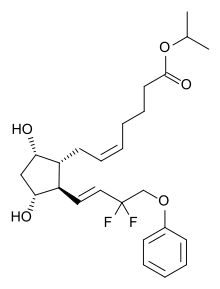
Tafluprost
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Saflutan, Taflotan, Tapros, Zioptan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Topical (eye drops) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Activation by ester hydrolysis, deactivation by beta oxidation |
| Onset of action | 2–4 hrs |
| Duration of action | ≥ 24 hrs |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.207.745 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H34F2O5 |
| Molar mass | 452.539 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Tafluprost (trade names Taflotan by Santen Pharmaceutical and Zioptan by Merck in the US) is a prostaglandin analogue. It is used topically (as eye drops) to control the progression of open-angle glaucoma and in the management of ocular hypertension, alone or in combination with other medication. It reduces intraocular pressure by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes.[1][2]
Adverse effects[]
The most common side effect is conjunctival hyperemia, which occurs in 4 to 20% of patients. Less common side effects include stinging of the eyes, headache, and respiratory infections. Rare side effects are dyspnoea (breathing difficulties), worsening of asthma, and macular oedema.[1][2][3]
Interactions[]
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can either reduce or increase the effect of tafluprost.[1] Timolol eye drops, a common kind of glaucoma medication, does not negatively interact with this drug.[2]
No interactions with systemic (for example, oral) drugs are expected because tafluprost does not reach relevant concentrations in the bloodstream.[2][3]
Pharmacology[]
Mechanism of action[]
Tafluprost is a prodrug of the active substance, tafluprost acid, a structural and functional analogue of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α). Tafluprost acid is a selective agonist at the prostaglandin F receptor, increasing outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes and thus lowering intraocular pressure.[2][3]
Other PGF2α analogues with the same mechanism include latanoprost and travoprost.[2]
Pharmacokinetics[]
Tafluprost, as a lipophilic ester, easily penetrates the cornea and is then activated to the carboxylic acid, tafluprost acid. Onset of action is 2 to 4 hours after application, the maximal effect is reached after 12 hours, and ocular pressure remains lowered for at least 24 hours.[2][3]
Tafluprost acid is inactivated by beta oxidation to 1,2-dinortafluprost acid, 1,2,3,4-tetranortafluprost acid, and its lactone, which are subsequently glucuronidated or hydroxylated. The cytochrome P450 liver enzymes play no role in the metabolism.[3]
An analogous pathway (at least up to the tetranor-metabolites) has been found for latanoprost and travoprost.

References[]
- ^ a b c Tafluprost Professional Drug Facts.
- ^ a b c d e f g Haberfeld H, ed. (2015). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
- ^ a b c d e Dinnendahl V, Fricke U, eds. (2011). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 9 (25 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- ^ Fukano Y, Kawazu K (August 2009). "Disposition and metabolism of a novel prostanoid antiglaucoma medication, tafluprost, following ocular administration to rats". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 37 (8): 1622–34. doi:10.1124/dmd.108.024885. PMID 19477946. S2CID 12425702.
- ^ Fukano Y, Kawazu K, Akaishi T, Bezwada P, Pellinen P (June 2011). "Metabolism and ocular tissue distribution of an antiglaucoma prostanoid, tafluprost, after ocular instillation to monkeys". Journal of Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 27 (3): 251–9. doi:10.1089/jop.2010.0178. PMID 21491995.
- Prostaglandins
- Secondary alcohols
- Alkene derivatives
- Merck & Co. brands
- Carboxylate esters
- Isopropyl esters
- Organofluorides
- Phenol ethers
- Ophthalmology drugs
