Solar eclipse of April 8, 2005
| Solar eclipse of April 8, 2005 | |
|---|---|
 Partial from Naiguatá, Venezuela | |
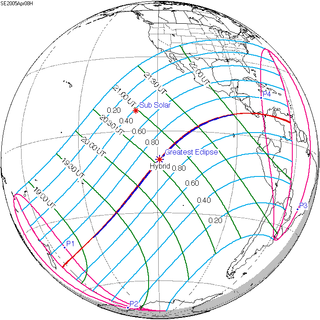 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Hybrid |
| Gamma | -0.3473 |
| Magnitude | 1.0074 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 42 sec (0 m 42 s) |
| Coordinates | 10°36′S 119°00′W / 10.6°S 119°W |
| Max. width of band | 27 km (17 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 20:36:51 |
| References | |
| Saros | 129 (51 of 80) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9519 |
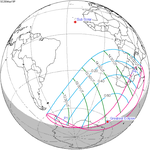
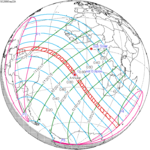
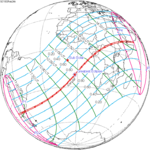
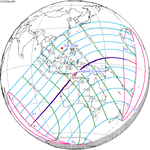
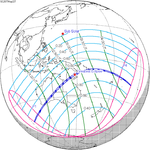
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node on April 8, 2005. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. This eclipse is a hybrid event, a narrow total eclipse, and beginning and ending as an annular eclipse.[citation needed]
It was visible within a narrow corridor in the Pacific Ocean. The path of the eclipse started south of New Zealand and crossed the Pacific Ocean in a diagonal path and ended in the extreme northwestern part of South America. The total solar eclipse was not visible on any land, while the annular solar eclipse was visible in the southern tip of Puntarenas Province of Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia and Venezuela.[1]
Images[]

Animated path
Gallery[]

Christchurch (NZ) at sunrise
Related eclipses[]
Eclipses of 2005[]
- A hybrid solar eclipse on April 8.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on April 24.
- An annular solar eclipse on October 3.
- A partial lunar eclipse on October 17.
Tzolkinex[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of February 26, 1998
- Followed: Solar eclipse of May 20, 2012
Half-Saros[]
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of April 4, 1996
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of April 15, 2014
Tritos[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of May 10, 1994
- Followed: Solar eclipse of March 9, 2016
Solar Saros 129[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of March 29, 1987
- Followed: Solar eclipse of April 20, 2023
Inex[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of April 29, 1976
- Followed: Solar eclipse of March 20, 2034
Solar eclipses 2004–2007[]
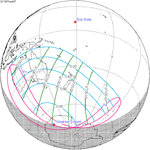
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
| showSolar eclipse series sets from 2004–2007 |
|---|
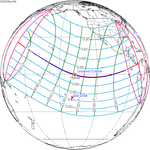
Saros 129[]
It is a part of Saros cycle 129, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 80 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on October 3, 1103. It contains annular eclipses on May 6, 1464 through March 18, 1969, hybrid eclipses from March 29, 1987 through April 20, 2023 and total eclipses from April 30, 2041 through July 26, 2185. The series ends at member 80 as a partial eclipse on February 21, 2528. The longest duration of totality was 3 minutes, 43 seconds on June 25, 2131 . All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon’s ascending node.[3]
| showSeries members 46–56 occur between 1901 and 2100: |
|---|
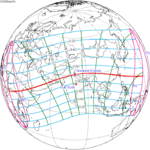
Metonic series[]
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| show21 eclipse events between June 21, 1982, and June 21, 2058 |
|---|
Notes[]
- ^ Espenak, Fred. "Hybrid Solar Eclipse of 2005 Apr 08 - Google Maps and Solar Eclipse Paths". NASA Eclipse Web Site.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Espenak, F. "NASA Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 129". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References[]
- Hybrid Solar Eclipse of 2005 April 08 (NASA.gov)
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Google Map
Photos:
- Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. South Pacific (MV Discovery)
- Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Pacific (MV Galapagos Legend)
- Spaceweather.com eclipse gallery
- Clouds, Plane, Sun, Eclipse, North Carolina, USA APOD 4/11/2005
- Hybrid Solar Eclipse, combined photo of totality 2,200 kilometers west of the Galapagos and annularity at Penonome Airfield APOD 5/6/2005
- A Rare Hybrid Solar Eclipse, APOD 11/3/2013
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2005 April 8. |
Coordinates: 10°34′01″S 118°59′13″W / 10.567°S 118.987°W
- Hybrid solar eclipses
- 21st-century solar eclipses
- 2005 in science
- April 2005 events
- 2005 in Costa Rica
- 2005 in Panama
- 2005 in Colombia
- 2005 in Venezuela