1935 New South Wales state election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 90 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly 46 Assembly seats were needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
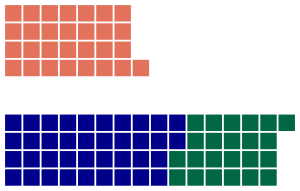 Legislative Assembly after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

The 1935 New South Wales state election was held on 11 May 1935. This election was for all of the 90 seats in the 31st New South Wales Legislative Assembly and was conducted in single member constituencies with compulsory preferential voting.[1][2][3]
The result of the election was:
- United Australia Party 38 seats
- Country Party 23 seats
- Australian Labor Party (NSW) 29 seats.
The UAP/Country Party coalition of Bertram Stevens/Michael Bruxner had a majority of 32 (down 10) and continued in government throughout the term.[4]
Labor (NSW) and the Federal Executive of the Australian Labor Party were still divided at the 1935 election and Federal Labor ran candidates in 22 seats without success. The parties were re-united in 1936. Jack Lang remained party leader and Leader of the Opposition throughout the term of the parliament.[5]
Key dates[]
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 10 February 1935 | Second Stevens ministry sworn in. |
| 12 April 1935 | The Legislative Assembly was dissolved, and writs were issued by the Governor to proceed with an election. |
| 18 April 1935 | Nominations for candidates for the election closed at noon. |
| 11 May 1935 | Polling day. |
| 10 June 1935 | The writs were returned and the results formally declared. |
| 12 June 1935 | Opening of 31st Parliament. |
Results[]
|
New South Wales state election, 11 May 1935 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrolled voters | 1,347,884[a] | |||||
| Votes cast | 1,255,419 | Turnout | 96.06 | −0.34 | ||
| Informal votes | 39,333 | Informal | 3.04 | 0.83 | ||
| Summary of votes by party | ||||||
| Party | Primary votes | % | Swing | Seats | Change | |
| Labor (NSW) | 532,486 | 42.42 | +2.26 | 29 | + 5 | |
| United Australia | 415,485 | 33.10 | –3.64 | 38 | – 5 | |
| Country | 162,178 | 12.92 | –0.24 | 23 | ± 0 | |
| Federal Labor | 59,694 | 4.75 | +0.51 | 0 | ± 0 | |
| Communist | 19,105 | 1.52 | +0.60 | 0 | ± 0 | |
| Independent UAP | 11,114 | 0.89 | +0.21 | 0 | ± 0 | |
| Centre | 7,489 | 0.60 | +0.60 | 0 | ± 0 | |
| Independent Labor | 3,774 | 0.30 | +0.16 | 0 | ± 0 | |
| Social Credit | 1,996 | 0.16 | +0.16 | 0 | ± 0 | |
| Independents | 42,098 | 3.35 | +1.17 | 0 | ± 0 | |
| Total | 1,255,419 | 90 | ||||
Retiring members[]
Labor[]
- William Brennan (Hamilton)
- Peter Connolly (Newcastle) — lost party endorsement
- Tom Keegan (Glebe)
United Australia[]
Changing seats[]
| Seats changing hands | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seat | 1932 | 1935 | ||||
| Party | Member | Member | Party | |||
| Arncliffe | United Australia | Horace Harper | Joseph Cahill | Labor (NSW) | ||
| Bathurst | Country | Gordon Wilkins | Gus Kelly | |||
| Canterbury | United Australia | Edward Hocking | Arthur Tonge | |||
| Goulburn | Peter Loughlin | Jack Tully | ||||
| Mudgee | Country | David Spring | Bill Dunn | |||
See also[]
- Candidates of the 1935 New South Wales state election
- Members of the New South Wales Legislative Assembly, 1935–1938
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ a b Green, Antony. "1935 election totals". New South Wales Election Results 1856-2007. Parliament of New South Wales. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- ^ Part 5B alphabetical list of all electorates and Members since 1856 (PDF). NSW Parliamentary Record. Parliament of New South Wales. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ "Former members of the New South Wales Parliament, 1856–2006". New South Wales Parliament. Retrieved 4 December 2019.
- ^ Ward, John M. "Stevens, Sir Bertram Sydney Barnsdale (1889–1973)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Melbourne University Press. ISSN 1833-7538. Retrieved 2021-11-02 – via National Centre of Biography, Australian National University.
- ^ Nairn, Bede. "Lang, John Thomas (Jack) (1876–1975)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Melbourne University Press. ISSN 1833-7538. Retrieved 2021-11-02 – via National Centre of Biography, Australian National University.
Bibliography[]
- Nairn, Bede (1995). Jack Lang the 'Big Fella':Jack Lang and the Australian Labor Party 1891–1949. Melbourne University Press Melbourne. ISBN 0522846963. OCLC 34416531.
- Elections in New South Wales
- 1935 elections in Australia
- 1930s in New South Wales
- May 1935 events

