Maronite mummies
Yasmine | |
|---|---|
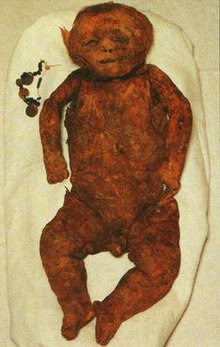 | |
| Born | around 1283 A.D. Asi-al-Hadath, Qadisha Valley |
| Died | around 1283 A.D. Asi-al-Hadath grotto |
| Cause of death | Mameluke Siege |
| Known for | First Maronite mummy ever uncovered |
The Maronite mummies are eight well preserved natural mummies of Maronite villagers dating back to around 1283 AD. They were uncovered by a team of speleologist/archaeologists during a rescue excavation in the Qadisha Valley of Lebanon in 1990. They are currently on display in the National Museum of Beirut.
Discovery[]
The mummies were found in the 'Asi-al Hadath cave located in the Kadisha Valley in Lebanon, on July 13, 1990 by a group of speleologists/archaeologists of the Groupe d'Etudes et de Recherches Souterraines du Liban- GERSL, namely Abi Aoun Pierre, Baroudy Fadi, Ghaouch Antoine and Khawaja Paul.[1] The find was the result of two years of excavation. Initially, the discovery consisted of a single four-month-old infant mummy.[2]
The infant was named Yasmine by her discoverers after a child whose name was mentioned in a manuscript discovered on-site. The infant was clothed and fully interred only 40 cm below ground, she was laid on her back alone in the grave, her head resting on a smooth stone. Yasmine was carefully wrapped in medical gauze and immobilized with splinting devices by the team and transported from the grotto to a customized laboratory, created by the Discoverers. Multiple other remains were found following the discovering, include seven bodies (four infants and three adults) as well as skeletal remains of several others.[3]
Analysis[]
The grotto[]

'Asi-al-Hadath Grotto is in the vicinity of Hadath-El-Gibbet.[4] The high altitude of the grotto makes access or regular use of it as living quarters difficult.[5] Yet, there is evidence of organized communal arrangements, a man-made water reservoir (3.5m x 1.4 m surface, 1.5 m depth, and 8 cubic meters volume); a stone basin for grinding grain by hand; and two well-like openings, probably used for retrieval and storage of water.[1] The grotto contains two main rooms: a large living quarter and the grave-yard room.[6]
Preservation[]
The preliminary examination of the bodies revealed that they were naturally mummified. The grotto in which they had been interred acted as a perfect cast for the buried bodies, eliminating the formation of air pockets that normally facilitate the process of decomposition. Moreover, the low humidity of the grotto's air and the lack of organisms in its soil slowed the total decay of the bodies.[7]
Dates[]
Research carried out by the GERSL [2] corroborated the date of 1283 AD, when the area around the cave was part of the County of Tripoli.[3]
Historical overview[]
Between 1102 and 1289, Mount-Lebanon including Hadath El Jebbeh fell within the confines of the County of Tripoli.[8] Tripoli was one of the four fundamental city units of the Crusaders Kingdom of Jerusalem [9] the County of Edessa, the Principality of Antioch, and the Royal Territories.[10] Meanwhile, the Mamelukes overtook Egypt, Syria, and Palestine, and set out to conquer Lebanon and expel the Crusaders. As modern scholars have pointed out, the Maronites, who constituted the majority population of that County,[11] presented a constant obstacle to the Mamluk:[12] "in fact, the effective military assistance rendered by the Maronites to the Franks of Tripoli must have been one of the factors that helped the County face repeated Muslim attacks successfully and outlast the other Crusader states."[13] It was not long before the Mamluks realized that in order for them to capture Tripoli, they must first subdue the Maronites.[14]
The Mamluks launched several assaults against the highland of Tripoli devastating Gibbet Bsharri, Baqufa, Kfarsaroun, Hasrun, al-Hadath and others between 1250 and 1289.[15] One particular raid was recorded in Ibn 'Abd az-Zahir's chronicle during his service as Secretary of the Court of three Mamluk Sultans (1223-1292 AD). Under the title of "the Account of Capturing the Patriarch of al-Hadath from the Region of Tripoli", he wrote: "It happened that a Patriarch of the region of Tripoli annoyed, behaved insolently, became haughty, and frightened the governor of Tripoli and all the Francs. He led astray these people of those mountains and the people of those valleys who are of the strayed people. And this continued until he was feared by every neighbor. He entrenched himself in al-Hadath and held his nose high with arrogance and no one succeeded in tricking him... It happened that the governors of the Sultan ambushed him several times but did not find him. Then the Turkmans sought him in his place and tricked him so that they captured and blind-folded him and took him prisoner. The Patriarch was one of the infidels and their impious ones, hence the Muslims were relieved of him and were spared his wickedness. His capture was a great conquest, greater even more than the conquest of a stronghold or a fortress..."[16]
Reports similar to that of Ibn 'Abd az-Zahir are to be found in the margins of two Bibles from the al-Hadath region near the Monastery of 'Mar Aboun' (Monastery of Saint Anthony of Qozhayya). The two Bibles were discovered by Patriarch Istephan Duwayhi during his research and writing of Tarikh al-Azmina between 1670 and 1704. The first Bible contains a note written in 1283 by an anonymous Christian who witnessed these events. The account contained in the second Bible is a copy of the first one, and it is dated 1504 AD. These accounts testify to the dramatic events unfolding in 'Asi al-Hadath during the 13th century. The witness and writer of the original account of 1283 tells us that: ‘’’ "On August 22, 1283 the Muslim soldiers headed toward al-Hadath where the inhabitants took refuge in a magnificent and inaccessible grotto called al-'Asi. The grotto was besieged for seven years. The soldiers received it through the Aman _ a pledge of security and a promise of protection given by Muslim(s) to non-Muslim(s) (Jews and Christians) belonging to dar al-harb (Abode of War) for a specific period of time. Those non-Muslims who belong to dar al-salam (Adobe of Islam) fall under the dhimmi status.,[17] then burned its prefecture (the al-Hadath village) by fire and took the women captives." ‘’’ [18]
These two references are testimonies about a tragic event that occurred in al-Hadath. The accounts coincide in time, place, and action, and confirm an offensive against al-Hadath, thereby providing some historical context for our understanding of this archaeological discovery.[3]
The artifacts[]

Apart from the mummies themselves, a wealth of artifacts found at the site suggest that the people buried there were Maronites from the al-Hadath village, and that their death occurred circa 1283, which corresponds to the reign of the Mamluks and the presence of the Crusaders. Among the many examples of medieval pottery excavated, one pot attracts attention by its Arabic inscription: "This belongs to Boutros from al-Hadath.".[19] Artistic and archaeological significance is manifested in the designs and motifs embroidered on textiles which are identical to designs found in the Syriac Rabbula Gospels, a 6th-century artistic masterpiece which belonged to the Maronite Patriarchate until the mid-15th century, but is now housed in Florence, Italy. A striking copy of two peacocks facing one another with a tree of life in-between remains vivid in color seven hundred years later.[20] From the Grotto over twenty manuscripts were unearthed. One of which is in Syriac and is a Maronite hymnody, another is in Arabic and bears the name and signature of George son of David, the Archdeacon of al-Hadath.[21] Among the discovered items, several engraved wooden double-toothed combs, thin teeth on one side and coarse on the other, are identical to the combs used by Mamluk women in Egypt and are on display at the Museum of Islamic Art in Cairo, Egypt.[22] Many poles, arrows, and notches have been found to be identical with the Mamluk era arrows now on display at the Traditional Art Museum of Aleppo in Syria.[23] An assortment of Crusader and Mamluk coins also invite the speculation that these mummies are of the 13th century.[24] However, the most important and uncontestable evidence comes from the mummies themselves.
Yasmine's clothes[]
Yasmine wore beneath her shroud three dresses [25] one blue, a beige dress over it, and a more elaborate dark beige dress embroidered with silk threads over both. Her head was covered with a headdress under which she wore a headband made of silk. She was adorned with one earring, and a necklace garnished with mouth-blown glass pearls and two coin pieces dated to the era of the Sultan Mamluk Baybars.[25]
Customs and rituals[]

Compared to the mummies of Egypt, these mummies were simply buried without any long term or elaborate preparation. A preliminary observation of the mummies already reveals striking parallels with customs and rituals still practiced in present-day Lebanon. An adult woman was found buried with her eighteen-month-old child. The infant was placed at the mother's left shoulder. We are almost certain that the infant is hers since this method of burial is still practiced today in Lebanon when the deaths of both mother and child are caused by complications in the birthing process.[21] Most interesting of all is the adult woman who is buried with her infant. She is found with pieces of cotton and cloth inserted in both her vaginal and anal orifices. This preparation of the deceased for viewing is still practiced to our day. In some areas of Lebanon such as the Bekaa Valley, the cotton and cloth pieces are wrapped around a small onion and inserted in the human orifices. Another cultural manifestation is the presence of long black human hair found between Yasmine's toes. It probably belonged to the child's mother. Local tradition has it, that the grieving mother will pull out her hair while kissing the feet of her lost child.[26] A talismanic prayer recovered from the grotto requests the intercession of saints in curing a sick child. This prayer resembles the ones still in practice and use among the Maronites in present-day Lebanon, e.g.,. 'Kitab Mar Antonios' -- the Talisman of Saint Anthony of Qozhayya.[27] A wooden house key was found on the body of one of the adult female mummies. In accordance with traditional customs, at the funeral of the last surviving member of a family, the key to the dead person's house will be tossed over the roof of that house indicating that the house of that family will forever be closed. In this case the person died in a besieged Grotto, so the key was tossed in the grave [28] similar circumstances mourners will comment by saying, "pity this family, their house is forever closed."
Importance[]

- These are the first mummies ever to be discovered in Lebanon.
- An outstanding and unique wooden arrow, discovered complete from tip to nock, with paper fletchings (not feathered, most likely to reduce drag and increase flight trajectory); worth-noting that other fragments of traditional wooden arrows were discovered, mostly with Turkish Nocks style.
- Many similarities exist between the burial of the mummies and some present-day Lebanese burials. For example, one of the infants had long strands of hair between its toes. According to local tradition in some areas of Lebanon today, a mother whose child dies will pull out her hair in lamentation while kissing the feet of her deceased child.[citation needed] Similarly, today in Lebanon, when the last member of a family dies, the key to the family house is thrown over the roof, indicating that no one will live in the house again.[citation needed] The presence of a key in the 'Asi-al Hadath cave may also indicate that the last member of a family had died there as well.
- Textiles were not only worn by the mummies, they were also scattered about the cave. Their robes, made from heavy cotton, are embroidered with squares and diamonds of crosses and flowers, which strongly resemble kilim patterns of Turkish nomads.
Images[]

Man made water basin remains to date inside 'Asi-al-Hadath Grotto.

A wooden key found in the cave.
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Abi Aoun B., Baroudy F., Ghaouch A. Khawaja P and alias Momies du Liban: Rapport préliminaire sur la découverte archaéologique de 'Asi-al-Hadat (XIIIe siècle), France, Édifra, 1994
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Publications | GERSL : Speleology : Lebanon".
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Asi l Hadath - Fortified Cave | GERSL : Speleology : Lebanon".
- ^ Dussaud, R. Topographie Historique de la Syrie Antique, (Paris, 1927), p. 72.
- ^ L'Architecture Libanaise du XV au XIXe Siècle, Beirut, 1985; Renan, E. Mission de Phenicie, (Paris, 1864); and M. Chronologie des plus anciennes installations de Byblos, "Revue Biblique", LVII, 1950, pp. 590-593, 584-603.
- ^ "Liban Souterrain", pp. 10-11.
- ^ Abi Aoun B., Baroudy F., Ghaouch A. Khawaja P and alias Momies du Liban: Rapport préliminaire sur la découverte archaéologique de 'Asi-al-Hadat (XIIIe siècle), France, Édifra, 1993
- ^ Salibi, K. "The Maronites of Lebanon under Frankish and Mamluk Rule (1099-1516)", Arabica; IV (1957), p. 291, 294; and Hiro, D. A History of the Lebanese Civil War, (New York, 1992), p. 1.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica, XVth edition, (1982), pp. 297-310.
- ^ Strayer, J., ed., Dictionary of the Middle Ages, (New York, 1982), vol. 4, p. 30.
- ^ Salibi, p. 288, 291; Richard, J. Le conte de Tripoli sous la dynastie Toulousaine, 1102-1187, (Paris, 1945), p. 86; and de Vitry, J. History of Jerusalem; translated by Stewart, A., (London, 1897), p. 79.
- ^ Hayton, Recueil des Historiens des Croisades, R. H. C. Arménien, (Paris, 1896), pp. 155-156; and Salibi, p. 294. See also de Tyre, G. A History of Deeds Done Beyond the Sea; translated by Babcock, F., (New York, 1943)
- ^ Salibi, p. 294.
- ^ Khoury-Harb, The Maronites, (Beirut, 1985), p. 82; and Salibi, p. 295
- ^ Salibi, p. 294; Al-Maqrizy, Kitab as-suluk li-ma'rifat dual al-Muluk, ed., Mustapha Ziada, (Cairo, 1936), p. 566; and Grousset, R. Histoire des Croisades et du Royaume Franc de Jerusalem, (Paris, 1936), p. 640
- ^ Ibn `Abd Al-Zahir, Tasrif al-'usur bi sirat al-Malik al-Mansur, ed., Murad Kamil, (Cairo, 1961), p. 4. Translation mine. Elsewhere, Salibi, K. The Maronite Church in the Middle Ages and its Union with Rome, Oriens Christianus, vol. 40, (1956) p. 98
- ^ The Encyclopedia of Islam_ (Leiden, 1960), p. 426.
- ^ Duwayhi, I., Patriarch T'arikh al-Azmina, ed., Fahd, B., (Beirut, 1983), p. 261. Translation mine. Elsewhere, Salibi, "Arabica", p. 294-295; and Momies Du Liban, p. 94
- ^ Momies du Liban, pp. 202-204
- ^ Momies du Liban, pp. 78-80.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Momies du Liban, pp. 146-210
- ^ Momies du Liban, p. 215, 240, 245, 251; and `Abd Ar-Raziq, A. La Femme au temps des Mamlouks en Egypte, (Cairo, 1973), pp. 321-322
- ^ Momies du Liban, pp. 206-208
- ^ Momies du Liban, pp. 198-201. See Slumberger, G. Numismatique de l'Orient Latin, (Paris, 1878); and Cox, D. The Tripolis Hoard of French Seignorial and Crusader's Coins, (New York, 1933)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Momies du Liban: Rapport préliminaire sur la découverte archéologique de 'Asi-l-Hadat (XIIIe siècle), GERSL, (France, 1993), p. 58.
- ^ Momies du Liban, p. 40
- ^ Salame-Sarkis, H. Talisman-higab Syriaque Trouve dans la Grotte-Refuge de Hadath al-Gubbeh dans le Liban Nord, "Liban Souterrain", (1989), July No.2, pp. 36-39
- ^ Momies du Liban, pp. 46-48
Books[]
- Abi Aoun B., Baroudy F., Ghaouch A. Khawaja P and alias Momies du Liban: Rapport préliminaire sur la découverte archaéologique de 'Asi-al-Hadat (XIIIe siècle), France, Édifra, 1993
External links[]
- Maronites
- Mummies
- Archaeological sites in Lebanon
- Archaeology of death
- Anthropology
- County of Tripoli
- 1990 archaeological discoveries

