Democratic Party of Georgia
Democratic Party of Georgia | |
|---|---|
| Chairperson | Nikema Williams |
| Senate Leader | Gloria S. Butler |
| House Leader | James Beverly |
| Headquarters | 501 Pulliam Street, Atlanta, GA 30312 |
| Ideology | Centrism Conservatism Modern liberalism Progressivism |
| Political position | Center to center-left |
| National affiliation | Democratic Party |
| Colors | Blue |
| Statewide Executive Offices | 0 / 13
|
| U.S. Senate Seats | 2 / 2
|
| U.S. House Seats | 6 / 14
|
| State Senate | 22 / 56
|
| State House | 77 / 180
|
| Website | |
| www | |
The Democratic Party of Georgia is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the U.S. state of Georgia. It is one of the two major political parties in the state and is chaired by Nikema Williams.
President Jimmy Carter was a Georgia Democrat. Since the passage of the Affordable Care Act, Georgia Democrats have advocated Medicaid expansion in the state, a policy that would provide a federally subsidized health insurance plan to approximately 500,000 Georgians. At $5.15 an hour, Georgia is one of only two states with a state minimum wage below the federal minimum wage; a priority for Georgia Democrats in the 2010s and 2020s has been increasing the minimum wage.
History[]

For over a century, the Democratic Party dominated Georgia state and local politics with a membership largely consisting of conservative Southern Democrats. From 1872 to 2002, the Democratic Party controlled the governorship, both houses of the state legislature, and most statewide offices.
In 1976, former Democratic governor Jimmy Carter (1971−1975) was elected the 39th president of the United States.
After switching to the Republican Party in 1998, Sonny Perdue went on to defeat Democrat Roy Barnes in the 2002 gubernatorial election. In 2004, the Democratic Party lost control of the Georgia House of Representatives, putting the party in the minority for the first time in state history.
The Democratic Party of Georgia entered the 2010 elections with hopes that former governor Roy Barnes could win back the governorship. Polls showed a tight race between Barnes and Republican gubernatorial nominee Nathan Deal,[1] with some predicting a runoff election.[2] However, on election day, Republicans won every statewide office.[3]
Since the passage of the Affordable Care Act, Georgia Democrats have advocated Medicaid expansion in the state, a policy that would provide a federally subsidized healthcare plan to about 500,000 Georgians.[4][5][6] At $5.15 an hour, Georgia is one of only two states with a state minimum wage below the federal minimum wage; a priority for Georgia Democrats in the 2010s and 2020s has been increasing the minimum wage.[7][8]
Since 2016, Georgia Democrats have begun to see better results, with them getting very close to winning the governorship in 2018. In 2020, Joe Biden narrowly won the state, the first time for a Democratic presidential candidate since 1992. Not long after that, Democrats Jon Ossoff and Raphael Warnock won both of the state's U.S. Senate seats in runoff elections in 2021.
Leadership[]
Officers of the Democratic Party of Georgia are elected by the state Democratic committee at a January meeting following each regular gubernatorial election.[9] Officers serve four-year terms, and there is no limit on the number of terms an individual can serve as a officer. Below are the current officers:[10]
- Chair: Nikema Williams
- First Vice Chair: Ted Terry
- Vice Chair of Candidate Recruitment: Adrienne White
- Vice Chair of Congressional District Chairs and County Party Liaison: Sarah Todd
- Vice Chair of Constituency Groups: Bee Nguyen
- Secretary: Justin Holsomback
- Treasurer: Jason Esteves
- House Leader: James Beverly[11]
- Senate Leader: Gloria Butler[12]
Caucuses and affiliates[]
- AAPI Caucus
- African American Caucus
- Democratic Women's Council
- Disability Caucus
- Georgia Democratic Rural Council
- Georgia Federation of Democratic Women
- Georgia House Democrats
- Georgia Senate Democrats
- Greening Georgia
- Latino Caucus
- LGBTQ Caucus
- Senior Caucus
- Veterans Caucus
- Young Democrats of Georgia[13]
Current elected officials[]


Members of Congress[]
Democrats hold six of Georgia's 14 seats in the U.S. House of Representatives and both of Georgia's seats in the U.S. Senate.
U.S. Senate[]
Democrats have controlled both of Georgia's seats in the U.S. Senate since 2021:
- Class II: Jon Ossoff (Senior Senator)
- Class III: Raphael Warnock (Junior Senator)
U.S. House of Representatives[]
- GA-02: Sanford Bishop
- GA-04: Hank Johnson
- GA-05: Nikema Williams
- GA-06: Lucy McBath
- GA-07: Carolyn Bourdeaux
- GA-13: David Scott
Statewide offices[]
The party controls none of the thirteen state constitutional offices.
State Legislature[]
Democrats control 22 of the 56 State Senate seats and 77 of the 180 State House seats. Two-year terms of office apply to both chambers, and the entire membership of each body is elected at the same time in even-numbered years.
- Senate
- Current senators
- Senate Minority Leader: Gloria S. Butler (SD55)
- Senate Deputy Minority Leader: Harold V. Jones II (SD22)
- Senate Minority Caucus Chair: Elena Parent (SD42)
- House
- Current representatives
- House Minority Leader: James Beverly (HD143)
- House Minority Whip: David Wilkerson (HD38)
- House Minority Caucus Chair: Billy Mitchell (HD88)
Presidential elections[]
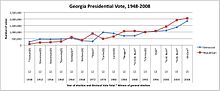
Since 1948, Democrats have won Georgia's presidential electoral votes 9 times, while Republicans have won Georgia 10 times. However, in the last 10 presidential elections, Democrats have won Georgia only twice, in 1992 and 2020.
List of chairs[]
Elected by the state convention[]
- Thomas Hardeman (1872)
- (1880)
- (1883)
- (1886)
- Hoke Smith (1888)
- William Yates Atkinson (1890–1892)
- (1892-1894)
- Alexander Stephens Clay (1894–1898)
- (1898–1900)
- (1902–1904)
- (1904–1906)
- (1906–1908)
- (1908–1909)
- (1909–1910)
- (1910–1912)
- William J. Harris (1912–1913)
- William S. West (1913–1914)
- (1914–1916)
- (1916–1920)
- (1920–1921)
- (1925–30)
- (1930–32)
- (1935–1937)
- (1937)
- (1939)
- (1942)
- (1943–1946)
- (1948–1954)
- (1954–1960)
- J.B. Fuqua (1962–1966)
- James H. Gray Sr. (1966–1970)
Appointed by the governor[]
- David Gambrell (1970–1972)
- Charles Kirbo (1972–1974)
- (1974–1982)
- (1982)
- Bert Lance (1982–1986)
- John Henry Anderson (1986–1990)
- (1990–1994)
- (1994–1998)
- (1998–2001)
- Calvin Smyre (2001–2004)
Elected by the state committee[]
- (2004–2007)
- Jane Kidd (2007–2010)
- Mike Berlon (2011–2013)
- Nikema Williams (2013)
- DuBose Porter (2013–2019)
- Nikema Williams (2019–present)
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Real Clear Politics: Georgia Governor - Deal vs. Barnes
- ^ WSB Radio Georgia Governor: Runoff Likely[permanent dead link]
- ^ WXIA-TV Republicans Sweep Statewide Races
- ^ "State Dems pan governor's healthcare plan, call for Medicaid expansion". 11 Alive. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ^ "With Rural Hospitals in Danger of Closing, Kemp, Duncan Continue to Rail against Medicaid Expansion". Georgia Democrats. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ^ Nolin, Jill. "Dem state lawmaker urges Kemp to expand Medicaid to fight COVID-19". Georgia Recorder. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ^ Hallerman, Tamar. "Minimum wage vote could become defining 2020 issue in Georgia". The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- ^ "Ossoff, Warnock join senators in seeking $15 minimum wage". FOX 5 Atlanta. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- ^ "Charter of the Democratic Party of Georgia" (PDF). Democratic Party of Georgia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-11-22.
- ^ "Officers". Georgia Democratic Party. 12 July 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "Representative Robert Trammell". www.house.ga.gov. Retrieved 2020-07-20.
- ^ "Senate Dems elect leadership team for 2013-14 term". AccessWDUN. Retrieved 2020-07-20.
- ^ "Caucuses". Georgia Democratic Party. 11 July 2016. Retrieved 22 November 2020.
External links[]
- Democratic Party of Georgia
- Democratic Party (United States) by state
- Political parties in Georgia (U.S. state)