Enprostil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
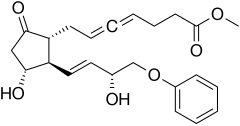
| Formula | C23H28O6 |
| Molar mass | 400.471 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Enprostil is a synthetic prostaglandin designed to resemble dinoprostone. Enprostil was found to be a highly potent inhibitor of gastric HCl secretion.[1] It is an analog of prostaglandin E2 but unlike this prostaglandin, which binds to and activates all four cellular receptors viz., EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4 receptors, enprostil is a more selective receptor agonist in that it binds to and activates primarily the EP3 receptor.[2] Consequently, enprostil is expected to have a narrower range of actions that may avoid some of the unwanted side-effects and toxicities of prostaglandin E2. A prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial conducted in Japan found combining enprostil with cimetidine was more effective than cimetidine alone in treating gastric ulcer.[3]
See also[]
- Prostaglandin receptors
- EP3 and peptic ulcer
References[]
- ^ Roszkowski, AP; Garay, GL; Baker, S; Schuler, M; Carter, H (1986). "Gastric antisecretory and antiulcer properties of enprostil, (+/−)-11 alpha, 15 alpha-dihydroxy-16-phenoxy-17,18,19,20-tetranor-9-oxoprosta-4,5,13(t)-trienoic acid methyl ester". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 239 (2): 382–9. PMID 3095537.
- ^ Moreno JJ (2017). "Eicosanoid receptors: Targets for the treatment of disrupted intestinal epithelial homeostasis". European Journal of Pharmacology. 796: 7–19. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.12.004. PMID 27940058. S2CID 1513449.
- ^ Murata H, Kawano S, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Hori M, Kamada T, Matsuzawa Y, Katsu K, Inoue K, Kobayashi K, Mitsufuji S, Bamba T, Kawasaki H, Kajiyama G, Umegaki E, Inoue M, Saito I (2005). "Combination of enprostil and cimetidine is more effective than cimetidine alone in treating gastric ulcer: prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial". Hepato-gastroenterology. 52 (66): 1925–9. PMID 16334808.
External links[]
- Toshina, K.; Hirata, I.; Maemura, K.; Sasaki, S.; Murano, M.; Nitta, M.; Yamauchi, H.; Nishikawa, T.; et al. (2000). "Enprostil, a Prostaglandin-E2 Analogue, Inhibits Interleukin-8 Production of Human Colonic Epithelial Cell Lines". Scandinavian Journal of Immunology. 52 (6): 570–5. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00815.x. PMID 11119262.
- Tari, Akira; Hamada, Masanori; Kamiyasu, Toshiki; Sumii, Koji; Haruma, Ken; Inoue, Masaki; Kishimoto, Shinya; Kajiyama, Goro; Walsh, John H. (1997). "Effect of enprostil on omeprazole-induced hypergastrinemia and inhibition of gastric acid secretion in peptic ulcer patients". Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 42 (8): 1741–6. doi:10.1023/A:1018825902055. PMID 9286243. S2CID 25069361.
- Ching, C. K.; Lam, S. K. (1995). "A comparison of two prostaglandin analogues (enprostil vs misoprostol) in the treatment of acute duodenal ulcer disease". Journal of Gastroenterology. 30 (5): 607–14. doi:10.1007/BF02367786. PMID 8574332. S2CID 6288648.
- Prostaglandins
- Phenol ethers
- Methyl esters
- Hoffmann-La Roche brands
- Gastrointestinal system drug stubs