2021 Pacific typhoon season
| 2021 Pacific typhoon season | |
|---|---|
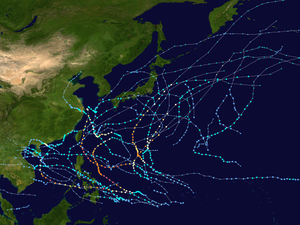 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 19, 2021 |
| Last system dissipated | Season ongoing |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Surigae |
| • Maximum winds | 220 km/h (140 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 895 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 29 |
| Total storms | 14 |
| Typhoons | 4 |
| Super typhoons | 2 (unofficial)[nb 1] |
| Total fatalities | 57 total |
| Total damage | $2.07 billion (2021 USD) |
| Related articles | |
| |
The 2021 Pacific typhoon season is an ongoing event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season runs throughout 2021, with no seasonal boundaries, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Dujuan, developed on February 16. The season's first typhoon, Surigae, reached typhoon status on April 16. It became the first super typhoon of the year on the next day, also becoming the strongest tropical cyclone in 2021 so far. Surigae was also the most powerful tropical cyclone on record in the Northern Hemisphere for the month of April.[1]
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean to the north of the equator between 100°E and 180th meridian. Within the northwestern Pacific Ocean, there are two separate agencies that assign names to tropical cyclones, which can often result in a cyclone having two names. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)[nb 2] names a tropical cyclone should it be judged to have 10-minute sustained wind speeds of at least 65 km/h (40 mph) anywhere in the basin, whilst the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones which move into or form as a tropical depression in their area of responsibility located between 135°E and 115°E and between 5°N and 25°N, regardless of whether or not a tropical cyclone has already been given a name by the JMA. Tropical depressions that are monitored by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC)[nb 3] are given a number with a "W" suffix.
Seasonal forecasts
| TSR forecasts Date |
Tropical storms |
Total Typhoons |
Intense TCs |
ACE | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (1965–2020) | 26 | 16 | 9 | 294 | [3] |
| May 11, 2021 | 24 | 15 | 9 | 270 | [3] |
| July 7, 2021 | 25 | 15 | 9 | 265 | [4] |
| August 9, 2021 | 25 | 13 | 7 | 230 | [5] |
| Other forecasts Date |
Forecast Center |
Period | Systems | Ref. | |
| December 27, 2020 | PAGASA | January–March | 0–3 tropical cyclones | [6] | |
| December 27, 2020 | PAGASA | April–June | 1–4 tropical cyclones | [6] | |
| June 23, 2021 | PAGASA | July–September | 5–9 tropical cyclones | [7] | |
| June 23, 2021 | PAGASA | October–December | 5–8 tropical cyclones | [7] | |
| 2021 season | Forecast Center |
Tropical cyclones |
Tropical storms |
Typhoons | Ref. |
| Actual activity: | JMA | 29 | 14 | 4 | |
| Actual activity: | JTWC | 19 | 15 | 6 | |
| Actual activity: | PAGASA | 11 | 9 | 3 | |
During the year, several national meteorological services and scientific agencies forecast how many tropical cyclones, tropical storms, and typhoons will form during a season and/or how many tropical cyclones will affect a particular country. These agencies included the Tropical Storm Risk (TSR) Consortium of University College London, PAGASA and Taiwan's Central Weather Bureau. The first forecast was released by PAGASA on December 27, 2020, in their monthly seasonal climate outlook predicting the first half of 2021.[6] The PAGASA predicts that only 0–3 tropical cyclones are expected to form or enter the Philippine Area of Responsibility between January and March, while 1–4 tropical cyclones are expected to form between April and June. PAGASA also predicted that the ongoing La Niña could persist until the end of the first quarter of 2021.[6] Tropical Storm Risk (TSR) issued their first extended range forecast on May 11, predicting a slightly below-average season with 24 tropical storms, 15 typhoons and 9 intense typhoons.[3]
On June 23, the PAGASA released their monthly climate outlook for the rest of 2021, predicting 5 to 9 tropical cyclones developing or entering their area of responsibility from July to September, and 5 to 8 tropical cyclones from October to December.[7] TSR issued an update to their forecast on July 7, reiterating their expectations for slightly below-average activity.[4] On August 9, TSR issued their final forecast for the season, slightly lowering their numbers to 25 named storms, 13 typhoons and 7 intense typhoons.[5]
Seasonal summary

The season began in January with a weak and short-lived tropical depression that brought damages to the Philippines. In mid-February, another tropical depression formed, before being assigned the local name Auring by the PAGASA. The system then strengthened into a tropical storm, being given the name Dujuan by the JMA, making it the first named storm of the year. Another tropical depression formed in March, though it was short-lived, dissipating shortly after forming. On April 12, a tropical depression formed to the south of Woleai. It strengthened into a tropical storm, being given the name Surigae by the JMA. On April 15, it was further upgraded into a severe tropical storm, before being upgraded to a typhoon on the next day, and to a super typhoon on April 17,[nb 1] making it the first of the season and the strongest recorded cyclone to form in the month of April in the Northern Hemisphere, however, it did not hit any landmasses. Then, in mid-May a new tropical depression was named Crising by the PAGASA and made landfall on Baganga, Davao Oriental as a weak tropical storm, bringing minimal damages due to its small size. Two tropical depressions formed on May 29 and 30 respectively, with the first being assigned the local name Dante by the PAGASA. Dante intensified into a tropical storm, being assigned the name Choi-wan, before moving over the Philippines and making landfall eight times, bringing widespread damages to the country. A tropical depression formed behind Choi-wan on May 30; it didn't develop further. The second typhoon of the season, Champi, briefly threatened the Ogasawara Islands before recurring through the main Japanese islands. Another depression formed at the end of June; it stayed from any landmasses while two tropical depressions formed in early-July with both of them affecting land. One of them was named Emong by PAGASA. In mid-July, In-fa formed and became the third typhoon of the season. The storm contributed to rainfall and flooding in eastern China as it made landfall near Shanghai. Meanwhile, tropical storm Cempaka affected southern China and northern Vietnam. Another tropical storm, Nepartak, formed as Cempaka made landfall. Nepartak affected Japan in late July, disrupting the 2020 Summer Olympics, before becoming extratropical in the sea of Japan. By the end of July, activity abruptly exploded as eight tropical depressions formed within a week. Half of them were short-lived and dissipated without becoming tropical storms. Another depression, and the remaining three were named Lupit, Nida, and Mirinae. Lupit and Mirinae both threatened Japan while Nida stayed out to sea. A system from the Central Pacific traveled a long distance and became Tropical Storm Omais over the Philippine Sea. After Omais, the tropics stayed quiet for the rest of August until early September, when Conson rapidly intensified to become a typhoon in less than 24 hours before hitting the Philippines and Chanthu becoming the second Category 5 super typhoon of the season.
Systems
Tropical Storm Dujuan (Auring)
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | February 16 – February 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 996 hPa (mbar) |
On 12:00 UTC on February 16, the JMA reported that a tropical depression had formed.[9] Two hours later, the JTWC issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (TCFA) for the system.[10] By February 17, the system moved into the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), being assigned the local name Auring from the PAGASA.[11] At 09:00 UTC on the same day, the JTWC upgraded the system to a tropical depression, giving it the designation 01W.[12] On February 18, as it neared the Philippines, both the JTWC and the PAGASA upgraded the system to a tropical storm.[13][14] The JMA followed suit soon after, assigning it the name Dujuan.[15] The PAGASA later upgraded Dujuan to a severe tropical storm; however, this only lasted for six hours.[16][17] On February 20, the storm significantly weakened due to high vertical wind shear, prompting the JTWC to downgrade the system back to a tropical depression,[18] though the JTWC briefly re-classified the system as a tropical storm due to improvements in the storm's structure.[19] By February 22, all agencies had downgraded the system to a tropical depression after the system's center had weakened prior to making landfall.[20][21][22] The JMA and the JTWC issued their final advisories moments after.[23] The storm made landfall over Batag Island in Laoang, Northern Samar at 09:00 PHT (01:00 UTC) on February 22,[24] dissipating thereafter.[25]
Dujuan briefly moved over Palau on February 16 as a tropical depression, bringing heavy rainfall to parts of the country.[26][27] In anticipation of the storm, the PAGASA raised Signal #1 warnings for the eastern section of Mindanao and on the eastern provinces of Visayas on February 19.[28][29][30] Signal 2 warnings were also issued for the majority of Samar Island, Southern Leyte, the Dinagat Islands, and Surigao del Norte on February 21, prior to its landfall.[31] Classes and government work were suspended on February 22 in parts of Eastern Visayas and Central Visayas, including Surigao del Sur.[32][33] A total of 242,194 individuals were affected in Northern Mindanao, Caraga, and in the Davao Region. At least 77,811 of the affected individuals were taken to 344 various evacuation shelters in each region. One person was reported dead with four others reported missing, with total damages to agriculture and infrastructure amounting to ₱159.8 million (US$3.29 million).[34]
Typhoon Surigae (Bising)
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | April 12 – April 24 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 220 km/h (140 mph) (10-min) 895 hPa (mbar) |
A low-pressure area south of Woleai developed into a tropical depression on April 12.[35][36] A few hours later, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the developing storm, with the PAGASA beginning to issue advisories for the tropical depression as it remained outside of the PAR.[37][38] On April 13, the JTWC upgraded the system to a tropical depression and assigned it the designation 02W.[39] At 18:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded the cyclone to a tropical storm and named it Surigae.[40] On April 15 at 00:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded Surigae to a severe tropical storm as an eye began forming.[41] Later that day, the JTWC upgraded the storm to a typhoon, making it the first of the season. Surigae then entered the PAGASA's Philippine Area of Responsibility, getting the local name Bising. The JMA followed suit early on the next day as a central dense overcast developed and filled the original eye. Surigae continued to rapidly intensify, and on April 16, the JTWC upgraded Surigae to a Category 2-equivalent typhoon on the SSHWS.[42] The system continued its rapid intensification until it reached Category 5 super typhoon status, becoming the most intense typhoon ever recorded in the month of April.[43][44] Surigae soon reached its peak intensity, with a minimum central pressure of 895 millibars (26.43 inHg), 10-minute maximum sustained winds of 220 km/h (140 mph), and 1-minute sustained winds of 305 km/h (190 mph).[45][46] After attaining peak intensity, signs of a concentric eyewall indicated that the storm was undergoing an eyewall replacement cycle, with the central dense overcast starting to warm and the eye becoming cloud-filled.[47][48] On April 19, following its eyewall replacement cycle, Surigae became annular.[49] A few days later, on April 22, Surigae began to weaken again, with the storm's structure deteriorating and its large eye dissipating.[50] Soon afterward, all of the remaining convection was sheared to the east as the storm moved over cooler waters.[51] As most of the remaining thunderstorms had dissipated, the JTWC assessed that Surigae transitioned into a subtropical cyclone on April 23.[52] Late on April 24, the JTWC issued their final advisory on the system as it was nearing the completion of its extratropical transition.[53] A few hours later, the JMA declared that Surigae had become extratropical.[54]
After being named, tropical storm watches and warnings were issued for Yap in the Federated States of Micronesia, as well as for Koror and Kayangel in Palau on April 14.[55] Warnings were eventually issued for Ngulu Atoll as well.[56] Winds of up to 30 mph (50 km/h) were recorded in Yap on that day as Surigae passed from the southwest.[57] Damage in Palau was estimated at US$4.8 million.[58] On April 16, as the storm tracked towards the Philippines, the PAGASA issued Signal #1 warnings for areas around the country, also issuing Signal #2 warnings the next day for Catanduanes and Samar.[59][60][61] Very strong winds and heavy rains affected the eastern part of the Philippines, with storm surge inundating parts of coastline nearest to the typhoon. Surigae killed a total of 8 people and left another 10 missing.[62][63] The storm also caused at least ₱272.55 million (US$5.65 million) in damages.[62]
Tropical Depression 03W (Crising)
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | May 12 – May 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 1004 hPa (mbar) |
On May 11, the JTWC noted a persistent area of convection in the Philippine Sea, approximately 184 nmi (341 km) west of Palau.[64] The JTWC issued a TCFA for the convection on May 12, as it further developed in an environment with low vertical wind shear and warm sea surface temperatures.[65] Just three hours later, the agency recognised that the area of convection had quickly consolidated into a tropical depression and assigned it with the identifier of 03W.[66] Around the same time, the JMA had also recognised the storm as a tropical depression while it was to the east of Mindanao.[67] Since the storm developed within the Philippine Area of Responsibility, the PAGASA immediately named the storm Crising once the agency recognized it as a tropical depression as well, and later raised Signal No. 2 warnings for areas in Mindanao.[68][69] In the early hours of May 13, the JTWC upgraded the system into a tropical storm, with the PAGASA following suit hours later.[70][71] Later that day, Crising's low-level circulation center became exposed due to wind shear, and it lost organization. At 8:20 p.m. Philippine Standard Time (12:20 UTC), Crising made landfall in Baganga, Davao Oriental as a weakening tropical storm. It quickly degraded as soon as it made landfall, with both the JTWC and the PAGASA downgrading it to a tropical depression at 15:00 UTC.[72][73] At 03:00 UTC on that day, the PAGASA reported that the system degenerated to an area of low-pressure in the vicinity of Piagapo in Lanao del Sur, thus lifting all warning signals on Mindanao and issuing their final advisory.[74] On May 14, the system dissipated over the Sulu Sea, and both the JMA and the JTWC issued their final advisories on the storm.
In preparations for the storm, the local government of Davao Occidental raised a blue alert on May 13, with the authorities in the area preparing rescue equipment in case of emergency.[75] The PAGASA also warned small vessels near the area to stay away from the rough seas caused by the storm.[76] Schools were ordered to be suspended from that day in Davao Occidental, including the submission of modules.[76] When Crising made landfall, it caused widespread rains and flooding across Mindanao and Southern Visayas. Gusty winds were also felt in parts of Mindanao where the storm passed.[77] In Baganga, some trees were knocked down by strong winds, while strong winds with heavy rainfall were reported in Cateel and Boston, all in the province.[75] Three men and a carabao were required to be rescued from the rising Kabacan River in the early hours of May 14; they were successfully released safely from the said river.[77] An evacuation center in South Upi, Maguindanao were reported to be flooded and some crops near the center were submerged in floodwaters, all due to a rising river near the area.[77] Agricultural damages were estimated at ₱23.2 million (US$486,000).[78]
Tropical Storm Choi-wan (Dante)
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | May 29 – June 5 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 998 hPa (mbar) |
On May 27, the JMA and the JTWC noted the persistence of an area of atmospheric convection about 425 nautical miles (787 km; 489 mi) south-southeast of Guam.[79] The area's nearby environment exhibited low wind shear and warm sea surface temperatures, which were ideal conditions for tropical cyclogenesis.[80] The JMA assessed the area to have developed into a Tropical depression on May 29 at 06:00 UTC.[81] The PAGASA made a similar assessment in a Tropical Cyclone Advisory issued at 15:00 UTC.[82] The JTWC later followed with their own assessment, identifying the center of the newly developed tropical depression and assigning the designation 04W.[83] As the system tracked westward, it entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility at 01:00 PHT (17:00 UTC).[84] The PAGASA then named the storm Dante in its first Tropical Cyclone Bulletin for the storm.[85] Dante further organized in the Philippine Sea,[86] and on May 30 at 15:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded it to a tropical storm,[87] with the PAGASA doing the same at 21:00 UTC.[88] On the next day at 00:00 UTC, the JMA also upgraded Dante into a tropical storm, giving it the international name Choi-wan.[89] Choi-wan's center was exposed due to a tropical upper tropospheric trough from the northeast, inducing shear on the system.[90] On June 1 at 12:30 UTC, Choi-wan made landfall on Sulat, Eastern Samar as a minimal tropical storm,[91] with the JTWC downgrading it to a tropical depression at 15:00 UTC.[92] It made a second landfall on Cataingan at 17:00 UTC.[93] Choi-wan made several more landfalls on the Philippines, making its third landfall on Balud, Masbate at 19:30 UTC. It made a fourth landfall on Romblon, Romblon on June 2 at 00:00 UTC, a fifth on San Agustin, Romblon at 00:50 UTC, a sixth on Pola, Oriental Mindoro at 06:00 UTC, a seventh on Tingloy, Batangas at 11:20 UTC, and an eighth and final landfall on the Calatagan Peninsula before moving into the South China Sea.[94] On June 3 at 03:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded Choi-wan back to a tropical storm.[95] At 03:00 UTC, the PAGASA removed all Tropical Cyclone Warning Signals as Choi-wan moved away from the country.[96] Choi-wan then exited the PAR on June 3 at 18:00 UTC[97] before weakening into a tropical depression on the next day at 06:00 UTC and re-entering the PAR at 08:00 UTC.[98] Then, it passed southeast of the island of Taiwan[99] before moving out near the Okinawa Prefecture and heading towards Japan.[citation needed] On June 5 at 06:00 UTC, the Japan Meteorological Agency issued their final advisory on the system.[100] 3 hours later at 09:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded Choi-wan back into a tropical storm,[101] however at 15:00 UTC, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center downgraded the system to a tropical depression, also issuing their final advisory on the system.[102]
Heavy rains caused floods in parts of Mindanao;[103] 11 fatalities were reported, 3 people were injured, and 2 people are missing.[104] As of June 4, 55,226 people were affected and 16,680 people are inside evacuation centers. A total of ₱307.2 million (US$6.39 million) of damages were incurred throughout the country, of which ₱152.1 million (US$3.17 million) was agricultural damages and ₱155.1 million (US$3.23 million) was related to infrastructure.[105] On June 1, classes and government work for parts of Davao de Oro, Eastern Samar, Leyte, and Surigao del Sur were suspended for the day.[106]
Tropical Storm Koguma
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | June 11 – June 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 996 hPa (mbar) |
On June 10, the JTWC started to monitor an area of low-pressure in the South China Sea, approximately 518 km (322 mi) to the south of Hong Kong, with the former classifying the system as a monsoon depression.[107] Tracking west-northwestward, the storm was located in a favourable environment for further development, with warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear, being offset by lack of divergence aloft.[108] At 06:00 UTC on June 11, the JMA upgraded the system into a tropical depression.[109][110] Six hours later, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the system.[111] On June 12 at 03:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded the system into a tropical depression, assigning it the designation 05W.[112] Three hours later at 06:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm, assigning it the name Koguma.[113] Another three hours later, the JTWC also upgraded the system to a tropical storm. On the next day, the storm made landfall in extreme northern Vietnam and dissipated later that day.
Typhoon Champi
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | June 20 – June 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
At 00:00 UTC on June 18, the JTWC started to monitor a broad area of convection nearly 250 km (160 mi) to the south-southwest of Pohnpei.[114] The system remained weak as it moved northwestwards in a favorable environment for further intensification, characterized by warm sea surface temperatures, low to moderate wind shear and good outflow; the disturbance remained weak as it moved northwestwards.[114][115] The JTWC issued a TCFA on the system two days later, though the system remained disorganised.[116][117] The JMA upgraded the system to a tropical depression at 00:00 UTC on June 21.[118] Meanwhile, the JTWC designated it as 06W in their first advisory on the system, with an exposed LLCC being evident on satellite imagery due to moderate wind shear, being induced by a tropical upper tropospheric trough to its north.[119][120] By 21:00 on June 21, 06W made its closest passage to the south-southwest of Guam, continuing its northwest track.[121][122] On June 22, at 06:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded the system into a tropical storm as it continued to move away from Guam.[123] The JMA followed and upgraded the system into a tropical storm, in June 23 at 00:00 UTC, and assigned it the name Champi.[124] At 18:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded the storm to a severe tropical storm as it turned northwestwards.[125] At this time, a microwave imagery scan of Champi revealed an eye feature emerging in the system; however, this was short lived as dry air continued to impact the storm from the west.[126] In addition, poleward outflow on the system remained weak on June 24, restricting Champi to significantly develop.[127] However, on the next day, as a shortwave trough crossed the Ryukyu Islands, the outflow increased on the storm which allowed it to intensify further.[128] On June 25, at 06:00 UTC, the JMA officially declared the storm a typhoon.[129] The JTWC soon followed, upgrading it into a Category 1 typhoon.[130] At this time, a Champi turned north and north-northwestwards, and subsequently reached its peak intensity of 120 km/h (75 mph) ten-minute maximum sustained winds with a minimum barometric pressure of 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) by 21:00 UTC on June 25, however it was downgraded to a tropical storm a day later.[131] The storm continued to weaken as it move towards the Japanese islands, until on June 27, the JMA issued its last advisory at 12:00 UTC as the system became an extratropical low.[132] The JTWC also issued its last warning for Champi at 09:00 UTC, same day.[133]
In the wake of the tropical depression, the National Weather Service in Guam issued a tropical storm watch for Rota in the Northern Mariana Islands and a tropical storm warning for the whole island of Guam on June 21.[134][135] Marine and flash flood warnings were also posted on the former and on Saipan, Tinian, and other islands in the east and south, while classes on an elementary and a high school in the latter were suspended on the next day due to a reported power outage.[136][137] Electrical disruptions were also experienced on Chalan Pago, Toto/Canada, and Santa Rita in Guam due to the system's near approach.[137] As it moved away from the island and the Marianas, the watch and warning on these areas were lifted at 01:00 UTC on June 22.[138] In the Bonin Islands, residents in the area were advised of rough seas and gusty winds caused by Champi.[139]
Tropical Depression 07W (Emong)
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 3 – July 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 1004 hPa (mbar) |
On July 2, the JTWC started to monitor a tropical disturbance to the southwest of Guam.[140] Moving northwestwards, the disturbance was located in an environment conducive for intensification in the Philippine Sea, with warm sea surface temperatures, and low wind shear, in addition to good poleward outflow, being induced by an upper-level trough to the northwest.[141][142] The JMA upgraded the broad and weak system to a tropical depression at 18:00 UTC on the next day,[143] followed by a TCFA being issued by the JTWC an hour and a half later.[144][145] The PAGASA subsequently upgraded the system to a tropical depression at 02:00 UTC on July 4, naming it Emong.[146][147] At 21:00 UTC, the JTWC also upgraded the system to a tropical depression, designating it as 07W.[148] On July 6, PAGASA issued its last advisory on Tropical Depression Emong at 03:00 UTC as it moved outside the PAR and also lift up the warnings which were imposed earlier in the wake of Emong.[149] Meanwhile, the JMA soon followed and issued its last advisory.[150] JTWC also issued its last advisory as its convection was significantly sheared and its low level circulation dissipated rapidly over six hours.[151][152]
In the Philippines, the depression's approach required the raising of Public Storm Warning Signal No. 1 in the provinces of Batanes and the northeastern portion of Cagayan, including the Babuyan Islands, starting on July 4.[153][154] The Office of Civil Defense of Cagayan were also on blue alert on the next day due to the storm, with the agency conducting a pre-disaster assessment with other government bureaus that day.[155] The residents in the coastal areas of Palanan, Divilacan, Maconacon and Dinapigue in Isabela were also warned of the storm while fishing activities in the region were prohibited due to Emong.[155]
Tropical Depression 08W
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 5 – July 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 1000 hPa (mbar) |
At 12:00 UTC on July 3, the PAGASA started to monitor a low-pressure area that developed near Torrijos, Marinduque or 149 kilometers to the south of Manila, followed by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC)'s advisory at 01:00 UTC on the next day, citing the system's development as "low".[156][157] In the latter's analysis on the disturbance, multispectral and microwave image scans on the system showed a weak low-level circulation center over the eastern part of Mindoro with flaring convection in the western periphery.[157] Traveling northwestwards, the storm was located in an environment conductive for further intensification, with warm sea surface temperatures of 30–31 °C (86–88 °F), low wind shear around the region and good equatorial outflow; however, model forecasts were split regarding the disturbance's strengthening trend.[157][158] Also that day at 15:00 UTC, the low-pressure area exited the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), which was followed by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) upgrading the storm to a tropical depression roughly three hours later.[159][160] Eventually, the JTWC upgraded the system's potential intensification trend to "high" and subsequently issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert at 00:30 UTC on June 6 as a circulation became well-defined.[161] It then changed its motion towards the west along the periphery of a subtropical ridge on the north and northwest as it approached the Hainan Island.[162] By 06:00 UTC on the next day, the disturbance moved inland on the region near Lingshui Li Autonomous County before emerging on the Gulf of Tonkin, in an area of low to moderate wind shear.[163][164][165] Later, the disturbance began to reorganize; however, strong wind gradient suppressed its intensification, with flaring convection displaced to the west.[164] Nine hours later, the JTWC upgraded the system to a weak tropical depression with maximum sustained winds of 45 km/h (30 mph); the JMA analysed the storm to be at 55 km/h (35 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg).[166][167][168] By the night of that day, the depression, with the identifier 08W from the JTWC made landfall on Thanh Hoa, Vietnam on that intensity, before subsequently issuing their final warning as the agency confirmed that the system dissipated inland, with the evidences of radar and satellite imagery.[169] The JMA continued to monitor the system until it dissipated at 00:00 UTC on July 8 over Laos.[170]
PAGASA issued rainfall advisories on July 6 as the depression's precursor low tracked near the Philippines.[171][172] The China Meteorological Administration (CMA), Hong Kong Observatory (HKO), and Macao Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau (SMG) issued tropical cyclone warnings on July 7.[173][174][175] The warnings imposed by the HKO and SMG were later lifted at 06:10 UTC (14:10 HKT) as the system moved away from Hong Kong and Macao.[173][176] As the depression approached Vietnam, the Vietnamese Ministry of Defense readied 264,272 soldiers and 1,979 vehicles for potential emergencies.[177][178] Aquaculture activities were also temporarily banned.[179] A peak rainfall total of 94 mm (3.7 in) was recorded at Sầm Sơn on July 7.[180] Rough seas and flooding were experienced in Thanh Hóa's Hoằng Hóa District.[181] About 7 hectares (17 acres) of rice crops and a water pipeline in Minh Luong commune, Van Ban district were both inundated and washed away by floods in Lào Cai.[182]
Typhoon In-fa (Fabian)
This section needs to be updated. (July 2021) |
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 16 – July 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min) 950 hPa (mbar) |
At 06:00 UTC on July 14, the JTWC started to monitor an area of low pressure west-northwest of Guam.[183] Located in an area favorable for intensification with warm sea surface temperatures as its outflow improved, the system struggled to develop under moderate wind shear before gradually intensifying, with the agency issuing a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert at 20:30 UTC on the next day.[183][184][185][186] On July 16, the PAGASA upgraded the disturbance to a tropical depression as it entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility, assigning it the local name Fabian.[187] The JMA later recognized the system as a tropical depression at 03:00 UTC on the same day,[188] with the JTWC doing the same at 09:00 UTC, designating it as 09W.[189] On July 18 at 00:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded it to a tropical storm assigning it the name In-fa.[190] The JTWC also upgraded it to a tropical storm at 03:00 UTC. The system had deep flaring convection, however its low-level circulation was broad and elongated.[191] On July 18, at 00:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded the system to a severe tropical storm.[192][193] In-fa started moving westwards,[194] and as it gradually strengthened, In-fa developed a formative eye on July 20, at 03:00 UTC.[195] At 09:00 UTC, the JTWC declared In-fa a typhoon as it had deep convection and robust outflow.[196][197] The JMA also followed suit and upgraded In-fa to a typhoon at 12:00 UTC, because of good upper-level outflow and higher sea-surface temperature, however its central dense overcast is still obscure.[198][199] On the next day at 03:00 UTC, In-fa strengthened into a Category 2-equivalent typhoon, as its central convection continued to deepen. The feeder bands became more compact and the eye of the typhoon became more clearer and defined.[200] The JTWC assessed that it peaked as a Category 2-equivalent typhoon with maximum wind speeds of 175 km/h (110 mph) at 03:00 UTC the same day.[201] Because of dry air,[citation needed] the JTWC later downgraded In-fa to a Category 1 typhoon at 03:00 UTC the next day, despite the presence of warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear.[202] On July 23 at 21:00 UTC, In-fa got further downgraded to a tropical storm by the JTWC, as its eyewall got fragmented and the deep convection was not continuous over the eye,[203] which later re-intensified into a Category 1 typhoon again, at 03:00 UTC the next day, as it regained convective depths and it managed to maintain a ragged eye.[204] At 09:00 UTC, PAGASA issued its final advisory as Typhoon In-fa moved northwards and exited the PAR.[205] On July 24, at 06:00 UTC, In-fa peaked as a typhoon with maximum 10-minute sustained wind speeds of 150 km/h (90 mph) and a minimum pressure of 950 hPa (28.05 inHg), according to the JMA[206] On the next day, the China Meteorological Administration (CMA) noted In-fa to have made landfall in Putuo Island at around 04:30 UTC.[207] After making landfall, the JTWC downgraded it to a tropical storm at 09:00 UTC as it eye structure began to degrade.[208] JMA later downgraded to a severe tropical storm at 12:00 UTC, because of influence of land and involvement of dry air.[209]
In Okinawa Prefecture, rough waves impacted coastal areas.[210] Rains began to pound Minamidaitō and Kitadaitōjima on July 19.[211] Winds up to 32.1 miles per hour (50 km/h) were recorded on Nanjō in the early hours of July 21, with 28.1 miles per hour (45 km/h) being recorded at Uruma and 26.9 miles per hour (45 km/h) being recorded at Naha. This was enough to down power lines, which affected 860 people in the main island of Okinawa and the villages of Iheya and Izena.[212][213] In Mainland China, record-breaking rainfall was reported, which caused flooding in the province of Henan. These devastating floods brought the death toll of the 2021 Henan floods to 99.[214] This was caused because of the moisture associated with Cempaka and In-fa, despite being far away.[215][216] The CMA issued a blue warning over the Fujian coast and north Zhejiang.[217] CMA later upgraded the warning to an orange warning as In-fa moved closer to China.[218] After making landfall, CMA downgraded its warning to a yellow warning as the threat of the typhoon lessened.[219] In Taiwan, the Central Weather Bureau issued a heavy rainfall warning for Kaohsiung, Pingtung County and Hengchun Peninsula and a sea warning for the northern and eastern coasts of the country as In-fa's periphery nears, however it was cancelled at 02:05 UTC (10:05 TST).[220][221] In the Philippines, In-fa strengthened the annual monsoon, causing heavy rainfall mainly in Luzon. Heavy rainfall and flooding have been reported in some areas.[222] As the typhoon moved southwest towards the Philippine Sea, PAGASA raised a Signal No. 1 warning for the province of Batanes and the Babuyan Islands in preparation of strong winds and heavy rainfall.[223] The warnings were later lifted as it exited the PAR.[205]
Severe Tropical Storm Cempaka
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 17 – July 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 990 hPa (mbar) |
On July 17, the JMA reported that a tropical depression had formed.[224][225] The JTWC later issued a TCFA for the system, as the aforementioned area of convection became more organized.[226] By the next day, the JTWC upgraded the system to a tropical depression and designated it as 10W, with the storm possessing an improved convective structure and a defined low-level circulation.[227][228] The JTWC upgraded the system to a tropical storm at 21:00 UTC as it had a defined low-level circulation center with improved banding structure.[229] At 00:00 UTC on July 19, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm, assigning it the name Cempaka.[230] At 21:00 UTC, the JTWC declared Cempaka to have strengthened into a Category 1 typhoon as it developed a ragged 15 nmi (28 km; 17 mi) wide eye.[231][232] The JMA later upgraded it to a severe tropical storm at 00:00 UTC on the next day.[233] On July 20, at 06:00 UTC, Cempaka peaked as a severe tropical storm with 10-sustained maximum wind speed of 55 kn (100 km/h; 65 mph) with minimum pressure of 990 hPa (29.23 inHg), according to JMA.[234] JTWC assessed that it peaked as a typhoon with maximum 1-minute sustained wind of 80 kn (150 km/h; 90 mph).[235] Cempaka made landfall near Jiangcheng District, Yangjiang, Guangdong Province,[236] and the JTWC downgraded it to a tropical storm at 18:00 UTC the same day as its low-level circulation center became obscure.[237] The JMA also downgraded Cempaka to a tropical storm at 00:00 UTC the next day as it moved further inland and its central dense overcast disappeared.[238][239] At 09:00 UTC, the JTWC further downgraded Cempaka to a tropical depression as its deep convection declined; however, it still retained a well-defined wind field.[240] After moving inland, Cempaka started moving westward at 00:00 UTC on July 21 due to weak steering flow.[241] Remaining inland, Cempaka maintained tropical storm intensity as it continued westward, but due to unfavorable conditions over land, it weakened into a tropical depression on the next day at 00:00 UTC.[242] On July 22, at 09:00 UTC, Cempaka then moved southwards towards the Gulf of Tonkin because of the influence of the monsoonal westerlies, while maintaining its tropical depression intensity inland.[243] Cempaka moved southward, crossed Móng Cái, Quảng Ninh Province in Vietnam and later entered the Gulf of Tonkin at 03:00 UTC.[244] However, Cempaka further weakened despite the presence of warm sea-surface temperatures because of high monsoonal wind shear and land interaction.[245][246] At 15:00 UTC, the JTWC issued its final warning on the system as it became a weakly defined system with an exposed low-level circulation center over Bạch Long Vĩ Island.[247] On July 26 at 00:00 UTC, the JMA issued its last advisory.[248]
In preparation for the tropical depression, the HKO issued a Signal No. 1 warning for Hong Kong at 13:40 UTC on July 18, which was later upgraded to a Signal No. 3 warning as Cempaka neared the Pearl River Delta. However, as it moved away from Hong Kong, the HKO downgraded it to a Signal No. 1 warning, which was later cancelled at 11:40 UTC.[249][250][251][252] The CMA issued an orange alert for the southern provinces of China as Cempaka moved closer to Guangdong, China, though it was later downgraded to a blue alert as it entered the Chinese mainland.[253][254] It was later lifted by the CMA, as the threat of Cempaka was minimal.[citation needed] As Cempaka made landfall in Guangdong, there were reports of heavy rainfall and rough waves in the region. Over 990 flights were cancelled in Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Zhuhai.[citation needed] The influence of Cempaka caused heavy rainfall in Henan Province, along with In-fa causing devastating floods in the region.[215]
Tropical Storm Nepartak
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 23 – July 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 990 hPa (mbar) |
At 06:00 UTC on July 22, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) started to monitor a tropical disturbance with subtropical features along the eastern portion of a monsoon trough, located approximately 466 nmi (865 km; 535 mi) to the north of Guam. A weak system, multispectral satellite imageries revealed that the disturbance was disorganized along the said trough, while advanced scaterrometer data showed another same feature with southerly convergent flow over the northern Mariana Islands. Environmental analysis depicted an unfavorable amount of wind shear, although the agency noted that the disturbance can form as a subtropical cyclone along the subtropical trough with the help of baroclinity.[255] Tracking northeastward, the system slowly organized, with low-level circulation center developing seen on meteorological satellite imageries. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) designated the disturbance as a tropical depression, seventeen hours later while the JTWC upgraded the system's potential intensification trend from "medium" to "high" and subsequently issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (TCFA) on the storm at 22:30 UTC that day.[256][257][258] At 12:00 UTC, Dvorak intensity observations and surface wind data from satellite scatterometer confirmed that the depression further intensified to the eight tropical storm of the season, whereupon the JMA named it as Nepartak.[259] The JTWC, however only issued its first warning on Nepartak as Tropical Depression 11W, three hours later as its LLCC further became broad and exposed with its center remaining weakly defined while being steered on the continued direction by a north–south oriented subtropical ridge.[260][261] Another nine hours later, the agency further upgraded the system to a subtropical storm as vigorous deep convection further became constant on the east of the still-exposed and elongated circulation center.[262][263] By July 24, Nepartak was guided north-northeastwards by an upper-level low and a trough. Baroclinic interaction with the latter also led to the development of a large and asymmetric wind field, with the maximum sustained winds of 35 kn (40 mph; 65 km/h) being far from the center.[263][264] Later, the system's core became ragged as it turned northwards and further northeast before shifting north again while remaining at that intensity. At 09:00 UTC of the next day, the JTWC noted two distinct vorticities, being spaced 350 nmi (650 km; 405 mi) to each other, with each having an elongated circulation from the south-southwest to the north-northeast.[265][266]
The intensity of Nepartak remained at 35 kn until 15:00 UTC on July 26, when the system slightly intensified to 40 kn (45 mph; 75 km/h) when it underwent a rapid structural evolution while moving west-northwestwards. At that time, the storm was now almost centered underneath an upper-level low, in which it interacted with for several days prior. Nepartak also began to accelerated as it moved poleward, while subsequently reaching its peak intensity 12 hours later, with winds of 45 kn (50 mph; 85 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 990 hPa (29.23 inHg).[267][268] As it turned towards the north, the system started to approach the Tōhoku region, and its circulation center became well-defined while located under the cold-core low, which was causing dry air intrusions within the cyclone. The system began to weaken to a low-end tropical storm before making landfall near the town of Minamisanriku in Miyagi Prefecture at 23:00 UTC as a subtropical depression.[269][270][271] As it rapidly crossed far western Honshu, its LLC became disorganized and ragged, with its convective signature collapsing as it crossed the Japanese Alps. At 15:00 UTC on July 28, the JTWC issued its final warning and bulletin on the system as it emerged over the Sea of Japan.[272][273] Meanwhile, the JMA continued to monitor the remaining remnants on the area until it dissipated at 12:00 UTC on July 31.[274]
The system was the first tropical cyclone to make landfall in any part of Miyagi Prefecture since reliable records began in 1951.[275] As Nepartak was anticipated to bring bad weather in the midst of the 2020 Summer Olympics, the rowing competitions were rescheduled. In addition, staff members were seen removing umbrellas in preparation for the approaching storm to avoid being blown off.[276][277]
Tropical Depression 12W
hideThis section has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | August 2 – August 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 1000 hPa (mbar) |
On August 1, the JTWC issued a TCFA for a disturbance in the open western Pacific as it had an ill-defined low-level circulation center and deep convection.[278] On the next day, at 00:00 UTC, the JMA recognized it as a tropical depression as it was located near Minami-Tori-shima. It was moving northwards at 10 kn (19 km/h; 12 mph).[279] A few hours later, the JTWC upgraded the system to a tropical depression, giving it the designation 12W. At that time, the LLC of the storm remained exposed and its strongest convection or thunderstorms were displaced to the west.[280] A deep-layered subtropical ridge to the east guided the depression to move to the north-northwest while being near from a monsoon gyre.[280] Despite being located in a favorable environment for additional strengthening, another system to the south slowly interacted with the depression, which made the storm's overall intensity weak. It reached its intensity peak that day, with winds of 35 kn (40 mph; 65 km/h) in both the estimates of JMA and JTWC and a minimum barometric pressure of 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg).[281][282] On the next day, the JTWC issued its last bulletin for the system as the depression's convection became sheared to the northeast.[283] Meanwhile, the JMA continued monitoring the system until it dissipated on that day, at 18:00 UTC.[284]
Tropical Storm Lupit (Huaning)
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | August 2 – August 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 985 hPa (mbar) |
On August 2, the JMA noted a tropical depression near Zhanjiang had formed.[285] Soon afterwards, the JTWC issued a TCFA on the disturbance situated approximately 153 nm west-southwest of Hong Kong.[286] On the same day at 21:00 UTC, the JTWC assessed the system as a tropical depression and accordingly designated it as 13W.[287] Twenty four hours later, the agency upgraded the system to a tropical storm.[288] On August 4 at 12:00 UTC, the JMA followed suit and designated the system as a tropical storm, assigning it the name Lupit.[289] A day later at 03:20 UTC, it made landfall over Nan'ao County in Shantou, Guangdong Province.[citation needed] At 08:50 UTC, it made another landfall over Dongshan County in Zhangzhou, Fujian Province.[290] On August 7, it headed eastward and briefly entered the PAR, and was named Huaning by PAGASA.[291] On August 8, at 18:00 UTC, Lupit peaked as a tropical storm with maximum 10-minute sustained winds of 45 kn (85 km/h; 50 mph) and minimum pressure of 985 mb (29.09 inHg).[292] Maximum 1-minute sustained speed of Lupit was 55 kn (100 km/h; 65 mph).[293] On August 9, at 00:00 UTC, the JMA issued its final warning, as it completed its extratropical transition.[294] At 21:00 UTC, the JTWC followed and issued its final warning.[295]
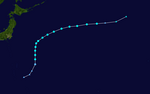
Severe Tropical Storm Nida
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | August 3 – August 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 992 hPa (mbar) |
On August 3, at 06:00 UTC, the JMA noted a tropical depression north of the Mariana Islands which was moving northwards at 10 kn (19 km/h; 12 mph).[296] At 03:00 UTC, the next day, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the system. By that time, it had developed a partially obscured low-level circulation center.[297] At 15:00 UTC, the JTWC recognized it as a tropical depression, designating it as 15W.[298] On August 5, 03:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded it to a tropical storm, as its low-level circulation center became more defined.[299][300] Three hours later, the JMA followed and named it Nida. Satellite imagery showed that convective bursts were organized into a curved band and that the system was exhibiting good anticyclone outflow.[301] On August 6, at 18:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded it to a severe tropical storm, as it had distinct anticyclonic outflow.[302] Nida then started moving eastwards at 6:00 UTC the next day, because a mid-level subtropical high-pressure area along with the westerlies.[303] On August 7, at 09:00 UTC, the JTWC issued the last advisory for the system, as its low-level circulation center was partly exposed due to the westerlies inflicting shear upon the storm.[304] However, the JMA continued to publish bulletins for the system. Nida continued its trajectory. On August 7, 12:00 UTC, the JMA downgraded it to a tropical storm due to shear and a generally less conductive environment.[305] The JMA further downgraded it to an extratropical low at 00:00 UTC the next day as it completed its extratropical transition.[306]
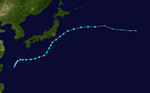
Tropical Storm Mirinae (Gorio)
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | August 3 – August 10 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
On August 3, at 18:00 UTC, the JMA issued a tropical cyclone advisory for a tropical depression which was located off the east coast of Taiwan and north of the Philippines.[307] The JMA later issued its first prognostic reasoning at the same time, stating that clusters of convective bursts were scattered around the low-level circulation.[308] At 22:00 UTC, the same day, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the system, as it had a consolidating low-level circulation, and it was located in a very conductive environment with high sea surface temperatures and low to moderate vertical wind shear.[309] On the next day, at 03:00 UTC, the PAGASA recognized it as a tropical depression and named it Gorio, as it was located inside the PAR.[310] At 06:00 UTC, the JTWC did the same and designated it as 14W, as satellite imagery showed a fully exposed mesovortex.[311][312] On August 5, at 06:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded it to a tropical storm, naming it as Mirinae. Clusters of convective bursts were gathering around the center with a curved manner, with Mirinae having distinct anticyclonic outflow.[313] At 15:00 UTC, the JTWC followed and upgraded it to a tropical storm, as the storm developed a partially exposed low-level circulation center. Flaring convection was present, though it was affected by moderate westerly wind shear.[314][315] On August 7, at 18:00 UTC, Mirinae peaked as a tropical storm with maximum 10-sustained wind speed of 45 kn (85 km/h; 50 mph) and minimum barometric pressure of 980 mb (28.94 inHg).[316] Maximum 1-minute sustained wind speed of Mirinae was 50 kn (95 km/h; 60 mph).[317] On August 9, at 09:00 UTC, the JTWC issued its final warning for the system.[318] The JMA later issued its last warning on the next day at 00:00 UTC, as it became an extratropical cyclone.[319]
Severe Tropical Storm Omais (Isang)
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | August 10 – August 24 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 994 hPa (mbar) |
On August 6, the Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) first noted an area of disturbed weather positioned around 1,000 mi (1,610 km) south-southwest of Honolulu.[320] Four days later, the low-pressure area crossed the International Date Line, and on August 10, at 06:00 UTC, the JMA declared it as a tropical depression as it was located northeast of Ratak.[321][322] By 13:00 UTC, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the system as satellite imagery showed it had developed a well-defined low-level circulation.[323] At 15:00 UTC, the JTWC recognized it as a tropical depression and designated it as 16W as satellite imagery depicted developing spiral bands and a defined low-level circulation center.[324][325] The system briefly became a tropical storm;[326] However, at 21:00 UTC, the JTWC downgraded it to a tropical depression[327] as its convection struggled to organize itself.[328] It regained its intensity at 09:00 UTC the next day[329] as its convection became more organized. Satellite imagery also continued to indicate the presence of a well-defined low-level circulation center.[330] It was downgraded to a tropical depression again on the next day[331] as its low-level circulation center became less defined.[332] On August 16, at 00:00 UTC, the JMA issued its final advisory for the system, losing its tropical cyclone characteristics because of unfavorable conditions.[333] Later at 00:00 UTC, the next day, the JMA started tracking the system again.[334] At 09:00 UTC, the JTWC issued its final advisory as the system's convection became further disorganized despite the presence of a marginally favorable environment.[335] At 19:30 UTC on August 18, the JTWC issued a TCFA for its remnants as its low-level circulation center improved significantly.[336] On August 19, the system was upgraded by PAGASA to a tropical depression, and a few hours later, it received the local name Isang as it entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility.[337] At 15:00 UTC, the system was re-upgraded to a tropical depression by the JTWC,[338] as its deep convection started to become more organized over the low-level center.[339] On August 20, at 12:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded to a tropical storm, naming it as Omais. Favorable conditions like high sea-surface temperatures, high tropical cyclone heat potential, and low wind shear helped it to develop over the past few hours.[340] The JTWC did the same thing at 21:00 UTC, the same day.[341] At 18:00 UTC the next day, the JMA upgraded it to a severe tropical storm as satellite imagery showed convective bursts gathering around the center in a curved manner;[342] however, shortly after at 06:00 UTC on August 22, it weakened into a tropical storm due to increasing wind shear from the westerlies.[343] At 03:00 UTC on August 23, the JTWC downgraded it to a tropical depression[344] as its convection was severely affected by the extremely high westerly wind shear.[345] On August 24 at 00:00 UTC, the JMA issued its final advisory as the system became an extratropical cyclone over the Sea of Japan.[346] Nine hours later, the JTWC followed and issued its last warning for Omais.[347]
As the system neared the islands of Guam, the NWS issued a tropical storm watch at 22:36 UTC on August 14.[348] At 10:00 UTC on August 15, the NWS issued a tropical storm watch for the island of Rota.[349] However, all watches were lifted by the NWS at 09:14 UTC the next day as the system further weakened.[350]
Tropical Depression 17W
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 1 – September 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 1008 hPa (mbar) |
On September 1 of 00:00 UTC, the JMA noticed a tropical depression near Wake Island.[351] At 06:00 UTC, the JTWC gave a medium chance of formation for the system over the same area, despite being classified as subtropical depression, as it developed a well defined, partially exposed low-level circulation center.[352] At 20:00 UTC, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the system,[353] and at 03:00 UTC the next day, it was upgraded to a tropical depression and was designated as 17W,[354] as its low-level circulation center became more defined but still partially exposed.[355] The system maintained its defined convective structure,[356][357][358][359] however at 09:00 UTC on September 3, it struggled to consolidate because of presence of dry air causing its convective structure to diminish.[360][361] At 21:00 UTC, the JTWC issued its final advisory as its remaining convection was sheared by the incoming westerlies.[362] At 12:00 UTC on September 4, the JMA stopped tracking the system.[363]
Severe Tropical Storm Conson (Jolina)
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 5 – September 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 985 hPa (mbar) |
On September 3, a disturbance was noted by the JTWC, approximately 195 nmi (225 mi; 360 km) from Andersen Air Force Base in Yigo, Guam, as it developed a weakly defined low-level circulation center.[364] The disturbance gradually intensified, and on September 5, the JMA recognized the system as a tropical depression.[365] Later that day, the JTWC issued a TCFA as its low-level circulation center and its surrounding convection became well organized.[366] The agency recognized the system as a tropical depression around four hours later.[367] At 21:00 UTC, the PAGASA recognized the system as a tropical depression, with the agency assigning it the local name Jolina.[368] The next day on 06:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm, assigning it the international name Conson, with the JTWC following suit three hours later.[369][370] At 12:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded it typhoon before downgrading it into a tropical storm at 18:00 UTC.[371] Three hours later, the JMA upgraded it to a severe tropical storm.[372] At the same moment, Conson rapidly intensified into a typhoon according to the PAGASA as it made its first landfall on Hernani, Eastern Samar.[373] Conson then made another landfall at 02:30 PhST (18:30 UTC) in Daram, Samar, and another one at 03:40 PhST (19:40 UTC) in Santo Niño, Samar.[374] At 06:30 PhST (22:30 UTC), Conson made a fourth landfall in Almagro, Samar. At 00:00 UTC on September 7, the JMA downgraded it to a tropical storm as it was significantly weakened by multiple landfalls.[375] Conson then made a fifth landfall in Dimasalang, Masbate at 11:00 PhST (03:00 UTC), later weakening into a severe tropical storm, according to PAGASA.[376][377] Conson then made a sixth landfall over Torrijos, Marinduque.[378] Conson continued to pummel through more islands, making a seventh landfall over the area in Lobo, Batangas.[379] After making its eighth landfall at San Juan, Batangas, Conson traversed the Batangas – Cavite area as the PAGASA declared it to have weakened back into a tropical storm.[380] Conson made its ninth and final landfall in the vicinity of Mariveles, Bataan.[381] At 12:00 UTC, Conson re-intensified into a severe tropical storm, as it entered the West Philippine Sea.[382] Three hours later, the PAGASA issued its final bulletin for Conson as it exited the PAR and accelerated westward.[383]
As Conson moved westward, it came in contact with unfavorable conditions such as increasing vertical wind shear and land interaction with Vietnam. These conditions made Conson weaken, prompting the JMA to downgrade it to a tropical storm at 12:00 UTC on September 11 and further downgrading it to a tropical depression at 18:00 UTC the same day, with the JTWC downgrading it to a tropical depression at 03:00 UTC on September 12.[384][385][386] It stalled off the coast of Vietnam near Quang Nam because of the confluence of three ridges.[387][388][389] At 21:00 UTC, the JTWC issued its final advisory as it made landfall near Da Nang, Vietnam which caused the system to weakened rapidly. Satellite imagery showed that its low-level circulation center weakened significally and became less defined.[390] By 18:00 UTC of September 13, the JMA stopped tracking Conson,[391] as the agency last noted it at 12:00 UTC.[392]
According to the NDRRMC, as of September 15, 20 people have died from the storm, with combined infrastructural and agricultural damages totalling up to ₱1.59 billion (US$31.8 million) in damages.[393] In Vietnam, 2 people were killed by flooding.[394] Agriculture damages on the offshore island of Lý Sơn is estimated to be about 100 billion ₫ (US$4.3 million).[395]
Typhoon Chanthu (Kiko)
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 5 – September 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 215 km/h (130 mph) (10-min) 905 hPa (mbar) |
At 06:00 UTC on September 5, the JTWC began monitoring on an area of convection that had formed 446 nmi (513 mi; 826 km) from Legazpi, Philippines. Satellite imagery depicted a fairly defined low-level circulation center.[396] At 18:00 UTC the same day, the JMA declared it as a tropical depression.[397] Five and half hours later, the JTWC issued a TCFA as its low-level circulation center and its surrounding convection had improved significantly.[398] At 09:00 UTC the next day, the JTWC upgraded the disturbance to a tropical depression, designating it as 19W.[399] At 21:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded it to a tropical storm as it developed a compact low-level circulation center with intense deep convection surrounding it, also noting the formation of an eye-like feature.[400] The JMA later did the same at 00:00 UTC on September 7, naming it Chanthu.[401] At 09:30 UTC, the PAGASA reported that Chanthu entered the PAR, assigning it the name Kiko.[402] At 12:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded it to a severe tropical storm.[403] At the same moment, Chanthu started its rapid intensification as it quickly became a Category 1-equivalent typhoon. Satellite imagery indicated the development of a vertical hot tower over its center, with microwave imagery indicating that it had developed a very small eye feature.[404][405] At 15:00 UTC, it became a Category 2-equivalent typhoon as it continued its explosive intensification, with a pinhole eye developing by that time.[406] Six hours later, the typhoon reached Category 4-equivalent status with one-minute sustained wind speeds of 125 kn (230 km/h; 145 mph).[407] By the next day at 09:00 UTC, it reached Category 5-equivalent intensity, developing a 5 nmi (10 km; 5 mi)-wide eye which was surrounded by very compact, intense convection,[408][409] making it the second super typhoon of the year, and marking the storm's initial peak intensity. After reaching its initial peak, Chanthu was downgraded to a Category 4-equivalent super typhoon at 09:00 UTC on September 9, as its pinhole-shaped eye started to fade, indicating the start of an eyewall replacement cycle, which began a weakening trend.[410] At 15:00 UTC, Chanthu was further downgraded to a Category 4-equivalent typhoon while the eye-like feature slightly degraded.[411] At 03:00 UTC on September 10, Chanthu re-intensified into a super typhoon, clearing out its eye once again. Infrared satellite imagery showed that the typhoon had undergone a secondary eyewall replacement cycle.[412] Chanthu further intensified into a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon at 09:00 UTC that day as its eye became clearer.[413] On 05:00 PhST on September 11 (21:00 UTC on September 10), the PAGASA reported that Chanthu passed to the east of the Babuyan Islands;[414] at 08:30 PhST (00:30 UTC), Chanthu made landfall in Ivana, Batanes as the storm began to weaken slightly.[415][416]
At 15:00 UTC on September 11, Chanthu weakened into a Category 4 typhoon as it continued to move northwards because of the presence of dry air.[417] It was further downgraded to a Category 3-equivalent typhoon by the JTWC on September 12 at 03:00 UTC as it moved towards the east coast of Taiwan, experiencing multiple eyewall replacement cycles and increasing wind shear and dry air from the westerlies.[418] Three hours later, the PAGASA issued its last bulletin for Chanthu since it exited the PAR.[419] At 15:00 UTC, Chanthu weakened to a Category 2-equivalent typhoon as the dry air started to hamper the typhoon's convective structure. According to satellite imagery, the low-level circulation center had become ill-defined and the eye started to collapse.[420] The weakening trend of Typhoon Chanthu continued as it moved further northwards towards the Korean Peninsula, because of increasing wind shear and dry air and cool sea-surface temperature although it was warm enough to support its intensity.[421][422] At 09:00 UTC of September 13, Chanthu further weakened into a Category 1 typhoon as it moved further north towards Shanghai, China.[423] By 15:00 UTC, the eye of Chanthu has completely collapsed.[424] Chanthu remained quasi-stationary near Shanghai because of a weak steering flow.[425][426] At 06:00 the next day, the JMA downgraded to a severe tropical storm, as it moved south-eastwards.[427] Three hours the JTWC downgraded to a tropical storm, as it low-level circulation center became partially exposed with remaining convection to the north and west.[428] At 12:00 UTC, the JMA further downgraded it to a tropical storm, as it slowly moved south-eastwards towards Japan.[429] At 00:00 UTC the next day, JMA re-upgraded it to a severe tropical storm, because of the decreasing wind shear and marginally warm sea-surface temperature.[430] On September 17 of 09:00 UTC, Chanthu crossed near the town of Ikitsuki, Nagasaki in Japan.[431] It continued to move northwards as it moves through the rugged Japanese islands which caused to weaken significally.[432] This caused the JMA to downgrade it to a tropical storm at 12:00 UTC.[433] At 21:00 UTC, the JTWC downgraded it to a tropical depression as it rapidly collapsed because of the rugged terrain, and was undergoing an extratropical transition.[434] On September 18 at 08:00 UTC, the JTWC issued its final warning for the system.[435]
Chanthu caused devastating effects in the islands of Batanes as it was made a direct hit from the typhoon. According the local residents it was the most ferocious storm even seen.[436] More than 30,000 residents were affected from Region I, II, III and CAR. Four municipalities went without power and none were restored and one municipality experienced water supply outage and none were restored. There were also reports of landslide and flooding mostly from Region I and III. As of September 15, total damages from the typhoon were up to ₱37.4 million (US$748,000).[437] On September 12, Chanthu passed east of Taiwan. This caused heavy rainfall over the island including the capital city Taipei. Upto 13 cm (5.1 in) of rainfall was recorded and winds upto 164 km/h (102 mph) were reported.[438] In China, the storm shut down both Shanghai Port, the world’s largest container port, and Ningbo-Zhoushan Port, the world’s largest port by cargo throughput, briefly on 12-14 September, with about 86 vessels waiting outside the ports. [439] As Chanthu passed near the island of Jeju, it caused winds upto 30 to 40 m/s (110 to 145 km/h; 65 to 90 mph) and 50 mm (2.0 in) of rainfall. There were reports of structural damage and overwhelmed drainage system over the island. 23 flight were cancelled and 48 ferries were grounded.[440]
Other systems

During January 19, the JMA reported that a tropical depression had developed to the east of Luzon, Philippines.[441] The precursor to the depression brought scattered showers and thunderstorms to Mindanao, Palawan, and Visayas on January 18.[442] The JMA, however, discontinued advisories for the system on the next day.[443] The depression also brought stormy weather to Luzon on January 20. The PAGASA warned residents of possible flash flooding and mudslides due to heavy rainfall.[444] The system's precursor was associated with a frontal system, with its combined effects bringing heavy rainfall over much of Visayas, the Bicol Region, and Northern Mindanao, resulting in three deaths and agricultural damages of up to ₱642.5 million (US$13.2 million).[445]
On March 9, a low-pressure area entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility, though it was not expected to develop at that time.[446][447] On March 14, the low-pressure area intensified into a tropical depression over the Sulu Sea before quickly degenerating back into a low-pressure area.[448][449] The system brought light to moderate rains over parts of the Philippines, with the PAGASA advising residents of the possibility of floods and landslides.[450]
On May 29, the JTWC issued a TCFA for a tropical disturbance that was roughly 622 nautical miles (1,152 km; 716 mi) to the southeast of Guam, near the Nomoi Islands. The system gradually developed as it was experiencing warm sea surface temperatures and low vertical wind shear.[451] On the next day at 00:00 UTC, the JMA recognized the system as a tropical depression.[452] On the same day, the JTWC cancelled the TCFA for the system as its structure degraded,[453] with the JMA last recognizing the system as a tropical depression on June 1 at 18:00 UTC.[454]
On June 29, an area of convection formed 425 nmi (787 km; 489 mi) from Guam with satellite imagery revealing that the system had a deep convection with a weak low level circulation.[455] Within a favorable environments with low-to-moderate wind shear, and warm sea surface temperatures, the system gradually became more organized with a more defined low level circulation. On June 30, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the system.[456][457] On July 1, animated multispectral satellite imagery indicated a very broad and ill-defined low level circulation with convection being sheared to the south-southwest of the disturbance, which prompted the JTWC to cancel the system's TCFA and downgrade its development chances within the next day to low.[458] The JMA no longer considered it a tropical depression in their tropical disturbance summary advisories on the same day.[459]
On July 19, at 00:00 UTC, a tropical depression formed near 29°N 164°E / 29°N 164°E, which was moving northwards at the speed of 10 kn (20 km/h; 10 mph), according to the JMA.[460] It lasted for two days until July 21, when it became a remnant low at 00:00 UTC.[461]
On July 28, at 00:00 UTC, the JMA noted a tropical depression near 29°N 152°E / 29°N 152°E, which was moving northwards slowly.[462]
On July 30, at 00:00 UTC, the JMA noted a tropical depression near 28°N 142°E / 28°N 142°E, which was moving northwestward slowly.[463]
On July 31, a tropical depression formed over the open Pacific at 18:00 UTC.[464] By August 1, at 05:30 UTC, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the system as it had an exposed low-level circulation with persistent disorganized convection.[465] The agency canceled the alert on the next day as it had little remaining convection and it had moved over cooler waters.
On August 1, at 18:00 UTC, JMA noted a tropical depression near Taiwan.[466]
The JMA began tracking on a tropical depression that had formed to the east of Hainan on September 7.[467] The system moved westward towards Vietnam and was last noted the next day.
Storm names
Within the Northwest Pacific Ocean, both the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assign names to tropical cyclones that develop in the Western Pacific, which can result in a tropical cyclone having two names.[468] The Japan Meteorological Agency's RSMC Tokyo — Typhoon Center assigns international names to tropical cyclones on behalf of the World Meteorological Organization's Typhoon Committee, should they be judged to have 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 65 km/h (40 mph).[469] PAGASA names to tropical cyclones which move into or form as a tropical depression in their area of responsibility located between 135°E and 115°E and between 5°N and 25°N even if the cyclone has had an international name assigned to it.[468] The names of significant tropical cyclones are retired, by both PAGASA and the Typhoon Committee.[469] Should the list of names for the Philippine region be exhausted then names will be taken from an auxiliary list of which the first ten are published each season. Unused names are marked in gray.
International names
A tropical cyclone is named when it is judged to have 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 65 km/h (40 mph).[470] The JMA selected the names from a list of 140 names, that had been developed by the 14 members nations and territories of the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee.[471] Retired names, if any, will be announced by the WMO in 2022; though replacement names will be announced in 2023. The next 28 names on the naming list are listed here along with their international numeric designation, if they are used. During the season, the names Surigae, Koguma, and Cempaka were used for the first time after they replaced Mujigae, Koppu, and Melor in the 2015 season.
|
|
Philippines
PAGASA uses its own naming scheme for typhoons that will either develop within or move into their self-defined area of responsibility.[472] The names were taken from a list of names, that was last used during 2017 and are scheduled to be used again during 2025.[472] All of the names are the same except Uwan and Verbena which replaced the names Urduja and Vinta after they were retired.[472]
|
|
|
Auxiliary list
|
|
|
|
|
Season effects
This table summarizes all the systems that developed within or moved into the North Pacific Ocean, to the west of the International Date Line during 2021. The tables also provide an overview of a systems intensity, duration, land areas affected and any deaths or damages associated with the system.
| Name | Dates active | Peak classification | Sustained wind speeds |
Pressure | Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD | January 19 – 20 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1008 hPa (29.77 inHg) | Philippines | $13.2 million | 3 | [445] |
| Dujuan (Auring) | February 16 – 23 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 996 hPa (29.41 inHg) | Palau, Philippines | $3.29 million | 1 | [34] |
| TD | March 14 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | Philippines | None | None | |
| Surigae (Bising) | April 12 – 24 | Typhoon | 220 km/h (140 mph) | 895 hPa (26.43 inHg) | Caroline Islands, Palau, Sulawesi, Philippines | $10.5 million | 10 | [62][63][58] |
| 03W (Crising) | May 12 – 14 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Philippines | $486,000 | None | [78] |
| Choi-wan (Dante) | May 29 – June 5 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 998 hPa (29.47 inHg) | Palau, Philippines, Taiwan, Japan | $6.39 million | 11 | [104][105] |
| TD | May 30 – June 1 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Koguma | June 11 – 13 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 996 hPa (29.41 inHg) | South China, Vietnam, Laos | $9.87 million | 1 | [473][474] |
| Champi | June 20 – 27 | Typhoon | 120 km/h (75 mph) | 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) | Mariana Islands | None | None | |
| TD | June 30 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1010 hPa (29.83 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| 07W (Emong) | July 3 – 6 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan | None | None | |
| 08W | July 5 – 8 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | Philippines, South China, Vietnam | None | None | |
| In-fa (Fabian) | July 16 – 29 | Typhoon | 150 km/h (90 mph) | 950 hPa (28.05 inHg) | Philippines, Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan, China | $2 billion | 6 | |
| Cempaka | July 17 – 26 | Severe tropical storm | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | South China, Vietnam | $4.25 million | 3 | [475][476][477] |
| TD | July 19 – 20 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1012 hPa (29.88 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Nepartak | July 23 – 28 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | Japan | None | None | |
| TD | July 28 – 29 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| TD | July 30 – August 1 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 998 hPa (29.47 inHg) | Japan | None | None | |
| TD | July 31 – August 3 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 998 hPa (29.47 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| TD | August 1 – 3 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 996 hPa (29.41 inHg) | Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan | None | None | |
| 12W | August 2 – 6 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | Japan | None | None | |
| Lupit (Huaning) | August 2 – 9 | Tropical storm | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) | Vietnam, South China, Taiwan, Ryukyu Islands, Japan | $64.8 million | None | [478] |
| Nida | August 3 – 8 | Severe tropical storm | 95 km/h (60 mph) | 992 hPa (29.29 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Mirinae (Gorio) | August 3 – 10 | Tropical storm | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) | Ryukyu Islands, Japan | None | None | |
| Omais (Isang) | August 10 – 24 | Severe tropical storm | 95 km/h (60 mph) | 994 hPa (29.35 inHg) | Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Mariana Islands, Ryukyu Islands, South Korea | None | None | |
| 17W | September 1 – 4 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1008 hPa (29.77 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Conson (Jolina) | September 5 – 13 | Severe tropical storm | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) | Philippines, Hainan, Vietnam | $36.1 million | 22 | [393][394][395] |
| Chanthu (Kiko) | September 5 – 18 | Typhoon | 215 km/h (130 mph) | 905 hPa (26.72 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, Ryukyu Islands, South Korea, Japan | $748,000 | None | [437] |
| TD | September 7 – 8 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Vietnam | None | None | |
| Season aggregates | ||||||||
| 29 systems | January 19 – Season ongoing | 220 km/h (140 mph) | 895 hPa (26.43 inHg) | $2.08 billion | 57 | |||
See also
- Tropical cyclones in 2021
- Pacific typhoon season
- 2021 Atlantic hurricane season
- 2021 Pacific hurricane season
- 2021 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2020–21, 2021–22
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 2020–21, 2021–22
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 2020–21, 2021–22
Notes
- ^ Jump up to: a b A super typhoon is an unofficial category used by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) for a typhoon with winds of at least 240 km/h (150 mph).[8]
- ^ The Japan Meteorological Agency is the official Regional Specialized Meteorological Center for the western Pacific Ocean.
- ^ The Joint Typhoon Warning Center is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force task force that issues tropical cyclone warnings for the western Pacific Ocean and other regions.[2]
References
- ^ Jason Samenow and Matthew Cappucci (April 18, 2021). "Surigae sweeping past Philippines, after becoming strongest April typhoon on record". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved May 6, 2021.
- ^ "Joint Typhoon Warning Center Mission Statement". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 2011. Archived from the original on July 26, 2007. Retrieved July 25, 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Saunders, Mark; Lea, Adam (May 11, 2021). Extended Range Forecast for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2021 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Retrieved May 11, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Saunders, Mark; Lea, Adam (July 7, 2021). July Forecast Forecast Update for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2021 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Saunders, Mark; Lea, Adam (August 9, 2021). August Forecast Forecast Update for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2021 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d 131st Climate Forum Climate Outlook January–June 2021 (PDF) (Seasonal Climate Outlook). Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. December 27, 2020. Retrieved December 27, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c 137th Climate Forum July–December 2021 (PDF) (Seasonal Climate Outlook). Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. June 23, 2021. Retrieved June 23, 2021.
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions (Report). Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2012. Archived from the original on October 4, 2013. Retrieved September 22, 2012.
- ^ "WWJP25 RJTD 161200". Japan Meteorological Agency. February 16, 2021. Retrieved February 16, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 91W)". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. February 16, 2021. Archived from the original on February 16, 2021. Retrieved February 16, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Auring'" (PDF). PAGASA. February 17, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 17, 2021. Retrieved February 17, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. February 17, 2021. Archived from the original on February 17, 2021. Retrieved February 17, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 01W (One) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. February 18, 2021. Archived from the original on February 18, 2021. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #3 for Tropical Storm 'Auring'" (PDF). PAGASA. February 18, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 18, 2021. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information". Japan Meteorological Agency. February 18, 2021. Archived from the original on February 18, 2021. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #6 for Severe Tropical Storm 'Auring' (Dujuan)" (PDF). PAGASA. February 19, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 19, 2021. Retrieved February 19, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #7 for Tropical Storm 'Auring' (Dujuan)" (PDF). PAGASA. February 19, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 19, 2021. Retrieved February 19, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 01W (Dujuan) Warning No. 13 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. February 20, 2021. Archived from the original on February 20, 2021. Retrieved February 20, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 01W (Dujuan) Warning No. 17 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. February 21, 2021. Archived from the original on February 21, 2021. Retrieved February 21, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information". Japan Meteorological Agency. February 22, 2021. Archived from the original on February 22, 2021. Retrieved February 22, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 01W (Dujuan) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. February 22, 2021. Archived from the original on February 22, 2021. Retrieved February 22, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #19 for Tropical Depression 'Auring' (Dujuan)" (PDF). PAGASA. February 21, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 21, 2021. Retrieved February 21, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 01W (Dujuan) Warning No. 20 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. February 22, 2021. Archived from the original on February 22, 2021. Retrieved February 22, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #23 for Tropical Depression 'Auring' (Dujuan)" (PDF). PAGASA. February 21, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 21, 2021. Retrieved February 21, 2021.
- ^ "Weather Maps". Japan Meteorological Agency. February 23, 2021. Archived from the original on February 23, 2021. Retrieved February 23, 2021.
- ^ "WEATHER ROUNDUP FOR THE MARIANAS AND MICRONESIA". National Weather Service Tiyan GU. February 16, 2021. Archived from the original on February 16, 2021. Retrieved February 16, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert Graphic". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. February 16, 2021. Archived from the original on February 16, 2021. Retrieved February 16, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #5 for Tropical Storm 'Auring' (Dujuan)" (PDF). PAGASA. February 19, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 19, 2021. Retrieved February 19, 2021.
- ^ "Storm Signal No. 1 up in four Mindanao areas as Auring remains stationary over Philippine Sea". CNN Philippines. Retrieved February 19, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #7 for Tropical Storm 'Auring' (Dujuan)" (PDF). PAGASA. February 19, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 19, 2021. Retrieved February 19, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #18 for Tropical Storm 'Auring' (Dujuan)" (PDF). PAGASA. February 21, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 21, 2021. Retrieved February 21, 2021.
- ^ "Walang Pasok: Class, work suspensions on February 22 due to 'Auring'". Philstar.com. Retrieved February 22, 2021.
- ^ "Sitrep No. 04 re Preparedness Measures and Effects of Severe Tropical Storm "AURING"" (PDF). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. February 22, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 23, 2021. Retrieved February 23, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "SitRep no.13 re Preparedness Measures and Effects for STS Auring" (PDF). NDRRMC. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 120000". Japan Meteorological Agency. April 12, 2021. Archived from the original on April 12, 2021. Retrieved April 12, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 120600". Japan Meteorological Agency. April 12, 2021. Archived from the original on April 12, 2021. Retrieved April 12, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 94W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. April 12, 2021. Archived from the original on April 12, 2021. Retrieved April 12, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE ADVISORY #1 FOR: Tropical Depression" (PDF). pubfiles.pagasa.dost.gov.ph. April 12, 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 02W (Two) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. April 13, 2021. Archived from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information". Japan Meteorological Agency. April 13, 2021. Archived from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information". data.jma.go.jp. April 15, 2021. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved April 15, 2021.
- ^ "Typhoon 02W (Surigae) Warning NR 013". Join Typhoon Warning Center. April 16, 2021. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ Masters, Jeff (April 17, 2021). "Category 5 Super Typhoon Surigae brushes Philippines". Eye on the Storm. Yale Climate Connections. Retrieved April 18, 2021.
- ^ "Surigae Stirs Up the Pacific". Earth Observatory. NASA. April 19, 2021. Retrieved April 22, 2021.
- ^ Cappucci, Matthew; Samenow, Jason (April 17, 2021). "Super Typhoon Surigae to pass near Philippines at Category 5 strength Sunday". The Washington Post. Washington, D.C. Retrieved April 17, 2021.
- ^ Reasoning No. 20 for TY 2102 Surigae (RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. April 17, 2021. Archived from the original on April 18, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 02W (Surigae) Warning NR 019 (TXT) (Report). Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. April 18, 2021. Retrieved April 19, 2021 – via Iowa Environmental Mesonet.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 02W (Surigae) Warning NR 020 (TXT) (Report). Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. April 18, 2021. Retrieved April 19, 2021 – via Iowa Environmental Mesonet.
- ^ Cappucci, Matthew (April 19, 2021). "Typhoon Surigae intensified with surprising speed, bearing the fingerprint of climate change". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 20, 2020.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 02W (Surigae) Warning NR 037 (Report). Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. April 22, 2021.
- ^ "PROGNOSTIC REASONING FOR TROPICAL STORM 02W (SURIGAE) WARNING NR 041". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. April 23, 2021. Archived from the original on April 23, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Subtropical Storm 02W (Surigae) No 42". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. April 23, 2021. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021.
- ^ "SUBTROPICAL STORM 02W (SURIGAE) WARNING NR 046". Archived from the original on April 25, 2021.
- ^ "WTPQ50 RJTD 250000". Japan Meteorological Agency. April 25, 2021. Archived from the original on April 25, 2021. Retrieved April 27, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Storm Surigae (02W) Special Advisory Number 2A". Weather Forecast Office for Tiyan, Guam. April 14, 2021. Archived from the original on April 14, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Storm Surigae (02W) Special Advisory Number 6". Weather Forecast Office for Tiyan, Guam. April 14, 2021. Archived from the original on April 14, 2021.
- ^ Cappucci, Matthew. "Tropical Storm Surigae to intensify into powerful Pacific typhoon, brush past Philippines". Washington Post. Retrieved April 14, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Republic of Palau: Typhoon Surigae - Emergency Plan of Action (EPoA), DREF Operation n° 1 MDRPW001" (PDF). ReliefWeb. International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC/ICRC). April 26, 2021. Retrieved April 27, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #2 for Typhoon 'Bising' (Surigae)" (PDF). PAGASA. April 16, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 16, 2021. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #3 for Typhoon 'Bising' (Surigae)" (PDF). PAGASA. April 16, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 16, 2021. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #5 for Typhoon 'Bising' (Surigae)" (PDF). PAGASA. April 17, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 17, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "SitRep no. 10 re Preparedness Measures and Effects for Typhoon Bising" (PDF). ndrrmc.gov.ph. April 25, 2021. Retrieved April 25, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Karen Lema (April 21, 2021). "Four crew dead, 9 missing after cargo ship runs aground in Philippines". Yahoo! News. Retrieved April 21, 2021.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans (Reissued) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 11, 2021. Archived from the original on April 25, 2021. Alt URL
- ^
Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 96W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 13, 2021. Archived from the original on May 13, 2021. Retrieved May 13, 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 03W (Three) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 12, 2021. Archived from the original on May 12, 2021. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ WWJP90 RJTD 121800 (Report). Japan Meteorological Agency. May 12, 2021. Archived from the original on May 12, 2021. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Crising'" (PDF). PAGASA. May 12, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 12, 2021. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #5 for Tropical Depression 'Crising'" (PDF). PAGASA. May 12, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 12, 2021. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 03W (Three) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 13, 2021. Archived from the original on May 13, 2021. Retrieved May 13, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #3 for Tropical Storm 'Crising'" (PDF). PAGASA. May 13, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 13, 2021. Retrieved May 13, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 03W (Three) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 13, 2021. Archived from the original on May 13, 2021. Retrieved May 13, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #7 for Tropical Depression 'Crising'" (PDF). PAGASA. May 13, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 13, 2021. Retrieved May 13, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #11-FINAL for Low Pressure Area (formerly 'Crising')" (PDF). PAGASA. May 15, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 15, 2021. Retrieved May 15, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Malakas na ulan at hangin, naranasan sa Davao Oriental sa pag-landfall ng bagyong 'Crising'". ABS-CBN News (in Tagalog). May 13, 2021. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Arceo, Acor (May 13, 2021). "Crising weakens into tropical depression, makes landfall in Davao Oriental". Rappler. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "3 tao, 1 kalabaw, nailigtas sa rumaragasang ilog sa Cotabato". GMA News (in Tagalog). Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "SitRep no.06 re Preparedness Measures for Tropical Depression CRISING" (PDF). NDRRMC. May 28, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 270600". Archived from the original on May 29, 2021.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 27, 2021. Archived from the original on June 10, 2021. Retrieved May 27, 2021. Alt URL
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 290600". Japan Meteorological Agency. May 29, 2021. Archived from the original on May 29, 2021. Retrieved May 29, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Advisory #1 for Tropical Depression" (PDF). PAGASA. May 29, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 29, 2021. Retrieved May 29, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 04W (Four) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 29, 2021. Archived from the original on May 29, 2021. Retrieved May 29, 2021.
- ^ PAGASA-DOST [@dost_pagasa] (May 29, 2021). "TROPICAL CYCLONE UPDATE - 3:15 AM, 30 May 2021 - At 1:00 AM today, the Tropical Depression east of Mindanao entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility and was named "DANTE". Tropical Cyclone Bulletins will be issued beginning at 5:00 AM today" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Dante'" (PDF). PAGASA. May 29, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 29, 2021. Retrieved May 29, 2021.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 04W (Four) Warning NR 004". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 30, 2021. Archived from the original on May 31, 2021. Retrieved June 2, 2021 – via Tokyo Global Information System Centre.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 04W (Four) Warning NR 004". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 30, 2021. Archived from the original on May 31, 2021. Retrieved June 2, 2021 – via Tokyo Global Information System Centre.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #5 for Tropical Storm 'Dante'". PAGASA. May 30, 2021. Archived from the original on May 30, 2021. Retrieved June 2, 2021.
- ^ "WTPQ50 RJTD 310000". Japan Meteorological Agency. May 31, 2021. Archived from the original on May 31, 2021. Retrieved June 2, 2021 – via National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 04W (Four) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 31, 2021. Archived from the original on May 31, 2021. Retrieved May 31, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Storm Dante makes landfall over Eastern Samar". ABS-CBN News and Current Affairs. June 1, 2021. Retrieved June 2, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 04W (Choi-wan) Warning NR 012". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 1, 2021. Archived from the original on June 1, 2021. Retrieved June 2, 2021 – via National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (June 2, 2021). "Tropical Storm Dante heads for Romblon after 2nd landfall in Masbate". Rappler. Retrieved June 2, 2021.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (June 3, 2021). "Tropical Storm Dante makes 7th, 8th landfalls in Batangas". Rappler. Retrieved June 3, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 04W (Choi-wan) Warning NR 018". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 3, 2021. Archived from the original on June 3, 2021. Retrieved June 3, 2021 – via National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin no. 27 for Tropical Storm "Dante" (Choi-wan)". PAGASA. June 3, 2021. Archived from the original on June 3, 2021. Retrieved June 3, 2021.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (June 4, 2021). "Tropical Storm Dante exits PAR but may reenter". Rappler. Retrieved June 5, 2021.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (June 5, 2021). "Dante weakens into tropical depression, reenters PAR". Rappler. Retrieved June 5, 2021.
- ^ "Warning lifted after Choi-Wan downgraded to tropical depression - Focus Taiwan". focustaiwan.tw (in Chinese). Retrieved June 4, 2021.
- ^ "WTPQ50 RJTD 050600". Japan Meteorological Agency. June 5, 2021. Archived from the original on June 5, 2021. Retrieved June 12, 2021 – via National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
- ^ Tropical Storm 04W (Choi-wan) Warning No. 27 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 5, 2021. Archived from the original on June 5, 2021. Retrieved June 5, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 04W (Choi-wan) Warning NR 028". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 5, 2021. Archived from the original on June 5, 2021. Retrieved June 5, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Storm Choi-wan (GDACS, JTWC, PAGASA, WMO, media)". Directorate-General for European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations. May 31, 2021. Retrieved May 31, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b SitRep no.06 re Preparedness Measures and Effects of ITCZ enhanced by TS DANTE (PDF) (Report). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. June 6, 2021. Retrieved June 6, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "SitRep no.10 re Preparedness Measures and Effects of ITCZ enhanced by TS DANTE" (PDF). NDRRMC. Retrieved June 11, 2021.
- ^ "#WalangPasok: Hunyo 1 dahil sa bagyong Dante". ABS-CBN News and Current Affairs (in Tagalog). June 1, 2021. Retrieved June 1, 2021.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 100830Z-110600Z June 2021 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 10, 2021. Archived from the original on June 10, 2021. Retrieved June 11, 2021.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans 110600Z-120600Z June 2021 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 11, 2021. Archived from the original on June 11, 2021. Retrieved June 11, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 110000". Japan Meteorological Agency. June 11, 2021. Archived from the original on June 11, 2021. Retrieved June 11, 2021.
- ^ "WTPQ50 RJTD 110600". Japan Meteorological Agency. June 11, 2021. Archived from the original on June 11, 2021. Retrieved June 11, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 92W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 11, 2021. Retrieved June 11, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 05W (Five) Warning NR 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 12, 2021. Archived from the original on June 12, 2021. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information". Japan Meteorological Agency. June 12, 2021. Archived from the original on June 12, 2021. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 180000Z-180600Z June 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. June 18, 2021. Archived from the original on June 18, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans 180600Z-190600Z June 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Centre. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. June 18, 2021. Archived from the original on June 18, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert for Tropical Disturbance 94W (Invest)". Joint Typhoon Warning Centre. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. Archived from the original on June 20, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 201330Z-210600Z June 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Centre. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. Archived from the original on June 20, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 210000". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on June 21, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 06W (Six) Warning NR 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Centre. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. June 21, 2021. Archived from the original on June 21, 2021. Retrieved June 21, 2021.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 06W (Six) Warning NR 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. June 21, 2021. Archived from the original on June 21, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ Mike Middlebrook (June 22, 2021). "Tropical Depression 06W Intermediate Advisory Number 3A". Tiyan, Guam: National Weather Service. Archived from the original on June 22, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ Mike Middlebrooke (June 22, 2021). "Tropical Depression 06W Intermediate Advisory Number 4". Tiyan, Guam: National Weather Service. Archived from the original on June 22, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL STORM 06W (SIX) WARNING NR 006". www.metoc.navy.mil. Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 22, 2021. Archived from the original on June 22, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 230000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. June 23, 2021. Archived from the original on June 23, 2021. Retrieved June 23, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning No. 9 for STS 2105 CHAMPI (2105)". Joint Typhoon Warning Centre. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. June 24, 2021. Archived from the original on June 24, 2021. Retrieved June 24, 2021.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Champi) Warning NR 013". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Archived from the original on June 24, 2021. Retrieved June 24, 2021.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Champi) Warning NR 016". Joint Typhoon Warning Centre. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. Archived from the original on June 25, 2021. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Champi) Warning NR 017". Joint Typhoon Warning Centre. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. Archived from the original on June 25, 2021. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information about Typhoon 2105 (Champi)". www.data.jma.go.jp. Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. June 25, 2021. Archived from the original on June 25, 2021. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- ^ "TYPHOON 06W (CHAMPI) WARNING NR 018". www.metoc.navy.mil/jtwc. Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 25, 2021. Archived from the original on June 25, 2021. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Champi) Warning NR 020". Joint Typhoon Warning Centre. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. June 25, 2021. Archived from the original on June 25, 2021. Retrieved June 26, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information for Extratropical Low T2105 (Champi)". www.data.jma.go.jp. Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. June 27, 2021. Archived from the original on June 27, 2021. Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL STORM 06W (CHAMPI) WARNING NR 026". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 27, 2021. Archived from the original on June 27, 2021. Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- ^ Landon Aydlett (June 21, 2021). "Public Tropical Cyclone Advisory No. 1 for Tropical Depression 06W". Tiyan, Guam: National Weather Service, Guam. Archived from the original on June 21, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical storm warning now in effect for Guam". Pacific Daily News. June 21, 2021. Archived from the original on June 22, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "Flash flood warning, high surf and small craft advisories in effect". Saipan Tribune. June 22, 2021. Archived from the original on June 22, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Matanane, Sabrina Salas (June 22, 2021). "TD 06W CPA has passed; Notice of GDOE Classes Canceled; GPA Respond to Outages; Report Impassable Roadways to the JIC". Kuam News. Archived from the original on June 22, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ Landon Aydlett (June 21, 2021). "Tropical Depression 06W Intermediate Advisory Number 4A". Tiyan, Guam: National Weather Service. Archived from the original on June 22, 2021. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- ^ "Typhoon Champi approaching Ogasawara Islands". NHK (Japan Broadcasting Corporation). June 26, 2021. Archived from the original on June 26, 2021. Retrieved June 26, 2021.
- ^ "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 021830Z-030600Z July 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 2, 2021. Archived from the original on July 4, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- ^ "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans 030600Z-040600Z July 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 3, 2021. Archived from the original on July 4, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- ^ "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 031530Z-040600Z July 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 3, 2021. Archived from the original on July 4, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 031800". Japan Meteorological Agency. July 3, 2021. Archived from the original on July 3, 2021. Retrieved July 3, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 96W)". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 3, 2021. Archived from the original on July 3, 2021. Retrieved July 3, 2021.
- ^ "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 032000Z-040600Z July 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 3, 2021. Archived from the original on July 4, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- ^ Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) [@PAGASA] (July 4, 2021). "TROPICAL CYCLONE UPDATE 10:00AM, 04 July 2021 At 8:00 AM today, the Low Pressure Area east of Guiuan, Eastern Samar developed into Tropical Depression #EmongPH. Severe Weather Bulletins will be issued beginning 11:00 AM today" (Tweet). Retrieved July 4, 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (July 4, 2021). "LPA east of Eastern Samar develops into Tropical Depression Emong". Rappler. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL DEPRESSION 07W (SEVEN) WARNING NR 001". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 4, 2021. Archived from the original on July 5, 2021. Retrieved July 5, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #13-FINAL for Tropical Depression 'Emong'" (PDF). PAGASA. July 6, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 6, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP26 RJTD 120300". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meterological Agency. July 6, 2021. Archived from the original on July 6, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 07W (Seven) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 6, 2021. Archived from the original on July 6, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 07W (Seven) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 6, 2021. Archived from the original on July 6, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical depression Emong is here: Storm signal no.1 up in Batanes, Cagayan". ABS-CBN News. July 4, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Emong'" (PDF). PAGASA. July 4, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 14, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Visaya Jr., Villamor (July 5, 2021). "Cagayan Valley placed on blue alert ahead of 'Emong'". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Retrieved July 5, 2021.
- ^ "Weather Advisory Number 1 for Low Pressure Areas" (PDF). Weather Division of PAGASA. July 4, 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 4, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 040100Z-040600Z July 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 4, 2021. Archived from the original on July 4, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans 040600Z-050600Z July 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 4, 2021. Archived from the original on July 6, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ "Weather Advisory Number 4 for Southwest Monsoon" (PDF). Weather Division of PAGASA. July 5, 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 6, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 051800". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on July 5, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 97W)". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 5, 2021. Archived from the original on July 6, 2021. Retrieved July 7, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 97W) Reissued". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021. Retrieved July 7, 2021.
- ^ "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans 070600Z-080600Z July 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 8, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 070100Z-070600Z July 2021". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 8, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ "Passenger services suspended as tropical depression makes landfall in south China". Xinhua. July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 10, 2021. Retrieved July 9, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 08W (Eight) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021. Retrieved July 7, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 08W (Eight) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021. Retrieved July 7, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 070600". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 08W (Eight) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 080000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 8, 2021. Archived from the original on July 8, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ PAGASA [@dost_pagasa] (July 4, 2021). "RAINFALL ADVISORY No. 1 #NCR_PRSD Weather System: Low-Pressure Area (LPA) Issued at: 8:00 PM,04 July 2021" (Tweet). Archived from the original on July 10, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ PAGASA [@dost_pagasa] (July 4, 2021). "RAINFALL ADVISORY No. 2 #NCR_PRSD Weather System: Low-Pressure Area (LPA) Issued at: 11:00 PM,04 July 2021" (Tweet). Archived from the original on July 10, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Hong Kong Weather Warnings and Signals(07/Jul/2021)". www.hko.gov.hk. Hong Kong Observatory. July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021. Retrieved July 7, 2021.
- ^ Liu Shuqiao (July 6, 2021). "Blue Warning of Typhoon". www.cma.gov.cn. Beijing, China: China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021. Retrieved July 7, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information for T.D., 14:05 of July 6, 2021". Macau Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau. July 6, 2021. Archived from the original on July 6, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical storm Signal 1 raised". Macau Business. July 6, 2021. Archived from the original on July 10, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ "Phó Thủ tướng họp chỉ đạo ứng phó với áp thấp nhiệt đới và mưa lớn". Vietnam Disaster Management Authority (in Vietnamese). July 6, 2021. Archived from the original on July 8, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ "100% tàu thuyền nắm được thông tin áp thấp nhiệt đới, đã và đang vào bờ tránh trú". Bao Thanh Hoa (in Vietnamese). July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 8, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ "Chủ tịch UBND tỉnh Thanh Hóa ra công điện khẩn tập trung ứng phó với Áp thấp nhiệt đới". Bao Thanh Hoa (in Vietnamese). July 6, 2021. Archived from the original on July 8, 2021. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ "Thanh Hóa sẽ đón đợt mưa 200 mm, đề phòng sạt lở đất, lũ quét". Bao Thanh Hoa (in Vietnamese). July 7, 2021. Archived from the original on July 10, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ "Áp thấp nhiệt đới suy yếu, Thanh Hóa vẫn tiếp tục có mưa diện rộng, sóng lớn trên biển". Bao Thanh Hoa (in Vietnamese). July 8, 2021. Archived from the original on July 10, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ "Họp giao ban công tác phòng, chống thiên tai ngày 10/7/2021". Vietnam Disaster Management Authority (in Vietnamese). July 10, 2021. Archived from the original on July 10, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific 140600Z-150600Z July 2021 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 14, 2021. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans 150600Z-160600Z July 2021 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 15, 2021. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^
Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 152030Z-160600Z July 2021 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 15, 2021. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 98W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 15, 2021. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #01 for Tropical Depression 'Fabien'" (PDF). PAGASA. July 16, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ "JMA Weather map" (in Japanese). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 16, 2021. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 09W (Nine) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 16, 2021. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning No. 6 for Tropical Storm 2106 (In-fa)". Japan Meteorological Agency. July 17, 2021. Archived from the original on July 17, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 09W (In-fa) Warning No. 8 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 19, 2021. Archived from the original on July 19, 2021. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone No.11 for STS In-fa (2106)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 18, 2021. Archived from the original on July 18, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information about Severe Tropical Storm 2106 (In-fa)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 18, 2021. Archived from the original on July 19, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning No.15 for Severe Tropical Storm 2106 (In-fa". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 22, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 10W (In-fa) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ Typhoon 10W (In-fa) Warning No. 17 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 10W (In-fa) Warning No. 17 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information about Typhoon 2106 (In-fa)". www.jma.go.jp. Japan Meteorological Agency. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning No.11 For STS In-fa (2106)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 09W (In-fa) Warning No. 20 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ Typhoon 09W (In-fa) Warning No. 20 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ Typhoon 09W (In-fa) Warning No. 28 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 09W (In-fa) Warning No. 31 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 24, 2021. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 09W (In-fa) Warning No. 32 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 24, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #22F for Typhoon 'Fabian'" (PDF). PAGASA. July 24, 2021. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No.22 for Typhoon 2106 (In-fa)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on July 22, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ Hao Jing (July 25, 2021). "台风"烟花"登陆浙江省舟山普陀沿海 江浙沪等地有持续强风雨-中国气象局政府门户网站". www.cma.gov.cn (in Chinese). Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 09W (In-fa) Warning No. 37 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 25, 2021. Archived from the original on July 26, 2021. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning No. 37 for Severe Tropical Storm 2106 (In-fa)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 25, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ "台風6号 20日昼前にも暴風警報の可能性 沖縄本島中南部で". Okinawa Times. July 18, 2021. Archived from the original on July 18, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "台風6号:大東島地方はきょう休校 外周道路は通行止めに 船の欠航で食料品が品薄になる恐れ". Okinawa Times. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ "沖縄の南城市で最大瞬間32.3メートル 台風6号で690戸が停電 12人が避難【21日午後1時半】". Okinawa Times (in Japanese). July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "男性警備員が頭から血を流し死亡 倒れているのを同僚が発見 沖縄で台風6号が影響か". Okinawa Times (in Japanese). July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "河南:此轮强降雨已致99人遇难 失踪人员仍在核查中". July 29, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jackson Dill and Shawn Deng. "Typhoon In-fa strengthening while on track to impact Japan, Taiwan and China". CNN. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "Zhengzhou Henan: 12 dead and thousands evacuated in China floods". BBC News. July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ Liu Shuqiao (July 22, 2021). "Blue Warning for Typhoon In-fa". www.cma.gov.cn. Archived from the original on July 22, 2021. Retrieved July 22, 2021.
- ^ Liu Shuqiao (July 23, 2021). "Orange Warning for Typhoon In-fa". www.cma.gov.cn. Archived from the original on July 24, 2021. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^ Liu Shuqiao (July 26, 2021). "Yellow Warning for Typhoon In-fa". www.cma.gov.cn. Archived from the original on July 26, 2021. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ Everington, Keoni (July 21, 2021). "Typhoon In-Fa will bring heavy rain to Taiwan starting today". Taiwan News. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "Dismiss Heavy Rain Advisory, 10:05 TST 2021-07-21". Central Weather Bureau. July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on May 30, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "Fabian now a typhoon; enhanced southwest monsoon triggers more rain". Rappler. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #22 for Typhoon 'Fabian'" (PDF). PAGASA. July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP25 RJTD 170000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 17, 2021. Archived from the original on July 17, 2021. Retrieved July 17, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 170000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 17, 2021. Archived from the original on July 17, 2021. Retrieved July 17, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 99W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 17, 2021. Archived from the original on July 18, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 10W (Ten) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 18, 2021. Archived from the original on July 18, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Ten) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 18, 2021. Archived from the original on July 18, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 10W (Ten) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 18, 2021. Archived from the original on July 19, 2021. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information for Tropical Storm 2107 (Cempaka)". www.jma.go.jp. Japan Meteorological Agency. July 19, 2021. Archived from the original on July 19, 2021. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ Typhoon 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 19, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 19, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Information about Severe Tropical Storm 2107 (Cempaka)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No.7 of Severe Tropical Storm 2107 (Cempaka)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 09 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ "Typhoon Cempaka makes landfall in China's Guangdong, says Xinhua". July 21, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 10 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Progonostic Reasoning No. 9 for Severe Tropical Storm 2107 (Cempaka)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Progonostic Reasoning No. 10 for Severe Tropical Storm 2107 (Cempaka)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 12 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning No.10 for Tropical Storm 2107 (Cempaka)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 22, 2021.
- ^ "WTPQ51 RJTD 220000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 22, 2021. Archived from the original on July 22, 2021. Retrieved July 22, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 22, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 21 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 20 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 10W (Cempaka) Warning No. 21 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 260000". Japan Meteorological Agency. Tokyo, Japan. July 26, 2021. Archived from the original on July 26, 2021. Retrieved July 27, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Warning Bulletin for Tropical Depression". www.hko.gov.hk. Hong Kong Observatory. July 18, 2021. Archived from the original on July 18, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "Current Weather Warnings". www.hko.gov.hk. Hong Kong Observatory. July 19, 2021. Archived from the original on July 19, 2021. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Warning Bulletin for Typhoon Cempaka". www.hko.gov.hk. Hong Kong Observatory. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ "Weather Warning and Signals Record (20/Jul/2021)". www.hko.gov.hk. Hong Kong Observatory. July 20, 2021. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ Liu Shuqiao (July 20, 2021). "Orange Warning of Typhoon". www.cma.gov.cn. China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ Liu Shuqiao (July 21, 2021). "Blue Warning of Typhoon". www.cma.gov.cn. China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans 220600Z-230600Z July 2021 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 22, 2021. Archived from the original on July 29, 2021. Retrieved July 29, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 221800". Japan Meteorological Agency. July 22, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved July 30, 2021.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans Reissued 222230Z-230600Z July 2021 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 22, 2021. Archived from the original on July 30, 2021. Retrieved July 30, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 90W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 22, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved July 30, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning No. 3 for TS 2108 Nepartak (2108)". Japan Meteorological Agency. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved July 30, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved July 30, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 24, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 24, 2021. Archived from the original on July 24, 2021. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 5 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 24, 2021. Archived from the original on July 24, 2021. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 24, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^
Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 8 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 25, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 13A (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 26, 2021. Archived from the original on July 26, 2021. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 15 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 27, 2021. Archived from the original on July 27, 2021. Retrieved July 27, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 27, 2021. Archived from the original on July 27, 2021. Retrieved July 27, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 17 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 27, 2021. Archived from the original on July 27, 2021. Retrieved July 27, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 28, 2021. Archived from the original on July 27, 2021. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 20 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 28, 2021. Archived from the original on July 27, 2021. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 11W (Nepartak) Warning No. 21 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2021. Archived from the original on July 23, 2021. Retrieved August 1, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 311200". Japan Meteorological Agency. July 31, 2021. Archived from the original on July 31, 2021. Retrieved August 1, 2021.
- ^ Traylor, Daniel (July 28, 2021). "Miyagi sees first tropical storm landfall on record as Nepartak crosses Honshu". The Japan Times. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ 日本放送協会. "オリンピック ボート 台風8号影響で競技は28日以降に延期 (Competition postponed after 28th due to Olympic boat typhoon No. 8)". NHKニュース. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ "Olympic Rowing Competition Postponed Due to Tropical Storm Approaching Japan". NBC New York. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 98W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 1, 2021. Archived from the original on August 1, 2021. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 020000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 2, 2021. Archived from the original on August 2, 2021. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 12W (Twelve) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 2, 2021. Archived from the original on August 2, 2021. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 12W (Twelve) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 2, 2021. Archived from the original on August 2, 2021. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 020000". Japan Meteorological Agency. August 4, 2021. Archived from the original on August 2, 2021. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 09W (Nine) Warning No. 5 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 3, 2021. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 031800". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 3, 2021. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 040600". Japan Meteorological Agency. August 2, 2021. Archived from the original on August 2, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 90W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 2, 2021. Archived from the original on August 2, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 13W (Thirteen) Warning NN01". United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 2, 2021. Archived from the original on August 4, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 13W (Thirteen) Warning NR 005". United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 3, 2021. Archived from the original on August 4, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ "Japan Meteorological Agency Tropical Cyclone Information". Japan Meteorological Agency. August 4, 2021. Archived from the original on August 4, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ "1st LD-Writethru: Typhoon Lupit makes second landfall in southeast China's Fujian". August 5, 2021.
- ^ Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) [@PAGASA] (August 7, 2021). "At 5:00 AM today, Tropical Storm LUPIT entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility and was assigned the local name #HuaningPH. Tropical Cyclone Bulletins will be issued beginning at 11:00 AM today" (Tweet). Retrieved August 7, 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 24 for Tropical Storm 2109 (Lupit)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 8, 2021. Archived from the original on August 9, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 13W (Lupit) Warning No. 26 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 9, 2021. Archived from the original on August 9, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Advisory". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 9, 2021. Archived from the original on August 9, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 13W (Lupit) Warning No. 29 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 9, 2021. Archived from the original on August 9, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 030600". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 3, 2021. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 99W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 3, 2021. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 15W (Fifteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 4, 2021. Archived from the original on August 4, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 15W (Fifteen) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 5, 2021. Archived from the original on August 5, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 15W (Fifteen) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 5, 2021. Archived from the original on August 5, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 1 for Tropical Storm 2111 (Nida)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 5, 2021. Archived from the original on August 5, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 7 for Severe Tropical Storm 2111 (Nida)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 6, 2021. Archived from the original on August 7, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 9 for Severe Tropical Storm 2111 (Nida)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 7, 2021. Archived from the original on August 7, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 15W (Fifteen) Warning No. 12 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 7, 2021. Archived from the original on August 7, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 10 for Tropical Storm 2111 (Nida)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 7, 2021. Archived from the original on August 7, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 9, 2021. Archived from the original on August 8, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 3, 2021. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved August 5, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning No. 1 for Tropical Depression located at 23.6N 125.2E". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 3, 2021. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved August 5, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 97W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 3, 2021. Archived from the original on August 3, 2021. Retrieved August 5, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Gorio'" (PDF). PAGASA. August 4, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 14W (Fourteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 4, 2021. Archived from the original on August 4, 2021. Retrieved August 5, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 14W (Fourteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 4, 2021. Archived from the original on August 4, 2021. Retrieved August 5, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No.7 for Tropical Storm 2110 (Mirinae)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 5, 2021. Archived from the original on August 5, 2021. Retrieved August 5, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 14W (Mirinae) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 5, 2021. Archived from the original on August 5, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 14W (Mirinae) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 5, 2021. Archived from the original on August 5, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 17 for Tropical Storm 2110 (Mirinae)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 7, 2021. Archived from the original on August 8, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 14W (Mirinae) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 8, 2021. Archived from the original on August 8, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 14W (Mirinae) Warning No. 21 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 9, 2021. Archived from the original on August 9, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 10, 2021. Archived from the original on August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ Jon Jelsema (August 6, 2021). "Five-Day Graphic Tropical Weather Outlook". nhc.noaa.gov. Honolulu, Hawaii: Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ Tina Stall (August 10, 2021). "Five-Day Graphic Tropical Weather Outlook". nhc.noaa.gov. Honolulu, Hawaii: Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 100600". Japan Meteorological Agency. August 10, 2021. Archived from the original on August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 91C) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 10, 2021. Archived from the original on August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 10, 2021. Archived from the original on August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 11, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 10, 2021. Archived from the original on August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 11, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 11 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2021. Archived from the original on August 13, 2021. Retrieved August 13, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 14 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2021. Archived from the original on August 14, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 14 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2021. Archived from the original on August 14, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 14, 2021. Archived from the original on August 14, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 14, 2021. Archived from the original on August 14, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 15, 2021. Archived from the original on August 16, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 15, 2021. Archived from the original on August 16, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 5 for the Tropical Depression located at 14.0N 152.0E". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 16, 2021. Archived from the original on August 16, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP90 RJTD 170000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 17, 2021. Archived from the original on August 17, 2021. Retrieved August 17, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 28 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Archived from the original on August 17, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 16W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Archived from the original on August 17, 2021.
- ^ PAGASA-DOST [@dost_pagasa] (August 19, 2021). "At 10:00 AM today, the tropical depression east of Luzon entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility and was assigned the local name #IsangPH. Tropical Cyclone Bulletins will be issued beginning at 11:00 AM today" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 29 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 19, 2021. Archived from the original on August 19, 2021. Retrieved August 21, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 29 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 19, 2021. Archived from the original on August 19, 2021. Retrieved August 21, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 2 for Tropical Storm 2112 (Omais)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 20, 2021. Archived from the original on August 20, 2021. Retrieved August 21, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 16W (Omais) Warning No. 34 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 20, 2021. Archived from the original on August 20, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 7 for Severe Tropical Storm 2112 (Omais)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 21, 2021. Archived from the original on August 22, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 9 for Tropical Storm 2112 (Omais)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 22, 2021. Archived from the original on August 22, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 16W (Omais) Warning No. 43 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 23, 2021. Archived from the original on August 23, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 16W (Omais) Warning No. 43 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 23, 2021. Archived from the original on August 24, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 24, 2021. Archived from the original on August 24, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 16W (Omais) Warning No. 44 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 24, 2021. Archived from the original on August 24, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ Mike Ziobro (August 14, 2021). "Tropical Storm 16W Advisory Number 18". www.weather.gov/gum. Tiyan, Guam: National Weather Service. Archived from the original on August 16, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ Genevieve Cruz Miller (August 15, 2021). "Tropical Depression 16W Advisory Number 20". www.weather.gov/gum. Tiyan, Guam: National Weather Service. Archived from the original on August 16, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ Hong (August 16, 2021). "Tropical Depression 16W Advisory Number 24". www.weather.gov/gum. Tiyan, Guam: National Weather Service. Archived from the original on August 16, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 010000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 1, 2021. Archived from the original on September 1, 2021. Retrieved September 1, 2021.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and Southern Pacific Oceans (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 1, 2021. Archived from the original on September 1, 2021. Retrieved September 1, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 93W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 1, 2021. Archived from the original on September 1, 2021. Retrieved September 2, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 2, 2021. Archived from the original on September 2, 2021. Retrieved September 2, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 2, 2021. Archived from the original on September 2, 2021. Retrieved September 2, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 2, 2021. Archived from the original on September 2, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 2, 2021. Archived from the original on September 2, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 2, 2021. Archived from the original on September 2, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 5 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 3, 2021. Archived from the original on September 3, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 3, 2021. Archived from the original on September 3, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 7 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 3, 2021. Archived from the original on September 3, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 8 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 3, 2021. Archived from the original on September 3, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 040120". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 4, 2021. Archived from the original on September 4, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ Significant Advisory for Western and Southern Pacific (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 3, 2021. Archived from the original on September 3, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ "JMA Warning and Summary 051800". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 5, 2021. Archived from the original on September 6, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 94W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 5, 2021. Archived from the original on September 5, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 18W (Eighteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original on September 6, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Jolina' (Conson)" (PDF). PAGASA. September 5, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 5, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 1 Tropical Storm 2113 (Conson)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original on September 6, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Storm 18W (Conson) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original on September 6, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ "JTWC Best Track data for Typhoon 18W (Conson)". Honululu, Hawaii: Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 3 for Severe Tropical Storm 2113 (Conson)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #5 for Typhoon 'Jolina' (Conson)" (PDF). PAGASA. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 6, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (September 7, 2021). "Typhoon Jolina makes 2nd, 3rd landfalls in island towns of Samar province". Rappler. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 4 for Tropical Storm 2113 (Conson)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #9 for Typhoon 'Jolina' (Conson)". PAGASA. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #10 for Severe Tropical Storm 'Jolina' (Conson)". PAGASA. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ ABS-CBN News (September 7, 2021). "Jolina makes landfall in Marinduque". Head Topics. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #16 for Severe Tropical Storm 'Jolina' (Conson)". PAGASA. September 8, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 8, 2021. Retrieved September 8, 2021.
- ^ Gillan Ropero (September 8, 2021). "'Jolina' makes landfall in Batangas, 'Kiko' slightly intensifies: PAGASA". ABS-CBN News. Retrieved September 8, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Storm Jolina makes 9th landfall in Bataan". Rappler. Retrieved September 9, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 14 for Severe Tropical Storm 2113 (Conson)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 9, 2021. Archived from the original on September 9, 2021. Retrieved September 9, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #26-FINAL for Severe Tropical Storm 'Jolina' (Conson)" (PDF). PAGASA. September 9, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 9, 2021. Retrieved September 9, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 22 for Tropical Storm 2113 (Conson)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 11, 2021. Archived from the original on September 11, 2021. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 11, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 18W (Conson) Warning No. 25 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ "JMA Warning and Summary 120000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 18W (Conson) Warning No. 26 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 18W (Conson) Warning No. 27 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 18W (Conson) Warning No. 28-FINAL (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ "JMA Warning and Summary 131800". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 13, 2021. Archived from the original on September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ "JMA Warning and Summary 131200". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 13, 2021. Archived from the original on September 13, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Sitrep no.14 for Typhoon Jolina (2021)". NDRRMC. September 17, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Daily Report 13/09/2021
- ^ Jump up to: a b Vân Anh (September 13, 2021). "Thiệt hại ban đầu do bão số 5 gây ra". PetroTimes (in Vietnamese). Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Significant Advisory for Western and Southern Pacific (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original on September 5, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ "JMA Weather and Summary 051800". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 5, 2021. Archived from the original on September 6, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 95W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original on September 5, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 19W (Nineteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original on September 6, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 19W (Nineteen) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 6, 2021. Archived from the original on September 6, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 3 for Tropical Storm Chanthu (2114)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 5, 2021. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Typhoon 'Kiko' (Chanthu)". PAGASA. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 5 for Severe Tropical Storm Chanthu (2114)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 5 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 6A (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 7 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 8, 2021.
- ^ Supertyphoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 9 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 8, 2021. Archived from the original on September 8, 2021. Retrieved September 8, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Super Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 9 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 8, 2021. Archived from the original on September 8, 2021. Retrieved September 8, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Super Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 13 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 9, 2021. Archived from the original on September 9, 2021. Retrieved September 9, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 14 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 9, 2021. Archived from the original on September 9, 2021. Retrieved September 9, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Super Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 10, 2021. Archived from the original on September 10, 2021. Retrieved September 10, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Super Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 17 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 10, 2021. Archived from the original on September 10, 2021. Retrieved September 10, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #19 for Typhoon 'Kiko' (Chanthu)". PAGASA. September 9, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 9, 2021. Retrieved September 9, 2021.
- ^ @dost_pagasa (September 11, 2021). "At 8:30 AM today, Typhoon #KikoPH made landfall over Ivana, Batanes" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #21 for Typhoon 'Kiko' (Chanthu)". PAGASA. September 11, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 11, 2021. Retrieved September 11, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 22 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 11, 2021. Archived from the original on September 11, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 23 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #29-FINAL for Typhoon 'Kiko' (Chanthu)" (PDF). PAGASA. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 26 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 27 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 12, 2021. Archived from the original on September 12, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 28 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 13, 2021. Archived from the original on September 13, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 29 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 13, 2021. Archived from the original on September 13, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 30 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 13, 2021. Archived from the original on September 13, 2021. Retrieved September 14, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 31 for Typhoon 2114 (Chanthu)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 14, 2021. Archived from the original on September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 14, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 32 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 14, 2021. Archived from the original on September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 14, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 32 for Severe Tropical Storm 2114 (Chanthu)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 14, 2021. Archived from the original on September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 14, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 33 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 14, 2021. Archived from the original on September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 14, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 33 for Tropical Storm 2114 (Chanthu)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 14, 2021. Archived from the original on September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 14, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 39 for Severe Tropical Storm 2114 (Chanthu)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 16, 2021. Archived from the original on September 16, 2021. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 45 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 17, 2021. Archived from the original on September 17, 2021. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 46 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 17, 2021. Archived from the original on September 17, 2021. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ "RSMC Prognostic Reasoning No. 45 for Tropical Storm 2114 (Chanthu)". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 17, 2021. Archived from the original on September 17, 2021. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 47 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 17, 2021. Archived from the original on September 17, 2021. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Depression 19W (Chanthu) Warning No. 48-FINAL (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 18, 2021. Archived from the original on September 18, 2021. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ Peter Blaza; Jacqueline Wong (September 12, 2021). "Strong typhoon cuts power, causes flooding in northern Philippines". www.reuters.com. Reuters. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Sitrep no.7 for Typhoon Kiko (2021)". ndrrmc.gov.ph. National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. September 17, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ Associated Press (September 12, 2021). "Typhoon pours 5 inches of rain on Taiwan, heads for Shanghai". www.washingtonpost.com. The Washington Post. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Ji Siqi (September 14, 2021). "China's busiest container-shipping ports in Shanghai, Ningbo begin to reopen after Typhoon Chanthu". South China Morning Post. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ Yonhap (September 17, 2021). "Typhoon Chanthu passes near Jeju, flooding roads, homes, canceling flights". The Korea Herald. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 191800". Japan Meteorological Agency. January 19, 2021. Archived from the original on January 20, 2021. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Arayata, Cristina (January 18, 2021). "LPA, ITCZ to bring scattered rains Monday". pna.gov.ph. Philippine News Agency. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Warning and Summary 201200". Japan Meteorological Agency. January 20, 2021. Archived from the original on January 20, 2021. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (January 20, 2021). "Parts of Luzon rainy due to LPA off Aurora, tail-end of frontal system". rappler.com. Rappler. Retrieved January 21, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "SitRep No. 12 re Preparedness Measures and Effects for TEFS, LPAs, and ITCZ" (PDF). NDRRMC. January 29, 2021.
- ^ Flores, Helen (March 10, 2021). "Low-pressure area spotted off Davao". The Philippine Star. Retrieved March 14, 2021.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (March 12, 2021). "LPA still 'less likely' to become tropical depression but rain persists". Rappler. Retrieved March 14, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 140600" (TXT). Japan Meteorological Agency. March 14, 2021. Archived from the original on March 14, 2021. Retrieved March 14, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 150000" (TXT). Japan Meteorological Agency. March 15, 2021. Archived from the original on March 15, 2021. Retrieved March 15, 2021.
- ^ Vera-Ruiz, Ellayn De (March 12, 2021). "Rains to prevail over parts of PH due to LPA". Manila Bulletin. Retrieved April 1, 2021.
- ^
Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 90W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 29, 2021. Archived from the original on May 29, 2021. Retrieved May 29, 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 300000". Japan Meteorological Agency. May 30, 2021. Archived from the original on May 30, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 90W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 30, 2021. Archived from the original on May 30, 2021. Retrieved May 30, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 011800". Japan Meteorological Agency. June 1, 2021. Archived from the original on June 2, 2021. Retrieved June 8, 2021 – via Tokyo Global Information Centre.
- ^ "SIGNIFICANT TROPICAL WEATHER ADVISORY FOR THE WESTERN AND SOUTH PACIFIC OCEANS". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 29, 2021. Archived from the original on June 30, 2021. Retrieved June 30, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 95W)". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. June 30, 2021. Archived from the original on June 30, 2021. Retrieved June 30, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 300000". Japan Meteorological Agency. June 30, 2021. Archived from the original on June 30, 2021. Retrieved June 30, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert Cancellation (Invest 95W)". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 1, 2021. Archived from the original on July 1, 2021. Retrieved July 1, 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 00Z". Japan Meteorological Agency. July 1, 2021. Archived from the original on July 1, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 190000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 19, 2021. Archived from the original on July 19, 2021. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 210000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 21, 2021. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 280000". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 28, 2021. Archived from the original on July 28, 2021. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ "気象庁|天気図".
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 311800". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 31, 2021. Archived from the original on July 31, 2021. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 96W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 1, 2021. Archived from the original on August 1, 2021. Retrieved August 1, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 011800". Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 1, 2021. Archived from the original on August 1, 2021. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ "WWJP27 RJTD 070000". Japan Meteorological Agency. September 7, 2021. Archived from the original on September 7, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Padgett, Gary. "Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary December 1999". Australian Severe Weather. Archived from the original on August 28, 2012. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Typhoon Committee (February 21, 2013). "Typhoon Committee Operational Manual 2013" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. pp. 37–38. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 28, 2012. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
- ^ http://www.typhooncommittee.org/48th/docs/item%204%20technical%20presentations/4.1.Review2015TyphoonSeason.pdf
- ^ Zhou, Xiao; Lei, Xiaotu (2012). "Summary of retired typhoons within the Western North Pacific Ocean". Tropical Cyclone Research and Review. The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific/World Meteorological Organization's Typhoon Committee. 1 (1): 23–32. doi:10.6057/2012TCRR01.03. ISSN 2225-6032. Archived from the original on August 12, 2017. Retrieved December 21, 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Philippine Tropical Cyclone Names". Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Archived from the original on January 30, 2021. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
- ^ "Bão số 2 lướt qua gây thiệt hại tại Thái Bình, Hải Phòng". Vietnamnet (in Vietnamese). June 13, 2021. Retrieved June 13, 2021.
- ^ "Thiệt hại do thiên tai từ đầu năm 2021 (tính đến 07h00 ngày 17/6/2021)". Vietnam Disaster Management Authority (in Vietnamese). June 17, 2021. Archived from the original on June 17, 2021. Retrieved June 17, 2021.
- ^ "众志成城抹灾痕!阳西县把台风造成损失降至最低" [Committed to wipe out the scars of disaster! Yangxi County minimizes the damage caused by the typhoon]. 阳西县人民政府网站 [Yangxi County People's Government] (in Chinese). July 23, 2021.
- ^ Lo, Clifford; Leung, Christy (July 20, 2021). "Hong Kong hiker swept away by stream amid No 3 typhoon warning found dead after hours-long search by rescuers, divers". South China Morning Post.
- ^ "Mường Lát (Thanh Hóa): Hơn 300 hộ dân sơ tán vì mưa lũ" [Muong Lat (Thanh Hoa): More than 300 households evacuated because of floods]. Tổng cục Phòng chống thiên tai [General Department of Disaster Prevention] (in Vietnamese). July 24, 2021.
- ^ "豪雨致災農損破4.2億 嘉義縣受損最重" [Heavy rains cause damage to farmers in 420 million disasters, and Chiayi County suffers the most]. The Liberty Times (in Chinese). August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 11, 2021.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2021 Pacific typhoon season. |
- China Meteorological Agency
- Digital Typhoon
- Hong Kong Observatory
- Japan Meteorological Agency
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center
- Korea Meteorological Administration
- Malaysian Meteorological Department
- National Weather Service Guam
- Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
- Taiwan Central Weather Bureau
- TCWC Jakarta (in Indonesian)
- Thai Meteorological Department (in Thai)
- Typhoon2000
- Vietnam's National Hydro-Meteorological Service
- 2021 Pacific typhoon season
- Pacific typhoon seasons
- Tropical cyclones in 2021

 WikiMiniAtlas
WikiMiniAtlas