Start codon
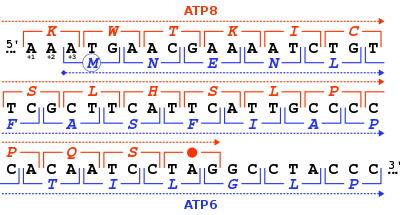
The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and Archaea and a N-formylmethionine (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria and plastids. The most common start codon is AUG (i.e., ATG in the corresponding DNA sequence).
The start codon is often preceded by a 5' untranslated region (5' UTR). In prokaryotes this includes the ribosome binding site.
Alternative start codons[]
Alternative start codons are different from the standard AUG codon and are found in both prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) and eukaryotes. Alternate start codons are still translated as Met when they are at the start of a protein (even if the codon encodes a different amino acid otherwise). This is because a separate transfer RNA (tRNA) is used for initiation.[1]
Eukaryotes[]
Alternate start codons (non-AUG) are very rare in eukaryotic genomes. However, naturally occurring non-AUG start codons have been reported for some cellular mRNAs.[2] Seven out of the nine possible single-nucleotide substitutions at the AUG start codon of dihydrofolate reductase were functional as translation start sites in mammalian cells.[3] In addition to the canonical Met-tRNA Met and AUG codon pathway, mammalian cells can initiate translation with leucine using a specific leucyl-tRNA that decodes the codon CUG.[4][5]
Candida albicans uses a CAG start codon.[6]
Prokaryotes[]
Prokaryotes use alternate start codons significantly, mainly GUG and UUG. These alternate start codons and the frequency of their use compared to eukaryotes has been studied and shown to refute the common ancestor theory.[7]
E. coli uses 83% AUG (3542/4284), 14% (612) GUG, 3% (103) UUG[8] and one or two others (e.g., an AUU and possibly a CUG).[9][10]
Well-known coding regions that do not have AUG initiation codons are those of lacI (GUG)[11][12] and lacA (UUG)[13] in the E. coli lac operon. Two more recent studies have independently shown that 17 or more non-AUG start codons may initiate translation in E. coli.[14][15]
Mitochondria[]
Mitochondrial genomes use alternate start codons more significantly (AUA and AUU in humans).[7] Many such examples, with codons, systematic range, and citations, are given in the NCBI list of translation tables.[16]
Standard genetic code[]
| Amino-acid biochemical properties | Nonpolar | Polar | Basic | Acidic | Termination: stop codon |
| 1st base |
2nd base | 3rd base | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | C | A | G | ||||||
| U | UUU | (Phe/F) Phenylalanine | UCU | (Ser/S) Serine | UAU | (Tyr/Y) Tyrosine | UGU | (Cys/C) Cysteine | U |
| UUC | UCC | UAC | UGC | C | |||||
| UUA | (Leu/L) Leucine | UCA | UAA | Stop (Ochre)[B] | UGA | Stop (Opal)[B] | A | ||
| UUG[A] | UCG | UAG | Stop (Amber)[B] | UGG | (Trp/W) Tryptophan | G | |||
| C | CUU | CCU | (Pro/P) Proline | CAU | (His/H) Histidine | CGU | (Arg/R) Arginine | U | |
| CUC | CCC | CAC | CGC | C | |||||
| CUA | CCA | CAA | (Gln/Q) Glutamine | CGA | A | ||||
| CUG[A] | CCG | CAG | CGG | G | |||||
| A | AUU | (Ile/I) Isoleucine | ACU | (Thr/T) Threonine | AAU | (Asn/N) Asparagine | AGU | (Ser/S) Serine | U |
| AUC | ACC | AAC | AGC | C | |||||
| AUA | ACA | AAA | (Lys/K) Lysine | AGA | (Arg/R) Arginine | A | |||
| AUG[A] | (Met/M) Methionine | ACG | AAG | AGG | G | ||||
| G | GUU | (Val/V) Valine | GCU | (Ala/A) Alanine | GAU | (Asp/D) Aspartic acid | GGU | (Gly/G) Glycine | U |
| GUC | GCC | GAC | GGC | C | |||||
| GUA | GCA | GAA | (Glu/E) Glutamic acid | GGA | A | ||||
| GUG | GCG | GAG | GGG | G | |||||
- A The codon AUG both codes for methionine and serves as an initiation site: the first AUG in an mRNA's coding region is where translation into protein begins.[17] The other start codons listed by GenBank are rare in eukaryotes and generally codes for Met/fMet.[18]
- B ^ ^ ^ The historical basis for designating the stop codons as amber, ochre and opal is described in an autobiography by Sydney Brenner[19] and in a historical article by Bob Edgar.[20]
Engineered start codons[]
Engineered initiator tRNAs (tRNAfMet2 with CUA anticodon) have been used to initiate translation at the amber stop codon UAG.[21] This type of engineered tRNA is called a nonsense suppressor tRNA because it suppresses the translation stop signal that normally occurs at UAG codons. One study has shown that the amber initiator tRNA does not initiate translation to any measurable degree from genomically-encoded UAG codons, only plasmid-borne reporters with strong upstream Shine-Dalgarno sites.[22]
See also[]
- Central dogma of molecular biology
- Codon
- Messenger RNA
- Missense mRNA
- Stop codon
- Transfer RNA
- Translation
References[]
- ^ Lobanov, A. V.; Turanov, A. A.; Hatfield, D. L.; Gladyshev, V. N. (2010). "Dual functions of codons in the genetic code". Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 45 (4): 257–65. doi:10.3109/10409231003786094. PMC 3311535. PMID 20446809.
- ^ Ivanov IP, Firth AE, Michel AM, Atkins JF, Baranov PV (2011). "Identification of evolutionarily conserved non-AUG-initiated N-terminal extensions in human coding sequences". Nucleic Acids Research. 39 (10): 4220–4234. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr007. PMC 3105428. PMID 21266472.
- ^ Peabody, D. S. (1989). "Translation initiation at non-AUG triplets in mammalian cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 264 (9): 5031–5. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)83694-8. PMID 2538469.
- ^ Starck, S. R.; Jiang, V; Pavon-Eternod, M; Prasad, S; McCarthy, B; Pan, T; Shastri, N (2012). "Leucine-tRNA initiates at CUG start codons for protein synthesis and presentation by MHC class I". Science. 336 (6089): 1719–23. Bibcode:2012Sci...336.1719S. doi:10.1126/science.1220270. PMID 22745432. S2CID 206540614.
- ^ Dever, T. E. (2012). "Molecular biology. A new start for protein synthesis". Science. 336 (6089): 1645–6. doi:10.1126/science.1224439. PMID 22745408. S2CID 44326947.
- ^ Santos, MA; Keith, G; Tuite, MF (February 1993). "Non-standard translational events in Candida albicans mediated by an unusual seryl-tRNA with a 5'-CAG-3' (leucine) anticodon". The EMBO Journal. 12 (2): 607–16. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05693.x. PMC 413244. PMID 8440250.
- ^ a b Watanabe, Kimitsuna; Suzuki, Tsutomu (2001). "Genetic Code and its Variants". Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. doi:10.1038/npg.els.0000810. ISBN 978-0470015902.
- ^ Blattner, F. R.; Plunkett g, G.; Bloch, C. A.; Perna, N. T.; Burland, V.; Riley, M.; Collado-Vides, J.; Glasner, J. D.; Rode, C. K.; Mayhew, G. F.; Gregor, J.; Davis, N. W.; Kirkpatrick, H. A.; Goeden, M. A.; Rose, D. J.; Mau, B.; Shao, Y. (1997). "The Complete Genome Sequence of Escherichia coli K-12". Science. 277 (5331): 1453–1462. doi:10.1126/science.277.5331.1453. PMID 9278503.
- ^ Sacerdot, C.; Fayat, G.; Dessen, P.; Springer, M.; Plumbridge, J. A.; Grunberg-Manago, M.; Blanquet, S. (1982). "Sequence of a 1.26-kb DNA fragment containing the structural gene for E.coli initiation factor IF3: Presence of an AUU initiator codon". The EMBO Journal. 1 (3): 311–315. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01166.x. PMC 553041. PMID 6325158.
- ^ Missiakas, D.; Georgopoulos, C.; Raina, S. (1993). "The Escherichia coli heat shock gene htpY: Mutational analysis, cloning, sequencing, and transcriptional regulation". Journal of Bacteriology. 175 (9): 2613–2624. doi:10.1128/jb.175.9.2613-2624.1993. PMC 204563. PMID 8478327.
- ^ E.coli lactose operon with lacI, lacZ, lacY and lacA genes GenBank: J01636.1
- ^ Farabaugh, P. J. (1978). "Sequence of the lacI gene". Nature. 274 (5673): 765–769. Bibcode:1978Natur.274..765F. doi:10.1038/274765a0. PMID 355891. S2CID 4208767.
- ^ NCBI Sequence Viewer v2.0
- ^ Hecht, Ariel; Glasgow, Jeff; Jaschke, Paul R.; Bawazer, Lukmaan A.; Munson, Matthew S.; Cochran, Jennifer R.; Endy, Drew; Salit, Marc (2017). "Measurements of translation initiation from all 64 codons in E. coli". Nucleic Acids Research. 45 (7): 3615–3626. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx070. PMC 5397182. PMID 28334756.
- ^ Firnberg, Elad; Labonte, Jason; Gray, Jeffrey; Ostermeir, Marc A. (2014). "A comprehensive, high-resolution map of a gene's fitness landscape". Molecular Biology & Evolution. 31 (6): 1581–1592. doi:10.1093/molbev/msu081. PMC 4032126. PMID 24567513.
- ^ Elzanowski, Andrzej; Ostell, Jim. "The Genetic Codes". NCBI. Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- ^ Nakamoto T (March 2009). "Evolution and the universality of the mechanism of initiation of protein synthesis". Gene. 432 (1–2): 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2008.11.001. PMID 19056476.
- ^ Blattner, F. R.; Plunkett g, G.; Bloch, C. A.; Perna, N. T.; Burland, V.; Riley, M.; Collado-Vides, J.; Glasner, J. D.; Rode, C. K.; Mayhew, G. F.; Gregor, J.; Davis, N. W.; Kirkpatrick, H. A.; Goeden, M. A.; Rose, D. J.; Mau, B.; Shao, Y. (1997). "The Complete Genome Sequence of Escherichia coli K-12". Science. 277 (5331): 1453–1462. doi:10.1126/science.277.5331.1453. PMID 9278503.
- ^ Brenner S. A Life in Science (2001) Published by Biomed Central Limited ISBN 0-9540278-0-9 see pages 101-104
- ^ Edgar B (2004). "The genome of bacteriophage T4: an archeological dig". Genetics. 168 (2): 575–82. PMC 1448817. PMID 15514035. see pages 580-581
- ^ Varshney, U.; RajBhandary, U. L. (1990-02-01). "Initiation of protein synthesis from a termination codon". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 87 (4): 1586–1590. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.1586V. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.4.1586. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 53520. PMID 2406724.
- ^ Vincent, Russel M.; Wright, Bradley W.; Jaschke, Paul R. (2019-03-15). "Measuring Amber Initiator tRNA Orthogonality in a Genomically Recoded Organism" (PDF). ACS Synthetic Biology. 8 (4): 675–685. doi:10.1021/acssynbio.9b00021. ISSN 2161-5063. PMID 30856316.
External links[]
- The Genetic Codes. Compiled by Andrzej (Anjay) Elzanowski and Jim Ostell, National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), Bethesda, Maryland, US [1]
- DNA
- Molecular genetics