Methidathion
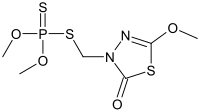
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
S-[(5-Methoxy-2-oxo-1,3,4-thiadiazol-3(2H)-yl)methyl] O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate | |
| Other names
Supracide, Ultracide, Suprathion
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.227 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C6H11N2O4PS3 |
| Molar mass | 302.331 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Methidathion is an organophosphate insecticide;[1] its use is banned in the European Union and USA.[2]
Methidathion has been used as an insecticide in many countries to control caterpillars of Indarbela quadrinotata.[3]
In 2012, residues on common vegetables were found in Thai vegetables at levels 100 times the legal limit, Thailand routinely uses many pesticides banned in the US and EU and in amounts far exceeding limits.[4]
References[]
- ^ Gokalp, Osman; Gulle, Kanat; Sulak, Osman; Cicek, Ekrem; Altuntas, Irfan (2016). "The effects of methidathion on liver: role of vitamins E and C". Toxicology and Industrial Health. 19 (2–6): 63–67. doi:10.1191/0748233703th176oa. PMID 15697176. S2CID 23209774.
- ^ [1]
- ^ "CONTROL OF BARK EATING CATERPILLAR" (PDF). German Development Cooperation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 August 2016. Retrieved 13 July 2016.
- ^ http://www.nationmultimedia.com/life/The-pesticides-on-our-plates-30188702.html
External links[]
Categories:
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
- Organophosphate insecticides
- Thiadiazoles
- Ethers
- Phosphorodithioates
- Organic compound stubs