Capecitabine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /kæpɪˈsaɪtəbiːn/ |
| Trade names | Xeloda, Xitabin, Kapetral, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a699003 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | chemotherapy agent |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Extensive |
| Protein binding | < 60% |
| Metabolism | liver, to 5'-DFCR, 5'-DFUR (inactive); neoplastic tissue, 5'-DFUR to active fluorouracil |
| Elimination half-life | 38–45 minutes |
| Excretion | kidney (95.5%), faecal (2.6%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.112.980 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H22FN3O6 |
| Molar mass | 359.354 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Capecitabine, sold under the brand name Xeloda among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat breast cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer.[1] For breast cancer it is often used together with docetaxel.[2] It is taken by mouth.[2]
Common side effects include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, and rashes.[2] Other severe side effects include blood clotting problems, allergic reactions, heart problems such as cardiomyopathy, and low blood cell counts.[2] It is not recommended in people with kidney problems.[2] Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby.[2] Capecitabine, inside the body, is converted to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) through which it acts.[2] It belongs to the class of medications known as fluoropyrimidines, which also includes 5-FU and tegafur.[3]
Capecitabine was patented in 1992 and approved for medical use in 1998.[4] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[5]
Medical uses[]
It is used in the treatment of the following cancers:[6][7][8]
- Colorectal cancer (either as neoadjuvant therapy with radiation, adjuvant therapy or for metastatic cases)
- Breast cancer (metastatic or as monotherapy/combotherapy; this is licensed as a second-line treatment in the UK)
- Gastric cancer (off-label in the US; this is a licensed indication in the UK)
- Oesophageal cancer (off-label in the US)
Adverse effects[]
Adverse effects by frequency:[9][10][11][12]
- Very common (>10% frequency)
Notes on adverse effects:
- ^ Includes: anaemia, lymphopenia, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
Contraindications[]
Contraindications include:[11]
- History of hypersensitivity to fluorouracil, capecitabine or any of its excipients
- DPD deficiency (see Pharmacogenetics)
- Pregnancy and lactation
- Severe leucopenia, neutropenia, or thrombocytopenia
- Severe hepatic impairment or severe renal impairment
- Treatment with sorivudine or its chemically related analogues, such as brivudine
Drug interactions[]
Drugs it is known to interact with include:[11]
- Sorivudine or its analogues, such as, brivudine.
- CYP2C9 substrates, including, warfarin and other coumarin-derivatives anticoagulants
- Phenytoin, as it increases the plasma concentrations of phenytoin.
- Calcium folinate may enhance the therapeutic effects of capecitabine by means of synergising with its metabolite, 5-FU. It may also induce more severe diarrhoea by means of this synergy.[6]
Pharmacogenetics[]
The dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) enzyme is responsible for the detoxifying metabolism of fluoropyrimidines, a class of drugs that includes capecitabine, 5-fluorouracil and tegafur.[3] Genetic variations within the DPD gene (DPYD) can lead to reduced or absent DPD activity, and individuals who are heterozygous or homozygous for these variations may have partial or complete DPD deficiency; an estimated 0.2% of individuals have complete DPD deficiency.[3][14] Those with partial or complete DPD deficiency have a significantly increased risk of severe or even fatal drug toxicities when treated with fluoropyrimidines; examples of toxicities include myelosuppression, neurotoxicity and hand-foot syndrome.[3][14]
Mechanism of action[]
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.[§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "FluoropyrimidineActivity_WP1601".
Capecitabine is metabolised to 5-FU which in turn is a thymidylate synthase inhibitor, hence inhibiting the synthesis of thymidine monophosphate (ThMP), the active form of thymidine which is required for the de novo synthesis of DNA.[7]
Drug synthesis[]
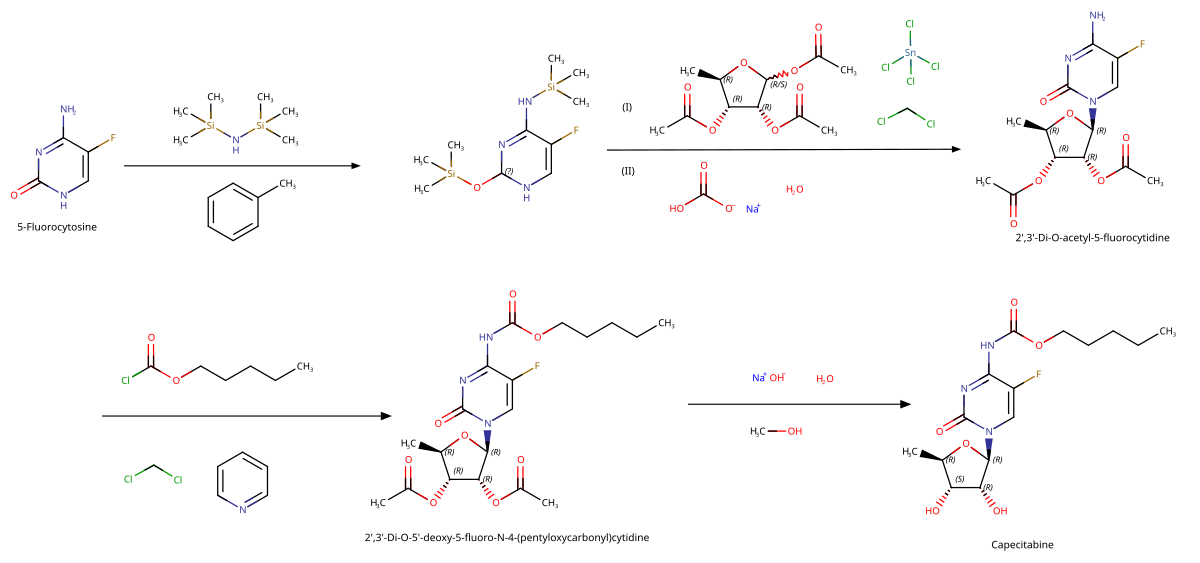
Society and culture[]
Brand names[]
This section does not cite any sources. (August 2020) |
One of the brand names is Xeloda, marketed by Genentech.
Others include Xitabin, Capcibin, Kapetral and Pecaset by .
References[]
- ^ British national formulary : BNF 69 (69 ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. pp. 585, 588. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Capecitabine". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 15 April 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ a b c d Caudle KE, Thorn CF, Klein TE, Swen JJ, McLeod HL, Diasio RB, Schwab M (December 2013). "Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase genotype and fluoropyrimidine dosing". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 94 (6): 640–5. doi:10.1038/clpt.2013.172. PMC 3831181. PMID 23988873.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 511. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ a b Rossi S, ed. (2013). Australian Medicines Handbook (2013 ed.). Adelaide: The Australian Medicines Handbook Unit Trust. ISBN 978-0-9805790-9-3.
- ^ a b "Xeloda (capecitabine) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. 25 January 2014. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014.
- ^ Joint Formulary Committee (2013). British National Formulary (BNF) (65 ed.). London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0-85711-084-8.
- ^ "XELODA (capecitabine) tablet, film coated [Genentech, Inc.]". DailyMed. Genentech, Inc. December 2013. Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 25 January 2014.
- ^ "Capecitabine Teva : EPAR – Product Information" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. Teva Pharma B.V. 10 January 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 February 2014. Retrieved 25 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "Capecitabine 150mg – Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)". electronic Medicines Compendium. Zentiva. 23 December 2013. Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 25 January 2014.
- ^ "NAME OF THE MEDICINE XELODA® Capecitabine" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Roche Products Pty Limited. 5 December 2013. Archived from the original on 11 September 2017. Retrieved 25 January 2014.
- ^ Reddening, swelling, numbness and desquamation on palms and soles
- ^ a b Amstutz U, Froehlich TK, Largiadèr CR (September 2011). "Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene as a major predictor of severe 5-fluorouracil toxicity". Pharmacogenomics. 12 (9): 1321–36. doi:10.2217/pgs.11.72. PMID 21919607.
Further reading[]
- Dean L (2016). "Capecitabine Therapy and DPYD Genotype". In Pratt VM, McLeod HL, Rubinstein WS, et al. (eds.). Medical Genetics Summaries. National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). PMID 28520372. Bookshelf ID: NBK385155.
External links[]
- "Capecitabine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Carbamates
- Fluoropyrimidines
- Genentech brands
- Hoffmann-La Roche brands
- Organofluorides
- Prodrugs
- Pyrimidine antagonists
- Pyrimidones
- Specialty drugs
- World Health Organization essential medicines
