Road signs in Sri Lanka

Road signs in Sri Lanka are standardized to closely follow those used in Europe with certain distinctions, and a number of changes have introduced road signs that suit as per local road and system. Sri Lankan government announced by a gazette that aimed to get a facelift and introduction of over 100 new road traffic signs. The new change will be replaced in colour and sizes and introduction of Variable-message sign & electronic digital sign boards in express highways. The Japanese government has granted LKR 1.24 billion to implement message signs in expressways.[1]
Language applicable traffic sign boards are in Sinhalese, Tamil and English. The motor traffic act (chapter 203) describes road traffic signs.[2]
Danger warning signs[]
Regulatory signs[]
Prohibitory signs[]

All vehicles prohibited

No parking
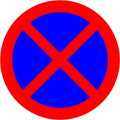
No parking and standing

No parking on odd-numbered days

No parking on even-numbered days
Restrictive signs[]

50 km/h speed limit
Mandatory signs[]
Priority signs[]
Additional panels[]
Additional panels to be used with regulatory signs

School (supplementing a regulatory sign)
Directional informative signs[]
National Highways[]
Provincial Roads[]
Expressways[]
Other signs useful for drivers[]
Route number signs[]
Additional panels[]
Additional Panels to be used with Directional Informative Signs
Miscellaneous signs[]
Road markings[]
Traffic light signals[]
Light signals for pedestrians[]
Prohibited distance[]
Prohibited distance for parking of vehicles
Hazard-warning plates[]
Hazard-warning plates fixed to transport vehicles
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "Sri Lanka's road traffic signs to get a facelift". Sunday Times. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- ^ "The Motor Traffic Act". Retrieved 8 January 2015.
- Road transport in Sri Lanka
- Road signs by country






