Estradiol undecylate
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌɛstrəˈdaɪɒl ənˈdɛsɪleɪt/ ES-trə-DY-ol un-DESS-il-ayt |
| Trade names | Delestrec, Progynon Depot 100, others |
| Other names | EU; E2U; Estradiol undecanoate; Estradiol unducelate; RS-1047; SQ-9993 |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection[1] |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | IM injection: High |
| Protein binding | Estradiol: ~98% (to albumin and SHBG)[2][3] |
| Metabolism | Cleavage via esterases in the liver, blood, and tissues[4][5] |
| Metabolites | Estradiol, undecanoic acid, estradiol metabolites[4][5] |
| Elimination half-life | Unknown |
| Duration of action | IM injection: • 10–12.5 mg: 1–2 months[6][7] • 25–50 mg: 2–4 months[8] |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.616 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H44O3 |
| Molar mass | 440.668 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
show
SMILES | |
show
InChI | |
Estradiol undecylate (EU), also known as estradiol undecanoate and formerly sold under the brand names Delestrec and Progynon Depot 100 among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men.[9][10][11][12][1] It has also been used as a part of hormone therapy for transgender women.[13][14][15] Although estradiol undecylate has been used in the past, it was discontinued and hence is no longer available.[11][16] The medication has been given by injection into muscle usually once a month.[1][17][12]
Side effects of estradiol undecylate in men may include breast tenderness, breast development, feminization, sexual dysfunction, infertility, fluid retention, and cardiovascular issues.[17] Estradiol undecylate is a synthetic estrogen and hence is an agonist of the estrogen receptor, the biological target of estrogens like estradiol.[5][4] It is an estrogen ester and a very long-lasting prodrug of estradiol in the body.[4][5] Because of this, it is considered to be a natural and bioidentical form of estrogen.[4][18][19] An injection of estradiol undecylate has a duration of about 1 to 4 months.[7][8][6][20]
Estradiol undecylate was first described in 1953 and was introduced for medical use by 1956.[7][21][8][22] It has been used in Europe as a parenteral estrogen to treat prostate cancer in men, although not as often as polyestradiol phosphate.[11][12]
Medical uses[]
Estradiol undecylate has been used as a form of high-dose estrogen therapy to treat prostate cancer, but has since largely been superseded for this indication by newer agents with fewer adverse effects (e.g., gynecomastia and cardiovascular complications) like GnRH analogues and nonsteroidal antiandrogens.[1][23] It has been assessed for this purpose in a number of clinical studies.[24][25][26][27][28] It has been used at a dosage of 100 mg every 3 to 4 weeks (or once a month) by intramuscular injection for this indication.[17][29]
Estradiol undecylate has been used to suppress sex drive in sex offenders.[30] It has been used for this indication at a dosage of 50 to 100 mg by intramuscular injection once every 3 to 4 weeks.[30]
Estradiol undecylate has also been used to treat breast cancer in women.[31] It has been used in menopausal hormone therapy as well, for instance in the treatment of hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms.[8] Along with estradiol valerate, estradiol cypionate, and estradiol benzoate, estradiol undecylate has been used as an intramuscular estrogen in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women.[13][14][15] It has been used at doses of 100 to as much as 800 mg per month by intramuscular injection for this purpose.[14][15][13][32][33][34]
Available forms[]
Estradiol undecylate was available as an oil solution for intramuscular injection provided in ampoules at a concentration of 100 mg/mL.[35][36]
Contraindications[]
Contraindications of estrogens include coagulation problems, cardiovascular diseases, liver disease, and certain hormone-sensitive cancers such as breast cancer and endometrial cancer, among others.[37][38][39][40]
Side effects[]
Estradiol undecylate and its side effects have been evaluated for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer in a phase III international multicenter randomized controlled trial headed by Jacobi and colleagues of the Department of Urology, University of Mainz.[17][41][42][43][44][25][45] The study consisted of 191 patients from 12 treatment centers, who were treated for 6 months with intramuscular injections of either 100 mg/month estradiol undecylate (96 men) or 300 mg/week cyproterone acetate (95 men).[41][43][44][25][45][46][47] Findings for a subgroup of 42 men at the University of Mainz center were initially reported in 1978 and 1980.[48][17][25][45] These men were age 51 to 84 years (mean 68 years), and men with pre-existing cardiovascular disease were excluded.[12][17][49] A considerable incidence of cardiovascular complications was reported for the estradiol undecylate group (76%; 16/21 incidence total); there was a 67% (14/21) incidence of cardiovascular morbidity and a 9.5% (2/21) incidence of cardiovascular mortality.[12][17][49] The cardiovascular morbidity in this group included peripheral edema and superficial thrombophlebitis (38%; 8/21), coronary heart disease (24%; 5/21), and a deep vein thrombosis (4.8%; 1/21), while the cardiovascular mortality included a myocardial infarction (4.8%; 1/21) and a pulmonary embolism (4.8%; 1/21).[17][49] Eight of the cases of cardiovascular complications in the estradiol undecylate group, including the two deaths, were regarded as "severe".[49][50] Conversely, no incidence of cardiovascular toxicity occurred in the cyproterone acetate comparison group (0%; 0/21).[12][17][49] Other side effects of estradiol undecylate included gynecomastia (100%; 21/21) and erectile dysfunction (90%; 19/21).[17] The cardiovascular complications with estradiol undecylate in this relatively small study are in contrast to large and high-quality clinical studies of high-dose polyestradiol phosphate and transdermal estradiol for prostate cancer, in which minimal to no cardiovascular toxicity has been observed.[51][52][53][54]
An expanded report of 191 patients, which included the 42 patients from the University of Mainz center plus an additional 149 patients from 11 other centers, was published in 1982.[41][47] The antitumor effectiveness of estradiol undecylate and cyproterone acetate in this study was equivalent.[41][43][55][44][25][45] The rates of improvement, no response, and deterioration were 52%, 41%, and 7% in the estradiol undecylate group and 48%, 44%, and 8% in the cyproterone acetate group, respectively.[41][44] However, the incidence of a selection of specific side effects, including gynecomastia, breast tenderness, and edema, was significantly lower in the cyproterone acetate group than in the estradiol undecylate group (37% vs. 94%, respectively).[41][43][44][56] Gynecomastia specifically occurred in 13% (12/96) of the patients in the cyproterone acetate group and 77% (73/95) of the patients in the estradiol undecylate group.[41][43] Erectile dysfunction occurred in "essentially all" patients in both groups.[47] Leg edema occurred in 18% (17/95) of the estradiol undecylate group and 4.2% (4/96) of the cyproterone acetate group, while the incidences of superficial thrombophlebitis and coronary heart disease both were not described.[41] The incidence of thrombosis was 4.2% (4/95) in the estradiol undecylate group and 5.3% (5/96) in the cyproterone acetate group.[41][46][47] There were five deaths in total, three in the estradiol undecylate group and two in the cyproterone acetate group.[41] Two of the deaths in each of the treatment groups were due to cardiovascular events, while the remaining death in the estradiol undecylate group was due to unknown causes.[41][44][47] The similar rate of cardiovascular complications besides edema between estradiol undecylate and cyproterone acetate that was observed is in contrast to the initial 42-patient report and to findings with other estrogens, such as diethylstilbestrol and estramustine phosphate, which have been shown to possess significantly higher cardiovascular toxicity than cyproterone acetate.[43] On the basis of the expanded study, the researchers concluded that cyproterone acetate was an "acceptable alternative" to estrogen therapy with estradiol undecylate, but with a "considerably more favorable" side-effect profile.[44]
After the completion of the initial expanded study, a 5-year extension trial primarily of the Ruhr University Bochum center subgroup, led by Tunn and colleagues, was conducted.[26][42][43][25][46][45] In this study, the cyproterone acetate group was changed from intramuscular injections to 100 mg/day oral cyproterone acetate.[26][43] Of the 39 patients in the study, the global 5-year survival rate was not significantly different between the estradiol undecylate and cyproterone acetate groups (24% and 26%, respectively).[26][43][25][46][45] In patients without metastases, the 5-year survival rate was 51% in the cyproterone acetate group relative to 43% in the estradiol undecylate group, although the difference was not statistically significant.[26][43] In terms of non-prostate cancer deaths, there were 5 in the CPA group and 6 in the EU group.[26] The incidence of cardiovascular-related mortality was 3 deaths in the CPA group and 3 deaths in the EU group.[26]
Side effects during therapy with massive doses of estradiol undecylate in women with advanced breast cancer have included appetite loss, nausea, vomiting, vaginal bleeding, vaginal discharge, nipple pigmentation, breast pain, rash, urinary incontinence, edema, drowsiness, hypercalcemia, and local injection-site reactions.[31] Like other estrogens, estradiol undecylate has been found to produce testicular abnormalities and disturbances of spermatogenesis in men.[57]
Overdose[]
Estradiol undecylate has been used clinically at massive doses of as much as 800 to 2,400 mg per month by intramuscular injection, given in divided doses of 100 to 200 mg per injection two to three times per week.[31][15][32][33][34] For purposes of comparison, a single 100 mg intramuscular injection of estradiol undecylate has been found to produce maximal estradiol levels of about 500 pg/mL.[58] Symptoms of estrogen overdosage may include nausea, vomiting, bloating, increased weight, water retention, breast tenderness, vaginal discharge, heavy legs, and leg cramps.[37] These side effects can be diminished by reducing the estrogen dosage.[37]
Interactions[]
Inhibitors and inducers of cytochrome P450 may influence the metabolism of estradiol and by extension circulating estradiol levels.[59]
Pharmacology[]

Pharmacodynamics[]
Esters of estradiol like estradiol undecylate are readily hydrolyzed prodrugs of estradiol, but have an extended duration when administered in oil via intramuscular injection due to a depot effect afforded by their fatty acid ester moiety.[5] As prodrugs of estradiol, estradiol undecylate and other estradiol esters are estrogens.[4][5] Estradiol undecylate is of about 62% higher molecular weight than estradiol due to the presence of its C17β undecylate ester.[9][11] Because estradiol undecylate is a prodrug of estradiol, it is considered to be a natural and bioidentical form of estrogen.[4][18][19]
The effects of estradiol undecylate on cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, testosterone, and prolactin levels as well as on the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis have been studied in men with prostate cancer and compared with those of high-dose cyproterone acetate therapy.[60][61][62][63][64][17][65][66][67][68] The effects of estradiol undecylate on serum lipids and ceruloplasmin levels have been studied as well.[69][70][71]
Antigonadotropic activity[]
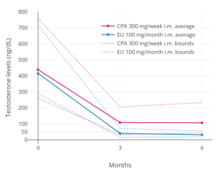

A phase III clinical trial comparing high-dose intramuscular cyproterone acetate (300 mg/week) and high-dose intramuscular estradiol undecylate (100 mg/month) in the treatment of prostate cancer found that estradiol undecylate suppressed testosterone levels into the castrate range (< 50 ng/dL)[74] within at least 3 months whereas testosterone levels with cyproterone acetate were significantly higher and above the castrate range even after 6 months of treatment.[17] With estradiol undecylate, testosterone levels fell from 416 ng/dL to 38 ng/mL (-91%) after 3 months and to 29.6 ng/dL (-93%) after 6 months, whereas with cyproterone acetate, testosterone levels fell from 434 ng/dL to 107 ng/mL (-75%) at 3 months and to 102 ng/mL (-76%) at 6 months.[17] In another study using the same dosages, estradiol undecylate suppressed testosterone levels by 97% while CPA suppressed them by 70%.[64] In accordance, whereas estrogens are well-established as able to suppress testosterone levels into the castrate range at sufficiently high dosages,[75] progestogens like cyproterone acetate on their own are able to decrease testosterone levels only up to an apparent maximum of around 70 to 80%.[76][77]
The long-term effects of estradiol undecylate on testicular morphology in transgender women have been studied.[57]
Pharmacokinetics[]
The pharmacokinetics of estradiol undecylate have been assessed in a few studies.[78][79][80][81][62][82][7][8] Following a single intramuscular injection of 100 mg estradiol undecylate in oil, mean levels of estradiol were about 500 pg/mL a day after injection and about 340 pg/mL 14 days after injection.[78] Levels of estradiol with intramuscular estradiol undecylate were reported to be very irregular and to vary by as much as 10-fold between individuals.[78] In another study, following a single intramuscular injection of 32.2 mg estradiol undecylate, levels of estradiol peaked at around 400 pg/mL after 3 days and decreased from this peak to around 200 pg/mL after 6 days.[79][83] In a continuous administration study of 100 mg/month estradiol undecylate, estradiol levels were about 560 pg/mL at 3 months and about 540 pg/mL at 6 months of therapy.[62] Due to its more protracted duration, doses of estradiol undecylate that are typical of other estradiol esters produce only "subthreshold" estradiol levels, and for this reason, higher single doses of estradiol undecylate are necessary for similar effects.[84][78][79] However, the relatively low levels of estradiol produced by lower doses of estradiol undecylate are favorable for menopausal replacement therapy.[84]
The duration of estradiol undecylate is markedly prolonged relative to that of estradiol benzoate, estradiol valerate, and many other estradiol esters.[58][6][20][18] A single intramuscular injection of 10 to 12.5 mg estradiol undecylate has a duration of 40 to 60 days (~1–2 months) and of 25 to 50 mg estradiol undecylate has an estimated duration of effect of 2 to 4 months in postmenopausal women.[7][8][6][20] A single intramuscular injection of 20 to 30 mg estradiol undecylate has been found to inhibit ovulation when used as an estrogen-only injectable contraceptive in premenopausal women for 1 to 3 months (mean 1.7 months) as well.[85] When used at a higher dose of 100 mg per injection in men with prostate cancer, estradiol undecylate has been given usually once a month.[17][29] After a single subcutaneous injection of estradiol undecylate in rats, its duration of effect was 80 days (about 2.5 months).[86][87][88] Due to its very prolonged duration, estradiol undecylate has been described in general as a favorable alternative to estradiol implants.[8]
The excretion of estradiol undecylate has been studied as well.[81]
Estradiol undecylate has not been used via oral administration. However, a closely related estradiol ester, estradiol decanoate (estradiol decylate), has been studied via the oral route, and has been found to possess significant oral bioavailability, to produce relatively high estradiol levels of about 100 pg/mL after a single 0.5 mg oral dose and about 100 to 150 pg/mL with continuous 0.25 mg/day oral therapy, and to have a much higher estradiol-to-estrone ratio than oral estradiol of about 2:1.[89][90][91] It is thought that this is due to absorption of estradiol decanoate by the lymphatic system and a consequent partial bypass of first-pass metabolism in the liver and intestines,[89][90][91] which is similarly known to occur with oral testosterone undecanoate.[92][93]

Estradiol levels after a short intravenous infusion of 20 mg estradiol in aqueous solution or an intramuscular injection of equimolar doses of estradiol esters in oil solution in postmenopausal women.[80][94] Assays were performed using radioimmunoassay with chromatographic separation.[80][94] Sources were Geppert (1975) and Leyendecker et al. (1975).[80][94]

Estradiol, testosterone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone levels with an intramuscular injection of 32.3 mg estradiol undecylate in oil in 3 postmenopausal women.[80][94] Assays were performed using radioimmunoassay with chromatographic separation.[94][80] Sources were Geppert (1975) and Leyendecker et al. (1975).[80][94]
Chemistry[]
Estradiol undecylate is a synthetic estrane steroid and an estradiol ester.[9][10] It is specifically the C17β undecylate (undecanoate) ester of estradiol.[9][10][11] The compound is also known as estradiol 17β-undecylate or as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol 17β-undecanoate.[10][11] The undecylic acid (undecanoic acid) ester of estradiol undecylate is a medium-chain fatty acid and is found naturally in many foods, some examples of which include coconut, fruits, fats, oils, and rice.[96]
Estradiol undecylate is a relatively long-chain ester of estradiol.[10][11] Its undecylate ester contains 11 carbon atoms.[10][11] For comparison, the ester chains of estradiol acetate, estradiol valerate, and estradiol enantate have 2, 5, and 7 carbon atoms, respectively.[10][11] As a result of its longer ester chain, estradiol undecylate is the most lipophilic of these estradiol esters, and for this reason, has by far the longest duration when administered in oil solution by intramuscular injection.[58][97][98]
A few estradiol esters related to estradiol undecylate include estradiol decanoate, estradiol diundecylate, and estradiol diundecylenate.[9][10] Estradiol undecylate shares the same undecylate ester as testosterone undecanoate, an androgen/anabolic steroid and very long-lasting testosterone ester.[9][10]
Estradiol undecylate is one of the longest-chain steroid esters that has been in common medical use.[99]
History[]
Estradiol undecylate was first described in the scientific literature, along with estradiol valerate and a variety of other estradiol esters, by Karl Junkmann of Schering AG in 1953.[100][7] It was introduced for medical use via intramuscular injection by 1956.[21][8][22] Syntex applied for a patent for estradiol undecylate in 1958, which was granted in 1961 and was given a priority date of 1957.[35][101] Estradiol undecylate was introduced for medical use and was employed for decades, but was eventually discontinued.[11][102][36] It remained in use in some countries as late as the 2000s.[35][11][103]
Harry Benjamin reported on the use of estradiol undecylate in transgender women in his book The Transsexual Phenomenon in 1966 and in a literature review in the Journal of Sex Research in 1967.[14][104]
Society and culture[]
Generic names[]
Estradiol undecylate is the generic name of the drug and its INN and USAN.[9][10][11][16] It is also spelled in some publications as estradiol unducelate and is also known as estradiol undecanoate.[58][9][10][11][16] In German, it is known under a variety of spellings including as estradiolundecylat, östradiolundecylat, östradiolundezylat, oestradiolundecylat, oestradiolundezylat, and others.[105] Estradiol undecylate is known by its former developmental code names RS-1047 and SQ-9993 as well.[9][10][11][16]
Brand names[]
The major brand name of estradiol undecylate is Progynon Depot 100.[9][10][11] It has also been marketed under other brand names including Delestrec, Depogin, Estrolent, Oestradiol D, Oestradiol-Retard Theramex, and Primogyn Depot [0,1 mg/ml], among others.[9][10][11][35][103]
Availability[]
Estradiol undecylate was available in the Europe (including in France, Germany, Great Britain, Monaco, the Netherlands, Switzerland), and Japan.[11][35][106][22][107] However, it has been discontinued and hence is no longer available.[102][36]
Research[]
Estradiol undecylate was studied by Schering alone as an estrogen-only injectable contraceptive at a dose of 20 to 30 mg once a month.[83][85][108][109] It was effective, lacked breast and thromboembolic complications, lacked other side effects besides amenorrhea, and prevented ovulation for 1 to 3 months (mean 1.7 months) following a single dose.[85] However, uterine growth of 1 to 2 cm was observed after one year, and endometrial hyperplasia was occasionally encountered.[83][85][108] The preparation was not further developed as a form of birth control due to the risks of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer associated with long-term unopposed estrogen therapy.[85]
Estradiol undecylate, in combination with norethisterone enantate (at doses of 5 to 10 mg and 50 to 70 mg, respectively), was studied by Schering as a combined injectable contraceptive and was found to be effective and well-tolerated, but ultimately was not marketed for this use.[110][109][85][111][112][113]
See also[]
- Estradiol undecylate/norethisterone enanthate
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Christoph Zink (1 January 1988). Dictionary of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Walter de Gruyter. p. 85. ISBN 978-3-11-085727-6.
- ^ Stanczyk, Frank Z.; Archer, David F.; Bhavnani, Bhagu R. (2013). "Ethinyl estradiol and 17β-estradiol in combined oral contraceptives: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and risk assessment". Contraception. 87 (6): 706–727. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2012.12.011. ISSN 0010-7824. PMID 23375353.
- ^ Tommaso Falcone; William W. Hurd (2007). Clinical Reproductive Medicine and Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 22, 362, 388. ISBN 978-0-323-03309-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Michael Oettel; Ekkehard Schillinger (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens II: Pharmacology and Clinical Application of Estrogens and Antiestrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 261,544. ISBN 978-3-642-60107-1.
Natural estrogens considered here include: [...] Esters of 17β-estradiol, such as estradiol valerate, estradiol benzoate and estradiol cypionate. Esterification aims at either better absorption after oral administration or a sustained release from the depot after intramuscular administration. During absorption, the esters are cleaved by endogenous esterases and the pharmacologically active 17β-estradiol is released; therefore, the esters are considered as natural estrogens.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Kuhl H (2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration" (PDF). Climacteric. 8 Suppl 1: 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947. S2CID 24616324.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d A. Labhart (6 December 2012). Clinical Endocrinology: Theory and Practice. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 551–553. ISBN 978-3-642-96158-8.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Wied GL (January 1954). "Östradiol-valerianat und Östradiol-undecylat; zwei neue protrahiert wirkende Östrogene. Wirkungsvergleich mit Östradiol-benzoat" [Estradiol valerate and estradiol undecylate, two new estrogens with prolonged action; comparison with estradiol benzoate]. Geburtshilfe und Frauenheilkunde (in German). 14 (1): 45–52. ISSN 0016-5751. PMID 13142295.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h Gouygou C, Gueritee N, Pye A (1956). "Un oestrogène-retard liposoluble: l'undecylate d'oestradiol" [A fat-soluble, delayed estrogen: the estradiol undecylate]. Thérapie (in French). 11 (5): 909–17. ISSN 0040-5957. PMID 13391788.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 898–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n A. D. Roberts (1991). Dictionary of Steroids: Chemical Data, Structures, and Bibliographies. CRC Press. p. 415. ISBN 978-0-412-27060-4. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis US. 2000. p. 405. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Norman G, Dean ME, Langley RE, Hodges ZC, Ritchie G, Parmar MK, Sydes MR, Abel P, Eastwood AJ (February 2008). "Parenteral oestrogen in the treatment of prostate cancer: a systematic review". Br. J. Cancer. 98 (4): 697–707. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604230. PMC 2259178. PMID 18268497.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Schlatterer K, von Werder K, Stalla GK (1996). "Multistep treatment concept of transsexual patients". Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes. 104 (6): 413–9. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1211479. PMID 9021341.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Harry Benjamin; Gobind Behari Lal; Richard Green; Robert E. L. Masters (1966). The Transsexual Phenomenon. Ace Publishing Company. p. 107.
Another preparation of even higher potency is Squibb's Delestrec, which at this writing is not yet on the market in the United States, but is well known in Germany and other European countries under the name of Progynon Depot (Schering). It is chemically Estradiol Undecylate in oil, likewise slowly absorbing, and containing 100 mg. to 1 cc. Injections of 1 cc. once or twice a month can be sufficient. Occasionally, however, larger doses are required to influence the patient's emotional distress.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Gianna E. Israel (March 2001). Transgender Care: Recommended Guidelines, Practical Information, and Personal Accounts. Temple University Press. pp. 64–. ISBN 978-1-56639-852-7.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Estradiol".
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Jacobi GH, Altwein JE, Kurth KH, Basting R, Hohenfellner R (1980). "Treatment of advanced prostatic cancer with parenteral cyproterone acetate: a phase III randomised trial". Br J Urol. 52 (3): 208–15. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410x.1980.tb02961.x. PMID 7000222.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c International Society of Urology (1973). Reports of the Congress. Livingstone. p. 252.
Progynon-Depot ist eine Oestrogenpräparat mit einem Depoteffekt von 4-6 Wochen. 1 ml Progynon Depot 100 mg enthält 100 mg Oestra- diolundecylat in öliger Lösung. Oestradiolundecylat ist ein Ester des natürlichen Oestrogens Oestradiol.
- ^ Jump up to: a b F. Lembeck; K.F. Sewing (7 March 2013). Pharmakologie-Fibel: Tafeln zur Pharmakologie-Vorlesung. Springer-Verlag. pp. 113–. ISBN 978-3-642-65621-7.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Percy Roberts Wilde; Carey Franklin Coombs; Arthur J. Rendle Short (1959). The Medical Annual: A Year Book of Treatment and Practitioner's Index ... Publishing Science Group.
As in the case of progestogens the esters of oestradiol vary in the duration of their effect. Oestradiol benzoate is short-acting (three days to a week). Oestradiol valerianate is somewhat longer-acting, and oestradiol enanthate and undecylate have considerably more prolonged duration of effectiveness. The undecylate may remain effective for some months, and should not be employed, [...]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Halkerston ID, Hillman J, Palmer D, Rundle A (1956). "Changes in the excretion pattern of neutral 17-ketosteroids during oestrogen administration to male subjects". J. Endocrinol. 13 (4): 433–8. doi:10.1677/joe.0.0130433. PMID 13345960.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Bishop, P. M. F. (1958). "Endocrine Treatment of Gynaecological Disorders". In Gardiner-Hill, H. (ed.). Modern Trends in Endocrinology. Modern Trends. 1. London: Butterworth & Co. pp. 231–244.
- ^ Ernst Mutschler; Hartmut Derendorf (1995). Drug Actions: Basic Principles and Therapeutic Aspects. CRC Press. p. 609. ISBN 978-0-8493-7774-7. Retrieved 30 January 2013.
- ^ Enfedjieff M (March 1974). "Erfahrungen mit der Hormonbehandlung des Prostatakarzinoms" [Experiences with hormonal treatment of prostatic carcinoma]. Z Urol Nephrol (in German). 67 (3): 171–3. ISSN 0044-3611. PMID 4848715.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Tunn, U. W. (1987). "Antiandrogene in der Therapie des fortgeschrittenen Prostatakarzinoms" [Antiandrogens in the Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer]. Konservative Therapie des Prostatakarzinoms [Conservative Therapy of Prostate Cancer] (in German). pp. 113–121. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-72613-2_12. ISBN 978-3-540-17724-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Saborowski, Karl-Johannes (1988), Konservative Therapie mit Cyproteronacetat und Estradiolundecylat beim Fortgeschrittenen Prostatacarcinom: Eine 5-Jahres-Studie [Conservative Therapy with Cyproterone Acetate and Estradiol Undecylate in Advanced Prostate Cancer: A 5-Year Study] (in German), Bochum, Univ., Diss., OCLC 917571781
- ^ Mollard P (March 1963). "Action clinique de l'œstradiol undécylate dans le traitement du cancer de la prostate" [Clinical action of estradiol undecylate in the treatment of prostatic cancer]. Lyon Med (in French). 209: 759–65. ISSN 0024-7790. PMID 13935867.
- ^ Schubert GE, Ziegler H, Völter D (1973). "Vergleichende histologische und zytologische Untersuchungen der Prostata unter besonderer Beruksichtigung oestrogeninduzierter Veranderungen" [Comparison of histological and cytological studies of the prostate with special reference to oestrogene induced changes]. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol (in German). 57: 315–8. ISSN 0070-4113. PMID 4142204.
- ^ Jump up to: a b R. S. Satoskar; S. D. Bhandarkar &nirmala N. Rege (1973). Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. Popular Prakashan. pp. 934–. ISBN 978-81-7991-527-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Howard Gethin Morgan; Margaret Hilary Morgan (1984). Aids to Psychiatry. Churchill Livingstone. p. 75. ISBN 978-0-443-02613-3.
Treatment of sexual offenders. Hormone therapy. [...] Oestrogens may cause breast hypertrophy, testicular atrophy, osteoporosis (oral ethinyl oestradiol 0.01-0.05 mg/day causes least nausea). Depot preparation: oestradiol [undecyleate] 50-100mg once every 3–4 weeks. Benperidol or butyrophenone and the antiandrogen cyproterone acetate also used.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Kennedy, BJ (April 1967). "Effect of massive doses of estradiol undecylate in advanced breast cancer". Cancer Chemother Rep. 51 (2): 491–495. ISSN 0069-0112.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Asscheman H, Gooren LJ, Assies J, Smits JP, de Slegte R (June 1988). "Prolactin levels and pituitary enlargement in hormone-treated male-to-female transsexuals". Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 28 (6): 583–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1988.tb03849.x. PMID 2978262. S2CID 29214187.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Asscheman H, Gooren LJ, Eklund PL (September 1989). "Mortality and morbidity in transsexual patients with cross-gender hormone treatment" (PDF). Metab. Clin. Exp. 38 (9): 869–73. doi:10.1016/0026-0495(89)90233-3. PMID 2528051.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gazzeri R, Galarza M, Gazzeri G (December 2007). "Growth of a meningioma in a transsexual patient after estrogen-progestin therapy". N. Engl. J. Med. 357 (23): 2411–2. doi:10.1056/NEJMc071938. PMID 18057351.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e A. Kleemann; J. Engel; B. Kutscher; D. Reichert (14 May 2014). Pharmaceutical Substances, 5th Edition, 2009: Syntheses, Patents and Applications of the most relevant APIs. Thieme. pp. 1167–1174. ISBN 978-3-13-179525-0.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Sweetman, Sean C., ed. (2009). "Sex hormones and their modulators". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. p. 2098. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Lauritzen C (September 1990). "Clinical use of oestrogens and progestogens". Maturitas. 12 (3): 199–214. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(90)90004-P. PMID 2215269.
- ^ Christian Lauritzen; John W. W. Studd (22 June 2005). Current Management of the Menopause. CRC Press. pp. 95–98, 488. ISBN 978-0-203-48612-2.
- ^ Laurtizen, Christian (2001). "Hormone Substitution Before, During and After Menopause" (PDF). In Fisch, Franz H. (ed.). Menopause – Andropause: Hormone Replacement Therapy Through the Ages. Krause & Pachernegg: Gablitz. pp. 67–88. ISBN 978-3-901299-34-6.
- ^ Midwinter, Audrey (1976). "Contraindications to estrogen therapy and management of the menopausal syndrome in these cases". In Campbell, Stuart (ed.). The Management of the Menopause & Post-Menopausal Years: The Proceedings of the International Symposium held in London 24–26 November 1975 Arranged by the Institute of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, The University of London. MTP Press Limited. pp. 377–382. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-6165-7_33. ISBN 978-94-011-6167-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k Jacobi, GH (June 1982). "Intramuscular cyproterone acetate treatment for advanced prostatic carcinoma: results of the first multicentric randomized trial". In Schröder, FH (ed.). Proceedings Androgens and Anti-androgens, International Symposium, Utrecht, June 5th, 1982. Schering Nederland BV. pp. 161–169. ISBN 978-9090004327. OCLC 11786945.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tunn, UW; Graff, J; Senge, Th (June 1982). "Treatment of inoperable prostatic cancer with cyproterone acetate". In Schröder, FH (ed.). Proceedings Androgens and Anti-androgens, International Symposium, Utrecht, June 5th, 1982. Schering Nederland BV. pp. 149–159. ISBN 978-9090004327. OCLC 11786945.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j Tunn, U. W.; Radlmaier, A.; Neumann, F. (1988). "Antiandrogens in Cancer Treatment". In Stoll, B. A. (ed.). Endocrine Management of Cancer: Contemporary Therapy. pp. 43–56. doi:10.1159/000415355. ISBN 978-3-8055-4686-7.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Schröder, Fritz H.; Radlmaier, Albert (2009). "Steroidal Antiandrogens". In V. Craig Jordan; Barrington J. A. Furr (eds.). Hormone Therapy in Breast and Prostate Cancer. Humana Press. pp. 325–346. doi:10.1007/978-1-59259-152-7_15. ISBN 978-1-60761-471-5.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f R. Ackermann; Jens E. Altwein; Peter Faul (13 March 2013). Aktuelle Therapie des Prostatakarzinoms. Springer-Verlag. pp. 276–277. ISBN 978-3-642-84264-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Namer M (October 1988). "Clinical applications of antiandrogens". J. Steroid Biochem. 31 (4B): 719–29. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(88)90023-4. PMID 2462132.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Jacobi, GR; Tunn, UW; Senge, TH (1 December 1982). "Clinical experience with cyproterone acetate for palliation of inoperable prostate cancer". In Jacobi, Günther H; Hohenfellner, Rudolf (eds.). Prostate Cancer. Williams & Wilkins. pp. 305–319. ISBN 978-0-683-04354-9.
- ^ Altwein JE, Jacobi GH, Hohenfellner R (1978). "Estrogen versus cyproterone acetate in untreated inoperable carcinoma of the prostate: first results of an open, prospective, randomized study". Abstracts 3rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, Monte Carlo.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Wenderoth, U. K.; Jacobi, G. H. (1983). "Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues for palliation of carcinoma of the prostate". World Journal of Urology. 1 (1): 40–48. doi:10.1007/BF00326861. ISSN 0724-4983. S2CID 23447326.
- ^ Jacobi, Günther H.; Wenderoth, Ulrich K. (1982). "Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Analogues for Prostate Cancer: Untoward Side Effects of High-Dose Regimens Acquire a Therapeutical Dimension". European Urology. 8 (3): 129–134. doi:10.1159/000473499. ISSN 0302-2838. PMID 6281023.
- ^ Ockrim J, Lalani EN, Abel P (October 2006). "Therapy Insight: parenteral estrogen treatment for prostate cancer--a new dawn for an old therapy". Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 3 (10): 552–63. doi:10.1038/ncponc0602. PMID 17019433. S2CID 6847203.
- ^ Lycette JL, Bland LB, Garzotto M, Beer TM (December 2006). "Parenteral estrogens for prostate cancer: can a new route of administration overcome old toxicities?". Clin Genitourin Cancer. 5 (3): 198–205. doi:10.3816/CGC.2006.n.037. PMID 17239273.
- ^ Russell N, Cheung A, Grossmann M (August 2017). "Estradiol for the mitigation of adverse effects of androgen deprivation therapy". Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 24 (8): R297–R313. doi:10.1530/ERC-17-0153. PMID 28667081.
- ^ Langley RE, Cafferty FH, Alhasso AA, Rosen SD, Sundaram SK, Freeman SC, Pollock P, Jinks RC, Godsland IF, Kockelbergh R, Clarke NW, Kynaston HG, Parmar MK, Abel PD (April 2013). "Cardiovascular outcomes in patients with locally advanced and metastatic prostate cancer treated with luteinising-hormone-releasing-hormone agonists or transdermal oestrogen: the randomised, phase 2 MRC PATCH trial (PR09)". Lancet Oncol. 14 (4): 306–16. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70025-1. PMC 3620898. PMID 23465742.
- ^ Tunn UW, Senge T, Jacobi GH (1983). "Erfahrungen mit Cyproteronacetat als Monotherapie beim Inoperablen Prostatakarzinom" [Experience with Cyproterone Acetate as Monotherapy for Inoperable Prostate Cancer]. In Klosterhalfen H (ed.). Therapie des Fortgeschrittenen Prostatakarzinoms. Vortragsveranstaltung fur Urologen, Berlin 1982/83 [Therapy of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Lecture Event for Urologists, Berlin 1982/83]. Wiss Buchreihe, Schering AG. pp. 67–76. ISBN 978-3921817162. OCLC 67592679.
- ^ Schröder, Fritz H. (1996). "Cyproterone Acetate — Results of Clinical Trials and Indications for Use in Human Prostate Cancer". Antiandrogens in Prostate Cancer. pp. 45–51. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-45745-6_4. ISBN 978-3-642-45747-0.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Schulze C (January 1988). "Response of the human testis to long-term estrogen treatment: morphology of Sertoli cells, Leydig cells and spermatogonial stem cells". Cell Tissue Res. 251 (1): 31–43. doi:10.1007/BF00215444. PMID 3342442. S2CID 22847105.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Vermeulen A (1975). "Long-acting steroid preparations". Acta Clin Belg. 30 (1): 48–55. doi:10.1080/17843286.1975.11716973. PMID 1231448.
- ^ Cheng ZN, Shu Y, Liu ZQ, Wang LS, Ou-Yang DS, Zhou HH (February 2001). "Role of cytochrome P450 in estradiol metabolism in vitro". Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 22 (2): 148–54. PMID 11741520.
- ^ Schürmeyer T, Graff J, Senge T, Nieschlag E (March 1986). "Effect of oestrogen or cyproterone acetate treatment on adrenocortical function in prostate carcinoma patients". Acta Endocrinol. 111 (3): 360–7. doi:10.1530/acta.0.1110360. PMID 2421511.
- ^ Spona J, Lunglmayr G (July 1980). "Prolaktin-Serumspiegel unter Behandlung des Prostatakarzinoms mit Östradiol-17 beta-undezylat und Cyproteronazetat". Verhandlungsbericht der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie [Serum Prolactin Levels During Therapy of Prostatic Cancer with Estradiol-17 beta-undecylate and Cyproterone Acetate]. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. Verhandlungsbericht der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie (in German). 92. pp. 494–7. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-81706-9_120. ISBN 978-3-540-11017-0. ISSN 0043-5325. PMID 6933738.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Jacobi, G.H.; Altwein, J.E. (1979). "Bromocriptin als Palliativtherapie beim fortgeschrittenen Prostatakarzinom:Experimentelles und klinisches Profil eines Medikamentes" [Bromocriptine as Palliative Therapy in Advanced Prostate Cancer: Experimental and Clinical Profile of a Drug]. Urologia Internationalis. 34 (4): 266–290. doi:10.1159/000280272. PMID 89747.
- ^ Schulze, H.; Senge, Th. (1987). Konservative Therapie des Prostatakarzinoms. pp. 89–98. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-72613-2_8. ISBN 978-3-540-17724-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Neumann, F.; El Etreby, M. F.; Habenicht, U.-F.; Radlmaier, A.; Bormacher, K. (1987). Konservative Therapie des Prostatakarzinoms [Options for androgen withdrawal and total blockage]. pp. 61–86. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-72613-2_6. ISBN 978-3-540-17724-1.
- ^ Tunn, U. W.; Senge, Th.; Neumann, F. (1981). "Serumkonzentrationen von Testosteron und Prolaktin nach operativer und medikamentöser Kastration — eine Langzeitstudie bei Prostatakarzinom-Patienten". Verhandlungsbericht der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie [Serum concentrations of testosterone and prolactin after surgical and medical castration-A long-term study in prostate cancer patients]. Verhandlungsbericht der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie. 32. pp. 419–421. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-81706-9_123. ISBN 978-3-540-11017-0. ISSN 0070-413X.
- ^ Baba, S.; Janetschek, G.; Wenderoth, U.; Jacobi, G. H. (1981). "Beeinflussung des intraprostatischen Testosteron-Stoffwechsels durch Cyproteronazetat und Östradiolundecylat bei Patienten mit Prostatakarzinom: In vivo-Untersuchungen". Verhandlungsbericht der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie [Influence of intraprostatic testosterone metabolism by cyproterone acetate and estradiol undecylate in patients with prostate cancer: in vivo studies]. Verhandlungsbericht der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie. 32. pp. 464–466. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-81706-9_138. ISBN 978-3-540-11017-0. ISSN 0070-413X.
- ^ Derra, Claus (1981), Hormonprofile unter Östrogen-und Antiandrogentherapie bei Patienten mit Prostatakarzinom: Östradiolundecylat versus Cyproteronacetat [Hormone profiles under estrogen and antiandrogen therapy in patients with prostate cancer: estradiol undecylate versus cyproterone acetate], Mainz, Universiẗat, Diss, OCLC 65055508
- ^ Jacobi, GH; Altwein, JE (1980). "Testosterone plasma kinetics in patients with prostatic carcinoma treated with estradiol undecylate, cyproterone acetate and estramustine phosphate: a preliminary report". Steroid receptors, metabolism and prostatic cancer: proceedings of a workshop of the Society of Urologic Oncology and Endocrinology, Amsterdam, 27-28 April, 1979. 494. Excerpta Medica. p. 144–151.
- ^ Nagel, R.; Schillinger, E.; Kölln, C.-P.; Pochhammer, K. (1973). 24. Tagung vom 13. Bis 16. September 1972 in Hannover [The behavior of serum lipids in patients with prostate cancer after treatment with estradiol undecylate]. Verhandlungsbericht der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie. 24. pp. 298–301. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-80738-1_75. ISBN 978-3-540-06186-1. ISSN 0070-413X.
- ^ Taupitz, Artur; Otaguro, K. (1959). "Quantitative Examination of Serum Components After Antiandrogenic Therapy Against Prostatic Cancer" [Quantitative Examination of Serum Components after Antiandrogenic Therapy Against Prostatic Cancer: Clinical and Experimental Observation]. The Japanese Journal of Urology. 50 (3): 153–162. doi:10.5980/jpnjurol1928.50.3_153. ISSN 0021-5287.
- ^ Götz, H.; Ehrmeier, H. (1971). "Oestrogene und Coeruloplasminspiegel" [Estrogens and ceruloplasmin levels]. Archiv für Gynäkologie. 211 (1–2): 204–206. doi:10.1007/BF00682878. ISSN 0003-9128. PMID 5108847. S2CID 38378905.
- ^ Jacobi GH, Altwein JE, Kurth KH, Basting R, Hohenfellner R (1980). "Treatment of advanced prostatic cancer with parenteral cyproterone acetate: a phase III randomised trial". Br J Urol. 52 (3): 208–15. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410x.1980.tb02961.x. PMID 7000222.
- ^ Jacobi, G.H.; Altwein, J.E. (1979). "Bromocriptin als Palliativtherapie beim fortgeschrittenen Prostatakarzinom:Experimentelles und klinisches Profil eines Medikamentes" [Bromocriptine as Palliative Therapy in Advanced Prostate Cancer: Experimental and Clinical Profile of a Drug]. Urologia Internationalis. 34 (4): 266–290. doi:10.1159/000280272. ISSN 1423-0399. PMID 89747.
- ^ Fabian M. Saleh (11 February 2009). Sex Offenders: Identification, Risk Assessment, Treatment, and Legal Issues. Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 176–. ISBN 978-0-19-517704-6.
- ^ Muhammad A. Salam (2003). Principles & Practice of Urology: A Comprehensive Text. Universal-Publishers. pp. 684–. ISBN 978-1-58112-412-5.
- ^ Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA (25 August 2011). Campbell-Walsh Urology: Expert Consult Premium Edition: Enhanced Online Features and Print, 4-Volume Set. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2938–. ISBN 978-1-4160-6911-9.
- ^ Kjeld JM, Puah CM, Kaufman B, Loizou S, Vlotides J, Gwee HM, Kahn F, Sood R, Joplin GF (1979). "Effects of norgestrel and ethinyloestradiol ingestion on serum levels of sex hormones and gonadotrophins in men". Clinical Endocrinology. 11 (5): 497–504. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1979.tb03102.x. PMID 519881. S2CID 5836155.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Vermeulen A (1975). "Longacting steroid preparations". Acta Clin Belg. 30 (1): 48–55. doi:10.1080/17843286.1975.11716973. PMID 1231448.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Leyendecker G, Geppert G, Nocke W, Ufer J (May 1975). "Untersuchungen zur Pharmakokinetik von Östradiol-17β, Östradiol-benzoat, Östradiol-Valerianat un Östradiol-Undezylat bei der Frau: Der Verlauf der Konzentration von Östradiol-17β, Östron, LH und FSH im Serum" [Estradiol 17β, estrone, LH and FSH in serum after administration of estradiol 17β, estradiol benzoate, estradiol valeriate and estradiol undecylate in the female]. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd (in German). 35 (5): 370–4. ISSN 0016-5751. PMID 1150068.
Estradiol 17β, estradiol benzoate, estradiol valerianate, and estradiol undecylate were injected intravenously and intramuscularly to postmenopausal woman and to female castrates. Equal doses were used corresponding to 20 mg of free estradiol 17β. Estradiol 17β, estrone, FSH and LH were measured in serum by radioimmunoassay before and after application of the hormone and the estradiol esters. Thus the depot effect of the different esters could be compared.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Gerhard Geppert (1975). Untersuchungen zur Pharmakokinetik von Östradiol-17β, Östradiol-Benzoat, Östradiol-Valerianat und Östradiol-Undezylat bei der Frau: der Verlauf der Konzentrationen von Östradiol-17β, Östron, LH und FSH im Serum [Studies on the pharmacokinetics of estradiol-17β, estradiol benzoate, estradiol valerate, and estradiol undecylate in women: the progression of serum estradiol-17β, estrone, LH, and FSH concentrations]. pp. 1–34. OCLC 632312599.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Zimmermann W, Buescher HK, Taupitz A, Thewalt K (1964). "Steroidhormonausscheidung bei patienten mit Erkrankungen der Prostata unter Behandlung mit natürlichen und synthetischen oestrogenen" [Steroid Hormone Excretion of Patients with Diseases of the Prostate under Treatment with Natural and Synthetic Estrogens]. Acta Endocrinol. (in German). 45 (4 Suppl 90): S211–25. doi:10.1530/acta.0.045S211. ISSN 0804-4643. PMID 14111328.
- ^ Oriowo MA, Landgren BM, Stenström B, Diczfalusy E (April 1980). "A comparison of the pharmacokinetic properties of three estradiol esters". Contraception. 21 (4): 415–24. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(80)80018-7. PMID 7389356.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Janet Brotherton (1976). Sex Hormone Pharmacology. Academic Press. pp. 226, 476. ISBN 978-0-12-137250-7.
- ^ Jump up to: a b JUCKER (8 March 2013). Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung / Progress in Drug Research / Progrès des recherches pharmaceutiques. Birkhäuser. pp. 243–. ISBN 978-3-0348-7044-3.
Estradiol undecylenate has a more protracted effect but it releases only subthreshold doses of steroid (advantage may be taken of this for the treatment of menopause).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Toppozada M (June 1977). "The clinical use of monthly injectable contraceptive preparations". Obstet Gynecol Surv. 32 (6): 335–47. doi:10.1097/00006254-197706000-00001. PMID 865726.
- ^ Kuhl H, Taubert HD (July 1973). "A new class of long-acting hormonal steroid preparation: synthesis of oligomeric estradiol derivatives". Steroids. 22 (1): 73–87. doi:10.1016/0039-128X(73)90072-X. PMID 4737545.
- ^ Kuhl, H.; Taubert, H. D. (1973). "Ein neuer Typ lang-wirksamer Steroid-Präparate: Synthese und biologische Wirksamkeit" [A New Type of Long-Acting Steroid Preparation: Synthesis and Biological Efficacy]. Archiv für Gynäkologie. 214 (1–4): 127–128. doi:10.1007/BF00671087. ISSN 0003-9128. PMID 4801412. S2CID 26261148.
- ^ Kuhl H, Auerhammer W, Taubert HD (October 1976). "Oligomeric oestradiol esters: a new class of long-acting oestrogens". Acta Endocrinol. 83 (2): 439–48. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0830439. PMID 989671.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kicovic PM, Luisi M, Franchi F, Alicicco E (July 1977). "Effects of orally administered oestradiol decanoate on plasma oestradiol, oestrone and gonadotrophin levels, vaginal cytology, cervical mucus and endometrium in ovariectomized women". Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 7 (1): 73–7. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1977.tb02941.x. PMID 880735. S2CID 13639429.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Luisi M, Kicovic PM, Alicicco E, Franchi F (1978). "Effects of estradiol decanoate in ovariectomized women". J. Endocrinol. Invest. 1 (2): 101–6. doi:10.1007/BF03350355. PMID 755846. S2CID 38187367.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ranjit Roy Chaudhury (1 January 1981). Pharmacology of Estrogens. Elsevier Science & Technology Books. p. 36. ISBN 978-0-08-026869-9.
- ^ J. Larry Jameson; Leslie J. De Groot (25 February 2015). Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2387–. ISBN 978-0-323-32195-2.
- ^ Eberhard Nieschlag; Hermann M. Behre (6 December 2012). Testosterone: Action - Deficiency - Substitution. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 300–. ISBN 978-3-642-72185-4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Leyendecker G, Geppert G, Nocke W, Ufer J (May 1975). "Untersuchungen zur Pharmakokinetik von Östradiol-17β, Östradiol-benzoat, Östradiol-Valerianat un Östradiol-Undezylat bei der Frau: Der Verlauf der Konzentration von Östradiol-17β, Östron, LH und FSH im Serum" [Estradiol 17β, estrone, LH and FSH in serum after administration of estradiol 17β, estradiol benzoate, estradiol valeriate and estradiol undecylate in the female]. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd (in German). 35 (5): 370–374. ISSN 0016-5751. PMID 1150068.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jacobi, G. H.; Altwein, J. E. (1979). "Bromocriptin als Palliativtherapie beim fortgeschrittenen Prostatakarzinom:Experimentelles und klinisches Profil eines Medikamentes" [Bromocriptine as Palliative Therapy in Advanced Prostate Cancer: Experimental and Clinical Profile of a Drug]. Urologia Internationalis. 34 (4): 266–290. doi:10.1159/000280272. ISSN 1423-0399. PMID 89747.
- ^ George A. Burdock (1997). Encyclopedia of Food and Color Additives. CRC Press. pp. 2870–. ISBN 978-0-8493-9412-6.
- ^ Junkmann K (1957). "Long-acting steroids in reproduction". Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 13: 389–419, discussion 419–28. PMID 13477813.
- ^ Junkmann K, Witzel H (1957). "Chemie und Pharmakologie von Steroidhormon-Estern" [Chemistry and pharmacology of steroid hormone esters]. Z Vitam Horm Fermentforsch (in German). 9 (1–2): 97–143 contd. PMID 13531579.
- ^ Armstrong, N.A.; James, K.C. (1980). "Drug release from lipid-based dosage forms. I". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 6 (3–4): 185–193. doi:10.1016/0378-5173(80)90103-9. ISSN 0378-5173.
- ^ Junkmann, Karl (1953). "Über protrahiert wirksame Östrogene" [Over protracted effective estrogens]. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv für Experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie (in German). 220 (5). doi:10.1007/BF00246561. ISSN 0028-1298. S2CID 20753905.
- ^ "17-undecenoate of estradiol".
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Micromedex".
- ^ Jump up to: a b Index Nominum: International Drug Directory. CRC Press. 2004. pp. 469–. ISBN 978-3-88763-101-7.
- ^ Benjamin, Harry (1967). "Transvestism and Transsexualism in the male and female1". Journal of Sex Research. 3 (2): 107–127. doi:10.1080/00224496709550519. ISSN 0022-4499.
- ^ Franz v. Bruchhausen; Gerd Dannhardt; Siegfried Ebel; August W. Frahm, Eberhard Hackenthal, Ulrike Holzgrabe (2 July 2013). Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis: Band 8: Stoffe E-O. Springer-Verlag. pp. 84–. ISBN 978-3-642-57994-3.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Boschann HW (July 1958). "Observations of the role of progestational agents in human gynecologic disorders and pregnancy complications". Ann N Y Acad Sci. 71 (5): 727–52. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb46803.x. PMID 13583829.
- ^ Peter Maxwell Farrow Bishop (1962). Chemistry of the Sex Hormones. Thomas. p. 78.
- ^ Jump up to: a b el-Mahgoub S, Karim M (February 1972). "Depot estrogen as a monthly contraceptive in nulliparous women with mild uterine hypoplasia". Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 112 (4): 575–6. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(72)90319-5. PMID 5008627.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Mokhtar K. Toppozada (1983). "Monthly Injectable Contraceptives". In Alfredo Goldsmith; Mokhtar Toppozada (eds.). Long-Acting Contraception. pp. 93–103. OCLC 35018604.
- ^ Toppozada MK (1994). "Existing once-a-month combined injectable contraceptives". Contraception. 49 (4): 293–301. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(94)90029-9. PMID 8013216.
- ^ Dr. S. S. Kadam (July 2007). Principles of Medicinal Chemistry Volume 2. Pragati Books Pvt. Ltd. pp. 381–. ISBN 978-81-85790-03-9.
- ^ Beck, L. R., Cowsar, D. R., & Pope, V. Z. (1980). Long-acting steroidal contraceptive systems. Research frontiers in fertility regulation, 1(1), 1-16. https://web.archive.org/web/20190308054952/http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/edb2/2b6176e781ee74afa5d13c908b54681604c0.pdf
- ^ Karim M, el-Mahgoub S (July 1971). "Conception control by cyclic injections of norethisterone enanthate and estradiol unducelate". Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 110 (5): 740–2. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(71)90268-7. PMID 5563241.
- Abandoned drugs
- Antigonadotropins
- Estradiol esters
- Estranes
- Hormonal antineoplastic drugs
- Phenols
- Prodrugs
- Prostate cancer
- Synthetic estrogens
- Undecanoate esters



