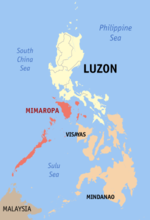
Palawan
Palawan | |
|---|---|
| Province of Palawan | |
 Palawan Provincial Capitol | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname(s): | |
 Location in the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 10°00′N 118°50′E / 10°N 118.83°ECoordinates: 10°00′N 118°50′E / 10°N 118.83°E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Mimaropa (in transition)[1][2] |
| Founded | 1818 |
| Capital | Puerto Princesa |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlalawigan |
| • Governor | Jose Alvarez (NPC) |
| • Vice Governor | Victorino Dennis M. Socrates (NUP) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 14,649.73 km2 (5,656.29 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 1st out of 81 |
| (excludes Puerto Princesa) | |
| Highest elevation | 2,086 m (6,844 ft) |
| Population (2020 census) [8] | |
| • Total | 939,594 |
| • Rank | 31st out of 81 |
| • Density | 64/km2 (170/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | 79th out of 81 |
| (excludes Puerto Princesa) | |
| Demonym(s) | Palaweño |
| Divisions | |
| • Independent cities | show
1 |
| • Component cities | 0 |
| • Municipalities | show
23 |
| • Barangays |
|
| • Districts | 1st to 3rd districts of Palawan (shared with Puerto Princesa City) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PHT) |
| ZIP Code | 5300–5322 |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)48 |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-PLW |
| Spoken languages |
|
| Website | www |
Palawan (pronounced /pəˈlɑːwən/), officially the Province of Palawan (Cuyonon: Probinsya i'ang Palawan; Tagalog: Lalawigan ng Palawan; Hiligaynon: Kapuoran sang Palawan; Cebuano: Lalawigan sa Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in terms of total area of jurisdiction. Its capital is the city of Puerto Princesa, but the city is governed independently from the province as a highly urbanized city.
The islands of Palawan stretch between Mindoro island in the northeast and Borneo in the southwest. It lies between the South China Sea and the Sulu Sea. The province is named after its largest island, Palawan Island (09°30′N 118°30′E / 9.500°N 118.500°E), measuring 450 kilometers (280 mi) long, and 50 kilometers (31 mi) wide.[9][10]
In 2019, Republic Act No. 11259 was passed providing for the division of Palawan into three separate provinces. It required a plebiscite to determine whether this division will be carried out.[11][12] The said plebiscite, which was postponed from May 2020 to March 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic,[13] rejected the move to split the province.[14][15][16]
History and prehistory[]
Prehistory[]
The early history of Palawan was determined by a team of researchers led by Dr. Robert B. Fox. They found evidence in the Tabon Caves that humans have lived in Palawan for more than 50,000 years. They also found human bone fragments, from an individual known as Tabon Man, in the municipality of Quezon, as well as tools and other artifacts.[9]
Two articulated phalanx bones of a tiger, besides another phalanx piece, were found amidst an assemblage of other animal bones and stone tools in Ille Cave near the village of New Ibajay. The other animal fossils were ascribed to macaques, deer, bearded pigs, small mammals, lizards, snakes and turtles. From the stone tools, besides the evidence for cuts on the bones, and the use of fire, it would appear that early humans had accumulated the bones.[17] Additionally, the condition of the tiger subfossils, dated to approximately 12,000 to 9,000 years ago, differed from other fossils in the assemblage, dated to the Upper Paleolithic. The tiger subfossils showed longitudinal fracture of the cortical bone due to weathering, which suggests that they had post-mortem been exposed to light and air. Tiger parts were commonly used as amulets in South and Southeast Asia, so it may be that the tiger parts were imported from elsewhere, as is the case with tiger canine teeth, which were found in Ambangan sites dating to the 10th to 12th centuries in Butuan, Mindanao. On the other hand, the proximity of Borneo and Palawan also makes it likely that the tiger had colonized Palawan from Borneo before the Early Holocene.[18][19]
Using the work of Von den Driesch,[20] all chosen anatomical features of appendicular elements' anatomical features which were chosen, besides molars, were measured to distinguish between taxa that had close relationships, and see morphometric changes over ages, though not for pigs or deer. For the latter two, cranial and mandibular elements, besides teeth of deer from Ille Cave were compared with samples of the Philippine brown deer (Cervus mariannus), Calamian hog deer (Axis calamianensis), and Visayan spotted deer (Cervus alfredi), and thus two taxa of deer have been identified from the fossils: Axis and Cervus.[21] Remains of pigs were compared with the Eurasian (Sus scrofa) and Palawanese wild boar (Sus ahoenobarbus). It is known that the Eurasian wild boar was imported as a domesticate to the islands from mainland Southeast Asia to the islands during the Terminal Holocene.[22][23][24][25][26]
Palawan was a major site for the Maritime Jade Road, one of the most extensive sea-based trade networks of a single geological material in the prehistoric world, operating for 3,000 years from 2000 BCE to 1000 CE.[27][28][29][30]
Pre-colonial period[]
Palawan is home to several indigenous groups. The oldest inhabitants are the Palaw'an, Batak, Tagbanwa, and Tau't Bato who are from the interiors and highlands of Palawan, as well as the Calamianes Islands. They traditionally practice animist anito religions. Palawan's coastlines were also settled by later groups that are now collectively known as "Palaweños". These groups are the Islamized Molbog people of southern Palawan (possibly originally from Sabah), and the Cuyonon and Agutaynon groups (from the nearby islands of Cuyo and Agutaya).[31][32]
Palawan was mentioned as "Pulaoan" or "Polaoan" by Antonio Pigafetta in 1521 during Magellan's expedition. They called it "la terra de missione" ("the land of promise") due to the fact that they were almost starving by the time they reached the island. The local datu made peace with the expedition through a blood compact. The ships' crews were welcomed to the island with rice cooked in bamboo tubes, rice wine, bananas, pigs, goats, chickens, coconuts, sugarcane, and other supplies. Pigafetta described the inhabitants as being farmers. Their primary weapons were blowguns with iron tips that could both shoot thick wooden or bamboo darts (some poisoned) and function as spears once their ammunition were exhausted. Pigafetta also described the islanders as keeping roosters for cockfighting.[33]
Spanish period[]

The northern Calamianes Islands were the first to come under Spanish authority, and were later declared a province separate from the Palawan mainland. In the early 17th century, Spanish friars sent out missions in Cuyo, Agutaya, Taytay and Cagayancillo but they met resistance from Moro communities. Before the 18th century, Spain began to build churches enclosed by garrisons for protection against Moro raids in the towns of Cuyo, Taytay, Linapacan and Balabac. In 1749, the Sultanate of Brunei ceded southern Palawan to Spain.[31]
In 1818, the entire island of Palawan, or Paragua as it was called, was organized as a single province named Calamianes, with its capital in Taytay.[citation needed] By 1858, the province was divided into two provinces, namely, Castilla, covering the northern section with Taytay as capital and Asturias in the southern mainland with Puerto Princesa as capital. It was later divided into three districts, Calamianes, Paragua and Balabac, with Principe Alfonso town as its capital. During the Spanish colonial period, Cuyo became the second capital of Palawan from 1873 to 1903.
American rule[]
In 1902, after the Philippine–American War, the Americans established civil rule in northern Palawan, calling it the province of Paragua. In 1903, pursuant to Philippine Commission Act No. 1363, the province was reorganized to include the southern portions and renamed Palawan, and Puerto Princesa declared as its capital.[31]
Many reforms and projects were later introduced in the province. Construction of school buildings, promotion of agriculture, and bringing people closer to the government were among the priority plans during this era.[31]
Japanese invasion[]

After the Japanese invasion, according to Stephen L. Moore, "Pro-Allied sentiment was strong, and it was later estimated that during the war as many as 1,154 Filipino guerrillas worked against the Japanese on the island. Those in the underground network would proudly refer to themselves as 'Palawan's Fighting One Thousand'." Early resistance leaders included Dr. Higinio Acosta Mendoza, his wife Triny, Thomas F. Loudon, and his son-in-law Nazario Mayor. Capt. Mayor organized Company D in Oct. 1943, and was responsible for the area encompassing Puerto Princesa south to Balabac Island. Capt. Mendoza covered the area north of Puerto Princesa to Caramay. Lt. Felipe Batul operated out of Danlig, while Capt. Carlos Amores operated out of Sibaltan. Overall command of the Palawan Special Battalion was under Maj. Pablo P. Muyco as part of the 6th Military District. The Palawan guerrillas helped any escaping American POWs, supported two coastwatcher groups sending regular radio broadcasts to General MacArthur on Japanese movements, and helped rescue downed airmen as well as survivors from the USS Flier submarine. Most importantly, they helped guide the 8th Army's troop landings.[34]
Palawan Massacre[]
During World War II, in order to prevent the rescue of prisoners of war by the advancing allies, on 14 December 1944, units of the Japanese Fourteenth Area Army (under the command of General Tomoyuki Yamashita) herded the remaining 150 prisoners of war at Puerto Princesa into three covered trenches which were then set on fire using barrels of gasoline. Prisoners who tried to escape the flames were shot down.[35] Only 11 men escaped the slaughter.[36]
Liberation[]
During the first phase of the Battle of Leyte Gulf, just off the coast of Palawan, two United States Navy submarines, USS Dace (SS-247) and USS Darter (SS-227) attacked a Japanese cruiser task force led by Admiral Takeo Kurita, sinking his flagship (in which he survived) Atago, and her sister ship Maya. Darter later ran aground that afternoon and was scuttled by USS Nautilus (SS-168).
The island was liberated from the Japanese Imperial Forces from February 28 to April 22, 1945, during the Invasion of Palawan.
Contemporary period[]
In 2005, Palawan was briefly made politically part of Western Visayas or Region VI through Executive Order 429 signed by then-President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo on May 23[37] as a political move to control the province and a response to getting more loans from China.[38] This decree was later deferred on August 18 within the same year reportedly due to the opposition of the province's Sangguniang Panlalawigan (Provincial Council).[39]
On July 21, 2007, its capital city, Puerto Princesa became a highly urbanized city.
Proposed division[]
In April 2019, a bill dividing Palawan into three provinces was passed into law.[40][41] The proposed three new provinces are Palawan del Norte, Palawan Oriental, and Palawan del Sur.[42][43] A plebiscite, originally scheduled in May 2020, was held on March 13, 2021, that decided whether Palawan will be divided into three provinces or not. Some civil society groups and Puerto Princesa residents opposed the proposed division, claiming that there was no extensive public consultation.[40][44][45][46] The Comelec announced on March 16, 2021, that the majority of Palawan residents opposed the division and thus, it will not be carried out.[14][15]
Geography[]
The province is composed of the long and narrow Palawan Island, plus a number of other smaller islands surrounding it, totalling roughly 1,780 islands and islets. The Calamianes Group of Islands to the northeast consists of Busuanga, Coron, Culion, and Linapacan islands. Balabac Island is located off the southern tip, separated from Borneo by the Balabac Strait. In addition, Palawan covers the Cuyo Islands in the Sulu Sea. The disputed Spratly Islands, located a few hundred kilometers to the west, are considered part of Palawan by the Philippines, and is locally called the "Kalayaan Group of Islands".
Palawan's almost 2,000 kilometers (1,200 mi) of irregular coastline is lined with rocky coves and sugar-white sandy beaches. It also harbors a vast stretch of virgin forests that carpet its chain of mountain ranges. The mountain heights average 1,100 meters (3,500 ft) in altitude, with the highest peak rising to 6,843 feet (2,086 m)[10] at Mount Mantalingahan. The vast mountain areas are the source of valuable timber. The terrain is a mix of coastal plain, craggy foothills, valley deltas, and heavy forest interspersed with riverine arteries that serve as irrigation.[9]
The province has a total land area of 14,649.73 square kilometers (5,656.29 sq mi).[47] When Puerto Princesa City is included for geographical purposes, its land area is 17,030.75 square kilometers (6,575.61 sq mi).[47] The land area is distributed to its mainland municipalities, comprising 12,239 square kilometers (4,726 sq mi), and the island municipalities, which altogether measure 2,657 square kilometers (1,026 sq mi). In terms of archipelagic internal waters, Palawan has the biggest marine resources that covers almost half of the Sulu Sea and a big chunk of the South China Sea that is within the municipal waters of Kalayaan Municipality which was official annexed to the Philippine jurisdiction by virtue of Presidential Decree 1596 dated June 11, 1978.
Climate[]

The province has two types of climate. The first, which occurs in the northern and southern extremities and the entire western coast, has two distinct seasons – six months dry and six months wet. The other, which prevails in the eastern coast, has a short dry season of one to three months and no pronounced rainy period during the rest of the year. The southern part of the province is virtually free from tropical depressions but northern Palawan experiences torrential rains during the months of July and August. Summer months serve as peak season for Palawan. Sea voyages are most favorable from March to early June when the seas are calm. The average maximum temperature is 31 °C (88 °F) with little variation all year.[9]
The island ecosystem of Palawan is threatened by climate change.[48][49] For example, though mangroves and barrier reefs protect Puerto Princesa's coastlines from supertyphoons, these barriers are subject to degradation due to El Niño, rising sea temperatures, and other climate change-related phenomena.[50] A study by the World Wide Fund for Nature revealed that a spike in ocean acidification in 2010 came from Palawan's waters.[51]
Administrative divisions[]
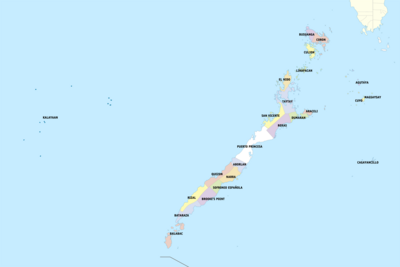
Palawan comprises 433 barangays in 23 municipalities and the capital City of Puerto Princesa. As an archipelago, Palawan has 13 mainland municipalities and 10 island towns. There are three congressional districts, namely: the first district comprising five northern mainland municipalities and nine island towns; the second district composed of six southern mainland towns and the island municipality of Balabac; and the third district covering the capital City of Puerto Princesa and the town of Aborlan. Thirteen municipalities are considered as mainland municipalities, namely Aborlan, Narra, Quezon, Sofronio Española, Brooke's Point, Rizal, and Bataraza (located south); San Vicente, Roxas, Dumaran, El Nido, and Taytay (found in the north). The remaining island municipalities are: Busuanga, Coron, Linapacan and Culion (forming the Calamianes group of islands), Cuyo, Agutaya and Magsaysay (the Cuyo group of islands), Araceli, Cagayancillo, Balabac and Kalayaan (Spratly Islands). The capital, Puerto Princesa is a highly urbanized city that governs itself independently from the province, but it usually grouped with the province for statistical and geographic purposes.
Had the March 2021 plebiscite (originally scheduled for May 2020 but delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic[13]) approved the partition, Palawan will be divided into three provinces.[52][53] The three provinces are Palawan del Norte (includes El Nido, Taytay, Coron, Linapacan, Culion, and Busuanga), Palawan Oriental (includes San Vicente, Roxas, Dumaran, Cuyo, Agutaya, Magsaysay, and Cagayancillo), and Palawan del Sur (includes Kalayaan, Aborlan, Narra, Sofronio Española, Brooke's Point, Rizal, Quezon, Bataraza and Balabac).[42][43]
- † Provincial capital and highly urbanized city
- Municipality
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Region[]
In 2001, the residents of Palawan voted in a plebiscite to reject inclusion into an expanded Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao.[56]
On 17 May 2002, Executive Order No. 103 divided Region IV into Region IV-A (Calabarzon) and Region IV-B (Mimaropa), placing the province of Palawan into Mimaropa.[57]
On 23 May 2005, Executive Order No. 429 directed that Palawan be transferred from Region IV-B to Region VI.[1] However, Palaweños criticized the move, citing a lack of consultation, with most residents in Puerto Princesa City and all municipalities but one preferring to stay with Region IV-B. Consequently, Administrative Order No. 129 was issued on 19 August 2005 that the implementation of EO 429 be held in abeyance pending approval by the President of its implementation Plan.[2] The Philippine Commission on Elections reported the 2010 Philippine general election results for Palawan as a part of the Region IV-B results.[58] As of 30 June 2011, the abeyance was still in effect and Palawan remained a part of Mimaropa.[7]
Demographics[]
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 35,696 | — |
| 1918 | 69,053 | +4.50% |
| 1939 | 93,673 | +1.46% |
| 1948 | 106,269 | +1.41% |
| 1960 | 162,669 | +3.61% |
| 1970 | 198,861 | +2.03% |
| 1975 | 254,356 | +5.06% |
| 1980 | 311,548 | +4.14% |
| 1990 | 436,140 | +3.42% |
| 1995 | 510,909 | +3.01% |
| 2000 | 593,500 | +3.26% |
| 2007 | 682,152 | +1.94% |
| 2010 | 771,667 | +4.59% |
| 2015 | 849,469 | +1.85% |
| 2020 | 939,594 | +2.00% |
| (excluding Puerto Princesa City) Source: Philippine Statistics Authority [54] [55] [59][60] | ||
The population of Palawan in the 2020 census was 939,594 people, [8] with a density of 64 inhabitants per square kilometre or 170 inhabitants per square mile. When Puerto Princesa is included for geographical purposes, the population is 1,104,585 people, with a density of 65/km2 (168/sq mi).
The province is a melting pot of 87 different cultural groups and races. Influx of migrants from other parts of the Philippines, particularly from Muslim Mindanao, accounts for the high population growth rate of 3.98% annually. The native-born Palaweños still predominate the populace. Eighteen percent is composed of cultural minority groups such as the Tagbanwa, Palawano, Batak, and Molbog.[citation needed]
Religion[]
Roman Catholicism[]

The predominant religion in Palawan is Roman Catholicism. In 2017, the Roman Catholic Apostolic Vicariate of Puerto Princesa had a 68.8% adherence while the Roman Catholic Apostolic Vicariate of Taytay (Northern Palawan) had an 91.6% adherence.[61][62] One of the religious orders that had a significant mission in the islands is the Order of Augustinian Recollects.
The Catholics in the province are governed by a single apostolic vicariate until 2002 when it was divided into two: the Apostolic Vicariate of Puerto Princesa in Southern Palawan and the Apostolic Vicariate of Taytay in Northern Palawan.[62][61]
Protestantism and other groups[]
Several Baptist and other Protestant denominations have a strong presence in Palawan as do the Church of the Foursquare Gospel in the Philippines, and the Seventh-day Adventists. Charismatic groups such as Jesus is Lord (JIL), (JTF) and the (formerly known at the Life Renewal Center).
The Members Church of God International popularly called Ang Dating Daan established three church districts namely Coron, Northern Palawan and Southern Palawan which signifies strong membership in the province.[citation needed]
Other Christian denominations including the indigenous Iglesia ni Cristo has many local congregations in the province. The United Church of Christ in the Philippines or (UCCP), the Jesus Miracle Crusade, the or PMCC (4th Watch) as well as the Iglesia Filipina Independiente (Philippine Independent Church or Aglipayan Church) which is standing as one diocese (The Diocese of Palawan). The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints has a growing membership in the island province. Jehovah's Witnesses have an active membership of 181,236 in the Philippines as of 2012. Special pioneers from the Witnesses have been preaching to prisoners at the Iwahig Prison and Penal Farm in Palawan, and were permitted to build a small Kingdom Hall right on the premises.[63]
Islam[]
Around 75,000 to 100,000 Palawan residents (10% to 13%) identify as Muslims, these being mostly the native Molbog who are concentrated in Balabac and Bataraza of the southern part of the island. Large numbers of Jama Mapun (Mapun Island) and Tausug (Sulu) migrants have also settled in southern Palawan, as well as a smaller number of Sama Pangutaran (Tawi-Tawi), Maranao (Lanao del Sur), and Yakan (Basilan). Maranao traders are more widely scattered throughout urban centers in Palawan, while the Yakan are mostly centered in the Rio Tuba area of Bataraza.[64][65]
Animism[]
Most of the ethnic minorities such as Batak and Tagbanwa are animists, many of which have continued to preserve their ancient traditions passed on by their ancestors and onto the next generations. However, Christian missionaries have interfered in some communities, to an extent where traditional ways have been obliterated by foreign and foreign-inspired religions.
Other religions[]
A notable Buddhist Temple in Palawan is Chùa Vạn Pháp. The temple was built by Vietnamese refugees. They were temporarily settled in Palawan during the Indochina refugee crisis, while they awaited permanent resettlement to third countries. Almost all of the refugees have moved on to other countries in 2005 and 2006.[66][67]
Language[]
There are 52 languages and dialects in the province, with Tagalog being spoken by more than 50 percent of the people. Languages native to the islands are Cuyonon (26.27 percent), and Palawano (4.0 percent). Kinaray-a is also present at 19 percent. Before mass immigration to Palawan by various groups of people from Southern Tagalog, Illocandia, and Central Luzon, and Panay, Cuyonon was an established lingua franca amongst many of its native peoples, i.e. the Agutaynen, Cagayanen, Tagbanua, Palawan, and others. The usage of Cuyonon significantly dropped during the approach of the new millennium being replaced by the now majority Tagalog. In the south of Palawan during the occupation of the Sulu Sultanate, Tausug was a lingua franca amongst the minority Islamfied ethnic groups i.e. Molbog, Tausug (non native), Muslim Palaw’an, and the migratory Sama. By the 19th century, Cuyonon had replaced Tausug as lingua franca.
Economy[]
Palawan's economy is basically agricultural. The three major crops are palay, corn and coconut. Mineral resources include nickel, copper, manganese, and chromite. Logging is also a major industry. Palawan has one of the richest fishing grounds in the country. About 45% of Manila's supply of fish comes from here. Having natural gas reserves of approximately 30,000 trillion cubic feet, the province is the only oil-producing province in the country.[75][76] In addition, tourism is also a thriving sector, having received 1.8 million tourists in 2018, a 21% year-over-year increase from 2017.[77]
Pearl diving used to be a significant economic activity for Palawan until the advent of plastics.[citation needed] The world's largest pearl, the 240 millimeters (9.4 in) diameter Pearl of Lao Tzu, was found off Palawan in 1934.
The economic and agricultural business growth of province is at 20% per annum.[76] Coconut, sugar, rice, lumber, and livestock are produced here.[10]
Flora and fauna[]
Unlike most of the Philippines, Palawan is biogeographically part of Sundaland, with a fauna and flora related to that found in Borneo.[78]
Palawan has 700,000 hectares of forests (as of 2010)[79] and has been called the Philippines' "last biodiversity frontier."[80]
Among the many endemic species are the Palawan peacock-pheasant, Philippine mouse-deer, Philippine pangolin, Palawan bearded pig, and Palawan birdwing. In the forests and grasslands, the air resonates with the songs of more than 200 kinds of birds. Over 600 species of butterflies flutter around the mountains and fields of Palawan, attracted to some 1500 hosts plants found here. Endangered sea turtles nest on white sand beaches.[81] Sea turtles usually go to the nutrient-rich coastal waters of Palawan to rest and look for food. Dugong numbers have fallen seriously, although Palawan still has a larger population than any other part of the country,[82] and organizations such as (C3) are working to end the unsustainable use of marine resources in Palawan and in Philippines.[83]
Total forest cover is about 56 percent of the total land area of the province while mangrove forest accounts for 3.35 percent based on the 1998 Landsat imagery. Grasslands dwindled from 19 percent in 1992 to 12.40 percent in 1998. This is an indication of improving soil condition as deteriorating soil is normally invaded by grass species. Brushlands increased to 25 percent of the total land area. Sprawled beneath the seas are nearly 11,000 square kilometers of coral reefs, representing more than 35% of the country's coral reefs.[81]

Palawan, the only Philippine island cited, is rated by the Condé Nast Traveler Readers as the most beautiful island in the world and is also rated by the National Geographic Traveler magazine as the best island destination in East and Southeast Asia region in 2007, and the equal 27th best island in the world having "incredibly beautiful natural seascapes and landscapes. One of the most biodiverse (terrestrial and marine) islands in the Philippines. The island has had a Biosphere Reserve status since the early 1990s, showing local interest for conservation and sustainable development".[84][85]
The province was also categorized as "doing well" in the 4th Destination Scorecard survey conducted by the National Geographic Center for Sustainable Destinations, and Conde Nast Traveler magazine voted its beaches, coves and islets as the tourist destination with the best beaches in Asia.[86] Renowned underwater explorer Jacques Cousteau has described the province as having one of the most beautiful seascapes in the world.[81] and Caril Ridley, founder of (PEMS) says the Islands of northern Palawan are destined to become a future destination for Asia's growing economic and environmental conferencing.
In 2007, a "shrew-eating pitcher plant", named Nepenthes attenboroughii was discovered in Mount Victoria. There were many species of pitcher plants discovered in this wild mountain paradise, the most recent is named Nepenthes leonardoi.[citation needed] In 2012, the purple crab was discovered here along with four other species.[citation needed]
Attractions[]
Calauit Game Preserve and Wildlife Sanctuary[]

A game reserve and wildlife sanctuary of exotic African animals and endangered endemic animals of Palawan. The reserve was established on August 31, 1976, by virtue of the Presidential Decree No. 1578,.[87] This was initiated in response to the appeal of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) to help save African wildlife when former President Ferdinand Marcos attended the 3rd World Conference in Kenya.[88] However, the IUCN, which has a policy against relocating animals outside of their natural range, bears no record of such a request.[89] By virtue of Republic Act 7611 (SEP), administrative jurisdiction of DENR was given to the local government of Palawan,[90] effective December 31, 1993. Management of the area is the responsibility of the Office of the Palawan Council of Sustainable Development (PCSD). It is located in Calauit Island in Busuanga.
Coron Reefs, Coron Bay, Busuanga[]
Seven lakes surrounded by craggy limestone cliffs attract hundreds of nature lovers to Coron Reefs in Northern Palawan, near the town of Coron. Busuanga Island, whose main town is Coron, is the jump-off point for numerous dive operators. The principal dive sites are 12 World War II Japanese shipwrecks sunk on September 24, 1944, by US Navy action. They range in depth from the surface to 40 meters. This large variety offers exciting wreck exploration for enthusiasts, from novice divers and snorkelers and recreational divers to experienced TEC divers.
The aquatic views from the sunken Japanese warships off Coron Island are listed in Forbes Traveler Magazine's top 10 best scuba sites in the world.[86]
El Nido Marine Reserve Park[]


The January 2008 issue of international magazine Travel + Leisure, published by the American Express Co. (which partnered with Conservation International) listed El Nido's sister hotel resorts El Nido Lagen Island and El Nido Miniloc Island in Miniloc and Lagen Islands as "conservation-minded places on a mission to protect the local environment". Travel + Leisure's 20 Favorite Green Hotels scored El Nido Resort's protection of Palawan's giant clam gardens and the re-introduction of endangered Philippine cockatoos.[91] Guest cottages on stilts are set above the crystalline ocean. The resorts are active in both reef and island conservation."[92]
Malampaya Sound Land and Seascape Protected Area[]
Located in the Municipality of Taytay, this important ecological and economic zone is a watershed and fishing ground, and the habitat of Bottle-nosed and Irrawaddy dolphins.[93]
UNESCO World Heritage Sites[]
- Puerto-Princesa Subterranean River National Park (1999)
Puerto Princesa City is the home of the Puerto Princesa Subterranean River National Park or the Underground River, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The 8-kilometer long tourist spot that showcases limestone karsts, diverse species and tropical rainforest is one of the world’s longest underground rivers and was also named as one of the “New 7 Wonders of Nature.”
- Tubbataha Reef Marine Park (1993)
The Tubbataha Reef Marine Park covers 332 km2, including the North and South Reefs. It is a unique example of an atoll reef with a very high density of marine species; the North Islet serving as a nesting site for birds and marine turtles. The site is an excellent example of a pristine coral reef with a spectacular 100 m perpendicular wall, extensive lagoons, and two coral islands.
Ursula Island[]
This game refuge and bird sanctuary is situated near the Municipality of Bataraza in southern Palawan. The islet is a migratory and wintering ground for shorebirds and seabirds.[93]
Rasa Island Wildlife Sanctuary[]
This 1,983-hectare (4,900-acre) protected area located in the municipality of Narra is a nesting ground of the endemic Philippine cockatoo or katala. It also harbors other rare bird species and marine turtles.
Security[]
The Armed Forces of the Philippines–Western Command in Canigaran and the Philippine National Police-Palawan Command with headquarters in Tiniguiban, Puerto Princesa, are responsible for maintenance of the peace and order. Military units in the province under the Western Command are the Naval Forces Northwest (Task Force 41 and 42), Philippine Air Force 4th Naval District IV, Delta Company and 10th Marine Battalion Landing Team located in Tiniguiban, Puerto Princesa. There has been discussion about dredging Ulugan Bay in order to build a larger naval base on Palawan, allowing the Philippines to project naval power into the South China Sea.[94][95]
The U.S. Department of State issued a travel warning in May 2015, advising foreigners against travel to the southern part of Palawan.[96] The warning continues to be in effect as of May 2017.[97]
Infrastructure[]
Communication[]
Four telecommunication companies provide local and international direct distance dialing and fax services. Inter island communications is available through the government's telegraph network and the Provincial Radio Communication System. In addition, there are 19 post offices, a number of cargo forwarders provide air parcel and freight services.[98]
The province has access to two satellite-linked television stations. Cable television in the City of Puerto Princesa offers dozens of foreign channels while smaller firms provide cable services in selected towns. Individual cable facility (Dream Cable) is available locally. Seven radio stations are based in Puerto Princesa, four on the AM and three on the FM bands. Community-based radio stations operate in some of the municipalities in the north and south of the province. Additional stations are expected to set up local affiliates in the capital city of Puerto Princesa.[98]
Two mobile phone companies, Smart Communications and Globe Telecom, are operating in the province. Sun Cellular is expected to start operations in the province soon.[98]
Health facilities[]

There are nine provincial government hospitals, two national government hospitals, one military hospital and nine private hospitals in the province. The Culion Sanitarium and General Hospital, Ospital ng Palawan, managed and administered by the Department of Health (DOH), MMG-PPC Cooperative Hospital, and the Palawan Adventist Hospital are located in Puerto Princesa.[98]
Utilities[]
The National Power Corporation has 14 electric facilities all over Palawan. It operates with a total of 51.363 megawatts of electricity. The effective power rates vary across different municipalities.[99] According to Palawan Electric Cooperative (PALECO), the main island composed of 19 city and municipalities, has 59% of electrification with 135,284 households connected to the grid.[100]
Water facilities in Palawan are classified as Level I (deepwell, handpump), Level II (communal faucet), or Level III (house connection). Among all of these types, Level I has the most units, accounting to 17,438; this is followed by Level III, with 1,688 units; and Level II, with only 94 units.[clarification needed][98]

Transportation[]
Air[]
The Puerto Princesa International Airport is the only international airport in Palawan, serving as the main gateway to the province. Other airports include:
Domestic[]
- Francisco B. Reyes Airport, Coron, Busuanga Island
- El Nido Airport, El Nido
- San Vicente Airport, San Vicente
- Cuyo Airport, Magsaysay
- Taytay Airport, Taytay
- , Roxas
- , Balabac (Bugsuk Island)
- , Rizal
- , Balabac
- , Bataraza
Other[]
- , Coron
- , Culion
- , Brooke's Point
- , Balabac (Candaraman Island)
- , San Vicente (under construction)
- Pamalican (Amanpulo) Airstrip, Cuyo (Pamalican Island)
- , Busuanga
- Rancudo Airfield, Kalayaan (military)
- , Rizal
Seaports[]
Port of Puerto Princesa is the main port on Palawan, serving both cargo and passenger traffic to the island. Scheduled passenger ferry services are running weekly from Manila to this port.[101] The port is managed by the Philippine Ports Authority. Other ports include:
- Port of Coron
- Port of El Nido
- Port Of Mangingisda
Education[]
The literacy rate in Palawan is increasing by 2% annually because of expanding access to education. Among these programs are the establishment of schools in remote barangays, non-formal education, multi-grade mobile teaching and the drop-out intervention program.[98]
Public schools in the province consist of 623 elementary schools, 126 secondary schools and two universities. Private schools are as follows: 26 elementary, 19 secondary, 4 private colleges, and 10 vocational schools.
Among the public institutions of higher education are the Palawan State University in Puerto Princesa City with 17 other campuses across the province, Western Philippines University with campuses in Aborlan and Puerto Princesa City, Coron College of Fisheries, Puerto Princesa School of Arts and Trade and the Palawan College of Arts and Trade in Cuyo, Palawan.
Some of the private institutions are the Holy Trinity University run by the Dominican Sisters of Saint Catherine of Siena, Palawan Polytechnical College Inc., in Roxas, San Vicente and Puerto Princesa City, Systems Technology Institute (STI), AMA Computer Learning Center (ACLC) in Puerto Princesa City, San Francisco Javier College run by the Augustinian Recollect Sisters in Narra, Loyola College in Culion run by the Jesuits, St. Joseph Academy in Cuyo, St. Augustine Academy in Coron, Coron Technical School, Sacred Heart of Jesus High School in Brooke's Point; Northern Palawan Christian Institute (owned and manage by the Iglesia Filipina Independiente, Palawan Diocese) and the unique educational institution called the St. Ezekiel Moreno Dormitory located in barangay Macarascas, Puerto Princesa City, founded by Bishop Broderick Pabillo, the present auxiliary bishop of the Archdiocese of Manila. The Palawanologist, Andrei Ustares Acosta of El Nido, Palawan, founded the new discipline on the studies of Palawan called the Palawanology.[98]
See also[]
- Legislative districts of Palawan
- Dewil Valley
- List of islands of the Philippines
- Puerto Princesa Subterranean River National Park
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b President of the Philippines (23 May 2005). "Executive Order No. 429 s. 2005". Official Gazette. Philippine Government.
- ^ Jump up to: a b President of the Philippines (19 August 2005). "Administrative Order No. 129 s. 2005". Official Gazette. Philippine Government.
- ^ "The Mysterious Paradise of Palawan". Private Islands Magazine. Retrieved 12 February 2015.
A naturally rich region with abundant forests and fishing, there’s little wonder that early Spanish explorers referred to Palawan as the ‘Land of Promise’.
- ^ "World's Best Islands 2013".Travel + Leisure. 2016. Retrieved 16 September 2016
- ^ "Environment and development in coastal regions and in small islands: The points man in the Philippines' last frontier" (Extract from UNESCO Sources (131) published on February, 2001, page 14). UNESCO. February 2001. Retrieved 12 February 2015.
The Island Province of Palawan, often called the Philippines’ last frontier, has a unique concentration of UNESCO coastal and small island initiatives.
- ^ "Palawan Biodiversity Corridor The Philippines' last biodiversity frontier". Conservation International Philippines. Archived from the original on 12 February 2015. Retrieved 12 February 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Archived from the original on 12 February 2008. Retrieved 14 May 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Census of Population (2020). Highlights of the Philippine Population 2020 Census of Population. PSA. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d WowPhilippines:Palawan - the Philippines' Last Frontier. Accessed August 27, 2008. Archived June 10, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jump up to: a b c MSN Encarta: Palawan Archived 2008-07-25 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed September 05, 2008.
- ^ Roque, EJ (13 April 2019). "PRRD signs law dividing Palawan into 3 provinces". Philippine News Agency. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ "Republic Act No. 11259". Official Gazette (Philippines). 13 April 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019. (full text)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Magdayao, Aira Genesa (26 March 2020). "Postponement of Palawan division plebiscite sought". Palawan News Online. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Palawan residents vote 'No' to division of province into three".
- ^ Jump up to: a b "'No' votes win in Palawan plebiscite".
- ^ "Palawan rejects dividing province into three".
- ^ Piper, P. J.; Ochoa, J.; Lewis, H.; Paz, V.; Ronquillo, W. P. (2008). "The first evidence for the past presence of the tiger Panthera tigris (L.) on the island of Palawan, Philippines: extinction in an island population". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 264 (1–2): 123–127. Bibcode:2008PPP...264..123P. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.04.003.
- ^ Van der Geer, A.; Lyras, G.; De Vos, J.; Dermitzakis, M. (2011). "15 (The Philippines); 26 (Carnivores)". Evolution of Island Mammals: Adaptation and Extinction of Placental Mammals on Islands. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 220–347. ISBN 9781444391282.
- ^ Ochoa, J.; Piper, P. J. (2017). "Tiger". In Monks, G. (ed.). Climate Change and Human Responses: A Zooarchaeological Perspective. Springer. pp. 79–80. ISBN 978-9-4024-1106-5.
- ^ Von den Driesch, A. (1976). "A Guide to the Measurement of Animal Bones from Archaeological Sites". Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University.
- ^ Piper, Philip J.; Ochoa, Janine; Robles, Emil C.; Lewis, Helen; Paz, Victor (15 March 2011). "Palaeozoology of Palawan Island, Philippines". Quaternary International. Elsevier. 233 (2): 142–158. Bibcode:2011QuInt.233..142P. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2010.07.009.
- ^ Larson, G.; Dobney, K.; Albarella, U.; Fang, M.; Matisso-Smith, E.; Robins, J.; Lowden, S.; Finlayson, H.; Brand, T.; Willersley, E.; Rowley-Conwy, P.; Andersson, L.; Cooper, A. (2005). "Worldwide Phylogeography of wild boar reveals multiple centers of pig domestication". Science. 307 (5715): 1618–1621. Bibcode:2005Sci...307.1618L. doi:10.1126/science.1106927. PMID 15761152. S2CID 39923483.
- ^ Larson, G.; Cucchi, T.; Fujita, M.; Matisoo-Smith, E.; Robins, J.; Anderson, A.; Rolett, B.; Spriggs, M.; Dolman, G.; Kim, T.-H.; Thi, N.; Thuy, D.; Randi, E.; Doehrty, M.; Due, R. A.; Bolt, R.; Griffin, B.; Morwood, M.; Piper, P.; Bergh, G.v.d.; Dobney, K. (2007). "Phylogeny and ancient DNA of Sus provides insight into Neolithic expansion in Island Southeast Asia and Oceania". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (12): 4834–4839. Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.4834L. doi:10.1073/pnas.0607753104. PMC 1829225. PMID 17360400.
- ^ Dobney, K.; Cucchi, T.; Larson, G. (2008). "The pigs of Island Southeast Asia and the Pacific: new evidence for taxonomic status and human-mediated dispersal" (PDF). Asian Perspectives. 47 (1): 59–74. doi:10.1353/asi.2008.0009. JSTOR 42928732. S2CID 55390219.
- ^ Cucchi, T.; Fujita, M.; Dobney, K. (2009). "New insights into pig taxonomy, domestication and human dispersal in Island Southeast Asia: molar shape analysis of Sus remains from Niah Caves, Sarawak". International Journal of Osteoarchaeology. 19 (4): 508–530. doi:10.1002/oa.974.
- ^ Piper, P. J.; Hung, H.-C.; Campos, F. Z.; Bellwood, P.; Santiago, R. (2009). "A 4,000 year old introduction of domestic pigs into the Philippine archipelago: implications for understanding routes of human migration into through Island Southeast Asia and Wallacea". Antiquity. 83: 687–695. doi:10.1017/S0003598X00098914. S2CID 161296257.
- ^ Tsang, Cheng-hwa (2000), "Recent advances in the Iron Age archaeology of Taiwan", Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association, 20: 153–158, doi:10.7152/bippa.v20i0.11751
- ^ Turton, M. (2021). Notes from central Taiwan: Our brother to the south. Taiwan’s relations with the Philippines date back millenia, so it’s a mystery that it’s not the jewel in the crown of the New Southbound Policy. Taiwan Times.
- ^ Everington, K. (2017). Birthplace of Austronesians is Taiwan, capital was Taitung: Scholar. Taiwan News.
- ^ Bellwood, P., H. Hung, H., Lizuka, Y. (2011). Taiwan Jade in the Philippines: 3,000 Years of Trade and Long-distance Interaction. Semantic Scholar.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "History of Palawan". Palawan Tourism Council. Archived from the original on 31 July 2008. Retrieved 27 August 2008.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- ^ "People and Culture". Puerto Princesa: The Official Website of the City Government. City Management Information System Division, Puerto Princesa City. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ Pigafetta, Antonio (1906). "Primo Viaggio Intorno Al Mondo". In Emma Helen Blair; James Alexander Robertson (eds.). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1898, Volume XXXIII, 1519–1522. Arthur H. Clark Company.
- ^ Moore, Stephen (2016). As Good As Dead: The Daring Escape of American POWs From A Japanese Death Camp. New York: Caliber. pp. 61–62, 115–116, 123–128, 144, 260–261, 335. ISBN 9780399583551.
- ^ Gevinson, Alan. "American POWs in Japanese Captivity." Teachinghistory.org, accessed 10 September 2011.
- ^ Wilbanks, Bob (2004). Last Man Out. Jefferson: McFarland & Company, Inc., Publishers. pp. 154–156. ISBN 9780786418220.
- ^ "Executive Order No. 429, s. 2005". Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines. 23 May 2005. Archived from the original on 4 April 2018. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- ^ Felipe, Cecille Suerte (4 June 2005). "Palawan now with Region 6". The Philippine Star. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- ^ Espina, Rolly (9 August 2005). "Palawan transfer to Region VI may never materialize". The Philippine Star. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rosario, Ben (25 October 2018). "Move to divide Palawan into 3 provinces assailed". Manila Bulletin News. Archived from the original on 25 October 2018. Retrieved 12 May 2019.
- ^ Mendoza, Victoria (14 April 2019). "PRRD signs law that divides Palawan". Philippine Information Agency. Archived from the original on 12 May 2019. Retrieved 12 May 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Salaverria, Leila B. (14 April 2019). "Plebiscite on splitting Palawan into 3 provinces set for 2020". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on 16 April 2019. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Paghahati ng Palawan sa 3 probinsiya batas na | Pilipino Star Ngayon". philstar.com. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- ^ "Dividing Palawan: Residents look to challenge Palawan split into 3 provinces". ABS-CBN News. 15 April 2019. Archived from the original on 15 April 2019. Retrieved 12 May 2019.
- ^ Colcol, Erwin (16 April 2019). "Splitting Palawan into 3 won't solve poverty in the province —group". GMA News Online. Archived from the original on 18 April 2019. Retrieved 12 May 2019.
- ^ "Palawan congressmen want province split into 3". Philippine Daily Inquirer. 2 April 2018. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Province: Palawan". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ Chandran, Rina (8 October 2018). "Philippine resort city chooses 'morally correct' low-carbon path". Reuters. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ "Editorial - Palawan stays as one". Philstar. 19 March 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ Anda, Redempto D. (1 December 2014). "Puerto prone to climate disaster–WWF". Inquirer. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ "Business Risk Assessment and the Management of Climate Change Impacts" (PDF). World Wildlife Fund for Nature. 2014.
- ^ Salaverria, Leila B. (14 April 2019). "Plebiscite on splitting Palawan into 3 provinces set for 2020". newsinfo.inquirer.net.
- ^ "Paghahati ng Palawan sa 3 probinsiya batas na - Pilipino Star Ngayon". philstar.com.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Census of Population (2015). Highlights of the Philippine Population 2015 Census of Population. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Census of Population and Housing (2010). Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities (PDF). NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ "Philippines 'rejects' Muslim self-rule". BBC. 15 August 2001. Retrieved 15 August 2008.
- ^ President of the Philippines (17 May 2002). "Executive Order No. 103". ncsb.gov.ph. Archived from the original on 29 May 2009. Retrieved 15 August 2008.
- ^ Philippine 2010 Election Results: Region IV-B, Philippine Commission on Elections.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region IV-B (Mimaropa)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ "Fact Sheet; Region IV-B; MIMAROPA' 2007 Census of Population" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority - Region IV-B. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Apostolic Vicariate of Taytay, Philippines". GCatholic. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Apostolic Vicariate of Puerto Princesa, Philippines". GCatholic. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- ^ 2003 & 2013 Yearbook of Jehovah's Witnesses published by Watchtower Bible and Tract Society of New York, INC
- ^ 2000 Census of Population and Housing: Palawan (PDF). Demographics and Housing Characteristics. Vol.1, Report No. 2. National Statistics Office, Republic of the Philippines. 2003.
|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ Eder, James F. (2010). "Muslim Palawan Diversity and Difference on the Periphery of Philippine Islam". Philippine Studies. 58 (3): 407–420.
- ^ "Chùa Vạn Pháp Trại Tỵ Nạn Palawan Philippines Hình Chụp Tháng !2 Năn 2013". vanninh.com.
- ^ Calunsod, Ronron (6 June 2014). "Vietnamese village in Philippines lives on". ABS-CBN News. Retrieved 21 April 2021.
- ^ "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/NSCB_LocalPovertyPhilippines_0.pdf; publication date: 29 November 2005; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2009%20Poverty%20Statistics.pdf; publication date: 8 February 2011; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Updated%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%20with%20Measures%20of%20Precision%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province_2015%20and%202018.xlsx; publication date: 4 June 2020; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ Palawan Profile at Home.comcast.net Archived 2009-09-23 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed August 28, 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Puerto Princesa website: Quick facts Archived 2008-10-20 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed August 28, 2008.
- ^ "Visitor arrivals rise 21% in Palawan in 2018". Palawan News Online. 8 April 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2019.
- ^ What is Sundaland?, retrieved 11 June 2010
- ^ "Converging efforts for Palawan's biodiversity and its people". Peace and Equity Foundation. 11 November 2019. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ "Protecting old-growth forests in Palawan". Forest Foundation Philippines. 15 July 2015. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c The Official Website of the Province of Palawan: Environment, archived from the original on 10 May 2009, retrieved 28 August 2008
- ^ Dugong Page: Philippines, retrieved 11 June 2010
- ^ Local Causes, Global Effects, Community Centred Conservation (C3), archived from the original on 17 November 2011
- ^ "Destinations Rated: Islands".
- ^ "4th Annual Places Rated: 111 Islands" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 March 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Dela Cruz, Roderick T. "Lagen, Miniloc resorts win world's green vote". Manilastandardtoday.com. Archived from the original on 20 January 2008. Retrieved 15 July 2012.
- ^ "Proclamation No. 1578, s. 1976". Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines. Archived from the original on 16 February 2018. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
- ^ "African wildlife thrives in Palawan". The Manila Times. 4 January 2016. Archived from the original on 4 August 2018. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
- ^ "How a Patch of the Kenyan Wild Ended up in Philippines". Owaahh. 21 August 2014. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- ^ "Republic Act 7611". Palawan Council for Sustainable Development. Archived from the original on 7 September 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
- ^ "Palawan resorts cited for being eco-friendly". The Philippine Star. 10 February 2008. Archived from the original on 8 December 2019. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
- ^ Times, Victoria (17 January 2008). "The world's greenest hotels, from Switzerland to Sri Lanka". Canada.com. Retrieved 15 July 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Palawan Environment". Palawan Tourism Council. Archived from the original on 31 July 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2008.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- ^ Kaplan, Robert D. (2014). Asia's Cauldron: The South China Sea and the End of a Stable Pacific. Random House. p. 137. ISBN 978-0-8129-9432-2.
- ^ "Philippines turning Ulugan Bay, Palawan, from sleepy village to military base". South China Morning Post. 17 June 2017. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
As fears grow that China is on an aggressive South China Sea territorial grab, a sleepy Philippine village is being transformed into a major naval base that may host US warships. [...] A small pier stands at the bay’s most prized asset, a deep inlet called Oyster Bay with rich fishing grounds that help sustain the 1,700 residents of the nearby village of Macarascas. As part of the upgrade, a much bigger pier, harbor, and support facilities are being built to serve as a base for the navy’s largest vessels, including two ex-US frigates acquired since 2011.
- ^ U.S. Department of State "Philippines Travel Advisory". May 20, 2015. Accessed May 18, 2017.
- ^ U.S. Department of State "Philippines Travel Advisory". December 20, 2016. Accessed May 18, 2017.
- ^ Agaton, Casper Boongaling; Karl, Helmut (2018). "A real options approach to renewable electricity generation in the Philippines". Energy, Sustainability and Society. 8 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/s13705-017-0143-y. ISSN 2192-0567. S2CID 13167065.
- ^ "Status of Electrification". PALECO. 2020. Retrieved 24 October 2020.
- ^ "Best way to get to Palawan from Manila". thetravelbrief.com. Retrieved 5 October 2019.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Palawan (province). |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Palawan. |
- Palawan
- 1818 establishments in the Philippines
- Biosphere reserves of the Philippines
- Island provinces of the Philippines
- Japanese prisoner of war and internment camps
- Mimaropa
- Provinces of the Philippines
- South China Sea
- States and territories established in 1818
- Sulu Sea