Biodiversity loss

Biodiversity loss includes the extinction of species worldwide, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, depending on whether the environmental degradation that leads to the loss is reversible through ecological restoration/ecological resilience or effectively permanent (e.g. through land loss). Global extinction is being driven by human activities which overreach beyond the planetary boundaries as part of the Anthropocene and has so far been proven to be irreversible.
Even though permanent global species loss is a more dramatic and tragic phenomenon than regional changes in species composition, even minor changes from a healthy stable state can have dramatic influence on the food web and the food chain insofar as reductions in only one species can adversely affect the entire chain (coextinction), leading to an overall reduction in biodiversity, possible alternative stable states of an ecosystem notwithstanding. Ecological effects of biodiversity are usually counteracted by its loss. Reduced biodiversity in particular leads to reduced ecosystem services and eventually poses an immediate danger for food security, but also can have more lasting public health consequences for humans.[1]
International environmental organizations have been campaigning to prevent biodiversity loss for decades, public health officials have integrated it into the One Health approach to public health practice, and increasingly preservation of biodiversity is part of international policy. For example, the UN Convention on Biological Diversity is focused on preventing biodiversity loss and proactive conservation of wild areas. The international commitment and goals for this work is currently embodied by Sustainable Development Goal 15 "Life on Land" and Sustainable Development Goal 14 "Life Below Water". However, the United Nations Environment Programme report on "Making Peace with Nature" released in 2020 found that most of these efforts had failed to meet their international goals.[2]
Loss rate[]

You know, when we first set up WWF, our objective was to save endangered species from extinction. But we have failed completely; we haven’t managed to save a single one. If only we had put all that money into condoms, we might have done some good.
The current rate of global diversity loss is estimated to be 100 to 1000 times higher than the (naturally occurring) background extinction rate, faster than at any other time in human history,[4] and expected to still grow in the upcoming years.[5][6][7] These rapidly rising extinction trends impacting numerous animal groups including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and ray-finned fishes have prompted scientists to declare a contemporary biodiversity crisis.[8]
Locally bounded loss rates can be measured using species richness and its variation over time. Raw counts may not be as ecologically relevant as relative or absolute[clarification needed] abundances. Taking into account the relative frequencies, many biodiversity indexes have been developed. Besides richness, evenness and heterogeneity are considered to be the main dimensions along which diversity can be measured.[1]
As with all diversity measures, it is essential to accurately classify the spatial and temporal scope of the observation. "Definitions tend to become less precise as the complexity of the subject increases and the associated spatial and temporal scales widen."[9] Biodiversity itself is not a single concept but can be split up into various scales (e.g. ecosystem diversity vs. habitat diversity or even biodiversity vs. habitat diversity[9]) or different subcategories (e.g. phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, genetic diversity, nucleotide diversity). The question of net loss in confined regions is often a matter of debate but longer observation times are generally thought to be beneficial to loss estimates.[10][11]
To compare rates between different geographic regions, latitudinal gradients in species diversity should also be considered.
In 2006, many more species were formally classified as rare or endangered or threatened; moreover, scientists have estimated that millions more species are at risk which have not been formally recognized.
In 2021, about 28 percent of the 134,400 species assessed using the IUCN Red List criteria are now listed as threatened with extinction—a total of 37,400 species compared to 16,119 threatened species in 2006.[12]
Causes[]
Biodiversity is commonly defined as the variety of life on Earth in all its forms, including the diversity of species, their genetic variations, and the interaction of these lifeforms. However, since the late 20th century loss of biodiversity caused by human behavior has caused more severe and longer-lasting impacts.[13] Top scientists and the landmark IPBES Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services assert that human population growth and overconsumption are the primary factors in this decline.[14][15][16][17][18] Human drivers of biodiversity loss include habitat alteration, pollution, and overexploitation of resources.[19]
Change in land use[]

Examples of changes in land use include deforestation, intensive monoculture, and urbanization.[21]
The 2019 IPBES Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services asserts that industrial agriculture is the primary driver collapsing biodiversity.[22][14] The UN's Global Biodiversity Outlook 2014 estimates that 70 percent of the projected loss of terrestrial biodiversity are caused by agriculture use.[needs update] Moreover, more than 1/3 of the planet's land surface is utilised for crops and grazing of livestock.[23][Link to precise page] Agriculture destroys biodiversity by converting natural habitats to intensely managed systems and by releasing pollutants, including greenhouse gases. Food value chains further amplify impacts including through energy use, transport and waste.[24] The direct effects of urban growth on habitat loss are well understood: building construction often results in habitat destruction and fragmentation. The rise of urbanization greatly reduced biodiversity when large areas of natural habitat are fragmented.[citation needed] Small habitat patches are unable to support the same level of genetic or taxonomic diversity as they formerly could while some of the more sensitive species may become locally extinct.[25]
According to a 2020 study published in Nature Sustainability, more than 17,000 species are at risk of losing habitat by 2050 as agriculture continues to expand to meet future food needs. The researchers suggest that greater agricultural efficiency in the developing world and large scale transitions to healthier, Plant-based diets could help reduce habitat loss.[26] Similarly, a Chatham House report also posited that a global shift towards largely plant-based diets would free up land to allow for the restoration of ecosystems and biodiversity, because in the 2010s over 80% of all global farmland was used to rear animals.[27]
Pollution[]
Air pollution[]

Four greenhouse gases that are commonly studied and monitored are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. In the past 250 years, concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane have increased, along with the introduction of purely anthropogenic emissions such as hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride into the atmosphere.[28] These pollutants are emitted into the atmosphere by the burning of fossil fuels and biomass, deforestation, and agricultural practices which amplify the effects of climate change.[29][30] As larger concentrations of greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere, this causes the Earth's surface temperature to increase. This is because greenhouse gases are capable of absorbing, emitting, and trapping heat from the Sun and into the Earth's atmosphere.[28] With the increase in temperature expected from increasing greenhouse gases, there will be higher levels of air pollution, greater variability in weather patterns, intensification of climate change effects, and changes in the distribution of vegetation in the landscape.[19][31]
Other pollutants that are released from industrial and agricultural activity are sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.[28] Once sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide are introduced into the atmosphere, they can react with cloud droplets (cloud condensation nuclei), raindrops, or snowflakes, forming sulfuric acid and nitric acid. With the interaction between water droplets and sulfuric and nitric acids, wet deposition occurs and creates acid rain.[32][33] As a result, these acids would be displaced into various environments and vegetation during precipitation, having significant aerial distance (hundreds of kilometres) from the emission source. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide can also be displaced onto vegetations through dry deposition.[34]
Sulfur dioxide and nitrous oxide concentration has many implication on aquatic ecosystems, including acidity change, increased nitrogen and aluminum content, and altering biogeochemical processes.[34] Typically, sulfur dioxide and nitrous oxide do not have direct physiological effects upon exposure; most effects are developed by accumulation and prolonged exposure of these gases in the environment, modifying soil and water chemistry.[34][35] Consequently, sulfur largely contributes to lake and ocean acidification, and nitrogen initiates eutrophication of inland and coastal water bodies that lack nitrogen. Both of these phenomena alter the native aquatic biota composition and influence the original food web with higher acidity level, minimizing aquatic and marine biodiversity.[33][34]
Nitrogen deposition has also affected terrestrial ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, alpine regions, and bogs.[34] The influx of nitrogen has altered the natural biogeochemical cycle and promoted soil acidification.[36] As a result, it is likely that plant and animal species composition and ecosystem functionality will decline with increased soil sensitivity; contribute to slower forest growth, tree damage at higher elevations, and replacement of native biota with nitrogen-loving species.[13][34] Additionally, sulfate and nitrate can be leached from the soil, removing essential nutrients such as calcium and magnesium, and be deposited into freshwater, coastal, and oceanic environments, promoting eutrophication.[34]
Noise pollution[]
Noises generated by traffic, ships, vehicles, and aircraft can affect the survivability of wildlife species and can reach undisturbed habitats.[37] Although sounds are commonly present in the environment, anthropogenic noises are distinguishable due to differences in frequency and amplitude.[38] Many animals use sounds to communicate with others of their species, whether that is for reproduction purposes, navigation, or to notify others of prey or predators. However, anthropogenic noises inhibit species from detecting these sounds, affecting overall communication within the population.[38] Species such as birds, amphibians, reptiles, fishes, mammals, and invertebrates are examples of biological groups that are impacted by noise pollution.[37][39] If animals cannot communicate with one another, this would result in reproduction to decline (not able to find mates), and higher mortality (lack of communication for predator detection).[37]
Noise pollution is common in marine ecosystems, affecting at least 55 marine species.[40] For many marine populations, sound is their primary sense used for their survival; able to detect sound hundreds to thousands kilometers away from a source, while vision is limited to tens of meters underwater.[40] As anthropogenic noises continue to increase, doubling every decade, this compromises the survivability of marine species.[41] One study discovered that as seismic noises and naval sonar increases in marine ecosystems, cetacean, such as whales and dolphins, diversity decreases.[42] Noise pollution has also impaired fish hearing, killed and isolated whale populations, intensified stress response in marine species, and changed species’ physiology. Because marine species are sensitive to noise, most marine wildlife are located in undisturbed habitats or areas not exposed to significant anthropogenic noise, limiting suitable habitats to forage and mate. Whales have changed their migration route to avoid anthropogenic noise, as well as altering their calls.[43] Noise pollution also impacts human livelihood. Multiple studies have noticed that fewer fishes, such as cod, haddock, rockfish, herring, sand seal, and blue whiting, have been spotted in areas with seismic noises, with catch rates declining by 40–80%.[40][44][45][46]
Noise pollution has also altered avian communities and diversity. Anthropogenic noises have a similar effect on bird population as seen in marine ecosystems, where noises reduce reproductive success; cannot detect predators due to interferences of anthropogenic noises, minimize nesting areas, increase stress response, and species abundances and richness declining.[38][40] Certain avian species are more sensitive to noises compared to others, resulting in highly-sensitive birds migrating to less disturbed habitats. There has also been evidence of indirect positive effects of anthropogenic noises on avian populations. In a study conducted by Francis and his colleagues, nesting bird predators, such as the western scrub-jay (Aphelocoma californica), were uncommon in noisy environments (western scrub-jay are sensitive to noise). Therefore, reproductive success for nesting prey communities was higher due to the lack of predators.[38]
Invasive species[]
Invasive species have major implications on biodiversity loss and have degraded various ecosystems worldwide. Invasive species are migrant species that have outcompeted and displaced native species, altered species richness and food webs, and changed ecosystems’ functions and services.[47][48] According to the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, invasive species are considered one of the top five factors which result in biodiversity loss.[49] In the past half century, biological invasions have increased immensely worldwide due to economic globalization, resulting in biodiversity loss.[48] Ecosystems that are vulnerable to biological invasions include coastal areas, freshwater ecosystems, islands, and places with a Mediterranean climate. One study conducted a meta-analysis on the impacts of invasive species on Mediterranean-type ecosystems, and observed a significant loss in native species richness.[49] Invasive species are introduced to new habitat, either intentionally or unintentionally, by human activities. The most common methods for the introduction of aquatic invasive species are by ballast water, on the hulls of ships, and attached to equipment such as fishing nets.[50]
Furthermore, global warming has changed typical conditions in various environments, allowing greater migration and distribution of species dependent on warm climate.[51] This phenomenon could either result in greater biodiversity (new species being introduced to new environments), or reduce biodiversity (promotion of invasive species). A biological invasion is deemed successful if the invasive species can adapt and survive in the new environment, reproduce, disperse, and compete with native communities.[49] Some invasive species are known to have high dispersal rates and have major implications on a regional scale. For example, in 2010, muskrat, raccoon dog, thrips, and Chinese mitten crab were identified to have affected 20 to 50 regions in Europe.[49]
Invasive species can become financial burdens for many countries. Due to ecological degradation caused by invasive species, this can alter the functionality and reduce the services that ecosystems provide. Additional costs are also expected to control the spread of biological invasion, to mitigate further impacts, and to restore ecosystems. For example, the cost of damage caused by 79 invasive species between 1906 and 1991 in the United States has been estimated at about US$120 billion.[49] In China, invasive species have reduced the country's gross domestic product (GDP) by 1.36% per year.[52] Management of biological invasion can also be costly. In Australia, the expense to monitor, control, manage, and research invasive weed species was approximately AU$116.4 million per year, with costs only directed to central and local government.[49] In some situations, invasive species may have benefits, such as economic returns. For instance, invasive trees can be logged for commercial forestry. However, in most cases, the economic returns are far less than the cost caused by biological invasion.[47][49]
Not only have invasive species caused ecological damage and economical losses, but they can also affect human health. With the alteration in ecosystem functionality (due to homogenization of biota communities), invasive species have resulted in negative effects on human well-being, which includes reduced resource availability, unrestrained spread of human diseases, recreational and educational activities, and tourism.[48][49] With regard to human health, alien species have resulted in allergies and skin damage to arise. Other similar diseases that invasive species have caused include human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), monkey pox, and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS).[49]
Overexploitation[]
Fossil fuel[]
Due to human dependency and demands, fossil fuel remains the dominant energy source globally; in the United States and other countries, approximately 78% of energy production derive from fossil fuels.[19][53] Extraction, processing, and burning of fossil fuels indirectly impacts biodiversity loss by contributing to climate change, while directly causing habitat destruction and pollution.[19] At fossil fuel extraction sites, land conversion, habitat loss and degradation, contamination, and pollution impacts biodiversity beyond terrestrial ecosystems; it impacts freshwater, coastal, and marine environments. Once fossil fuels have been extracted, they are transported, processed, and refined, which also impacts biodiversity as infrastructure development requires removal of habitats, and further pollution is emitted into the environment.[19] For example, the construction of roads, well pads, pipelines, reserve pits, evaporation ponds, and power lines leads to habitat fragmentation and noise pollution.[53]
Fossil fuel exploitation tends to occur in areas with high species richness and abundances, usually located in coastal and terrestrial environments. In one study, Harfoot and his colleagues identified 181 possible "high-risk" areas for fossil fuel exploitation, which were areas that also supported high levels of biodiversity. Out of the 181 identified locations, 156 of these high-risk fields were not protected areas, indicating that further biodiversity could be lost with fossil fuel exploitation.[19] It is predicted that future exploration for fossil fuel will occur in areas with low species richness and rarity, such as the oceans and in the Arctic.[citation needed] However, this prediction does not apply to Western Asia, Asia-Pacific, Africa, South America, and the Caribbean, where fossil fuel and coal exploitation is expected to occur in areas with high species richness.[19][needs update] For example, the Western Amazon (located in Brazil) is known to have high biodiversity. However, this region is also threatened by exploitation due to the large quantity of oil and natural gas reservoirs.[54] Typically, areas with large fossil fuel reservoirs have a greater likelihood of being extracted (based on the country's priorities). This is of concern as tropical environments contain high levels of biodiversity, which will indirectly result in greater deforestation for agricultural purposes and financial gains (e.g., exporting timber).[54]
Overfishing[]

Human demands and consumption have resulted in overfishing, which leads to a loss in biodiversity with reduction to fish species richness and abundances.[55] In 2020, global fish abundances have reduced by 38% compare to fish population in 1970.[56] Reduction in global fish populations were first noticed during the 1990s. Currently, many commercial fishes have been overharvested; approximately 27% of exploited fish stocks in the United States are classified overfished.[57] In Tasmania, it was observed that over 50% of major fisheries species, such as the eastern gemfish, southern rock lobster, southern bulkefin tuna, jack mackerel, and trumpeter, have declined over the past 75 years due to overfishing.[58]
Fishery methods, such as bottom trawling, have caused habitat destruction, resulting spatial diversity and regional species richness to decline.[56] Some studies, including the 2019 Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services report, found that overfishing is the main driver of mass species extinction in the oceans.[59][60]
With overfishing acting as one of the largest threats to fish biodiversity, there are many methods of which fish are attained. Overfishing can be done through use of longline fishing and bottom trawling.[61] What these methods cause is an issue of bycatch. The problem with bycatch is that there is a lack of reportage done from what species have been caught, a lot of the time an unwanted target is caught they are reported as "mixed fish" or are not reported.[61] Unwanted species caught within bycatch tend to be released,but it's common that captured fish die while in captivity, or die after being released. With an overexploitation of species being removed from their ecosystem, the trophic level becomes interrupted which in turn disrupts the food web.
Climate change[]

Effect on plants[]

Plant and animal populations are interconnected. There are a number of examples in nature that display this dependency. Consider pollinator reliant plant species that display an observable sensitivity to pollinator activity.[71] A 2007 study looked into the relationship between plant diversity and phenology, experimentally determining that plant diversity influenced the broader community flowering time.[71] Flowering time is important piece in the pollination puzzle as it impacts the food supply for pollinators.[72] This in turn can play a major role in agricultural pursuits [72] and global food security.[73]
While plants are essential for human survival, they have not received the same attention as the subject of conservation efforts as animals.[74] It's estimated that a third of all land plant species are at risk of extinction and 94% have yet to be evaluated in terms of their conservation status.[74]
Effects on Aquatic Macroinvertebrates and Microbes[]
Many scientists have studied the effects of climate change on the community structures and behaviors of aquatic macroinvertebrates and microbes – which are the prominent foundation of nutrient cycling in aquatic systems.[75] These organisms are responsible for breaking down organic matter into essential carbon and nutrients that get cycled throughout the system and maintain health and production of the entire habitat. However, there have been numerous studies (through experimental warming) that have shown increases in microbial respiration of carbon out of the system, with a simultaneous decrease in leaf litter breakdown caused by temperature-sensitive macroinvertebrates.[76] As temperatures are expected to increase largely due to anthropogenic influence, the abundance, type, and efficiency of macroinvertebrate and microbial organisms in aquatic systems will likely be dramatically altered.
Other factors[]
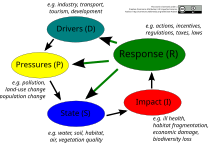
Major factors for biotic stress and the ensuing accelerating loss rate are, amongst other threats:[77]
- Habitat loss and degradation
- Climate change through heat stress and drought stress
- Excessive nutrient load and other forms of pollution
- Over-exploitation and unsustainable use (e.g. unsustainable fishing methods) we are currently using 25% more natural resources than the planet[clarification needed]
- Armed conflict, which disrupts human livelihoods and institutions, contributes to habitat loss, and intensifies over-exploitation of economically valuable species, leading to population declines and local extinctions.[79]
- Invasive alien species that effectively compete for a niche, replacing indigenous species[80]
- Drastic increases in the human population have greatly affected the Earth's ability to provide adequate resources for all forms of life. Recent IUCN Red List reports indicate that 41% of amphibians, 14% of birds, and 26% of mammal species are currently threatened with extinction.[81]
Types of loss[]
Terrestrial invertebrate loss[]
In 2017, various publications described the dramatic reduction in absolute insect biomass and number of species in Germany and North America over a period of 27 years.[82][83] As possible reasons for the decline, the authors highlight neonicotinoids and other agrochemicals. Writing in the journal PLOS One, Hallman et al. (2017) conclude that "the widespread insect biomass decline is alarming."[84]
For example, the critical decline of earthworms (over 80% on average) has been recorded under non-ecological agricultural practices.[85] Earthworms play an important role in ecosystem function.[85] For example, they help with biological processing in soil, water, and even green house gas balancing.[86] The decline of earthworm populations are said to be due to five reasons; soil degradation and destruction of habitat, climate change, biological invasion of nonnative species, poor soil management, and pollutant loading.[87] Factors like tillage practices and intensive land use decimate the soil and plant roots that earthworms use to create their biomass, causing carbon and nitrogen cycles to be impacted negatively. Knowledge of earthworm species diversity is quite limited as not even 50% of them have been described. More studies upon earthworms and how they provide their ecosystem services must be done to gain a better understanding of going about preserving their diversity.[87] With earthworm populations dwindling, this has caused for the Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity to take action and promote the restoration and maintenance of the many diverse species of earthworms.[87]
Birds loss[]
Certain types of pesticide, neonicotinoids, probably contribute to the decline of certain bird species.[88] A study funded by BirdLife International confirms that 51 species of birds are critically endangered and 8 could be classified as extinct or in danger of extinction. Nearly 30% of extinction is due to hunting and trapping for the exotic pet trade. Deforestation, caused by unsustainable logging and agriculture, could be the next extinction driver, because birds lose their habitat and their food. The biologist Luisa Arnedo said: "as soon as the habitat is gone, they're gone too".[89]
Within the Amazon rainforest there is an area called Bele´m and it is an area of endemism. In Bele´m 76% of the land has already been stripped of its natural resources, including the trees of the forest.[90] Within the area bird species are strongly affected by the deforestation, due to being put in that situation 56% of the birds are now in danger of going into extinction. With the climate changing as well as their habitat, the population of the birds will continue to decline. Even with protected areas of land, the efficiency in which birds are conserved are low.[90]
Freshwater species loss[]
Freshwater ecosystems ranging from swamps, deltas, to rivers make up to 1% of earths surface. Although making up such little proportion of the earth, freshwater ecosystems are important because these kind of habitats are home to approximately one third of vertebrate species.[91] Freshwater species are beginning to decline at twice the rate of other species such as those located on land or within the ocean, this rapid loss has already placed 27% of 29,500 species dependent on freshwater upon the IUCN Red List.[91] With freshwater species declining so quickly, it is due to the poor systems in place that don't provide any protection to their biodiversity.
A study by 16 global conservation organizations found that the biodiversity crisis is most acute in freshwater ecosystems, with a rate of decline double that of oceans and forests. Global populations of freshwater fish are collapsing from anthropogenic impacts such as pollution and overfishing. Migratory fish populations have declined by 76% since 1970, and large "megafish" populations have fallen by 94% with 16 species declared extinct in 2020.[92]
Native species richness loss[]
Humans have altered plant richness in regional landscapes worldwide, transforming more than 75% of the terrestrial biomes to "anthropogenic biomes." This is seen through loss of native species being replaced and out competed by agriculture. Models indicate that about half of the biosphere has seen a "substantial net anthropogenic change" in species richness.[93]
Marine species richness loss[]
Marine biodiversity encompasses any living organism which resides in the ocean, and describes various complex relationships within marine ecosystems.[57] On a local and regional scale, marine communities are better understood compared to marine ecosystems on a global scale. In 2018, it was estimated that approximately 240,000 marine species have been documented.[56] Based on this prediction, the discovery of total marine species ranges between 11% to 78% due to uncertainties regarding global marine biodiversity.[56] However, the number of described marine species remains low compared to terrestrial species due to various factors, which includes the assignment of different names for the same species, and insufficient taxa classification.[57] It is likely that many undocumented species has already disappeared. Because not all marine species have been described, it is difficult to provide an accurate estimate of global extinction in marine ecosystems. As a result, abundances of marine species remain uncertain, with estimates ranging between 178,000 to 10 million oceanic species.[57]
With anthropogenic pressure, this results in human activities having the strongest influences on marine biodiversity, with main drivers of global extinction being habitat loss, pollution, invasive species, and overexploitation.[94][95] Greater pressure is placed on marine ecosystems with human settlements near coastal areas.[96] Other indirect factors that have resulted in marine species to decline include climate change and change to oceanic biochemistry.[94]
Overexploitation has resulted in the extinction of over 20 described marine species, which includes seabirds, marine mammals, algae, and fishes.[57] Examples of extinct marine species include the Steller's sea cow (Hydrodamalis gigas) and the Caribbean monk seal (Monachus tropicalis). However, not all extinctions are because of humans. For example, in 1930, the eelgrass limpet (Lottia alveus) became extinct once the Zostera marina seagrass population declined upon exposure to a disease. The Lottia alveus were greatly impacted as the Zostera marina were their sole habitats.[57]
Impacts[]
Ecological effects of biodiversity loss[]
Biodiversity loss also threatens the structure and proper functioning of the ecosystem. Although all ecosystems are able to adapt to the stresses associated with reductions in biodiversity to some degree, biodiversity loss reduces an ecosystem's complexity, as roles once played by multiple interacting species or multiple interacting individuals are played by fewer or none.[31] The effects of species loss or changes in composition, and the mechanisms by which the effects manifest themselves, can differ among ecosystem properties, ecosystem types, and pathways of potential community change. At higher levels of extinction (40 to 60 percent of species), the effects of species loss ranked with those of many other major drivers of environmental change, such as ozone pollution, acid deposition on forests and nutrient pollution.[97] Finally, the effects are also seen on human needs such clean water, air and food production over-time. For example, studies over the last two decades[when?] have demonstrated that more biologically diverse ecosystems are more productive.[citation needed] As a result, there has been growing concern that the very high rates of modern extinctions – due to habitat loss, overharvesting and other human-caused environmental changes – could reduce nature's ability to provide goods and services like food, clean water and a stable climate.[98]
An October 2020 analysis by Swiss Re found that one-fifth of all countries are at risk of ecosystem collapse as the result of anthropogenic habitat destruction and increased wildlife loss.[99]
Impact on food and agriculture[]

In 2019, the UN's Food and Agriculture Organization produced its first report on The State of the World's Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture, which warned that "Many key components of biodiversity for food and agriculture at genetic, species and ecosystem levels are in decline."[100][101] The report states that this is being caused by "a variety of drivers operating at a range of levels" and more specifically that "major global trends such as changes in climate, international markets and demography give rise to more immediate drivers such as land-use change, pollution and overuse of external inputs, overharvesting and the proliferation of invasive species. Interactions between drivers often exacerbate their effects on biodiversity for food and agriculture (BFA). Demographic changes, urbanization, markets, trade and consumer preferences are reported [by the countries that provided inputs to the report] to have a strong influence on food systems, frequently with negative consequences for BFA and the ecosystem services it provides. However, such drivers are also reported to open opportunities to make food systems more sustainable, for example through the development of markets for biodiversity-friendly products."[102] It further states that "the driver mentioned by the highest number of countries as having negative effects on regulating and supporting ecosystem services [in food and agricultural production systems] is changes in land and water use and management" and that "loss and degradation of forest and aquatic ecosystems and, in many production systems, transition to intensive production of a reduced number of species, breeds and varieties, remain major drivers of loss of BFA and ecosystem services."[102]
The health of humans is largely dependent on the product of an ecosystem. With biodiversity loss, a huge impact on human health comes as well. Biodiversity makes it possible for humans to have a sustainable level of soils and the means to have the genetic factors to have food.[103]
Many activists and scholars have suggested that there is a connection between plant patent protection and the loss of crop biodiversity,[104] although such claims are contested.[105]
Human health[]

According to the biodiversity hypothesis, reduced contact of people with natural environment and biodiversity may adversely affect the human commensal microbiota and its immunomodulatory capacity. The hypothesis is based on the observation that two dominant socio-ecological trends – the loss of biodiversity and increasing incidence of inflammatory diseases – are interconnected.[106][107][108]
Urbanization and fragmentation of habitats increasingly lead to loss of connection between human and natural environment. Furthermore, immunological non-communicable diseases have become increasingly common in recent decades especially in urbanized communities.[109]Proposed solutions and economics[]
There are so many conservation challenges when dealing with biodiversity loss that a joint effort needs to be made through public policies, economic solutions, monitoring and education by governments, NGOs, conservationists etc.[110] Incentives are required to protect species and conserve their natural habitat and disincentivize habitat loss and degradation (e.g. implementing sustainable development including targets of SDG 15). Other ways to achieve this goal are enforcing laws that prevent poaching wildlife, protect species from overhunting and overfishing and keep the ecosystems they rely on intact and secure from species invasions and land use conversion.[111] Furthermore, conservation based models like the Global Safety Net are continuously being developed to consider the ecological connections that need to be addressed to effectively mitigate biodiversity loss.[112] According to the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) action to protect biodiversity is very cost effective because it reduces the risk of pandemics due to pathogens from wildlife.[113]
Conservationists and sustainable research scientists around the world have also developed systems-based approaches to help mitigate biodiversity loss. This methodology allows scientists to create contextual frameworks that consider the many nuances and linkages of environmental conservation like ecological footprints, planetary boundaries, ecological economics, etc.[114] Considering all the many ways in which the natural and human world intersect can help researchers understand the intricacies that lead to biodiversity loss and find patterns that can be applied to similar situations. One example of these type of frameworks is the triple bottom line, which has been adopted by many businesses and organizations to evaluate their impact and progress towards the marriage of social, environmental, and economic success.
International action[]

There are many organizations devoted to the cause of prioritizing conservation efforts such as the Red List of Threatened Species from the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) and the United States Endangered Species Act. British environmental scientist Norman Myers and his colleagues have identified 25 terrestrial biodiversity hotspots that could serve as priorities for habitat protection.[115]
Many governments in the world have conserved portions of their territories under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), a multilateral treaty signed in 1992–3. The 20 Aichi Biodiversity Targets, part of the CBD's Strategic Plan 2011–2020, were published in 2010.[116] Since 2010, approximately 164 countries have developed plans to reach their conservation targets, including the protection of 17 percent of terrestrial and inland waters and 10 percent of coastal and marine areas.[citation needed]
In 2019 the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), an international organization formed to serve a similar role to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC),[117] published the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services which said that up to a million plant and animal species are facing extinction because of human activities.[111][14] An October 2020 report by IPBES stated that the same human activities which are the underlying drivers of climate change and biodiversity loss, such as the destruction of wildlife and wild habitats, are also the same drivers of pandemics, including the COVID-19 pandemic.[118]
According to the 2020 United Nations' Global Biodiversity Outlook report, of the 20 biodiversity goals laid out by the Aichi Biodiversity Targets in 2010, only 6 were "partially achieved" by the deadline of 2020.[119] The report highlighted that if the status quo is not changed, biodiversity will continue to decline due to "currently unsustainable patterns of production and consumption, population growth and technological developments".[120] The report also singled out Australia, Brazil and Cameroon and the Galapagos Islands (Ecuador) for having had one of its animals lost to extinction in the past 10 years.[121] Following this, the leaders of 64 nations and the European Union pledged to halt environmental degradation and restore the natural world. Leaders from some of the world's biggest polluters, namely China, India, Russia, Brazil and the United States, were not among them.[122] Some experts contend that the refusal of the United States to ratify the Convention on Biological Diversity is harming global efforts to halt the extinction crisis.[123] Top scientists say that even if the 2010 targets had been met, it likely would not have resulted in any substantive reductions of current extinction rates.[16][17] Others have raised concerns that the Convention on Biological Diversity does not go far enough, and argue the goal should be zero extinctions by 2050, along with cutting the impact of unsustainable food production on nature by half. That the targets are not legally binding has also been subject to criticism.[124]
In 2020, with passing of the 2020 target date for the Aichi Biodiversity Targets, scientists proposed a measurable, near-term biodiversity target – comparable to the below 2 °C global warming target – of keeping described species extinctions to well below 20 per year over the next 100 years across all major groups (fungi, plants, invertebrates, and vertebrates) and across all ecosystem types (marine, freshwater, and terrestrial).[125]
A 2021 collaborative report by scientists from the IPBES and the IPCC says that biodiversity loss and climate change must be addressed simultaneously, as they are inexorably linked and have similar effects on human well being. Pamela McElwee, ecologist and co-author of the report, says "climate has simply gotten more attention because people are increasingly feeling it in their own lives – whether it's wildfires or hurricane risk. Our report points out that biodiversity loss has that similar effect on human wellbeing."[126]
See also[]
- 2020s in environmental history
- Biodiversity
- Global biodiversity
- Measurement of biodiversity
- Biodiversity offsetting
- Dark diversity
- Diversity and Distributions
- Defaunation
- Eco-costs
- Ecological extinction
- Extinction: The Facts (2020 documentary)
- Human overpopulation
- Mass extinction
- Holocene extinction
- No net loss
- Resource depletion
- Species reintroduction
- Ecological collapse
- The Sixth Extinction: An Unnatural History (2014 book)
- World Scientists' Warning to Humanity
Sources[]
![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0 License statement/permission on Wikimedia Commons. Text taken from The State of the World's Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture − In Brief, FAO, FAO.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0 License statement/permission on Wikimedia Commons. Text taken from The State of the World's Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture − In Brief, FAO, FAO.
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Cardinale BJ, Duffy JE, Gonzalez A, Hooper DU, Perrings C, Venail P, et al. (June 2012). "Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity" (PDF). Nature. 486 (7401): 59–67. Bibcode:2012Natur.486...59C. doi:10.1038/nature11148. PMID 22678280. S2CID 4333166.
...at the first Earth Summit, the vast majority of the world’s nations declared that human actions were dismantling the Earth’s ecosystems, eliminating genes, species and biological traits at an alarming rate. This observation led to the question of how such loss of biological diversity will alter the functioning of ecosystems and their ability to provide society with the goods and services needed to prosper.
- ^ United Nations Environment Programme (2021). Making Peace with Nature: A scientific blueprint to tackle the climate, biodiversity and pollution emergencies. Nairobi: United Nations.
- ^ Short R (13 May 2010). "A plague of people". Cosmos. Archived from the original on 6 November 2016.
- ^ Carrington D (February 2, 2021). "Economics of biodiversity review: what are the recommendations?". The Guardian. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ Ceballos G, Ehrlich PR, Barnosky AD, García A, Pringle RM, Palmer TM (June 2015). "Accelerated modern human-induced species losses: Entering the sixth mass extinction". Science Advances. 1 (5): e1400253. Bibcode:2015SciA....1E0253C. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1400253. PMC 4640606. PMID 26601195.
- ^ De Vos JM, Joppa LN, Gittleman JL, Stephens PR, Pimm SL (April 2015). "Estimating the normal background rate of species extinction" (PDF). Conservation Biology. 29 (2): 452–62. doi:10.1111/cobi.12380. PMID 25159086.
- ^ Ceballos G, Ehrlich PR, Raven PH (June 2020). "Vertebrates on the brink as indicators of biological annihilation and the sixth mass extinction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (24): 13596–13602. Bibcode:2020PNAS..11713596C. doi:10.1073/pnas.1922686117. PMC 7306750. PMID 32482862.
- ^ Andermann T, Faurby S, Turvey ST, Antonelli A, Silvestro D (September 2020). "The past and future human impact on mammalian diversity". Science Advances. 6 (36): eabb2313. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.2313A. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abb2313. PMC 7473673. PMID 32917612.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tagliapietra D, Sigovini M (2010). "Biological diversity and habitat diversity: a matter of Science and perception". Terre et Environnement (PDF). 88. pp. 147–155. ISBN 978-2-940153-87-9. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 2, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2019.
- ^ Gonzalez A, Cardinale BJ, Allington GR, Byrnes J, Arthur Endsley K, Brown DG, et al. (August 2016). "Estimating local biodiversity change: a critique of papers claiming no net loss of local diversity". Ecology. 97 (8): 1949–1960. doi:10.1890/15-1759.1. PMID 27859190. S2CID 5920426.
two recent data meta-analyses have found that species richness is decreasing in some locations and is increasing in others. When these trends are combined, these papers argued there has been no net change in species richness, and suggested this pattern is globally representative of biodiversity change at local scales
- ^ Cardinale B (June 2014). "Overlooked local biodiversity loss". Science. 344 (6188): 1098. doi:10.1126/science.344.6188.1098-a. PMID 24904146.
- ^ "The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved April 30, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Biodiversity loss (Encyc. Brit.)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Stokstad E (May 5, 2019). "Landmark analysis documents the alarming global decline of nature". Science. AAAS. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
For the first time at a global scale, the report has ranked the causes of damage. Topping the list, changes in land use—principally agriculture—that have destroyed habitat. Second, hunting and other kinds of exploitation. These are followed by climate change, pollution, and invasive species, which are being spread by trade and other activities. Climate change will likely overtake the other threats in the next decades, the authors note. Driving these threats are the growing human population, which has doubled since 1970 to 7.6 billion, and consumption. (Per capita of use of materials is up 15% over the past 5 decades.)
- ^ Pimm, S. L.; Jenkins, C. N.; Abell, R.; Brooks, T. M.; Gittleman, J. L.; Joppa, L. N.; Raven, P. H.; Roberts, C. M.; Sexton, J. O. (May 30, 2014). "The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection" (PDF). Science. 344 (6187): 1246752. doi:10.1126/science.1246752. PMID 24876501. S2CID 206552746.
The overarching driver of species extinction is human population growth and increasing per capita consumption.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Weston P (January 13, 2021). "Top scientists warn of 'ghastly future of mass extinction' and climate disruption". The Guardian. Retrieved January 19, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bradshaw CJ, Ehrlich PR, Beattie A, Ceballos G, Crist E, Diamond J, et al. (2021). "Underestimating the Challenges of Avoiding a Ghastly Future". Frontiers in Conservation Science. 1. doi:10.3389/fcosc.2020.615419.
- ^ Crist, Eileen; Cafaro, Philip, eds. (2012). Life on the Brink: Environmentalists Confront Overpopulation. University of Georgia Press. p. 83. ISBN 978-0820343853.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Harfoot MB, Tittensor DP, Knight S, Arnell AP, Blyth S, Brooks S, et al. (2018). "Present and future biodiversity risks from fossil fuel exploitation". Conservation Letters. 11 (4): e12448. doi:10.1111/conl.12448. ISSN 1755-263X.
- ^ Grantham HS, Duncan A, Evans TD, Jones KR, Beyer HL, Schuster R, et al. (December 2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ Oliver TH, Morecroft MD (2014). "Interactions between climate change and land use change on biodiversity: attribution problems, risks, and opportunities". WIREs Climate Change. 5 (3): 317–335. doi:10.1002/wcc.271. ISSN 1757-7799.
- ^ Vidal J (March 15, 2019). "The Rapid Decline Of The Natural World Is A Crisis Even Bigger Than Climate Change". The Huffington Post. Retrieved March 16, 2019.
- ^ "4. What factors lead to biodiversity loss?". www.greenfacts.org. Retrieved March 27, 2021.
- ^ "Causes and Consequences of Biodiversity Declines | Learn Science at Scitable". www.nature.com. Retrieved March 27, 2021.
- ^ Tomimatsu H, Ohara M (2003). "Genetic diversity and local population structure of fragmented populations of Trillium camschatcense (Trilliaceae)". Biological Conservation. 109 (2): 249–258. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(02)00153-2. ISSN 0006-3207.
- ^ Dunne D (December 22, 2020). "More than 17,000 species worldwide to lose part of habitat if agriculture continues to expand". The Independent. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ Carrington D (February 3, 2021). "Plant-based diets crucial to saving global wildlife, says report". The Guardian. Retrieved February 6, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Sabljic A (2009). Environmental and Ecological Chemistry – Volume I. EOLSS Publications. ISBN 978-1-84826-186-0.
- ^ Dudley N, Alexander S (2017). "Agriculture and biodiversity: a review". Biodiversity. 18 (2–3): 45–49. doi:10.1080/14888386.2017.1351892. ISSN 1488-8386. S2CID 134350972.
- ^ Rosa EA, Dietz T (2012). "Human drivers of national greenhouse-gas emissions". Nature Climate Change. 2 (8): 581–586. Bibcode:2012NatCC...2..581R. doi:10.1038/nclimate1506. ISSN 1758-6798.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Backhaus T, Snape J, Lazorchak J (October 2012). "The impact of chemical pollution on biodiversity and ecosystem services: the need for an improved understanding". Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management. 8 (4): 575–6. doi:10.1002/ieam.1353. PMID 22987515.
- ^ Singh A, Agrawal M (January 2008). "Acid rain and its ecological consequences". Journal of Environmental Biology. 29 (1): 15–24. PMID 18831326.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Payne RJ, Dise NB, Field CD, Dore AJ, Caporn SJ, Stevens CJ (2017). "Nitrogen deposition and plant biodiversity: past, present, and future". Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. 15 (8): 431–436. doi:10.1002/fee.1528. ISSN 1540-9309.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Lovett GM, Tear TH, Evers DC, Findlay SE, Cosby BJ, Dunscomb JK, et al. (April 2009). "Effects of air pollution on ecosystems and biological diversity in the eastern United States". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1162 (1): 99–135. Bibcode:2009NYASA1162...99L. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04153.x. PMID 19432647. S2CID 9368346.
- ^ Nowlan CR, Martin RV, Philip S, Lamsal LN, Krotkov NA, Marais EA, et al. (2014). "Global dry deposition of nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide inferred from space-based measurements". Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 28 (10): 1025–1043. Bibcode:2014GBioC..28.1025N. doi:10.1002/2014GB004805. ISSN 1944-9224.
- ^ Jandl R, Smidt S, Mutsch F, Fürst A, Zechmeister H, Bauer H, Dirnböck T (2012). "Acidification and Nitrogen Eutrophication of Austrian Forest Soils". Applied and Environmental Soil Science. 2012: 632602. doi:10.1155/2012/632602.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Sordello R, De Lachapelle FF, Livoreil B, Vanpeene S (2019). "Evidence of the environmental impact of noise pollution on biodiversity: a systematic map protocol". Environmental Evidence. 8 (1): 8. doi:10.1186/s13750-019-0146-6. ISSN 2047-2382.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Francis CD, Ortega CP, Cruz A (August 2009). "Noise pollution changes avian communities and species interactions". Current Biology. 19 (16): 1415–9. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.052. PMID 19631542. S2CID 15985432.
- ^ Kunc HP, Schmidt R (November 2019). "The effects of anthropogenic noise on animals: a meta-analysis". Biology Letters. 15 (11): 20190649. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2019.0649. PMC 6892517. PMID 31744413.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Weilgart LS (2008). "The Impact of Ocean Noise Pollution on Marine Biodiversity". www.semanticscholar.org. S2CID 13176067. Retrieved February 21, 2021.
- ^ Jovicic ST, Saric ZM, Turajlic SR (2005). "Application of the maximum signal to interference ratio criterion to the adaptive microphone array". Acoustics Research Letters Online. 6 (4): 232–237. doi:10.1121/1.1989785.
- ^ Fernández A, Edwards JF, Rodríguez F, Espinosa de los Monteros A, Herráez P, Castro P, et al. (July 2005). ""Gas and fat embolic syndrome" involving a mass stranding of beaked whales (family Ziphiidae) exposed to anthropogenic sonar signals". Veterinary Pathology. 42 (4): 446–57. doi:10.1354/vp.42-4-446. PMID 16006604. S2CID 43571676.
- ^ Richardson WJ (1995). Marine Mammals and Noise. San Diego: Academic Press.
- ^ Engås A, Løkkeborg S, Ona E, Soldal AV (2011). "Effects of seismic shooting on local abundance and catch rates of cod ((Gadus morhua) and haddock )(Melanogrammus aeglefinus)". Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. 53 (10): 2238–2249. doi:10.1139/f96-177. hdl:11250/108647.
- ^ Skalski JR, Pearson WH, Malme CI (2011). "Effects of Sounds from a Geophysical Survey Device on Catch-per-Unit-Effort in a Hook-and-Line Fishery for Rockfish (Sebastes spp.)". Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. 49 (7): 1357–1365. doi:10.1139/f92-151.
- ^ Slotte A, Hansen K, Dalen J, Ona E (2004). "Acoustic mapping of pelagic fish distribution and abundance in relation to a seismic shooting area off the Norwegian west coast". Fisheries Research. 67 (2): 143–150. doi:10.1016/j.fishres.2003.09.046. ISSN 0165-7836.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Molnar JL, Gamboa RL, Revenga C, Spalding MD (2008). "Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity". Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. 6 (9): 485–492. doi:10.1890/070064. ISSN 1540-9309.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Mazza G, Tricarico E, Genovesi P, Gherardi F (2014). "Biological invaders are threats to human health: an overview". Ethology Ecology & Evolution. 26 (2–3): 112–129. doi:10.1080/03949370.2013.863225. ISSN 0394-9370. S2CID 58888740.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Pyšek P, Richardson DM (2010). "Invasive Species, Environmental Change and Management, and Health". Annual Review of Environment and Resources. 35 (1): 25–55. doi:10.1146/annurev-environ-033009-095548. ISSN 1543-5938.
- ^ US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. "What is an invasive species?". oceanservice.noaa.gov.
- ^ Bellard C, Bertelsmeier C, Leadley P, Thuiller W, Courchamp F (April 2012). "Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity". Ecology Letters. 15 (4): 365–377. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01736.x. PMC 3880584. PMID 22257223.
- ^ Xu H, Ding H, Li M, Qiang S, Guo J, Han Z, Huang Z, Sun H, He S, Wu H, Wan F (2006). "The distribution and economic losses of alien species invasion to China". Biological Invasions. 8 (7): 1495–1500. doi:10.1007/s10530-005-5841-2. ISSN 1573-1464. S2CID 25890246.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jones NF, Pejchar L, Kiesecker JM (2015). "The Energy Footprint: How Oil, Natural Gas, and Wind Energy Affect Land for Biodiversity and the Flow of Ecosystem Services". BioScience. 65 (3): 290–301. doi:10.1093/BIOSCI/BIU224. S2CID 84259714.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Butt N, Beyer HL, Bennett JR, Biggs D, Maggini R, Mills M, et al. (October 2013). "Conservation. Biodiversity risks from fossil fuel extraction" (PDF). Science. 342 (6157): 425–6. Bibcode:2013Sci...342..425B. doi:10.1126/science.1237261. JSTOR 42619941. PMID 24159031. S2CID 206548697.
- ^ Rafferty RP (June 14, 2019). "Biodiversity loss". Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Luypaert T, Hagan JG, McCarthy ML, Poti M (2020). "Status of Marine Biodiversity in the Anthropocene". In Jungblut S, Liebich V, Bode-Dalby M (eds.). YOUMARES 9 – The Oceans: Our Research, Our Future: Proceedings of the 2018 conference for YOUng MArine RESearcher in Oldenburg, Germany. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 57–82. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-20389-4_4. ISBN 978-3-030-20389-4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Sala E, Knowlton N (2006). "Global Marine Biodiversity Trends". Annual Review of Environment and Resources. 31 (1): 93–122. doi:10.1146/annurev.energy.31.020105.100235. ISSN 1543-5938.
- ^ Edgar GJ, Samson CR, Barrett NS (2005). "Species Extinction in the Marine Environment: Tasmania as a Regional Example of Overlooked Losses in Biodiversity". Conservation Biology. 19 (4): 1294–1300. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1739.2005.00159.x. ISSN 1523-1739.
- ^ Pacoureau N, Rigby CL, Kyne PM, Sherley RB, Winker H, Carlson JK, et al. (January 2021). "Half a century of global decline in oceanic sharks and rays". Nature. 589 (7843): 567–571. Bibcode:2021Natur.589..567P. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-03173-9. PMID 33505035. S2CID 231723355.
- ^ Borenstein S (May 6, 2019). "UN report: Humans accelerating extinction of other species". AP News. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jones AA, Hall NG, Potter IC (2010). "Species compositions of elasmobranchs caught by three different commercial fishing methods off southwestern Australia, and biological data for four abundant bycatch species" (PDF). Fishery Bulletin. 108 (4): 365–381. ISSN 0090-0656.
- ^ "IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse gas fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems:Summary for Policymakers" (PDF).
- ^ "Summary for Policymakers — Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate". Retrieved December 23, 2019.
- ^ IPCC, Synthesis Report Summary for Policymakers, Section 3: Projected climate change and its impacts, in IPCC AR4 SYR 2007
- ^ Mammola, Stefano; Goodacre, Sara L.; Isaia, Marco (January 2018). "Climate change may drive cave spiders to extinction". Ecography. 41 (1): 233–243. doi:10.1111/ecog.02902. hdl:2318/1623725. S2CID 55362100.
- ^ Sahney, S., Benton, M.J. & Falcon-Lang, H.J. (2010). "Rainforest collapse triggered Pennsylvanian tetrapod diversification in Euramerica". Geology. 38 (12): 1079–1082. doi:10.1130/G31182.1.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Dadamouny, M.A.; Schnittler, M. (2015). "Trends of climate with rapid change in Sinai, Egypt". Journal of Water and Climate Change. 7 (2): jwc2015215. doi:10.2166/wcc.2015.215.
- ^ Sala OE, Chapin FS, Armesto JJ, et al. (March 2000). "Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100". Science. 287 (5459): 1770–4. doi:10.1126/science.287.5459.1770. PMID 10710299.
- ^ Duraiappah, Anantha K.; World Resources Institute (2006). Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Ecosystems And Human-well Being—biodiversity Synthesis. Washington, D.C: World Resources Institute. ISBN 978-1-56973-588-6.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Chapin III, F. Stuart; Zavaleta, Erika S.; Eviner, Valerie T.; Naylor, Rosamond L.; Vitousek, Peter M.; Reynolds, Heather L.; Hooper, David U.; Lavorel, Sandra; Sala, Osvaldo E. (May 2000). "Consequences of changing biodiversity". Nature. 405 (6783): 234–242. doi:10.1038/35012241. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 10821284. S2CID 205006508.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Benson E (2002). "Thinking Clinically. A New Study Shows How Clinicians' Theories Could Affect Their Diagnoses". APA Monitor on Psychology. 33 (11): 30. doi:10.1037/e300122003-026.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The hunger gaps: How flowering times affect farmland bees: Seasonal gaps in the supply of nectar from wildflowers could be leaving bees hungry at times when food is needed most". ScienceDaily. Retrieved March 29, 2021.
- ^ "Leading soil scientist warns of threat to food security". ECOS. 2012. doi:10.1071/ec12488.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Corlett RT (February 2016). "Plant diversity in a changing world: Status, trends, and conservation needs". Plant Diversity. 38 (1): 10–16. doi:10.1016/j.pld.2016.01.001. PMC 6112092. PMID 30159445.
- ^ Burgmer T, Hillebrand H, Pfenninger M (February 2007). "Effects of climate-driven temperature changes on the diversity of freshwater macroinvertebrates". Oecologia. 151 (1): 93–103. Bibcode:2007Oecol.151...93B. doi:10.1007/s00442-006-0542-9. PMID 16964502. S2CID 9261831.
- ^ Ferreira V, Chauvet E, Canhoto C (2015). "Effects of experimental warming, litter species, and presence of macroinvertebrates on litter decomposition and associated decomposers in a temperate mountain stream" (PDF). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. 72 (2): 206–16. doi:10.1139/cjfas-2014-0119.
- ^ "Global Biodiversity Outlook 3". Convention on Biological Diversity. 2010.
- ^ Allan E, Manning P, Alt F, Binkenstein J, Blaser S, Blüthgen N, et al. (August 2015). "Land use intensification alters ecosystem multifunctionality via loss of biodiversity and changes to functional composition". Ecology Letters. 18 (8): 834–843. doi:10.1111/ele.12469. PMC 4744976. PMID 26096863.
- ^ Daskin JH, Pringle RM (January 2018). "Warfare and wildlife declines in Africa's protected areas". Nature. 553 (7688): 328–332. Bibcode:2018Natur.553..328D. doi:10.1038/nature25194. PMID 29320475. S2CID 4464877.
- ^ Walsh JR, Carpenter SR, Vander Zanden MJ (April 2016). "Invasive species triggers a massive loss of ecosystem services through a trophic cascade". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (15): 4081–5. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113.4081W. doi:10.1073/pnas.1600366113. PMC 4839401. PMID 27001838.
- ^ "The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved April 30, 2021.
- ^ Dicks LV, Viana B, Bommarco R, Brosi B, Arizmendi MD, Cunningham SA, et al. (November 2016). "Ten policies for pollinators" (PDF). Science. 354 (6315): 975–976. Bibcode:2016Sci...354..975D. doi:10.1126/science.aai9226. PMID 27884996. S2CID 26844944.
- ^ "Where have all the insects gone?". Science | AAAS. May 9, 2017. Retrieved October 20, 2017.
- ^ Hallmann CA, Sorg M, Jongejans E, Siepel H, Hofland N, Schwan H, et al. (October 18, 2017). Lamb EG (ed.). "More than 75 percent decline over 27 years in total flying insect biomass in protected areas". PLOS ONE. Public Library of Science (PLoS). 12 (10): e0185809. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1285809H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0185809. PMC 5646769. PMID 29045418.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Blakemore RJ (2018). "Critical Decline of Earthworms from Organic Origins under Intensive, Humic SOM-Depleting Agriculture". Soil Systems. 2 (2): 33. doi:10.3390/soilsystems2020033.
- ^ Dewi WS, Senge M (2015). "Earthworm diversity and ecosystem services under threat". Reviews in Agricultural Science. 3: 25–35. doi:10.7831/ras.3.0_25.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Dewi WS, Senge M (2015). "Earthworm Diversity and Ecosystem Services under Threat". Reviews in Agricultural Science. 3: 25–35. doi:10.7831/ras.3.0_25. ISSN 2187-090X.
- ^ Pennisi E (September 12, 2019). "Common pesticide makes migrating birds anorexic". Science. Retrieved September 19, 2019.
- ^ "These 8 Bird Species Have Disappeared This Decade". Environment. September 5, 2018. Retrieved September 25, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b de Moraes KF, Santos MP, Gonçalves GS, de Oliveira GL, Gomes LB, Lima MG (July 17, 2020). "Climate change and bird extinctions in the Amazon". PLOS ONE. 15 (7): e0236103. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1536103D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0236103. PMC 7367466. PMID 32678834.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tickner D, Opperman JJ, Abell R, Acreman M, Arthington AH, Bunn SE, et al. (April 2020). "Bending the Curve of Global Freshwater Biodiversity Loss: An Emergency Recovery Plan". BioScience. 70 (4): 330–342. doi:10.1093/biosci/biaa002. PMC 7138689. PMID 32284631.
- ^ Harvey F (February 23, 2021). "Global freshwater fish populations at risk of extinction, study finds". The Guardian. Retrieved February 24, 2021.
- ^ Ellis EC, Antill EC, Kreft H (January 17, 2012). "All is not loss: plant biodiversity in the anthropocene". PLOS ONE. 7 (1): e30535. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...730535E. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030535. PMC 3260302. PMID 22272360.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Worm B, Barbier EB, Beaumont N, Duffy JE, Folke C, Halpern BS, et al. (November 2006). "Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services". Science. 314 (5800): 787–90. Bibcode:2006Sci...314..787W. doi:10.1126/science.1132294. JSTOR 20031683. PMID 17082450. S2CID 37235806.
- ^ Gamfeldt L, Lefcheck JS, Byrnes JE, Cardinale BJ, Duffy JE, Griffin JN (2015). "Marine biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: what's known and what's next?". Oikos. 124 (3): 252–265. doi:10.1111/oik.01549. ISSN 1600-0706.
- ^ Halpern BS, Frazier M, Potapenko J, Casey KS, Koenig K, Longo C, et al. (July 2015). "Spatial and temporal changes in cumulative human impacts on the world's ocean". Nature Communications. 6 (1): 7615. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.7615H. doi:10.1038/ncomms8615. PMC 4510691. PMID 26172980.
- ^ Ecosystem effects
- ^ Causes, effects, solutions
- ^ Carrington D (October 12, 2020). "Fifth of countries at risk of ecosystem collapse, analysis finds". The Guardian. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
- ^ Bélanger J, Pilling D, eds. (2019), The State of the World's Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture, Rome: FAO Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture
- ^ McGrath M (February 22, 2019), UN: Growing threat to food from decline in biodiversity, BBC
- ^ Jump up to: a b In brief – The State of the World's Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture (PDF). Rome: FAO. 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 4, 2019. Alt URL
- ^ "Biodiversity". World Health Organization. Retrieved May 3, 2019.
- ^ Mooney PR (1979). Seeds of the Earth: A private or public resource?. Inter Pares for the Canadian Council for International Co-operation and the International Coalition for Development Action. p. 71. ISBN 0969014937.
- ^ Heald PJ, Chapman S (2012). "Veggie Tales: Pernicious Myths about Patents, Innovation, and Crop Diversity in the Twentieth Century". University of Illinois Law Review: 1051–1102.
- ^ Jump up to: a b von Hertzen L, Hanski I, Haahtela T (October 2011). "Natural immunity. Biodiversity loss and inflammatory diseases are two global megatrends that might be related". EMBO Reports. 12 (11): 1089–93. doi:10.1038/embor.2011.195. PMC 3207110. PMID 21979814.
- ^ Hanski I, von Hertzen L, Fyhrquist N, Koskinen K, Torppa K, Laatikainen T, et al. (May 2012). "Environmental biodiversity, human microbiota, and allergy are interrelated". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (21): 8334–9. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.8334H. doi:10.1073/pnas.1205624109. PMC 3361383. PMID 22566627.
- ^ Haahtela T, Holgate S, Pawankar R, Akdis CA, Benjaponpitak S, Caraballo L, Demain J, Portnoy J, von Hertzen L, et al. (WAO Special Committee on Climate Change and Biodiversity) (January 2013). "The biodiversity hypothesis and allergic disease: world allergy organization position statement". The World Allergy Organization Journal. 6 (1): 3. doi:10.1186/1939-4551-6-3. PMC 3646540. PMID 23663440.
- ^ The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Steering Committee (April 1998). "Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema: ISAAC". Lancet. London, England. 351 (9111): 1225–32. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)07302-9. PMID 9643741. S2CID 26889807.
- ^ Ehrlich PR, Pringle RM (August 2008). "Colloquium paper: where does biodiversity go from here? A grim business-as-usual forecast and a hopeful portfolio of partial solutions". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105 Suppl 1 (Supplement 1): 11579–86. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10511579E. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801911105. PMC 2556413. PMID 18695214.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Biodiversity loss – Ecological effects". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved March 23, 2020.
- ^ Dinerstein E, Joshi AR, Vynne C, Lee AT, Pharand-Deschênes F, França M, et al. (September 2020). "A "Global Safety Net" to reverse biodiversity loss and stabilize Earth's climate". Science Advances. 6 (36): eabb2824. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.2824D. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abb2824. PMC 7473742. PMID 32917614.
- ^ Tonissen P (July 12, 2020). "IPBES #PandemicsReport Media Release". IPBES. Retrieved April 11, 2021.
- ^ Liu J, Mooney H, Hull V, Davis SJ, Gaskell J, Hertel T, et al. (February 2015). "Sustainability. Systems integration for global sustainability". Science. 347 (6225): 1258832. doi:10.1126/science.1258832. PMID 25722418.
- ^ Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GA, Kent J (February 2000). "Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities". Nature. 403 (6772): 853–8. Bibcode:2000Natur.403..853M. doi:10.1038/35002501. PMID 10706275. S2CID 4414279.
- ^ "Aichi Biodiversity Targets". Convention on Biological Diversity. May 11, 2018. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- ^ "Biodiversity crisis is worse than climate change, experts say". ScienceDaily. January 20, 2012. Retrieved May 21, 2021.
- ^ Mcelwee P (November 2, 2020). "COVID-19 and the biodiversity crisis". The Hill. Retrieved November 3, 2020.
- ^ Cohen L (September 15, 2020). "More than 150 countries made a plan to preserve biodiversity a decade ago. A new report says they mostly failed". CBS News. Retrieved September 16, 2020.
- ^ Yeung J (September 16, 2020). "The world set a 2020 deadline to save nature but not a single target was met, UN report says". CNN. Retrieved September 16, 2020.
- ^ Kilvert N (September 16, 2020). "Australia singled out for mammal extinction in UN's dire global biodiversity report". ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved September 16, 2020.
- ^ Niranjan A (September 28, 2020). "Countries pledge to reverse destruction of nature after missing biodiversity targets". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^ Jones, Benji (May 20, 2021). "Why the US won't join the single most important treaty to protect nature". Vox. Retrieved May 21, 2021.
- ^ Cox, Lisa (July 23, 2021). "Nature's Paris moment: does the global bid to stem wildlife decline go far enough?". The Guardian. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^ Rounsevell MD, Harfoot M, Harrison PA, Newbold T, Gregory RD, Mace GM (June 2020). "A biodiversity target based on species extinctions" (PDF). Science. 368 (6496): 1193–1195. Bibcode:2020Sci...368.1193R. doi:10.1126/science.aba6592. PMID 32527821. S2CID 219585428.
- ^ Kapoor, Kanupriya (June 10, 2021). "Climate change and biodiversity loss must be tackled together – report". Reuters. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
Further reading[]
- "Fewer than 20 extinctions a year: does the world need a single target for biodiversity?". Nature. 583 (7814): 7–8. July 2020. Bibcode:2020Natur.583....7.. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01936-y. PMID 32606472.
- Ehrlich PR (1988). "Chapter 2, The Loss of Diversity Causes and Consequences". In Wilson EO, Peter FM (eds.). Biodiversity. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US).
- Griffin N, ed. (2015). Biodiversity Loss in the 21st Century. Ml Books International – Ips. ISBN 978-1632390943.
- Perrings C (2008). Biodiversity Loss: Economic and Ecological Issues. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521588669.
- Waldron A, Miller DC, Redding D, Mooers A, Kuhn TS, Nibbelink N, et al. (November 2017). "Reductions in global biodiversity loss predicted from conservation spending". Nature. Springer Nature. 551 (7680): 364–367. Bibcode:2017Natur.551..364W. doi:10.1038/nature24295. hdl:10044/1/52628. PMID 29072294. S2CID 205261276.
- Wood A (2000). The Root Causes of Biodiversity Loss. Routledge. ISBN 978-1853836992.
- Worm B, Barbier EB, Beaumont N, Duffy JE, Folke C, Halpern BS, et al. (November 2006). "Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services". Science. American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). 314 (5800): 787–90. Bibcode:2006Sci...314..787W. doi:10.1126/science.1132294. PMID 17082450. S2CID 37235806.
External links[]
- Shah A (2014). "Loss of Biodiversity and Extinctions". globalissues.org.
- "How does Biodiversity loss affect me and everyone else?". panda.org.
- "TOPICS IN BIODIVERSITY LOSS". Global Change Project of the Paleontological Research Institution. Archived from the original on December 19, 2016. Retrieved January 24, 2017.
- "Forests, desertification and biodiversity". United Nations Sustainable Development. Retrieved March 5, 2018.
- "Climate Change and Biodiversity Loss". Center for Health and the Global Environment. July 19, 2017. Archived from the original on March 6, 2018. Retrieved March 5, 2018.
- "How Overpopulation Leads to Habitat Loss and Mass Extinction". Max Katz-Balmes.
- "Biodiversity loss could be making us sick – here's why". The Conversation. August 4, 2020.
- Global Biodiversity Outlook Convention on Biological Diversity
- Biodiversity: Why the nature crisis matters, in five graphics. BBC, September 30, 2020
- Scientists describe 'hidden biodiversity crisis' as variation within species is lost. Phys.org, March 1, 2021.
- Biodiversity
- Biogeography
- Environmental issues
- Extinction
- Food security