The Holocaust in Latvia
This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. (March 2021) |
| The Holocaust in Latvia | |
|---|---|
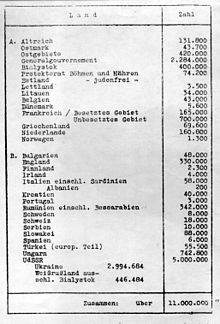 Exhibit presented at the Wannsee Conference on January 20, 1942, showing only 3,500 Jews left alive in Latvia out of about 60,000 in the country at the time of the Nazi invasion. | |
| Also known as | Churbns Lettlands |
| Location | Latvia |
| Date | 22 June 1941 to late 1944 |
| Incident type | Genocide through imprisonment, mass shootings, concentration camps, ghettos, forced labor, starvation |
| Perpetrators | Rudolf Lange, Friedrich Jeckeln, Franz Walter Stahlecker, Viktors Arājs |
| Organizations | Einsatzgruppen, Order Police battalions, Wehrmacht, Arajs Kommando, Latvian Auxiliary Police, Kriegsmarine |
| Victims | About 66,000 Latvian Jews; 19,000 German, Austrian and Czech Jews; unknown numbers of Lithuanian and Hungarian Jews; unknown but substantial number of Roma, communists, and mentally disabled persons |
The Holocaust in Latvia refers to the crimes against humanity committed by Nazi Germany and collaborators victimizing Jews during the occupation of Latvia.
German occupation[]

The German army crossed the Soviet frontier early morning on Sunday, 22 June 1941, on a broad front from the Baltic Sea to Hungary. The Germans advanced through Lithuania towards Daugavpils and other strategic points in Latvia. The Nazi police state included an organisation called the Security Service (German: Sicherheitsdienst), generally referred to as the SD, and its headquarters in Berlin was known as the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA).[1]
The SD in Latvia[]
In advance of the invasion, the SD had organised four Einsatzgruppen, mobile death squads. The Einsatzgruppen name ("special assignment units") was a euphemism, as their real purpose was to kill large numbers of people whom the Nazis regarded as "undesirable". These included Communists, Gypsies, the mentally ill, homosexuals and, especially, Jews. The Einsatzgruppen followed closely behind the German invasion forces and established a presence in Latvia within days, and sometimes hours, of the occupation of a given area of the country by the German Wehrmacht.[1]
The SD in Latvia can be distinguished in photographs and descriptions by their uniforms. The full black of the Nazi SS was seldom worn; instead, the usual attire was the grey Wehrmacht uniform with black accents.[1] They wore the SD patch on the left sleeve, a yellowish shirt, and the Death's Head (Totenkopf) symbol on their caps. The SD ranks were identical to the SS. The SD did not wear the SS lightning rune symbol on their right collar tabs but replaced it with either the Totenkopf or the letters "SD".[1]
The SD first established its power in Latvia through Einsatzgruppe A, which was subdivided into units called Einsatzkommandos 1a, 1b, 2 and 3.[1] As the front line moved further east, Einsatzgruppe A moved out of Latvia, remaining in the country only a few weeks, after which its functions were taken over by the "resident" SD, under the authority of the Kommandant der Sicherheitspolizei un SD, generally referred to by the German initials of KdS. The KdS took orders both from RSHA in Berlin and from another official called the Befehlshaber (commander) der Sicherheitspolizei und des SD, or BdS. Both the KdS and the BdS were subordinate to another official called the Ranking (or Higher) SS and Police Commander (Höherer SS-und Polizeiführer), or HPSSF.[1] The lines of authority were overlapping and ambiguous.[2] The eastern part of Latvia, including Daugavpils and the Latgale region, was assigned to Einsatzkommandos 1b (EK 1b) and 3 (EK 3).[1] EK 1b had about 50 to 60 men and was commanded by Erich Ehrlinger.[1]
Murders commence with Nazi invasion[]

In Latvia, the Holocaust started on the night of 23 to 24 June 1941, when in the Grobiņa cemetery an SD detachment killed six local Jews, including the town pharmacist.[3] On the following days 35 Jews were exterminated in Durbe, Priekule and . On June 29 the Nazi invaders started forming the first Latvian SD auxiliary unit in Jelgava. , member of the Pērkonkrusts organisation, was chosen to head it. In the summer of 1941, 300 men in the unit took part in the murder of about 2000 Jews in Jelgava and other places in Zemgale.[4] The killing was supervised by the officers of the German SD Rudolf Batz and , who involved the SS people of the Einsatzgruppe in the action. The main Jelgava Synagogue was burnt down through their joint effort. After the invasion of Riga, Walter Stahlecker, assisted by the members of Pērkonkrusts and other local collaborationists, organised the pogrom of Jews in the capital of Latvia. Viktors Arājs, aged 31 at the time, a possible former member of Pērkonkrusts and a member of a student fraternity, was appointed direct executor of the action. He was an idle eternal student who was supported by his wife, a rich shop owner, who was ten years older than he was. Arājs had worked in the for a certain period of time.[5] He stood out with his power-hungry and extreme thinking. The man was well fed, well dressed, and "with his student's hat proudly cocked on one ear".
Arajs Kommando formed[]


On 2 July Viktors Arājs started to form his armed unit of men who were responding to the appeal of Pērkonkrusts to take arms and to clear Latvia of Jews and communists. In the beginning, the unit mainly included members of different student fraternities. In 1941 altogether about 300 men had applied. The closest assistants of Viktors Arājs included , , and Herberts Cukurs.[6] On the night of July 3, Arājs Kommando started arresting, beating and robbing the Riga Jews. On 4 July, the choral synagogue at Gogoļa Street was burnt, and thereafter, the synagogues at Maskavas and Stabu Streets. Many Jews were killed during those days, including the refugees from Lithuania. In carts and blue buses, the men of Arajs Kommando went to different places in Courland, Zemgale and Vidzeme, killing thousands of Jews there.
These killings were supposed to serve as an example to other anti-Semitic supporters of the Nazi invaders. Individual Latvian Selbstschutz units were also involved in the mass murder of Jews.[7] In the district of Ilūkste, for instance, Jews were killed by the Selbstschutz death unit of commander , which consisted of 20 cold-blooded murderers. All killings were supervised by the officers of the German SS and SD. In July 1941, the mass killing of Riga Jews took place in the . About 4,000 people died there. The executions were headed by Sturmbannführers (majors) , , and the newly appointed chief of the Riga SD Rudolf Lange.
Massacres[]
As stated by the Latvian historian Andrievs Ezergailis, this was the beginning of "the greatest criminal act in the history of Latvia". From July 1941 the Jews of Latvia were also humiliated in different ways and deprived of the rights that were enjoyed by the other citizens of Latvia. Jews were strictly forbidden to leave their homes in the evening, at night and in the morning. They were allotted lower food rations, they could only shop in some special stores, and they had to wear the mark of recognition – the yellow Star of David on their clothes. It was forbidden for them to attend places where public events took place, including cinemas, athletic fields and parks.[8] They were not allowed to use trains and trams, to go to bath-houses, use pavements, attend libraries and museums or to go to schools, and they had to hand over bicycles and radios. Jewish doctors were only allowed to advise and treat Jews, and they were forbidden to run pharmacies.[9][10] Maximum norms for furniture, clothes and linen were also soon introduced for Jews. All articles above the norm were subject to confiscation for the needs of the Reich. All jewelry, securities, gold and silver coins had to be surrendered on demand. Anti-Semitism thus became the source of enrichment of Nazi officials and their local collaborators who confiscated Jewish property. The extermination of Jews suited them since nobody would remain alive to demand the return of stolen items.[11]
Liepāja[]
In Liepāja the first mass killing of Jews took place on July 3 and 4, when about 400 people were shot dead, and on July 8 when 300 Jews were killed. The German group of SD and policemen did the shooting, while the members of Latvian Selbstschutz convoyed victims to the killing site.[citation needed] On July 13, the destroying of the sizeable choral synagogue of Liepāja began. The Scripture rolls were spread on the Ugunsdzēsēju Square, and the Jews were forced to march across their sacred things, with watchers merrily laughing at the amusing scene. The above operations took place under the direct leadership of Erhard Grauel, commander of the Einsatzgruppe's Sonderkommando.
Ventspils[]
After that, Grauel went to Ventspils. The killings were jointly carried out by German Ordnungspolizei and the men of the local Selbstschutz. On July 16-July 18, 300 people were shot dead in the . In July–August, the remaining 700 Jews from town were shot dead, while the Jews of the region were killed in the autumn. The shooting was carried out by German, Latvian and Estonian SD men who had arrived by ship. Soon a poster appeared on the Kuldīga-Ventspils highway, which said that Ventspils was Judenfrei (free of Jews).
Daugavpils[]
In Daugavpils the murder of Jews was initially commanded by Erich Ehrlinger, chief of .[12] By July 11 they had killed about 1,150 people. Ehrlinger's work was continued by Joachim Hamann, who was liable for the killing of 9012 Jews in the city and in southern Latgale. The chief of the local auxiliary police had rendered active assistance by ensuring the moving of the Jews to the Grīva ghetto and transporting them to the killing places.
Rēzekne[]
In Rēzekne killings were carried out by a German SD group, which was helped by Selbstschutz men and Arajs Kommando. About 2,500 people were murdered. By October 1941, altogether about 35,000 Latvian Jews were killed.
There are two known instances of people rescuing Jews in Rēzekne – Old Believer Ulita Varushkyna who at the plea of his parents took in their two-year-old son Mordechai Tager that she later adopted, and the Polish Matusevich family that hid Haim Israelit and his nephew Yakov for three years. Both Varushkyna and the Matusevich family have been awarded the title Righteous Among the Nations for their actions.[13]
Varakļāni[]
Varakļāni, a relatively small town, had about 540 remaining Jews when the Germans gained control. They were shot into graves they were forced to dig on August 4, 1941. The fate of this small town is similar to many other towns, documented by JewishGen and others.[14]
Jungfernhof concentration camp[]
Confinement[]
Riga Ghetto[]




| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
On July 27, 1941, State Commissar (Reichskommissar) Hinrich Lohse (earlier Gauleiter of Schleswig-Holstein), ruler of the Baltic lands and Belarus or Ostland as the territory was called by the invaders – made his guidelines on Jewish question public. Jews, in his opinion, had to be used as a cheap labour force by paying them minimum wages or by providing them with a minimum food ration – with whatever may be left over after supplying the indigenous Aryan population. In order to govern the Jews they had to be moved to special areas where ghettos would be arranged and they would be forbidden to leave the area. Walter Stahlecker protested against the idea of Hinrich Lohse and demanded that the extermination of the Jews be continued. Berlin, however, passed the power to the civil administration of occupation force and it did things its own way. The area of the Latgale suburbs in Riga was chosen for the Riga Ghetto.[15] It was mainly inhabited by poor people: Jews, Russians and Belarusians. The ghetto bordered on Maskavas, Vitebskas, Ebreju (Jewish), Līksnas, Lauvas, Lazdonas, Lielā Kalnu, Katoļu, Jēkabpils and Lāčplēša Streets. About 7,000 non-Jews were moved from there to other flats in Riga. More than 23,000 Riga Jews were ordered to move to the territory of the ghetto. There now were more than 29,000 inmates in the ghetto, including those who had already previously resided there. The Jewish Council was formed within the ghetto, which was assigned the task of regulating social life. The Jewish police force for the maintenance of order formed there. It consisted of 80 men armed with sticks and rubber truncheons. The ghetto was enclosed by a barbed-wire fence. Wooden barriers (logs) were placed on the main streets at the entrance, and the Latvian police were stationed as guards there. Jews were allowed to leave the ghetto only in work columns and in the accompaniment of guards. Individual Jewish specialists could come and go by displaying a special yellow ID. Leaving independently was severely punished.[16]
In the ghetto, the Jews were very crowded: 3-4 square metres were allotted per person. There was also high poverty, as food rations were given only to those who worked, i.e. to about half of the ghetto inmates. They had to maintain their 5,652 children and 8,300 elderly and disabled people. The ghetto only had 16 groceries, a pharmacy and a laundry, and a hospital was arranged, which was headed by Professor , a surgeon. The Council of the ghetto was situated in the former Jewish school building at 141 Lāčplēša Street. The historian Marģers Vestermanis writes: "The members of the Jewish Council, including the lawyers , and , and their volunteer assistants did all they could to somehow relieve general suffering."[17] Jewish policemen, too, tried to somehow protect their fellowmen. The inmates strived to preserve themselves, and there was even an illusion of survival. A resistance group was formed that bought weapons.[18]
Daugavpils ghetto[]
The Daugavpils Ghetto was set up in Grīva at the end of July, 1941, when all surviving Jews in the city were moved there. Jews from other towns and villages of Latgale and even Vidzeme were also brought there. Altogether the ghetto had about 15,000 prisoners. The engineer ran the Council of the ghetto. His father had headed the city of Daugavpils in 1918 during the previous period of German occupation.[12]
Gypsy Holocaust in Latvia[]
Less is known about the Holocaust of the Romani people (called "Gypsy" in English and Ziguener in German) than for other groups.[19] Most of the available information about the persecution of the Gypsies in Nazi-occupied eastern Europe comes from Latvia.[20] According to Latvia's 1935 census, 3,839 Gypsies lived in the country, the largest population of any of the Baltic States. Many of them did not travel about the country, but lived settled, or "sedentary" lives.[20]
On December 4, 1941, Hinrich Lohse issued a decree which stated:
Gypsies who wander about in the countryside represent a two-fold danger.
1. As carriers of contagious diseases, especially typhus; 2. As unreliable elements who neither obey the regulations issued by German authorities, nor are willing to do useful work.
There exists well-founded suspicion that they provide intelligence to the enemy and thus damage the German cause. I therefore order that they are to be treated as Jews.[20]
Although Lohse's name was on the order, it was actually issued at the behest of ,[21] the Ordnungspolizei chief in the Baltic States. Jedicke in turn was subordinate to Friedrich Jeckeln, the senior SS man in the Baltic States and Belarus.[22]
Gypsies were also forbidden to live along the coast. Historian Lewy believes this restriction may have occasioned the first large killing of Gypsies in Latvia. On December 5, 1941, the Latvian police in Liepāja arrested 103 Gypsies (24 men, 31 women, and 48 children). Of these people, the Latvian police turned over 100 to the custody of the German police chief Fritz Dietrich "for follow up" (zu weiteren Veranlassung), a Nazi euphemism for murder.[20] On December 5, 1941, all 100 were all killed near Frauenburg.[20]
On January 12, 1942, Jedicke distributed Lohse's order of December 4, 1941, ordering his subordinates that in all cases, they were to make sure to implement the necessary "follow up."[22] By May 18, 1942, the German police and SS commander in Liepāja indicated in a log that over a previous unspecified period, 174 Gypsies had been killed by shooting.[22] The German policy on Gypsies varied. In general, it seemed that wandering or "itinerate" Gypsies (vagabundierende Zigeuner) were targeted, as opposed to the non-wandering, or "sedentary" population. Thus, on May 21, 1942, the SS commander in Liepāja police and SS commander recorded the execution of 16 itinerate Gypsies from the Hasenputh district.[22] The documentation, however, does not always distinguish between different Gypsy groups, thus on April 24, 1942, EK A reported having killed 1,272 people, including 71 Gypsies, with no further description.[22] In addition, the Nazi policy shifted back and forth as to how the Gypsies were to be treated, and the treatment of any particular group of Gypsies did not necessarily reflect what might appear to have been the official policy of the moment.[23]
Like the Jews, the killing of the Gypsies proceeded through Latvia's smaller towns, and with the aid of Latvians. The Arajs Kommando was reported to have killed many Gypsies between July and September 1941.[20] In April 1942, 50 Gypsies, mostly women and small children, were assembled at the jail in Valmiera, then taken out and shot.[22] Other massacres were reported at Bauska and Tukums.[22]
It is not known how many of Latvia's Romani people were killed by the Nazis and their Latvian collaborators.[24] Professor Ezergailis estimated that one-half of the Gypsy population was killed, but there will probably never be a more definite number.[25]
Justice[]
Some of the Rumbula murderers were captured after the fact.
- Hinrich Lohse was a member of a Nazi class that "was to receive surprisingly light treatment" at the Nuremberg trials.[26] In Lohse's case, apparently because the British authorities believed him to have been innocent of the Nazi crimes in the Baltic states, he was handed over to a West German "denazification" court. Sentenced to the maximum of 10 years, Lohse was released early in 1951 "on the familiar grounds of ill health."[27][Died 1964]
- Viktors Arājs was charged in a British court with war crimes, but was released in 1948, and afterwards hid out in West Germany for many years; although he was still a wanted war criminal, he found work as a driver for a British military unit in the western occupation zone.[27] Eventually Arājs was caught, and, in 1979, tried and convicted of murder in a West German court.[27][28][29]
- , a Nazi policeman who had been instrumental in setting up the Riga Ghetto and organizing the march out to the pits, was likewise apprehended and tried in West Germany in the 1970s.[30]
- Herberts Cukurs escaped to South America, where he was later murdered. It is said that he was assassinated by Mossad agents, who attracted him from Brazil to Uruguay under a fake intention of starting an aviation business,[31] after it was found out that he would not stand trial for his alleged participation in the Holocaust.[32]
- Eduard Strauch, SS Lieutenant Colonel, commanded a subunit of the Rumbula killers called "Einsatzkommando 2.".[33] Despite an effort to sham mental illness, he was convicted by the Nuremberg Military Tribunal in the Einsatzgruppen trial for having a key role in the Rumbula and a number of other mass murders in Eastern Europe. On April 9, 1948, Presiding judge Michael Musmanno pronounced the tribunal's sentence on Strauch: "Defendant EDUARD STRAUCH, on the counts of the indictment on which you have been convicted, the Tribunal sentences you to death by hanging."[34] Unlike his co-defendants Otto Ohlendorf and Paul Blobel, Strauch did not hang. Instead, he was handed over to authorities in Belgium, where he had committed other crimes, for trial. He died in Belgian custody on September 11, 1955.[35]
- Friedrich Jeckeln came into Soviet custody after the war. He was interrogated, tried, convicted and hanged in Riga on February 3, 1946. Against popular misconception, the execution did not happen in the territory of the former Riga ghetto, but in (Uzvaras laukums).[36]
- Fritz Dietrich (Nazi) was tried in the Dachau Trials and hanged in 1948 for killing POWS
Historiography and memorials[]
Soviet period[]
During the Second World War, the Soviet Union again occupied Latvia, this time from 1944 to 1991. It did not suit Soviet purposes to memorialize the Rumbula site or to acknowledge that the victims were Jewish. Until 1960 nothing was done to preserve or memorialize the killing grounds. In 1961 young Jews from Riga searched for the site and found charred bones and other evidence of the murders. In 1962 the Soviets staged an officially sanctioned memorial service at Bikernieki (another murder site) which made no mention of the Jews but spoke only of "Nazi victims". In 1963 groups of young Jews from Riga came out to Rumbula weekly and cleaned up and restored the site using shovels, wheelbarrows and other hand tools.[37] The site has been marked by a series of makeshift memorials over the years. Throughout the Soviet domination of Latvia the Soviets refused to allow any memorial which would specifically identify the victims as Jews.
The Soviet Union suppressed research into and memorials of the Holocaust in Latvia until 1991, when Soviet rule over Latvia ended.[38] In one case a memorial at Rumbula of which the authorities did not approve was simply hauled away in the middle of the night, with no explanation given. Occasional references were made to the Holocaust in literature during the Soviet era. A folkloric figure called "žīdu šāvējs" (Jew shooter) turned up in stories on occasion. The poet Ojārs Vācietis often referred to the Holocaust in his work, including in particular his well-regarded poem "Rumbula", written in the early 1960s.[39] One notable survivor of the Latvian Holocaust was Michael Genchik, who escaped from Latvia and joined the Red Army, where he served for 30 years. His family was killed at Rumbula. Many years later he recalled:
In later years the officials held memorial services every year in November or December. There were speeches reminding of the atrocities of the Nazis. But saying kaddish was forbidden. Once after the official part of the meeting, Jews tried to say Kaddish and tell a little about the ghetto, but the police didn't permit to do so. Until 1972, when I retired from the army, I did my best to keep the place neat.[37]
Independent Latvia[]
In Latvia, Holocaust scholarship could only be resumed once Soviet rule had ended.[40] Much of the post-1991 work was devoted to identification of the victims.[41] This was complicated by the passage of time and the loss of some records and the concealment of others by the NKVD and its successor agencies of the Soviet secret police.[41]
On November 29, 2002, sixty-one years after the murders, the highest officials of the Republic of Latvia, together with representatives of the Latvian Jewish community, foreign ambassadors, and others attended a memorial dedication at the Rumbula site. The President and the Prime Minister of the Republic walked to the forest from where the Riga ghetto had been. Once they arrived, President Vaira Vīķe-Freiberga addressed the gathering:
The Holocaust, in its many forms, has painfully struck Latvia. Here in Rumbula where the earthly remains of Latvia's Jews rest, we have come to honour and remember them. I wish therefore to extend a special greeting to the representatives of Latvia's Jewish community for whom this is special day of mourning, all the more so since here lie their loved ones, relatives, and members of their faith. * * * This is an atrocious act of violence, an atrocious massacre. And it is our duty, the duty of those of us who have survived, to pass on the commemoration of these innocent victims to future generations, to remember with compassion, sorrow and reverence. Our duty is to teach our children and children's children about it, our duty is to seek out the survivors and record their recollections, but, above all, our duty is to see that this will never happen again.[42]
See also[]
- Segodnya (Riga)
- Sonderaktion 1005
- Konrāds Kalējs
Notes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h Ezergailis, The Holocaust in Latvia, at page 245.
- ^ Ezergailis, The Holocaust in Latvia, at page 253
- ^ Ezergailis, The Holocaust in Latvia, at page 211
- ^ "Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact and its Consequences". Archived from the original on January 31, 2004. Retrieved 2013-08-17.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- ^ "Mark Aarons, Fingering the SS". Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ "Latvia & Lithuania: Viktors Arajs and the guy Klimatis • Axis History Forum". Axis History Forum. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ "What bloody Aizsargi?". Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ "Timeline". Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ "Lita (Lithuania) Pages 89-118". www.jewishgen.org. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ "History of Jews in Bukowina [Volume II, pages 167-178]". www.jewishgen.org. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ ALEXANDER DONAT (18 March 1963). "THE HOLOCAUST KINGDOM AMEMOIR". HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON. Retrieved 18 March 2018 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Seligman, Jon. "The Holocaust in Kraslava". www.seligman.org.il. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ Strods, Kaspars (March 18, 2020). "Between fear and compassion. Saving Jews in Nazi-occupied Rēzekne". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. Retrieved March 18, 2020.
- ^ "Latvia SIG - Varaklani". www.jewishgen.org. Retrieved 2017-01-11.
- ^ "Encyclopaedia Judaica, Jews in Latvia". Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ "This Day ... In Jewish History". Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ Vestermanis M. Juden in Riga. Ein historischer Wegweiser. Bremen, 1996, S. 29.
- ^ Latvia's Jewish Community: History, Tragedy, Revival Archived 2009-05-11 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Niewyk, The Columbia Guide to the Holocaust, at 47.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Lewy, The Nazi Persecution of the Gypsies, at page 123.
- ^ Some sources give the name Georg Jedicke.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Lewy, The Nazi Persecution of the Gypsies, at page 124.
- ^ Lewy, The Nazi Persecution of the Gypsies, at pages 125 to 126.
- ^ "Hancock, "Genocide of the Roma"". Archived from the original on October 26, 2009. Retrieved 2010-12-08.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- ^ Ezergailis, The Holocaust in Latvia, at page 100, n.5
- ^ Bloxham, Genocide on Trial, at page 198
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Bloxham, Genocide on Trial, at pages 197-199
- ^ Schneider, Unfinished Road
- ^ Fleming, Hitler and the Final Solution, at 93n: "After 199 days of court proceedings, on 21 December 1979, the Hamburg assize court condemned the former SS-Sturmbahnführer of the Latvian Legion and former Police Major Viktors Arājs to a life term in prison. Arājs had been living in an underground existence in Frankfurt for twenty-five years after the war under a false name and was arrested in 1975."
- ^ Ezergailis, The Holocaust in Latvia, at pages 16 and 245-248
- ^ Kuenzle, Anton and Shimron, Gad, The Execution of the Hangman of Riga: The Only Execution of a Nazi War Criminal by the Mossad, Valentine Mitchell, London 2004 ISBN 0-85303-525-3
- ^ "Home - Simon Wiesenthal Center". www.wiesenthal.com. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ Einsatzgruppen judgment, at 563-567
- ^ Einsatzgruppen judgment, at 589
- ^ (in Italian)Eduard Strauch, biography and photo at Olokaustos.org
- ^ Edelheit, History of the Holocaust, at page 340: Jeckeln was " ... responsible for the murder of Jews and Communist Party officials ... convicted and hanged in the former ghetto of Riga on February 3, 1946.
- ^ Jump up to: a b http://www.rumbula.org/quesans.shtml Rumbula.org: Statement of Michael Genchik
- ^ Ezergailis, in World Reacts to the Holocaust, at 354-88, provides a comprehensive guide to the Soviet historiographical treatment of the Holocaust in Latvia.
- ^ Ezergailis, in World Reacts to the Holocaust, at 373-374
- ^ According to the Latvia Institute (an agency of the Republic of Latvia): "There was no Holocaust research during Soviet rule in Latvia (1944–91). The victims of the Holocaust were subsumed under the rubric 'Nazi murder of peaceful Soviet citizens,' usually with unsubstantiated and highly inflated numbers. Research in the West was mainly based on accounts of survivors and court cases against Nazi criminals. Only after regaining independence in 1991, could Latvian historians begin to assess the situation and make use of documentation available locally."
- ^ Jump up to: a b Anders and Dubrovskis
- ^ Republic of Latvia, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Rumbula memorial unveiled, December 2002
References[]
Historiographical[]
- Anders, Edward, and Dubrovskis, Juris, "Who Died in the Holocaust? Recovering Names from Official Records", Holocaust and Genocide Studies 17.1 (2003) 114-138
- (in German) Angrick, Andrej, and Klein, Peter, Die "Endlösung" in Riga., (English: The Final Solution in Riga), Darmstadt 2006, ISBN 3-534-19149-8
- Bloxham, Donald, Genocide on Trial; war crimes trials and the formation of Holocaust History and Memory, Oxford University Press, New York NY 2001 ISBN 0-19-820872-3
- Browning, Christopher, and Matthäus, Jürgen, The Origins of the Final Solution: The Evolution of Nazi Jewish Policy, September 1939 – March 1942, University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, NE 2004 ISBN 978-0-8032-5979-9
- Dribins, Leo, Gūtmanis, Armands, and Vestermanis, Marģers, "Latvia's Jewish Community: History, Trajedy, Revival", Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Latvia
- Edelheit, Abraham J. and Edelheit, Hershel, History of the Holocaust : A Handbook and Dictionary, Westview Press, Boulder, CO 1994 ISBN 0-8133-1411-9
- Eksteins, Modris, Walking Since Daybreak: A story of Eastern Europe, World War II, and the Heart of our Century, Houghton Mifflin, Boston 1999 ISBN 0-395-93747-7
- Ezergailis, Andrew, The Holocaust in Latvia 1941-1944—The Missing Center, Historical Institute of Latvia (in association with the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum) Riga 1996 ISBN 9984-9054-3-8
- Ezergailis, Andrew, "Latvia", in The World Reacts to the Holocaust, Wyman, David S., and Rosenzveig, Charles H., Eds., at pages 354-388, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore 1996 ISBN 0-8018-4969-1
- Fleming, Gerald, Hitler and the Final Solution, Berkeley : University of California Press, Berkeley,1994 ISBN 0-520-06022-9
- Friedländer, Saul, The years of extermination : Nazi Germany and the Jews, 1939-1945, New York, NY 2007 ISBN 978-0-06-019043-9
- Hancock, Ian, "Genocide of the Roma in the Holocaust", Excerpted from Charny, Israel, W., Encyclopedia of Genocide (1997) available on-line at the Patrin Web Journal at the Wayback Machine (archived October 26, 2009)
- Hilberg, Raul, The Destruction of the European Jews (3d Ed.) Yale University Press, New Haven, CT 2003. ISBN 0-300-09557-0
- Kaufmann, Max, Die Vernichtung des Judens Lettlands (The Destruction of the Jews of Latvia), Munich, 1947, English translation by Laimdota Mazzarins available on-line as Churbn Lettland -- The Destruction of the Jews of Latvia (all references in this article are to page numbers in the on-line edition) ISBN 978-3866283152
- Klee, Ernst, Dressen, Willi, and Riess, Volker, eds., The Good Old Days: The Holocaust as seen by its Perpetrators and Bystanders, (English translation) MacMillan Free Press, NY 1991 ISBN 0-02-917425-2
- Latvia Institute, The Holocaust in German-Occupied Latvia
- Lewy, Guenter, The Nazi Persecution of the Gypsies, Oxford University Press 2000 ISBN 0-19-512556-8
- Lumans, Valdis O., Latvia in World War II, New York : Fordham University Press, 2006 ISBN 0-8232-2627-1
- Michelson, Frida, I Survived Rumbuli, Holocaust Library, New York, NY 1979 ISBN 0-89604-029-1
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Latvia, Holocaust Remembrance - Rumbula Memorial Site Unveiled, December 2002
- Niewyk, Donald L., and Nicosia, Francis R., The Columbia Guide to the Holocaust, New York : Columbia University Press, 2003
- Press, Bernhard (2000). The Murder of the Jews in Latvia: 1941-1945. Northwestern University Press. ISBN 978-081011729-7.
- Reitlinger, Gerald, The SS—Alibi of a Nation, at 186, 282, Viking Press, New York, 1957 (Da Capo reprint 1989) ISBN 0-306-80351-8
- Roseman, Mark, The Wannsee Conference and the Final Solution—A Reassessment, Holt, New York, 2002 ISBN 0-8050-6810-4
- Rubenstein, Richard L., and Roth, John K., Approaches to Auschwitz, page 179, Louisville, Ky. : Westminster John Knox Press, 2003. ISBN 0-664-22353-2
- (in German) Scheffler, Wolfgang, "Zur Geschichte der Deportation jüdischer Bürger nach Riga 1941/1942", Volksbund Deutsche Kriegsgräberfürsorge e.V. – 23.05.2000
- Schneider, Gertrude, ed., The Unfinished Road: Jewish Survivors of Latvia Look Back, Praeger Publishers (1991) ISBN 978-0-275-94093-5
- Smith, Lyn, Remembering: Voices of the Holocaust, Carroll & Graf, New York 2005 ISBN 0-7867-1640-1
- Winter, Alfred, "Rumbula Viewed From The Riga Ghetto" from The Ghetto of Riga and Continuance - A Survivor's Memoir 1998
War crimes trials and evidence[]
- Bräutigam, Otto, Memorandum dated 18 Dec. 1941, "Jewish Question re correspondence of 15 Nov. 1941" translated and reprinted in Office of the United States Chief of Counsel For Prosecution of Axis Criminality, OCCPAC: Nazi Conspiracy and Aggression, Exhibit 3666-PS, Volume VII, pages 978-995, USGPO, Washington DC 1946 ("Red Series")
- Jeckeln, Friedrich, excerpts from minutes of interrogation, 14 December 1945 (Maj. Zwetajew, interrogator, Sgt. Suur, interpreter), pages 8–13, from the Historical State Archives, as reprinted in Fleming, Hitler and the Final Solution, at pages 95–100 (Portions of the Jeckeln interrogation are also available online at the Nizkor website).
- Stahlecker, Franz W., "Comprehensive Report of Einsatzgruppe A Operations up to 15 October 1941", Exhibit L-180, translated in part and reprinted in Office of the United States Chief of Counsel For Prosecution of Axis Criminality, OCCPAC: Nazi Conspiracy and Aggression, Volume VII, pages 978–995, USGPO, Washington DC 1946 ("Red Series")
- Trials of War Criminals before the Nuernberg Military Tribunals under Control Council Law No. 10, Nuernberg, October 1946 - April 1949, Volume IV, ("Green Series) (the "Einsatzgruppen case") also available at Mazel library (well indexed HTML version)
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to The Holocaust in Latvia. |
- The Death of the Jewish Community of Kraslava
- Holocaust in the Baltics, a site by Professor Dovid Katz of the Vilnius Yiddish Institute at Vilnius University
- Propagandistic German video showing the entrance of the Wehrmacht in Riga.
- Mārtiņš Ķibilds (27 July 2018). The Jews of Valdemārpils – killed and then forgotten. Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- The Holocaust in Latvia
- The Holocaust by country
- Local participation in the Holocaust
- Military history of Latvia during World War II
- World War II prisoners of war massacres
- Eastern Front (World War II)
