy herds[]
Before the rapid rise in demand for meat products and dairy, roaming dairy herds had contributed an insignificant amount of nitrate pollution to the underlying groundwater systems. However, within the past few decades, the increasing amount of cattle has been one of the main contributors of nitrate contamination in the groundwater systems of California.[30] Roughly around 1960, cattle were openly grazing pastures, and because of the large amount of lands which they roamed manure was not intensively managed.[31] However, even though manure was not closely managed, "Nitrogen excretion and deposition in pastures likely did not exceed pasture buffering capacity and had no significant leaching to groundwater".[32] Since the transition to dry-lot and free stall-based dairy farming in the mid 1970s, coupled with irrigated forage crops, dairy herds have contributed to nitrogen contamination.
Possible solutions and alternatives[]
The large dairy herds create manure, which is used to create the fertilizers that is applied to the crop fields. As demand for crops increases, farmers look to lower the costs of production. Using manure-based fertilizers is cost effective since manure is a by-product of large dairy farms and herds. The alternative to manure, which contains a high level of nitrates, is composting. Composting however is relatively expensive compared to using manure as fertilizer, since it is not as effective and is more timely/costly to make because of the large amount of aeration needed.[33]
Incidents of Nitrates in Groundwater[]
Nitrates have found their way into the aquifers around the San Joaquin Valley, affecting over 250,000 people in communities that are poor and rural.[27] In 2006, the State Water Resources Board took samples from domestic wells in Tulare County; they found that 40% of 181 domestic wells had nitrate levels above the 10 mg/L legal limit.[34] Though locals have typically used filters for their water, the filters need to be installed correctly and replaced frequently, which may not be economically feasible for the residents in Orosi.[35] Table 2 on page 20 from Pacific Institute's "The Human Costs of Nitrate-contaminated Drinking Water in the San Joaquin Valley" indicates the water systems that were contaminated with nitrates over the legal limit, the percentage of the population affected that are non-white and that are below or near poverty-level, and the year since the violations began.[34]

The Turlock Basin is a sub-basin of the San Joaquin Valley groundwater basin found within Stanislaus County and Merced County in the Central Valley.[36] In California's Groundwater Bulletin 118, a chart, linked below, illustrates the number of non-compliant public supply wells with nitrates over the MCL. According to this chart, there were eight wells which had nitrate levels above the 10 mg/L MCL, out of 90 sampled for nitrates in 2006.[36]
Nitrates are of concern because it interferes with the blood's ability to carry oxygen, and can have severe health effects on pregnant women, infants under 6 months, and children using tap water for their formula.[37] Because nitrates interfere with blood's capacity to carry oxygen, infants are at high risk of death from blue-baby syndrome, which can occur when there are high nitrate levels in the blood that are untreated.[37]
Medical interest[]
San Joaquin Valley Fever is one common term for coccidioidomycosis, a fungal infection caused by Coccidioides immitis through the inhalation of airborne dust or dirt. The valley is just one of the areas in the southwestern United States where the illness is endemic due to C. immitis residing in the soil.
Cities and counties[]
Cities with more than 500,000 inhabitants[]
- Fresno
Cities with 100,000 to 500,000 inhabitants[]
- Bakersfield
- Clovis
- Modesto
- Stockton
- Visalia
Cities with 20,000 to 100,000 inhabitants[]
Cities with fewer than 20,000 inhabitants[]
- Arvin
- Avenal
- Badger
- Caruthers
- Chowchilla
- Coalinga
- Dos Palos
- Earlimart
- East Porterville
- Exeter
- Farmersville
- Firebaugh
- Grayson
- Gustine
- Hilmar
- Hughson
- Ivanhoe
- Kerman
- Kettleman City
- Kingsburg
- Lamont
- Lathrop
- Laton
- Lemon Cove
- Lindsay
- Livingston
- Lost Hills
- McFarland
- Mendota
- Newman
- Orange Cove
- Parlier
- Pixley
- Ripon
- San Joaquin
- Seville
- Stevinson
- Strathmore
- Taft
- Three Rivers
- Waterford
- Westley
- Woodlake
- Yettem
In popular culture[]
- Referenced in the movie starring Humphrey Bogart, The Treasure of the Sierra Madre. Sitting by the campfire they mention growing peaches in the San Joaquin Valley.
- The operations of the fictional Sons of Anarchy Motorcycle Club in the hit FX television show Sons of Anarchy, are centered in San Joaquin Valley, often referred to as "Sanwa".
- The surviving stronghold of civilization on the West Coast in popular Science-Fiction book Lucifer's Hammer.[clarification needed]
See also[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to San Joaquin Valley. |
- Groundwater-related subsidence
- John Buttencourt Avila, "father of the sweet potato industry."
- List of California rivers
- Sacramento Valley
- San Joaquin (soil)
- Water in California
References[]
- ^ "San Joaquin Valley Fact Sheet". Valley Clean Air Now. Archived from the original on October 22, 2014. Retrieved October 18, 2014.
Seven counties comprise the San Joaquin Valley, including all of Kings County, most of Fresno, Kern, Merced, and Stanislaus counties, and portions of Madera, San Luis Obispo, Tulare counties
- ^ Capace, Nancy (1999). Encyclopedia of California. North American Book Dist LLC. Page 410. ISBN 9780403093182.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "NASA Report: Drought Causing Valley Land to Sink" (PDF). California Department of Water Resources. August 19, 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved May 27, 2016.
- ^ "NASA: California Drought Causing Valley Land to Sink". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. August 19, 2015. Archived from the original on May 5, 2016. Retrieved May 27, 2016.
- ^ "San Joaquin Valley/Hanford, CA". National Weather Service Forecast Office. Archived from the original on November 16, 2011. Retrieved November 13, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 20, 2017.
- ^ 2007 Overview - Agricultural Statistical Review Archived 2009-05-02 at the Wayback Machine - California Agricultural Resource Directory 2008–2009
- ^ Henry Miller Papers Collection, "Correspondance to Superintendant Turner," 18 July 1912, Special Collections, Henry Madden Library, California State University, Fresno
- ^ Paving Paradise: A New Perspective on California's Farmland Conversion, American Farmland Trust, November 2007
- ^ "California drought will affect the global agriculture industry". Los Angeles News.Net. August 17, 2014. Archived from the original on August 19, 2014. Retrieved August 18, 2014.
- ^ "Big West to Suspend Operations at its Refinery on Rosedale Highway". KGET News. January 28, 2009. Archived from the original on June 12, 2012. Retrieved November 13, 2011.
- ^ "Occidental Announces Major Oil and Gas Discovery in Kern County". California Energy News. July 23, 2009. Archived from the original on October 9, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- ^ 2006 California Department of Conservation, 2006 Oil and Gas Statistics Archived 2017-05-25 at Archive-It, p. 4
- ^ Central California Hip Hop Archived 2015-04-04 at the Wayback Machine sites.google.com 04-05-2015 Retrieved. 04-05-2015
- ^ “The Colts” by (JIM DAWSON) Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine www.electricearl.com 14-05-2015 Retrieved. 14-05-2015
- ^ The Def Dames- Billboard Hot 100 Carts Archived 2016-01-06 at the Wayback Machine www.billboard.com 14-05-2015 Retrieved. 14-05-2015
- ^ Sherley Ann Williams – Poetry Soup Archived 2015-05-18 at the Wayback Machine www.poetrysoup.com 14-05-2015 Retrieved. 14-05-2015
- ^ Fresno Bee, August 29, 2007
- ^ On rich soil: Kern County families provide grapes aplent Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine, The Bakersfield Californian, By Jeff Nickell, Saturday, Jun 30, 2012 12:00 AM
"...Marin Caratan than he was the first Croatian to come to the area to grow grapes...said Mark Zaninovich ..., but it is also fair to mention the Carics, Jakoviches, Radoviches, Bozaniches, Buskas, Sousas, Kovacaviches, Bidarts, Sandrinis, and Paviches." - ^ Jump up to: a b Borrell, Brendan (December 3, 2018). "In California's Fertile Valley, a Bumper Crop of Air Pollution". Undark. Archived from the original on September 27, 2019. Retrieved September 27, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bustillo, Miguel (November 14, 2008) L.A.'s the Capital of Dirty Air Again Archived 2016-03-06 at the Wayback Machine Los Angeles Times
- ^ Richter, Lauren (December 19, 2017). "Constructing insignificance: critical race perspectives on institutional failure in environmental justice communities". Environmental Sociology. 4: 107–121. doi:10.1080/23251042.2017.1410988. S2CID 7434845.
- ^ Pacific Institute (March 2011). "The Human Costs of Nitrate-contaminated Water in the San Joaquin Valley" (PDF). Pacific Institute. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 14, 2017.
- ^ Harter, Thomas (2009). "Agricultural Impacts on Groundwater Nitrate" (PDF). Southwest Hydrology. 8: 22–23. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved April 20, 2017.
- ^ "Groundwater Shock: The Polluting of the World's Major Freshwater Stores | Worldwatch Institute". www.worldwatch.org. Archived from the original on March 18, 2017. Retrieved March 5, 2017.
- ^ Agence France-Presse (September 20, 2016). "Nitrates poison water in California's Central Valley". Yahoo! News. Associated Newspapers Ltd. Retrieved March 23, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b AFP (September 19, 2016). "Nitrates Poison Water in California's Central Valley". Community Water Center. Archived from the original on May 5, 2017.
- ^ Community Water Center (December 2013). "Water & Health in the Valley: Nitrate Contamination of Drinking Water and the Health of San Joaquin Valley Residents" (PDF). Community Water Center. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2017.
- ^ Burow, Karen. "Assessment of regional change in nitrate concentrations in groundwater in the Central Valley, California, USA, 1950s–2000s" (PDF). Ca Water Usgs. 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 30, 2017. Retrieved March 23, 2017.
- ^ Moore, Eli. "Human Costs of Nitrate-contaminated Drinking Water in the San Joaquin Valley" (PDF). Pacific Institute. Pacific Institute. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 14, 2017. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- ^ Burow, Karen. "Assessment of regional change in nitrate concentrations in groundwater in the Central Valley, California, USA, 1950s–2000s" (PDF). Ca Water Usgs. 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 30, 2017. Retrieved March 23, 2017.
- ^ Pacific Institute (March 2011). "The Human Costs of Nitrate-contaminated Water in the San Joaquin Valley" (PDF). Pacific Institute. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 14, 2017.
- ^ Gamroth, Mike. "Composting: An Alternative for Livestock Manure Management and Disposal of Dead Animals" (PDF). Oregon State University. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved April 18, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Pacific Institute (March 2011). "The Human Costs of Nitrate-contaminated Water in the San Joaquin Valley" (PDF). Pacific Institute. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 14, 2017.
- ^ Carroll, Gerald (November 14, 2006). "Tulare County Private Wells Test High for Nitrates" (PDF). Visalia Times-Delta. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b water.ca.gov (April 11, 2017). "California's Groundwater Bulletin 118" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Nitrates and Nitrites" (PDF). EPA. 2006. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 21, 2017. Retrieved April 20, 2017.
External links[]
- San Joaquin Valley
- Valleys of California
- Regions of California
- San Joaquin River
- Valleys of Fresno County, California
- Valleys of Kern County, California
- Valleys of Kings County, California
- Valleys of Madera County, California
- Valleys of Merced County, California
- Valleys of San Joaquin County, California
- Valleys of Stanislaus County, California
- Valleys of Tulare County, California
- Geography of the Central Valley (California)


