Northern Europe
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2015) |

Northern Europe is a loosely defined geographical and cultural region in Europe. Narrower definitions may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology. A broader definition would include the area of Europe north of the Alps (but excluding Eastern Europe).
Historically, when Europe was dominated by the Roman Empire, the parts of Europe that were not near the Mediterranean region were deemed Northern European,[citation needed] including southern Germany, all of the Low Countries, and Austria. This meaning is still used today in some contexts, for example, discussions of the Northern Renaissance.
During the Early Middle Ages, the Roman Catholic Church expanded into Northern Europe and spread Christianity among the Germanic peoples.[1] Christianity reached the Vikings and other Scandinavians in later centuries. The Latin alphabet gradually replaced the runic alphabet in Scandinavia and England as the influence of Catholic Christianity spread northward from Rome, leading to English, German, Dutch, Danish, Norwegian, Swedish, and Icelandic. During the Protestant Reformation, which began in Northern Europe according to some looser definitions of the region, Protestantism was embraced in Northern Europe to an extent unseen in other parts of Europe such as Southern Europe and Eastern Europe, and the vast majority of Northern European countries, by any definition, are mostly Protestant historically.
Climate[]

The climate is mainly Humid continental climate (Dfb), Subarctic climate (Dfc), and Tundra (ET).
Geography[]
Northern Europe might be defined roughly to include some or all of the following areas: British Isles, Fennoscandia, the peninsula of Jutland, the Baltic plain that lies to the east and the many islands that lie offshore from mainland Northern Europe and the main European continent. In some cases, Greenland is also included.
The area is partly mountainous, including the northern volcanic islands of Iceland and Jan Mayen, and the mountainous western seaboard, Scotland and Scandinavia, and also often includes part of the large plain east of the Baltic sea.
The entire region's climate is at least mildly affected by the Gulf Stream. From the west climates vary from maritime and maritime subarctic climates. In the north and central climates are generally subarctic or Arctic and to the east climates are mostly subarctic and temperate/continental.
Just as both climate and relief are variable across the region, so too is vegetation, with sparse tundra in the north and high mountains, boreal forest on the north-eastern and central regions temperate coniferous forests (formerly of which a majority was in the Scottish Highlands and south west Norway) and temperate broadleaf forests growing in the south, west and temperate east.
Classifications[]
There are various definitions of Northern Europe which often include the Nordic countries and the Baltic states and sometimes the British Isles, northern Germany, northern Belarus and northwest Russia.
CIA World Factbook[]
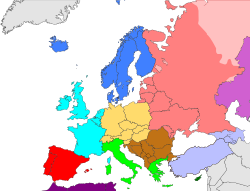
In the CIA World Factbook, the description of each country includes information about "Location" under the heading "Geography", where the country is classified into a region. The following countries are included in their classification "Northern Europe":[2]
- Denmark
- Finland
- Iceland
- Norway
- Sweden
as well as the dependent areas:
- Faroe Islands
- Jan Mayen
- Svalbard
In this classification Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania are included in Eastern Europe.
EuroVoc[]

EuroVoc is a multilingual thesaurus maintained by the Publications Office of the European Union, giving definitions of terms for official use. In the definition of "Northern Europe", the following countries are included:[3]
- Estonia
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Denmark
- Finland
- Iceland
- Norway
- Sweden
as well as the dependent area:
- Faroe Islands
UN geoscheme classification[]

The United Nations geoscheme is a system devised by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) which divides the countries of the world into regional and subregional groups, based on the M49 coding classification. The partition is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories.[4]
In the UN geoscheme, the following countries are classified as Northern Europe:[4]
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Norway
- Sweden
- United Kingdom
as well as the dependent areas:
- Åland Islands
- Channel Islands
- Guernsey
- Jersey
- Sark
- Faroe Islands
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
Demographics[]
This section does not cite any sources. (December 2019) |

Countries in Northern Europe generally have developed economies and some of the highest standards of living in the world. They often score highly on surveys measuring quality of life, such as the Human Development Index. They generally have a small population relative to their size, most of whom live in cities. Most peoples living in Northern Europe are traditionally Protestant Christians, although many are non-practising. There are also growing numbers of non-religious people and people of other religions, especially Muslims, due to immigration. The quality of education in much of Northern Europe is rated highly in international rankings, with Estonia and Finland topping the list among the OECD countries in Europe. The Hansa group in the European Union comprises most of the Northern European states, plus Ireland and the Netherlands.
See also[]
- Arctic
- Arctic Circle
- Baltic languages
- Baltic region
- Baltic states
- Baltoscandia
- British Isles
- Central Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Euroregion Baltic
- Finno-Ugric languages
- Germanic languages
- Nordic-Baltic Eight
- Nordic Council
- Nordic countries
- Nordic Estonia
- North Sea Region
- Northern Dimension
- Northern Future Forum
- Northwestern Europe
- Sápmi
- Scandinavia
- Southern Europe
- Western Europe
References[]
- ^ Tanner, Norman. New Short History of the Catholic Church. p. 41.
- ^ CIA. "The World Factbook".
- ^ Publications Office of the European Union. "EU Vocabularies 7206 Europe". EuroVoc.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "UNSD — Methodology". unstats.un.org. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
External links[]
 Media related to Northern Europe at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Northern Europe at Wikimedia Commons
- Northern Europe
- Regions of Europe