Sex hormone
| Sex hormone | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
 Estradiol, an important estrogen sex hormone in both women and men. | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Sex steroid; Gonadal steroid |
| Use | Various |
| Biological target | Sex hormone receptors |
| Chemical class | Steroidal; Nonsteroidal |
| In Wikidata | |
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors.[1] The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effects are mediated by slow genomic mechanisms through nuclear receptors as well as by fast nongenomic mechanisms through membrane-associated receptors and signaling cascades.[2] The polypeptide hormones luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone are usually not regarded as sex hormones, although they play major sex-related roles.
Production[]
Natural sex hormones are made by the gonads (ovaries or testes),[3] by adrenal glands, or by conversion from other sex steroids in other tissue such as liver or fat.[4]
| Sex | Sex hormone | Reproductive phase |
Blood production rate |
Gonadal secretion rate |
Metabolic clearance rate |
Reference range (serum levels) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI units | Non-SI units | ||||||
| Men | Androstenedione | –
|
2.8 mg/day | 1.6 mg/day | 2200 L/day | 2.8–7.3 nmol/L | 80–210 ng/dL |
| Testosterone | –
|
6.5 mg/day | 6.2 mg/day | 950 L/day | 6.9–34.7 nmol/L | 200–1000 ng/dL | |
| Estrone | –
|
150 μg/day | 110 μg/day | 2050 L/day | 37–250 pmol/L | 10–70 pg/mL | |
| Estradiol | –
|
60 μg/day | 50 μg/day | 1600 L/day | <37–210 pmol/L | 10–57 pg/mL | |
| Estrone sulfate | –
|
80 μg/day | Insignificant | 167 L/day | 600–2500 pmol/L | 200–900 pg/mL | |
| Women | Androstenedione | –
|
3.2 mg/day | 2.8 mg/day | 2000 L/day | 3.1–12.2 nmol/L | 89–350 ng/dL |
| Testosterone | –
|
190 μg/day | 60 μg/day | 500 L/day | 0.7–2.8 nmol/L | 20–81 ng/dL | |
| Estrone | Follicular phase | 110 μg/day | 80 μg/day | 2200 L/day | 110–400 pmol/L | 30–110 pg/mL | |
| Luteal phase | 260 μg/day | 150 μg/day | 2200 L/day | 310–660 pmol/L | 80–180 pg/mL | ||
| Postmenopause | 40 μg/day | Insignificant | 1610 L/day | 22–230 pmol/L | 6–60 pg/mL | ||
| Estradiol | Follicular phase | 90 μg/day | 80 μg/day | 1200 L/day | <37–360 pmol/L | 10–98 pg/mL | |
| Luteal phase | 250 μg/day | 240 μg/day | 1200 L/day | 699–1250 pmol/L | 190–341 pg/mL | ||
| Postmenopause | 6 μg/day | Insignificant | 910 L/day | <37–140 pmol/L | 10–38 pg/mL | ||
| Estrone sulfate | Follicular phase | 100 μg/day | Insignificant | 146 L/day | 700–3600 pmol/L | 250–1300 pg/mL | |
| Luteal phase | 180 μg/day | Insignificant | 146 L/day | 1100–7300 pmol/L | 400–2600 pg/mL | ||
| Progesterone | Follicular phase | 2 mg/day | 1.7 mg/day | 2100 L/day | 0.3–3 nmol/L | 0.1–0.9 ng/mL | |
| Luteal phase | 25 mg/day | 24 mg/day | 2100 L/day | 19–45 nmol/L | 6–14 ng/mL | ||
show
Notes and sources
Notes: "The concentration of a steroid in the circulation is determined by the rate at which it is secreted from glands, the rate of metabolism of precursor or prehormones into the steroid, and the rate at which it is extracted by tissues and metabolized. The secretion rate of a steroid refers to the total secretion of the compound from a gland per unit time. Secretion rates have been assessed by sampling the venous effluent from a gland over time and subtracting out the arterial and peripheral venous hormone concentration. The metabolic clearance rate of a steroid is defined as the volume of blood that has been completely cleared of the hormone per unit time. The production rate of a steroid hormone refers to entry into the blood of the compound from all possible sources, including secretion from glands and conversion of prohormones into the steroid of interest. At steady state, the amount of hormone entering the blood from all sources will be equal to the rate at which it is being cleared (metabolic clearance rate) multiplied by blood concentration (production rate = metabolic clearance rate × concentration). If there is little contribution of prohormone metabolism to the circulating pool of steroid, then the production rate will approximate the secretion rate." Sources: See template. | |||||||
Types[]
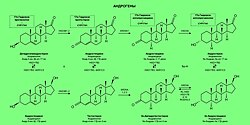
In many contexts, the two main classes of sex hormones are androgens and estrogens, of which the most important human derivatives are testosterone and estradiol, respectively. Other contexts will include progestogens as a third class of sex steroids, distinct from androgens and estrogens. Progesterone is the most important and only naturally occurring human progestogen. In general, androgens are considered "male sex hormones", since they have masculinizing effects, while estrogens and progestogens are considered "female sex hormones"[5] although all types are present in each sex at different levels.
Sex hormones include:
- Progestogens
- Pregnenolone → Progesterone → Allopregnanedione → Allopregnanolone
- 17α-Hydroxypregnenolone → 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone
- Androgens
- Dehydroepiandrosterone → Androstenedione → Androstanedione → Androsterone
- Androstenediol → Testosterone → Dihydrotestosterone → Androstanediol
- Estrogens
- 2-Hydroxyestrone ← Estrone → 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- 2-Hydroxyestradiol ← Estradiol → Estriol → Estetrol
Synthetic sex steroids[]
There are also many synthetic sex steroids. Synthetic androgens are often referred to as anabolic steroids. Synthetic estrogens and progestins are used in methods of hormonal contraception. Ethinylestradiol is a semi-synthetic estrogen. Specific compounds that have partial agonist activity for steroid receptors, and therefore act in part like natural steroid hormones, are in use in medical conditions that require treatment with steroid in one cell type, but where systemic effects of the particular steroid in the entire organism are only desirable within certain limits.[6]
See also[]
- List of investigational sex-hormonal agents
- Sexual motivation and hormones
- Sex hormone therapy
References[]
- ^ Guerriero, G (April 2009). "Vertebrate sex steroid receptors: evolution, ligands, and neurodistribution". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1163: 154–68. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04460.x. PMID 19456336.
- ^ Thakur, MK; Paramanik, V (2009). "Role of steroid hormone coregulators in health and disease". Hormone Research. 71 (4): 194–200. doi:10.1159/000201107. PMID 19258710.
- ^ Brook, CG (1999). "Mechanism of puberty". Hormone Research. 51 Suppl 3 (3): 52–4. doi:10.1159/000053162. PMID 10592444.
- ^ Catherine Panter-Brick; Agustín Fuentes. "Glossary". Health, Risk, and Adversity - Volume 2 of Studies of the Biosocial Society. Berghahn Books, 2011. p. 280.
- ^ ElAttar, TM; Hugoson, A (1974). "Comparative metabolism of female sex steroids in normal and chronically inflamed gingiva of the dog". Journal of Periodontal Research. 9 (5): 284–9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.1974.tb00683.x. PMID 4281823.
- ^ Copland, JA; Sheffield-Moore, M; Koldzic-Zivanovic, N; Gentry, S; Lamprou, G; Tzortzatou-Stathopoulou, F; Zoumpourlis, V; Urban, RJ; Vlahopoulos, SA (June 2009). "Sex steroid receptors in skeletal differentiation and epithelial neoplasia: is tissue-specific intervention possible?". BioEssays. 31 (6): 629–41. doi:10.1002/bies.200800138. PMID 19382224.
External links[]
- Sex+Steroid+Hormones at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
show
Endogenous steroids | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursors |
| ||||||
| Corticosteroids |
| ||||||
| Sex steroids |
| ||||||
| Neurosteroids |
| ||||||
| Others |
| ||||||
show
Major chemical drug groups – based upon the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System | |
|---|---|
| gastrointestinal tract / metabolism (A) |
|
| blood and blood forming organs (B) |
|
| cardiovascular system (C) |
|
| skin (D) |
|
| genitourinary system (G) |
|
| endocrine system (H) |
|
| infections and infestations (J, P, QI) |
|
| malignant disease (L01–L02) |
|
| immune disease (L03–L04) |
|
| muscles, bones, and joints (M) |
|
| brain and nervous system (N) |
|
| respiratory system (R) |
|
| sensory organs (S) |
|
| other ATC (V) |
|
| |
| show Sex steroidergics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| show | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| National libraries | |
| Other | |
- Sex hormones
- Animal reproductive system
- Human sexuality
- Animal sexuality
- Hormones of the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad axis
- Intersex and medicine
- CS1: long volume value
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Articles with GND identifiers
- Articles with LCCN identifiers
- Articles with NDL identifiers
- Articles with MA identifiers
- Articles with multiple identifiers