Tornadoes of 2022
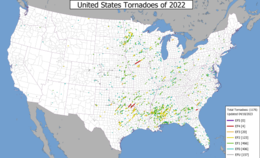 Map of the 2022 United States tornado paths from the results of preliminary surveys | |
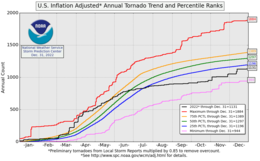 A chart of the 2022 United States tornado count estimated from the number of preliminary reports | |
| Timespan | January 1 – ongoing |
|---|---|
| Maximum rated tornado | EF4 tornado
|
| Tornadoes in U.S. | 149 |
| Damage (U.S.) | unknown |
| Fatalities (U.S.) | 10 |
| Fatalities (worldwide) | 12 |
This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2022. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Bangladesh, and Eastern India, but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina, Australia and New Zealand. Tornadic events are often accompanied by other forms of severe weather, including strong thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail.
There have been 167 preliminary filtered reported tornadoes in the United States in 2022, of which 148 have been confirmed.[1] Worldwide, 12 tornado-related deaths have been confirmed: ten in the United States and two in Poland.
The ongoing La Niña, continuing from summer 2020, is predicted to continue well into spring (possibly summer) of 2022, which may produce an active tornado/severe thunderstorm season.[2][3]
Events[]
 class=notpageimage| Approximate touchdown location of killer tornadoes in 2022 |
United States yearly total[]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 54 | 67 | 22 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 150 |
January[]
There were 37 tornadoes confirmed in the United States in the month of January.
January 1–3[]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A small outbreak of mostly weak tornadoes impacted the Southeastern United States starting with 13 confirmed tornadoes on New Year's Day. One strong tornado, rated EF2, moved through Hopkinsville, Kentucky, damaging several businesses, a church, and a gas station.[6][7] A weak EF0 tornado embedded within larger area straight-line winds also caused damage in Bowling Green, an area previously impacted by two strong tornadoes during the previous month, which killed 17 people and injured 63 others.[8][9] In Madison County, Alabama, a high-end EF0 tornado damaged several businesses, snapped tree branches, and ripped the roof off a mobile home. One person was injured, the only casualty of the outbreak.[10] Three weak, brief EF0 tornadoes touched down in Georgia and Florida on January 2. Two weak tornadoes also touched down in North Carolina during the morning hours of January 3 before the outbreak ended. In all, 19 tornadoes touched down, with only one injury reported.
January 8–9[]

| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
From the evening of January 8 into the afternoon of the next day, several mostly weak tornadoes moved through the Greater Houston area in Southeast Texas, along with Sabine Parish, Louisiana, and southern Alabama. An EF2 tornado struck the community of Peason, Louisiana, damaging at least 30 homes and injuring six people.[11] Overall, 11 tornadoes were confirmed.
January 16[]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Several tornadoes occurred over coastal areas of Florida during the morning hours of January 16, most of which were the result of waterspouts moving onshore. A strong EF2 tornado caused major damage to three mobile home parks in the Fort Myers suburb of Iona. 108 mobile homes were damaged, 30 of which were destroyed and 51 of which sustained major damage. The tornado, which injured three, was caught on video by many people living in the surrounding areas.[12][13][14] An EF0 tornado in Collier County also caused an injury.[15] In all, four people were injured by the tornadoes.
February[]
There were 10 tornadoes confirmed in the United States in the month of February.
February 3[]

| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Several tornadoes occurred in central Alabama ahead of a cold front, including in Hale County, where one person was killed near Sawyerville by an EF2 tornado.[16] In total, three EF2 tornadoes were produced in Western Alabama, all by the same supercell. In addition to the fatality, eight others were injured. Two additional tornadoes, both rated EF0, impacted Elmore County, resulting in minimal damage.
February 17 (Europe)[]
| FU | F0 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0 | 7 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
As European Windstorm Dudley moved across Europe, it produced at least 24 tornadoes in Poland and Germany. The first tornado of the day hit the village of Casekow in eastern Germany. Strong damage was done to a big farm building and a small forest area. Some residential buildings were also hit.[17][18] In Poland, houses got heavily damaged or partly destroyed by several F2 tornadoes.[19][20][21] In the city of Kraków, a short-lived tornado caused a crane to collapse resulting in two deaths and two injuries.[22][17] One other tornado was reported in Italy, which was caused by a different weather system. In total, two people were killed and five others were injured by the tornadoes in Poland. [23]
March[]
There have been 102 tornadoes confirmed in the United States in the month of March.
March 5–7[]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 11 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
A tornado outbreak, spawned from a strong, negatively tilted shortwave trough, struck the Midwestern United States, in particular the state of Iowa. Multiple tornadoes have been reported in Iowa, leading to considerable damage. Six people were killed by a violent, long-tracked low-end EF4 tornado near Winterset. The tornado also caused severe damage near the towns of Norwalk and Pleasant Hill, before dissipating near Newton, after nearly 70 mi (110 km) miles on the ground.[24][25] An EF3 tornado near Chariton also killed one person while other strong tornadoes caused damage in Corydon, Gilman, and Vinton. The storms then congealed into a squall line, producing damaging straight-line winds and isolated weak tornadoes eastward to Ontario and Ohio before weakening and dissipating. Activity refired in Arkansas and Missouri the next day, with several tornadoes reported. One long-track intense supercell moved from southeast Arkansas northeastward across the entire state, producing four tornadoes. The strongest was a low-end EF2 tornado that struck Sage, Arkansas injuring six, including one seriously. Other severe storms formed that evening and produced more damaging winds and isolated weak tornadoes before weakening the next morning on March 7. One non-tornadic fatality occurred early that morning when semi truck carrying logs was blown over on U.S. 641 near Hazel, Kentucky, ejecting and killing the passenger.[26] A large squall line produced widespread wind damage in Northeastern United States that afternoon, but no tornadoes touched down. A total of 29 tornadoes were confirmed, with seven tornadic fatalities, one non-tornadic fatality, and at least 12 injuries.
March 21–23[]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | 26 | 11 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
A tornado outbreak unfolded in the Southern region of the United States. The Storm Prediction Center issued a moderate risk in anticipation for the event, as favorable conditions for severe weather positioned themselves over east-central Texas, where a 15%, hatched area for tornadoes, indicating the possibility of strong tornadoes, was introduced.[27] Multiple supercell thunderstorms developed over the area on March 21, prompting the issuance of numerous tornado warnings in Texas and southern Oklahoma, including several PDS tornado warnings. An EF3 tornado caused major damage in Jacksboro, Texas before the same storm produced an EF2 tornado in Sherwood Shores, Texas caused major damage, killed one person and injured 11 others before crossing the state line and causing more damage in Kingston, Oklahoma.[28] An EF1 tornado near Bowie, Texas, injured three people, an EF2 tornado injured 10 people in Crockett, and another EF2 tornado injured seven in Upshur and Marion Counties Tornadic activity continued into March 22 as the system moved eastward into Louisiana and Mississippi where another moderate risk, including a 15%, hatched area for tornadoes, was issued. Numerous tornadoes reported in both states as well as Alabama. Parts of the New Orleans metropolitan area, including Gretna, Algiers, Arabi, and New Orleans East, were severely damaged by an EF3 wedge tornado that evening, with one death and numerous injuries being reported. Another EF3 tornado struck rural Kemper County, Mississippi near , producing severe tree damage and heavily damaging a few homes. On March 23, more tornadoes were confirmed in the Eastern United States, including EF2 tornadoes near Pickens, South Carolina, and .
See also[]
- Weather of 2022
- Tornado
- Tornadoes by year
- Tornado records
- Tornado climatology
- Tornado myths
- List of tornado outbreaks
- List of F5 and EF5 tornadoes
- List of North American tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of 21st-century Canadian tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of European tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tornadoes and tornado outbreaks in Asia
- List of Southern Hemisphere tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tornadoes striking downtown areas
- Tornado intensity
References[]
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Annual Report Summary - 2022". NWS Storm Prediction Center. Retrieved February 7, 2022.
- ^ "What (if Anything) is Climage Change Doing to Tornadoes". Economist Magazine. Retrieved December 23, 2021.
- ^ "The 6 things We'd Like to See Under 2022 Weather". The Weather Channel. Retrieved December 23, 2021.
- ^ "Annual U.S. Killer Tornado Statistics". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved February 3, 2022.
- ^ "One dead, others critically injured after radar-indicated tornado in Hale County". abc3340.com. February 3, 2022. Retrieved February 3, 2022.
- ^ NWS Damage Survey for 01/01/22 Tornado Event (Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service in Paducah, Kentucky. January 2, 2022. Retrieved January 2, 2022.
- ^ "Preliminary Local Storm Report". Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service in Paducah, Kentucky. January 2, 2022. Retrieved January 2, 2022.
- ^ "SPC Storm Reports for 01/01/22". Storm Prediction Center. January 1, 2022. Retrieved January 2, 2022.
- ^ "NWS Damage Survey for 01/01/2022 Tornado Event". Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service in Louisville, Kentucky. January 2, 2022. Retrieved January 2, 2022.
- ^ NWS Damage Survey for 01/01/22 Tornado Event (Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service Huntsville, Alabama. January 2, 2022. Retrieved January 2, 2022.
- ^ NWS Damage Survey for 1/09/22 Tornado Event - Update (Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service in Shreveport, Louisiana. January 10, 2022. Retrieved January 10, 2022.
- ^ NWS Damage Survey for 01/16/22 Tornado Event Fort Myers Tornado Event - Update #1 (Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office in Tampa, Florida. January 18, 2022. Retrieved January 18, 2022.
- ^ NWS Damage Survey for 01/16/22 Victoria Falls/Lely Resort (Report). Miami, Florida: Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office in Miami, Florida. January 16, 2022. Retrieved January 16, 2022.
- ^ "Neighborhoods assess damage as possible tornadoes rake across Southwest Florida". WFTX. January 16, 2022. Retrieved January 16, 2022.
- ^ NWS Damage Survey for 01/16/22 Victoria Falls/Lely Resort (Report). Miami, Florida: Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office in Miami, Florida. January 16, 2022. Retrieved January 16, 2022.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved February 4, 2022.
- ^ a b "European Severe Weather Database". eswd.eu. Retrieved February 17, 2022.
- ^ "[F1] Casekow, BB". www.tornadomap.org (in German). Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ "European Severe Weather Database". Archived from the original on February 22, 2022.
- ^ Kurzyński, Andrzej (February 17, 2022). "Potężna wichura w powiecie kaliskim. Wiatr zrywał dachy. Straty są ogromne. ZDJĘCIA". Kalisz Nasze Miasto (in Polish). Retrieved February 17, 2022.
- ^ "To był armagedon! Pozrywane dachy na domach i budynkach gospodarczych". Sieradz Nasze Miasto (in Polish). Retrieved February 17, 2022.
- ^ "Przewrócony dźwig budowlany przy ulicy Domagały w Krakowie. Dwóch poszkodowanych nie żyje. WIDEO". www.radiokrakow.pl (in Polish). Retrieved February 17, 2022.
- ^ Pucik, Tomas. "Windstorms and tornado outbreak of February 2022 | European Severe Storms Laboratory". Retrieved February 28, 2022.
- ^ "'A dark night:' Tornadoes and severe storms bring multiple deaths, damage to Iowa". KCCI. March 6, 2022. Retrieved March 6, 2022.
- ^ "Initial interrogation of photos and videos from around Winterset suggests at least EF3 tornado damage occurred late Saturday afternoon. NWS survey teams will be out Sunday to thoroughly investigate the damage and further assess a potential rating". Twitter. National Weather Service Forecast Office in Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved March 6, 2022.
- ^ "SPC Filtered Storm Reports for 03/06/22". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. March 6, 2022. Retrieved March 6, 2022.
- ^ Mar 21, 2022 2000UTC Convective Outlook (Report). National Weather Service. Retrieved March 21, 2022.
- ^ "At least one confirmed dead from Monday night's tornadoes". www.kten.com. Retrieved March 22, 2022.
- Tornadoes of 2022
- 2022 meteorology
- 2022 natural disasters
- 2022-related lists
- Tornado-related lists by year
- Tornado-related lists