Subdivisions of the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria
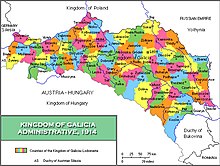

The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria was subdivided into a number of counties for administrative purposes. In 1877 there were 73 administrative counties and in 1900 there were 78 counties. The administrative counties were responsible for storing vital records. The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria was the largest and most populous crownland of Cisleithenia between 1772 and 1918. More widely, the central European region of Galicia is today split between the modern states of Poland and Ukraine. Despite having passed through several intermediate states during the great wars of the 20th century, the regions have mainly preserved their territorial integrity and continue to demarcate the jurisdiction of local government authorities in their successor states.
Administrative counties in present-day Poland[]
In Poland today, there are parts of three provinces (voivodeships) that collectively formed the western part of the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria. [1]
Only Subcarpathia (Podkarpackie Voivodeship) was entirely contained in the Kingdom. The majority of the territory of Lesser Poland Voivodeship was contained in the Kingdom. From 1795 to 1815, three counties (powiats) that are situated north of the River Vistula were briefly part of the Kingdom: Olkusz County, Miechów County and Proszowice County. By the terms of the treaties of the Congress of Vienna they were annexed to Russian Poland ("Congress Poland") where they remained until the end of World War I. Additionally, the northernmost part of the land-county of Kraków around the villages of Sułoszowa, Skała and Słomniki were similarly allocated to Congress Russia; the remaining parts of the county were located in the Kingdom. The third voivodeship of Silesia contained only a small part of the Kingdom. The Silesian city-county of Jaworzno was originally part of the Kingdom's Chrzanowski county. The majority of the territory of the latter county is still an extant county in modern Poland - Chrzanów County - which is today located in the Lesser Poland voivodeship. The south-eastern Silesian land-counties of Żywiec County and Bielsko County along with the city-county of Bielsko-Biała formed the most westerly part of the Kingdom. The remaining 32 counties of Silesia were never part of the Kingdom.
| Modern Provincial Entity | Modern Counties of the Province |
Equivalent Counties of Galicia |
|---|---|---|
| Lesser Poland Voivodeship | ||
| Kraków (city-county) | Kraków | |
| Tarnów (city-county) | Tarnów | |
| Nowy Sącz (city-county) | Nowy Sącz | |
| Kraków County | Partly in Kraków and partly in Wadowice | |
| Nowy Sącz County | Partly in Nowy Sącz, Grybów and Muszyna | |
| Tarnów County | Partly in Tarnów and Pilzno | |
| Nowy Targ County | Nowy Targ (northern part) | |
| Wadowice County | Wadowice | |
| Oświęcim County | Partly in Biala and partly in Wadowice | |
| Chrzanów County | Chrzanów | |
| Limanowa County | Limanowa | |
| Myślenice County | Myślenice eastern part) | |
| Gorlice County | Gorlice | |
| Wieliczka County | Wieliczka | |
| Bochnia County | Bochnia | |
| Brzesko County | Brzesko | |
| Sucha County | Myślenice western part) | |
| Tatra County | Nowy Targ (southern part) | |
| Dąbrowa County | Dąbrowa | |
| Silesian Voivodeship | ||
| Jaworzno (city-county) | Chrzanów (western part) | |
| Bielsko-Biała (city-county) | Biala | |
| Bielsko County | Biala | |
| Żywiec County | Żywiec | |
| Subcarpathia voivodeship | ||
| Rzeszów city-county | Rzeszów (partly) | |
| Przemyśl city-county | Przemyśl | |
| Tarnobrzeg city-county | Tarnobrzeg (part of) | |
| Krosno city-county | Krosno | |
| Rzeszów County | Rzeszów (partly) | |
| Mielec County | Mielec | |
| Dębica County | Pilzo (partly) | |
| Jarosław County | Jarosław (eastern part) | |
| Jasło County | Jasło | |
| Krosno County | Krosno | |
| Lubaczów County | Lubaczów | |
| Stalowa Wola County | Northern part in Tarnobrzeg and southern part in Nisko | |
| Sanok County | Sanok | |
| Przeworsk County | Jarosław (western part) | |
| Łańcut County | Łańcut (south of the river Wisłoka) | |
| Ropczyce-Sędziszów County | Ropczyce | |
| Przemyśl County | Przemyśl (To the north) and Dobromil (To the south) | |
| Leżajsk County | Łańcut (north of the river Wisłoka) | |
| Nisko County | Nisko | |
| Brzozów County | Brzozów | |
| Strzyżów County | Strzyżów | |
| Kolbuszowa County | Kolbuszowa | |
| Tarnobrzeg County | Tarnobrzeg (western part) | |
| Lesko County | Lesko (western part) | |
| Bieszczady County | Lesko (eastern part) (Ceded by the USSR) |
Administrative raions in present-day Ukraine[]
Parts of this article (those related to needs to be updated taking into account the 2020 administrative reform; most of these raions have been abolished) need to be updated. (April 2021) |
In Ukraine today, there are three provinces (oblasts) that formed the eastern part of the Kingdom of Galicia. Two of these, Lviv Oblast and Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast were entirely contained in the kingdom; the third oblast of Ternopil was mainly in the kingdom apart from four of its most northerly counties (raions). These four counties, Kremenets Raion, Shumsk Raion, Lanivtsi as well as the northern half of Zbarazh Raion, were formerly part of the county of Krzemieniec in the Wolyn voivodeship (province) of the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period. Prior to World War I, they were part of Congress Poland. They never formed part of the Kingdom of Galicia. The remaining counties of Ternopil Oblast were all part of the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria.
| Modern Oblast of Ukraine |
Modern Raions of the Oblast |
Equivalent Counties of Galicia |
|---|---|---|
| Lviv Oblast | Brody Raion | Southern part of Brody county. |
| Brody city-county | Brody | |
| Busk Raion | Złoczów | |
| Busk city-county | Złoczów | |
| Drohobych Raion | Drohobycz | |
| Drohobych city-county | Drohobycz | |
| Horodok Raion | Grodek (southern part) and Rudky (southern part) | |
| Kamianka-Buzka Raion | Kamionka | |
| Mostyska Raion | Mosciska | |
| Mykolaiv Raion | Żydaczów (Only the northern part of the county.) | |
| Peremyshliany Raion | Przemyślany and the northern part of Bóbrka | |
| Pustomyty Raion | Lviv county | |
| Radekhiv Raion | Northern part of Brody county and northern part of Kamionka. | |
| Sambir Raion | Sambor and Rudky | |
| Skole Raion | All of the old county of Stryj south of modern Stryi Raion. | |
| Sokal Raion | To the north Sokal and To the south Rawa-Ruska. | |
| Staryi Sambir Raion | Stari Sambor | |
| Stryi Raion | Stryj (Only the northern part of the county.) | |
| Turka Raion | Turka | |
| Yavoriv Raion | Jaworów and Grodek (northern part) | |
| Zhovkva Raion | To the north Rawa-Ruska and To the south Żółkiew | |
| Zhydachiv Raion | Żydaczów (Excluding the northern part of the county.) | |
| Zolochiv Raion | Eastern part of Żółkiew county and western part of Peremyshliany. | |
| Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast | ||
| Bohorodchany Raion | ||
| Verkhovyna Raion | ||
| Verkhovyna | ||
| Halych Raion | Stanislavov | |
| Halych (City) | ||
| Horodenka Raion | ||
| Horodenka (City) | ||
| Dolyna Raion | ||
| Dolyna (City) | ||
| Kalush Raion | ||
| Kalush (City) | ||
| Kolomyia Raion | ||
| Kolomyia (City) | ||
| Kosiv Raion | ||
| Kosiv (City) | ||
| Nadvirna Raion | ||
| Nadvirna (City) | ||
| Rohatyn Raion | ||
| Rohatyn (City) | ||
| Rozhniativ Raion | ||
| Rozhniativ (City) | ||
| Sniatyn Raion | ||
| Sniatyn (City) | ||
| Tysmenytsia Raion | ||
| Tysmenytsia (City) | ||
| Tlumach Raion | ||
| Tlumach (City) | ||
| Ternopil Oblast | ||
| Berezhany Raion | Western part of Brzeżany county. | |
| Borshchiv Raion | Borszczów | |
| Buchach Raion | Buczacz county | |
| Chortkiv Raion | Czortków and the southern part of Kopychyntsi county | |
| Husiatyn Raion | Kopychyntsi | |
| Kozova Raion | Eastern part of Brzeżany county except for the city of Brzeżany itself. | |
| Monastyryska Raion | Western part of Buczacz county. | |
| Pidhaitsi Raion | Western part of Podhajce county. | |
| Pidvolochysk Raion | Skalat county and the eastern part of Zbaraż county | |
| Terebovlia Raion | Trembowla county in the east and Podhajce county in the west. | |
| Ternopil Raion | Tarnopol county | |
| Zalishchyky Raion | Zalishchyky | |
| Zbarazh Raion | The western part of Zbaraż county and the southern part of Brody county. | |
| Zboriv Raion | Zborów county |
Carpathian Ruthenia, today largely contained in the Ukrainian oblast of Zakarpattia, was never part of the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria nor of modern Poland. Instead, it was part of transleithanian lands of the Kingdom of Hungary.
Jewish Administrative Centers[]
The government assigned some towns the status of Jewish Administrative Center. These Administrative Centers were responsible for maintaining Jewish vital records.
See also[]
- Subdivisions of Ukraine
- Voivodeships of Poland
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria. |
- ^ Galician Distant Cousins Archived 2006-08-15 at the Wayback Machine
- 1877 Galician Administrative Districts from JewishGen
- 1900 Galicia: Administrative Districts from PolishRoots
- Galician Administrative Districts from The Polish Genealogical Society of America
- 74 Administrative Districts in Galicia
- Galician Administrative Map
- Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria
- Former subdivisions of Ukraine
- Former subdivisions of Poland
- Subdivisions of former countries