Tegafur/gimeracil/oteracil
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Tegafur | Antineoplastic drug |
| Enzyme inhibitor | |
| Enzyme inhibitor | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Teysuno, TS-1 |
| Other names | S-1[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | UK Drug Information |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
Tegafur/gimeracil/oteracil, sold under the brand names Teysuno and TS-1,[3][4] is a fixed-dose combination medication used for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer when used in combination with cisplatin,[3] and also for the treatment of head and neck cancer, colorectal cancer, non–small-cell lung, breast, pancreatic, and biliary tract cancers.[5]: 213
The most common severe side effects when used in combination with cisplatin include neutropenia (low levels of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell), anaemia (low red blood cell counts) and fatigue (tiredness).[3]
Tegafur/gimeracil/oteracil (Teysuno) was approved for medical use in the European Union in March 2011.[3] It has not been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).[5]: 213
Medical uses[]
In the European Union tegafur/gimeracil/oteracil is indicated in adults for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer when given in combination with cisplatin.[3]
Contraindications[]
In the European Union, tegafur/gimeracil/oteracil must not be used in the following groups:
- people receiving another fluoropyrimidine (a group of anticancer medicines that includes tegafur/gimeracil/oteracil) or who have had severe and unexpected reactions to fluoropyrimidine therapy;[3]
- people known to have no DPD enzyme activity, as well as people who, within the previous four weeks, have been treated with a medicine that blocks this enzyme;[3]
- pregnant or breastfeeding women;[3]
- people with severe leucopenia, neutropenia, or thrombocytopenia (low levels of white cells or platelets in the blood);[3]
- people with severe kidney problems requiring dialysis;[3]
- people who should not be receiving cisplatin.[3]
Mechanism of action[]
Tegafur is the actual chemotherapeutic agent. It is a prodrug of the active substance fluorouracil (5-FU).[medical citation needed] Tegafur, is a cytotoxic medicine (a medicine that kills rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells) that belongs to the ‘anti-metabolites’ group. Tegafur is converted to the medicine fluorouracil in the body, but more is converted in tumor cells than in normal tissues.[3] Fluorouracil is very similar to pyrimidine.[3] Pyrimidine is part of the genetic material of cells (DNA and RNA).[3] In the body, fluorouracil takes the place of pyrimidine and interferes with the enzymes involved in making new DNA.[3] As a result, it prevents the growth of tumor cells and eventually kills them.[3]
inhibits the degradation of fluorouracil by reversibly blocking the dehydrogenase enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD). This results in higher 5-FU levels and a prolonged half-life of the substance.[6]
mainly stays in the gut because of its low permeability, where it reduces the production of 5-FU by blocking the enzyme orotate phosphoribosyltransferase. Lower 5-FU levels in the gut result in a lower gastrointestinal toxicity.[6]
Within the medication, the molar ratio of the three components (tegafur:gimeracil:oteracil) is 1:1:0.4.[7]
The maximum tolerated dose differed between Asian and Caucasian populations (80 mg/m2 and 25 mg/m2 respectively), perhaps due to differences in CYP2A6 genotype.[5]: 213
Research[]
It is being developed for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.[8] and has activity in esophageal,(Perry Chapter 33) breast,[citation needed] cervical,[citation needed] and colorectal cancer.[9]

Tegafur
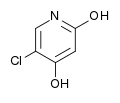
Gimeracil

Oteracil potassium
References[]
- ^ Liu TW, Chen LT (201). "S-1 with leucovorin for gastric cancer: how far can it go?". Lancet Oncol. 17 (1): 12–4. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00478-7. PMID 26640038.
- ^ "Teysuno 20mg/5.8mg/15.8mg hard capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). Retrieved 30 July 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Teysuno EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 30 July 2020. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ https://www.taiho.co.jp/patients/ts-1/
- ^ Jump up to: a b c DeVita, DeVita; Lawrence, TS; Rosenberg, SA (2015). DeVita, Hellman, and Rosenberg's Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology (10th ed.). LWW. ISBN 978-1451192940.
- ^ Jump up to: a b A. Klement (22 July 2013). "Dreier-Kombination gegen Magenkrebs: Teysuno". Österreichische Apothekerzeitung (in German) (15/2013): 23.
- ^ Peters GJ, Noordhuis P, Van Kuilenburg AB et al. (2003). "Pharmacokinetics of S-1, an oral formulation of ftorafur, oxonic acid and 5-chloro-2,4-dihydroxypyridine (molar ratio 1:0.4:1) in patients with solid tumors". Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 52 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1007/s00280-003-0617-9. PMID 12739060. S2CID 10858817.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ http://www.biocentury.com/BCIQ
- ^ Miyamoto Y, Sakamoto Y, Yoshida N, Baba H (2014). "Efficacy of S-1 in colorectal cancer". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 15 (12): 1761–70. doi:10.1517/14656566.2014.937706. PMID 25032886. S2CID 23637808.
External links[]
- "Tegafur". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Gimeracil". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Oteracil". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Antineoplastic drugs
- Combination drugs
- Pyrimidine antagonists
- Taiho Pharmaceutical



