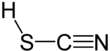Thiocyanic acid
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Thiocyanic acid[3] | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.672 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 25178 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | thiocyanic+acid | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula
|
CHNS | ||
| Molar mass | 59.09 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless, oily liquid | ||
| Odor | pungent | ||
| Density | 2.04 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 5 °C (41 °F; 278 K) | ||
| Miscible | |||
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether | ||
| log P | 0.429 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.926 | ||
| Basicity (pKb) | 13.071 | ||
| Hazards | |||
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
|||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R20/21/22, R32, R52/53 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S2), S13 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanenitriles
|
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Thiocyanic acid is a chemical compound with the formula HSCN which exists as a tautomer with isothiocyanic acid (HNCS).[4] The iso- form tends to dominate with the material being about 95% isothiocyanic acid in the vapor phase.[5]
 Tautomerism between thiocyanic acid (left) and isothiocyanic acid (right)
Tautomerism between thiocyanic acid (left) and isothiocyanic acid (right)
It is a moderately strong acid,[6] with a pKa of 1.1 at 20 °C and extrapolated to zero ionic strength.[7]
HSCN is predicted to have a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. It has been observed spectroscopically but has not been isolated as a pure substance.[8]
The salts and esters of thiocyanic acid are known as thiocyanates. The salts are composed of the thiocyanate ion (−SCN) and a suitable metal cation (e.g., potassium thiocyanate, KSCN). The esters of thiocyanic acid have the general structure R–SCN.
Isothiocyanic acid, HNCS, is a Lewis acid whose free energy, enthalpy and entropy changes for its 1:1 association with a variety of Lewis bases in carbon tetrachloride solution at 25°C have been reported.[9] HNCS acceptor properties are discussed in the ECW model.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Thiocyanic acid. |
References[]
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9257.
- ^ Richter, Victor von; Spielmann, Percy E., trans. (1922). Organic Chemistry or Chemistry of the Carbon Compounds. vol. 1. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S.A.: P. Blakiston's Son & Co. p. 466.
|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 784. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Beard, C. I.; Dailey, B. P. (1950). "The Structure and Dipole Moment of Isothiocyanic Acid" (PDF). The Journal of Chemical Physics. 18 (11): 1437. Bibcode:1950JChPh..18.1437B. doi:10.1063/1.1747507. hdl:1721.1/4934.
- ^ http://pubs.sciepub.com/wjce/1/1/4/index.html
- ^ Martell, A. E.; Smith, R. M.; Motelaitis, R. J. (2001). NIST Database 46. Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology.
- ^ Wierzejewska, M.; Mielke, Z. (2001). "Photolysis of Isothiocyanic Acid HNCS in Low-Temperature Matrices. Infrared Detection of HSCN and HSNC Isomers". Chemical Physics Letters. 349 (3–4): 227–234. Bibcode:2001CPL...349..227W. doi:10.1016/S0009-2614(01)01180-0.
- ^ . Barakat, T. M.; Nelson, J.; Nelson, S. M.; Pullin, A. D. E. (1969.) “Spectra and hydrogen-bonding of characteristics of thiocyanic acid. Part 4.—Association with weak proton acceptors”. Trans. Faraday Soc., 1969,65, 41-51
- Mineral acids
- Thiocyanates