Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a polymer consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane of most bacteria, forming the cell wall. The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the N-acetylmuramic acid is a peptide chain of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer.[1] Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. Peptidoglycan is also involved in binary fission during bacterial cell reproduction.
The peptidoglycan layer is substantially thicker in Gram-positive bacteria (20 to 80 nanometers) than in Gram-negative bacteria (7 to 8 nanometers).[2] Depending on pH growth conditions, the peptidoglycan forms around 40 to 90% of the cell wall's dry weight of Gram-positive bacteria but only around 10% of Gram-negative strains. Thus, presence of high levels of peptidoglycan is the primary determinant of the characterisation of bacteria as Gram-positive.[3] In Gram-positive strains, it is important in attachment roles and serotyping purposes.[4] For both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, particles of approximately 2 nm can pass through the peptidoglycan.[5]
The peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications have been described by Schleifer and Kandler.[6] Archaea do not contain peptidoglycan (murein).[7][6] Some Archea contain pseudopeptidoglycan (pseudomurein).[8]
Structure[]

The peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall is a crystal lattice structure formed from linear chains of two alternating amino sugars, namely N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc or NAGA) and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc or NAMA). The alternating sugars are connected by a β-(1,4)-glycosidic bond. Each MurNAc is attached to a short (4- to 5-residue) amino acid chain, containing L-alanine, D-glutamic acid, meso-diaminopimelic acid, and D-alanine in the case of Escherichia coli (a Gram-negative bacterium) or L-alanine, D-glutamine, L-lysine, and D-alanine with a 5-glycine interbridge between tetrapeptides in the case of Staphylococcus aureus (a Gram-positive bacterium). Peptidoglycan is one of the most important sources of D-amino acids in nature.
Cross-linking between amino acids in different linear amino sugar chains occurs with the help of the enzyme DD-transpeptidase and results in a 3-dimensional structure that is strong and rigid. The specific amino acid sequence and molecular structure vary with the bacterial species.[9]

The structure of peptidoglycan. NAG = N-acetylglucosamine (also called GlcNAc or NAGA), NAM = N-acetylmuramic acid (also called MurNAc or NAMA).

Gram-positive cell wall
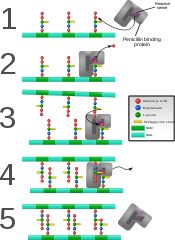
Penicillin binding protein forming cross-links in newly formed bacterial cell wall.
Biosynthesis[]
The peptidoglycan monomers are synthesized in the cytosol and are then attached to a membrane carrier bactoprenol. Bactoprenol transports peptidoglycan monomers across the cell membrane where they are inserted into the existing peptidoglycan.[10]
In the first step of peptidoglycan synthesis, glutamine, which is an amino acid, donates an amino group to a sugar, fructose 6-phosphate. This turns fructose 6-phosphate into . In step two, an acetyl group is transferred from acetyl CoA to the amino group on the glucosamine-6-phosphate creating .[11] In step three of the synthesis process, the N-acetyl-glucosamine-6-phosphate is isomerized, which will change N-acetyl-glucosamine-6-phosphate to .[11]
In step 4, the N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphate, which is now a monophosphate, attacks UTP. Uridine triphosphate, which is a pyrimidine nucleotide, has the ability to act as an energy source. In this particular reaction, after the monophosphate has attacked the UTP, an inorganic pyrophosphate is given off and is replaced by the monophosphate, creating UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (2,4). (When UDP is used as an energy source, it gives off an inorganic phosphate.) This initial stage, is used to create the precursor for the NAG in peptidoglycan.
In step 5, some of the UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) is converted to UDP-MurNAc (UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid) by the addition of a lactyl group to the glucosamine. Also in this reaction, the C3 hydroxyl group will remove a phosphate from the alpha carbon of phosphoenolpyruvate. This creates what is called an enol derivative that will be reduced to a “lactyl moiety” by NADPH in step six.[11]
In step 7, the UDP–MurNAc is converted to UDP-MurNAc pentapeptide by the addition of five amino acids, usually including the dipeptide D-alanyl-D-alanine.[11] Each of these reactions requires the energy source ATP.[11] This is all referred to as Stage one.
Stage two occurs in the cytoplasmic membrane. It is in the membrane where a lipid carrier called bactoprenol carries peptidoglycan precursors through the cell membrane. Bactoprenol will attack the UDP-MurNAc penta, creating a PP-MurNac penta, which is now a lipid. UDP-GlcNAc is then transported to MurNAc, creating Lipid-PP-MurNAc penta-GlcNAc, a disaccharide, also a precursor to peptidoglycan.[11] How this molecule is transported through the membrane is still not understood. However, once it is there, it is added to the growing glycan chain.[11] The next reaction is known as tranglycosylation. In the reaction, the hydroxyl group of the GlcNAc will attach to the MurNAc in the glycan, which will displace the lipid-PP from the glycan chain. The enzyme responsible for this is transglycosylase.[11]
Inhibition[]
Some antibacterial drugs such as penicillin interfere with the production of peptidoglycan by binding to bacterial enzymes known as penicillin-binding proteins or DD-transpeptidases.[4] Penicillin-binding proteins form the bonds between oligopeptide crosslinks in peptidoglycan. For a bacterial cell to reproduce through binary fission, more than a million peptidoglycan subunits (NAM-NAG+oligopeptide) must be attached to existing subunits.[12] Mutations in genes coding for transpeptidases that lead to reduced interactions with an antibiotic are a significant source of emerging antibiotic resistance.[13] Muraymycins are one subclass of nucleoside antibiotics which act as competitive inhibitors for the natural substrate UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide (UM5A) of Phospho-N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide translocase (MraY).[14]
Lysozyme, which is found in tears and constitutes part of the body's innate immune system exerts its antibacterial effect by breaking the β-(1,4)-glycosidic bonds in peptidoglycan (see above).
Pseudopeptidoglycan (Pseudomurein)[]
In some archaea, i.e. members of the Methanobacteriales and in the genus Methanopyrus, pseudopeptidoglycan (pseudomurein) has been found.[8] In pseudopeptidoglycan the sugar residues are β-(1,3) linked N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid. This makes the cell walls of such archaea insensitive to lysozyme.[15] The biosynthesis of pseudopeptidoglycan has been described.[16]
References[]
- ^ "Animation of Synthesis of Peptidoglycan Layer".
- ^ Purcell A (18 March 2016). "Bacteria". Basic Biology.
- ^ C.Michael Hogan. 2010. Bacteria. Encyclopedia of Earth. eds. Sidney Draggan and C.J.Cleveland, National Council for Science and the Environment, Washington DC
- ^ a b Salton MR, Kim KS (1996). "Structure". In Baron S, et al. (eds.). Structure. In: Baron's Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). Univ of Texas Medical Branch. ISBN 978-0-9631172-1-2.
- ^ Demchick PH, Koch AL (1 February 1996). "The permeability of the wall fabric of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis". Journal of Bacteriology. 178 (3): 768–73. doi:10.1128/jb.178.3.768-773.1996. PMC 177723. PMID 8550511.
- ^ a b Schleifer, Karl-Heinz; Kandler, Otto (1972). "Peptidoglycan Types of Bacterial Cell Walls and their Taxonomic Implications". Bacteriological Reviews. 36 (4): 407–775. doi:10.1128/MMBR.36.4.407-477.1972. PMC 408328. PMID 4568761.
- ^ Kandler, Otto; Hippe, Hans (1977). "Lack of peptidoglycan in the cell walls of Methanosarcina barkeri". Archives of Microbiology. 113 (1–2): 57–60. doi:10.1007/BF00428580. PMID 889387.
- ^ a b Kandler, Otto; König, Helmut (1998). "Cell wall polymers in Archaea (Archaebacteria)". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 54 (4): 305–308. doi:10.1007/s000180050156. PMID 9614965.
- ^ Ryan KJ, Ray CG, eds. (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 978-0-8385-8529-0.
- ^ "II. THE PROKARYOTIC CELL: BACTERIA". Archived from the original on 26 July 2010. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h White, D. (2007). The physiology and biochemistry of prokaryotes (3rd ed.). NY: Oxford University Press Inc.
- ^ Bauman R (2007). 2nd (ed.). Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy. Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 978-0-8053-7679-1.
- ^ Spratt BG (April 1994). "Resistance to antibiotics mediated by target alterations". Science. 264 (5157): 388–93. Bibcode:1994Sci...264..388S. doi:10.1126/science.8153626. PMID 8153626. S2CID 30578841.
- ^ Saeid Malek Zadeh (September 2, 2020). "Theoretical Study of Intermolecular Interactions between Critical Residues of Membrane Protein MraYAA and Promising Antibiotic Muraymycin D2". ACS Omega. 5 (36): 22739–22749. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c01551. PMC 7495448. PMID 32954121. S2CID 221782183.
- ^ Madigan, M. T., J. M. Martinko, P. V. Dunlap, and D. P. Clark. Brock biology of microorganisms. 12th ed. San Francisco, CA: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings, 2009.
- ^ König, Helmut; Kandler, Otto; Hammes, Walter (1989). "Biosynthesis of pseudomurein: isolation of putative precursors from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum". Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 35 (1): 176–181. doi:10.1139/m89-027. PMID 2720492.
External links[]
- Membrane biology
- Glycobiology


