Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols
This article includes a list of general references, but it remains largely unverified because it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (May 2014) |
| Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols | |
|---|---|
| Script type | Semisyllabary
(letters for onsets and rimes; diacritics for tones) |
| Creator | , Taiwan NLC |
Time period | 1946 to the present, used as ruby characters in Taiwan |
| Related scripts | |
Parent systems | Oracle Bone Script
|
Sister systems | Simplified Chinese, Kanji, Hanja, Chữ Nôm, Khitan large script, Khitan small script |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Bopo, , Bopomofo |
| Unicode | |
Unicode alias | Bopomofo |
Unicode range | U+3100–U+312F, U+31A0–U+31BF |
| Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 臺語方音符號 | ||
| Simplified Chinese | 台语方音符号 | ||
| |||
| Chinese romanization |
|---|
| Mandarin |
| Wu |
| Yue |
| Min |
| Gan |
| Hakka |
| Xiang |
| See also |

Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols (Chinese: 臺語方音符號; TPS: ㄉㄞˊ ㆣ丨ˋ ㄏㆲ 丨ㆬ ㄏㄨˊ ㄏㄜ˫) constitute a system of phonetic notation for the transcription of Taiwanese languages, especially Taiwanese Hokkien. The system was designed by Professor , a member of the National Languages Committee in Taiwan, in 1946.[1] The system is derived from Mandarin Phonetic Symbols by creating additional symbols for the sounds that do not appear in Mandarin phonology. It is one of the phonetic notation systems officially promoted by Taiwan's Ministry of Education.[2]
Symbols[]
There are 49 symbols used in standard Taiwanese Hokkien. Of these 49 symbols, 26 are from the original Mandarin Phonetic Symbols, while 23 are additional, created for Taiwanese languages.
| Initial symbols (21) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ㄅ | ㆠ | ㄆ | ㄇ | ㄉ | ㄊ | ㄋ | ㄌ | ㄍ | ㆣ | ㄎ | ㄫ | ㄏ | ㄐ | ㆢ | ㄑ | ㄒ | ㄗ | ㆡ | ㄘ | ㄙ | |||
| [p] | [b] | [pʰ] | [m] | [t] | [tʰ] | [n] | [l] | [k] | [g] | [kʰ] | [ŋ] | [h] | [t͡ɕ] | [d͡ʑ] | [t͡ɕʰ] | [ɕ] | [t͡s] | [d͡z] | [t͡sʰ] | [s] | |||
| Final symbols (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ㄚ | ㆩ | ㆦ | ㆧ | ㄜ | ㆤ | ㆥ | ㄞ | ㆮ | ㄠ | ㆯ | ㆰ | ㆱ | ㆬ | ㄢ | ㄣ | ㄤ | ㆲ | ㄥ | ㆭ | ㄧ | ㆪ | ㄨ | ㆫ |
| [a] | [ã] | [ɔ] | [ɔ̃] | [ə] | [e] | [ẽ] | [ai] | [ãĩ] | [au] | [ãũ] | [am] | [ɔm] | [m̩] | [an] | [ən] | [aŋ] | [ɔŋ] | [əŋ] | [ŋ̍] | [i] | [ĩ] | [u] | [ũ] |
- The symbols in blue do not exist in Mandarin phonology.
- Four voiceless consonants ㄅ, ㄉ, ㄍ, ㄏ may be written in small form to represent the unreleased coda, as in ㆴ [p̚ ], ㆵ [t̚ ], ㆶ [k̚ ], ㆷ [ʔ]. However, due to technical errors, the coda symbol for ㄍ was mistaken as ㄎ. Unicode encoded ㆻ (31BB) in its version 13.0, and added a note under ㆶ (31B6), indicating 31BB is preferred.[3]
- Some extra symbols are used in other Taiwanese dialects: ㄬ[ɲ], ㄛ [o], ㄝ [ɛ], ㆨ [ɨ].
Images[]
Images below are a collection of Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols:
![]()
![]()
- For Taiwanese Hokkien and Taiwanese Hakka:
 ,
,  ,
, 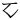 ,
, 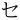 ,
, 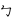 ,
, 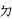 ,
, 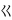 ,
, 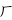
- For Taiwanese Hakka only:
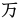 ,
, 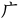
- For Taiwanese Hokkien only:
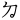 ,
,  ,
, 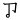 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 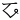 ,
, 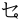 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 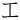 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 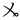
- For Standard Chinese only:
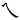 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 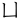
- For Taiwanese Hakka and Standard Chinese:
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
 represents [x] in Standard Chinese and [h] in Taiwanese Hokkien and Taiwanese Hakka.
represents [x] in Standard Chinese and [h] in Taiwanese Hokkien and Taiwanese Hakka.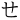 /
/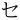 represent [ɛ]/[e] in Taiwanese Hokkien respectively, but they represent [e]/[ɛ] in Taiwanese Hakka.[4][5]
represent [ɛ]/[e] in Taiwanese Hokkien respectively, but they represent [e]/[ɛ] in Taiwanese Hakka.[4][5]- Vowel [ɨ] is represented with
 in Hokkien and
in Hokkien and  in Hakka.[5]
in Hakka.[5]
Etymology[]
| Initials | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Symbol | IPA | POJ | TL | BP | Notes | Example |
| Bilabial | ㄅ | p | p | b | Same value as in Mandarin | 邊 (ㄅㄧㄢ pian) | |
| ㆠ | b | b | bb | Derived from ㄅ as a voiced counterpart | 文 (ㆠㄨㄣˊ bûn) | ||
| ㄆ | pʰ | ph | p | Same value as in Mandarin | 波 (ㄆㄜ pho) | ||
| ㄇ | m | m | bbn | Same value as in Mandarin | 毛 (ㄇㆦ mo͘ ) | ||
| Alveolar | ㄉ | t | t | d | Same value as in Mandarin | 地 (ㄉㆤ˫ tē) | |
| ㄊ | tʰ | th | t | Same value as in Mandarin | 他 (ㄊㆩ thaⁿ) | ||
| ㄋ | n | n | ln | Same value as in Mandarin | 耐 (ㄋㄞ˫ nāi) | ||
| ㄌ | l | l | l | Same value as in Mandarin | 柳 (ㄌㄧㄨˋ liú) | ||
| Velar | ㄍ | k | k | g | Same value as in Mandarin | 求 (ㄍㄧㄨˊ kiû) | |
| ㆣ | g | g | gg | Derived from ㄍ as a voiced counterpart | 語 (ㆣㄧˋ gí) | ||
| ㄎ | kʰ | kh | k | Same value as in Mandarin | 去 (ㄎㄧ˪ khì) | ||
| ㄫ | ŋ | ng | ggn | Once appeared in old Mandarin | 雅 (ㄫㄚˋ ngá) | ||
| Glottal | ㄏ | h | h | h | Different value to Mandarin, in Mandarin [x] | 喜 (ㄏㄧˋ hí) | |
| Alveolo- palatal |
ㄐ | t͡ɕ | chi | tsi | zi | Same value as in Mandarin | 尖(ㄐㄧㆰ tsiam) |
| ㆢ | d͡ʑ | ji | zzi | Derived from ㄐ as a voiced counterpart | 入 (ㆢㄧㆴ. ji̍p) | ||
| ㄑ | t͡ɕʰ | chhi | tshi | ci | Same value as in Mandarin | 手 (ㄑㄧㄨˋ tshiú) | |
| ㄒ | ɕ | si | si | Same value as in Mandarin | 寫 (ㄒㄧㄚˋ siá) | ||
| Alveolar | ㄗ | t͡s | ch | ts | z | Same value as in Mandarin | 曾 (ㄗㄢ chan) |
| ㆡ | d͡z | j | zz | Derived from ㄗ as a voiced counterpart | 熱 (ㆡㄨㄚㆷ. jua̍h) | ||
| ㄘ | t͡sʰ | chh | tsh | c | Same value as in Mandarin | 出 (ㄘㄨㆵ chhut) | |
| ㄙ | s | s | s | Same value as in Mandarin | 衫 (ㄙㆩ saⁿ) | ||
| Rhymes and medials | |||||||
| Group | Symbol | IPA | POJ | TL | BP | Notes | Example |
| Vowels | ㄚ | a | a | a | Same value as in Mandarin | 查 (ㄘㄚ cha) | |
| ㆩ | ã | aⁿ | ann | na | Derived from ㄚ as a nasalized counterpart | 衫 (ㄙㆩ saⁿ) | |
| ㆦ | ɔ | o͘ | oo | oo | New symbol solely used in Taiwanese | 烏 (ㆦ o͘ ) | |
| ㆧ | ɔ̃ | oⁿ | onn | noo | Derived from ㆦ as a nasalized counterpart | 翁 (ㆧ oⁿ) | |
| ㄜ | ə | o | o | Different value from Mandarin, in Mandarin [ɰɤ]. May written as ㄛ and pronounced [o] in some dialects | 高 (ㄍㄜ ko) | ||
| ㆤ | e | e | e | New symbol solely used in Taiwanese | 禮 (ㄌㆤˋ lé) | ||
| ㆥ | ẽ | eⁿ | enn | ne | Derived from ㆤ as a nasalized counterpart | 生 (ㄙㆥ seⁿ) | |
| Diph- thongs |
ㄞ | ai | ai | ai | Same value as in Mandarin | ||
| ㆮ | ãĩ | aiⁿ | ainn | nai | Derived from ㄞ as a nasalized counterpart | ||
| ㄠ | au | au | ao | Same value as in Mandarin | WIKI | ||