Hydromadinone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
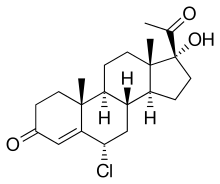
| Formula | C21H29ClO3 |
| Molar mass | 364.91 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Hydromadinone (INN), also known as 6α-chloro-17α-hydroxyprogesterone, is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group which was patented in 1967 but was never marketed.[1] The C17α acetate ester of hydromadinone, hydromadinone acetate, also exists, but similarly was never marketed.[1]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ a b Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. p. 1037. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
Categories:
- Drugs not assigned an ATC code
- Diketones
- Organochlorides
- Pregnanes
- Progestogens
- Abandoned drugs
- Steroid stubs