1852 United States presidential election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
296 members of the Electoral College 149 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 69.6%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
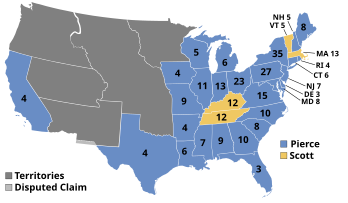  Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Pierce/King and buff by Scott/Graham. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes cast by each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1852 United States presidential election was the 17th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1852. Democrat Franklin Pierce, a former Senator from New Hampshire, defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott.
Incumbent Whig President Millard Fillmore had succeeded to the Presidency in 1850 upon the death of President Zachary Taylor. Endorsement of the Compromise of 1850 and enforcement of the Fugitive Slave Law earned Fillmore Southern voter support and Northern voter opposition. On the 53rd ballot of the sectionally divided 1852 Whig National Convention, Scott defeated Fillmore for the nomination. Democrats divided among four major candidates at the 1852 Democratic National Convention. On the 49th ballot, dark horse candidate Franklin Pierce won nomination by consensus compromise. The Free Soil Party, a third party opposed to the extension of slavery in the United States and into the territories, as in their name free-soil meaning land should be free instead of slave, nominated New Hampshire Senator John P. Hale.
With few policy differences between the two major candidates, the election became a personality contest. Though Scott had commanded in the Mexican–American War, Pierce also served. Scott strained Whig Party unity as his anti-slavery reputation gravely damaged his campaign in the South. A group of Southern Whigs and a separate group of Southern Democrats each nominated insurgent tickets, but both efforts failed to attract support.
Pierce and running mate William R. King won a comfortable popular majority, carrying 27 of the 31 states. Pierce won the highest share of the electoral vote since James Monroe's uncontested 1820 re-election. Overwhelming defeat and disagreement about slavery soon drove the Whig Party to disintegrate.
Not until 1876 would Democrats again win a popular majority vote for president and not until 1932 would they win both a popular majority vote and the Presidency with Democratic nominee Franklin D. Roosevelt.
Nominations[]
The 1852 presidential election conventions of the parties are considered below in order of the party's popular vote.
Democratic Party nomination[]
| 1852 Democratic Party ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Franklin Pierce | William R. King | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Former U.S. Senator from New Hampshire (1837–1842) |
U.S. Senator from Alabama (1819–1844 & 1848–1852) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

- Franklin Pierce, former U.S. Senator from New Hampshire
- Lewis Cass, U.S. Senator from Michigan
- James Buchanan, former U.S. Secretary of State from Pennsylvania
- William L. Marcy, former U.S. Secretary of War from New York
- Stephen Douglas, U.S. Senator from Illinois

Former Senator
Franklin Pierce
from New Hampshire
Senator
Lewis Cass
from Michigan
Former Secretary of State
James Buchanan
Former Secretary of War
William L. Marcy
Senator
Stephen A. Douglas
from Illinois
As Democrats convened in Baltimore in June 1852, four major candidates vied for the nomination: Lewis Cass of Michigan, the nominee in 1848, who had the backing of northerners in support of the Compromise of 1850; James Buchanan of Pennsylvania, popular in the South as well as in his home state; Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois, candidate of the expansionists and the railroad interests; and William L. Marcy of New York, whose strength was centered in his home state. Throughout the balloting, numerous favorite son candidates received a few votes.
Cass led on the first nineteen ballots, with Buchanan second, and Douglas and Marcy exchanging third and fourth places. Buchanan took the lead on the 20th ballot and retained it on each of the next nine tallies. Douglas managed a narrow lead on the 30th and 31st ballots. Cass then recaptured first place through the 44th ballot. Marcy carried the next four ballots. Franklin Pierce of New Hampshire, a former Congressman and Senator, did not get on the board until the 34th ballot, when the Virginia delegation brought him forward as a compromise choice. He consolidated his support in subsequent voting and was nominated nearly unanimously on the 49th ballot.[2]
In a peace gesture to the Buchanan wing of the party, Pierce's supporters allowed Buchanan's allies to fill the second position, knowing that they would select Alabama Senator William R. King. On the second ballot, with only minor opposition, King finally obtained the Democratic vice-presidential nomination. During the ensuing campaign, King's tuberculosis, which he believed he had contracted while in Paris, France, denied him the active behind-the-scenes role that he might otherwise have played, although he worked hard to assure his region's voters that New Hampshire's Pierce was a "northern man with southern principles." King died shortly after his inauguration on April 4, 1853.
Whig Party nomination[]
| 1852 Whig Party ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Winfield Scott | William A. Graham | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd Commanding General of the U.S. Army (1841–1861) |
20th U.S. Secretary of the Navy (1850–1852) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

- Winfield Scott, Commanding General of the U.S. Army from New Jersey
- Millard Fillmore, President of the United States from New York
- Daniel Webster, U.S. Secretary of State from Massachusetts

Commanding General
Winfield Scott
President
Millard Fillmore
U.S. Secretary of State
Daniel Webster
The 1852 Whig National Convention, held in Baltimore, Maryland, was bitterly divided. Supporters of President Fillmore pointed to the successful Compromise of 1850 and the failure of a nascent secession movement in the Southern states in 1850–1851. The northern Whigs believed that the Compromise of 1850 favored the slaveholding South over the North. Northern Whigs favored heroic Mexican–American War General Winfield Scott of New Jersey. Scott had earned the nickname of "Old Fuss and Feathers" in the military due to his insistence on appearance and discipline, and while respected, was also seen by the people as somewhat foppish. A deadlock occurred because most New England delegates supported Daniel Webster. On the first ballot, Fillmore received all delegate votes from the South save four, but only received eighteen northern delegate votes. The vote was 133 for Fillmore, 131 for Scott, and 29 for Webster. Scott was nominated on the 53rd ballot by a margin of 159–112 (with 21 for Webster), again with a highly sectional vote; Scott won the North by a 142–11 vote (with 21 for Webster) while Fillmore won the South by a margin of 101–17.
William Alexander Graham was chosen as the vice-presidential nominee. 1852 would be the last time the Whig Party would nominate its own candidate for president, albeit it would endorse Fillmore's run as a Know Nothing candidate in 1856. Within the decade, the party fell apart and ceased to exist, principally due to regional divisions caused by the slavery issue.
Free Soil Party nomination[]
- John P. Hale, U.S. Senator from New Hampshire

Senator John P. Hale
from New Hampshire
The Free Soil Party was still the strongest third party in 1852. However, following the Compromise of 1850, most of the "Barnburners" who supported it in 1848 had returned to the Democratic Party while most of the Conscience Whigs rejoined the Whig Party. The second Free Soil National Convention assembled in the Masonic Hall in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. New Hampshire Senator John P. Hale was nominated for president with 192 delegate votes (sixteen votes were cast for a smattering of candidates). George Washington Julian of Indiana was nominated for vice-president over Samuel Lewis of Ohio and Joshua R. Giddings of Ohio.
Union Party nomination[]
The Union party was formed in 1850, an offshoot of the Whig party in several Southern states, including Georgia. As the 1852 presidential election approached, Union party leaders decided to wait and see who was nominated by the two major parties. The movement to nominate Daniel Webster as a third-party candidate began in earnest following the Whig Convention, largely driven by those who had been strenuously opposed to Winfield Scott's nomination, among them Alexander Stephens, Robert Toombs, and George Curtis. While Webster was against what he perceived as a "revolt" from the Whig Party and preferred not to be nominated, he let Americans vote for him should the party choose to nominate him.
The Union Party held its Georgia state convention on August 9, 1852, and nominated Webster for president and Charles J. Jenkins of Georgia for vice-president. A formal convention was held at Faneuil Hall in Boston, Massachusetts, on September 15, affirming the nominations made at the state convention in Georgia and rejecting Winfield Scott as nothing more than a military figure. The Webster/Jenkins ticket received nationwide support, particularly among Southern Whigs, but also in Massachusetts and New York, but it was largely perceived by many as nothing more than getting voters who would, in different circumstances, support Scott.
Webster had no real chance of winning the election, but even the new Know-Nothing party endorsed Webster, nominating him without even his own permission. However, Webster died nine days before the election of a cerebral hemorrhage on October 24, 1852.
Native American (Know-Nothing) Party nomination[]
Around the mid-1830s, nativists were present in New York politics, under the aegis of the American Republican Party. The American Republican party was formed in 1843 in major opposition to immigration and Catholicism. In 1845, the party changed its name to the Native American Party. Their opponents nicknamed them the "Know Nothings" and the party liked the name and it became the nickname of the party after that until it collapsed in 1860. In 1852, the original candidate planned by the Native American Party was Daniel Webster, the nominee of the Union party as well as Secretary of State. They nominated Webster without his permission, with George Corbin Washington (grandnephew of George Washington) as his running mate. Webster died of natural causes nine days before the election, and the Know-Nothings quickly replaced Webster by nominating Jacob Broom as president and replaced Washington with Reynell Coates. With Webster collecting a few thousand votes, Broom received too few and lost the election. In the future, former president Millard Fillmore would be their candidate in 1856.
Southern Rights Party nomination[]
- George Troup, former U.S. senator from Georgia

Former Senator George Troup
from Georgia
The Southern Rights Party was an offshoot of the Democratic party in several Southern states which advocated secession from the Union, electing a number of Congressmen and holding referendums on secession in a number of southern states, none of which were successful.
It was unclear in early 1852 if the Party would contest the presidential election. When the Alabama state convention was held in early March, only nine counties were represented. The party decided to see who was nominated by the two major national parties and support one of them if possible. When Georgia held its state convention, it acted as the state Democratic Party and sent delegates to the national convention.
After the Democratic National Convention, the Party was not sure that it wanted to support Franklin Pierce, the Democratic nominee. Alabama held a state convention from July 13–15 and discussed at length the options of running a separate ticket or supporting Pierce. The convention was unable to arrive at a decision, deciding to appoint a committee to review the positions of Scott and Pierce with the option of calling a "national" convention if the two major-party candidates appeared deficient. The committee took its time reviewing the positions of Pierce and Scott, finally deciding on August 25 to call a convention for a Southern Rights Party ticket.
The convention assembled in Montgomery, Alabama, with 62 delegates present, a committee to recommend a ticket being appointed while the delegates listened to speeches in the interim. The committee eventually recommended former Senator George Troup of Georgia for President, and former Governor John Quitman of Mississippi for Vice-President; they were unanimously nominated.
The two nominees accepted their nominations soon after the convention, which was held rather late in the season. Troup stated in a letter, dated September 27 and printed in the New York Times on October 16, that he had planned to vote for Pierce and had always wholeheartedly supported William R.D. King. He indicated in the letter that he preferred to decline the honor, as he was rather ill at the time and feared that he would die before the election. The Party's executive committee edited the letter to excise those portions which indicated that Troup preferred to decline, a fact which was revealed after the election.
Liberty Party nomination[]
The Liberty Party had ceased to become a significant political force after most of its members joined the Free Soil Party in 1848. Nonetheless, some of those who rejected the fusion strategy held a Liberty Party National Convention in Buffalo, New York. There were few delegates present, so a ticket was recommended and a later convention called. The Convention recommended Gerrit Smith of New York for president and Charles Durkee of Wisconsin for vice-president. A second convention was held in Syracuse, New York, in early September 1852, but it too failed to draw enough delegates to select a nominee. Yet a third convention gathered in Syracuse later that month and nominated William Goodell of New York for president and of Virginia for vice-president.
General election[]
Fall campaign[]

The Whigs' platform was almost indistinguishable from that of the Democrats, reducing the campaign to a contest between the personalities of the two candidates. The lack of clearcut issues between the two parties helped drive voter turnout down to its lowest level since 1836. The decline was further exacerbated by Scott's antislavery reputation, which decimated the Southern Whig vote at the same time as the pro-slavery Whig platform undermined the Northern Whig vote. After the Compromise of 1850 was passed, many of the southern Whig Party members broke with the party's key figure, Henry Clay.[3]
Finally, Scott's status as a war hero was somewhat offset by the fact that Pierce was himself a Mexican–American War brigadier general.
The Democrats adopted the slogan: The Whigs we Polked in forty-four, We'll Pierce in fifty-two, playing on the names of Pierce and former President James K. Polk.[4]
Just nine days before the election, Webster died, causing many Union state parties to remove their slates of electors. The Union ticket appeared on the ballot in Georgia and Massachusetts, however.
Results[]

When American voters went to the polls, Pierce won the electoral college in a landslide; Scott won only the states of Kentucky, Tennessee, Massachusetts, and Vermont, while the Free Soil vote collapsed to less than half of what Martin Van Buren had earned in the previous election, with the party taking no states. The fact that Daniel Webster received a substantial share of the vote in Georgia and Massachusetts, even though he was dead, shows how disenchanted voters were with the two main candidates.
In the popular vote, while Pierce outpolled Scott by 220,000 votes, 17 states were decided by less than 10%, and eight by less than 5%. A shift of 69,000 votes to Scott in Delaware, Maryland, New York, North Carolina, Ohio and Pennsylvania would have left the electoral college in a 148–148 tie, forcing a contingent election in the House of Representatives.
As a result of the devastating defeat and the growing tensions within the party between pro-slavery Southerners and anti-slavery Northerners, the Whig Party quickly fell apart after the 1852 election and ceased to exist. Some Southern Whigs would join the Democratic Party, and many Northern Whigs would help to form the new Republican Party in 1854.
Some Whigs in both sections would support the so-called "Know-Nothing" party in the 1856 presidential election. Similarly, the Free Soil Party rapidly fell away into obscurity after the election, and the remaining members mostly opted to join the former Northern Whigs in forming the Republican Party.
The Southern Rights Party effectively collapsed following the election, attaining only five percent of the vote in Alabama, and a few hundred in its nominee's home state of Georgia. It would elect a number of Congressmen in 1853, but they would rejoin the Democratic Party upon taking their seats in Congress.
This was the last election in which the Democrats won Michigan until 1932,[a] the last in which the Democrats won Iowa, Maine, New Hampshire, Ohio[b] or Rhode Island until 1912, the last in which the Democrats won Wisconsin until 1892, the last in which the Democrats won Connecticut until 1876 and the last in which the Democrats won New York until 1868. It was, however, the last election in which the Democrats' chief opponent won Kentucky until 1896,[c][5] and indeed the last until 1928 in which the Democrats' opponent obtained an absolute majority in the Bluegrass State.

| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote[d] | Electoral vote |
Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Electoral vote | ||||
| Franklin Pierce | Democratic | New Hampshire | 1,607,510 | 50.84% | 254 | William Rufus DeVane King | Alabama | 254 |
| Winfield Scott | Whig | New Jersey | 1,386,942 | 43.87% | 42 | William Alexander Graham | North Carolina | 42 |
| John Parker Hale | Free Soil | New Hampshire | 155,210 | 4.91% | 0 | George Washington Julian | Indiana | 0 |
| Daniel Webster[e] | Union[f] | Massachusetts | 6,994 | 0.22% | 0 | Charles Jones Jenkins | Georgia | 0 |
| Jacob Broom | Native American | Pennsylvania | 2,566 | 0.08% | 0 | Reynell Coates | New Jersey | 0 |
| George McIntosh Troup | Southern Rights | Georgia | 2,331 | 0.07% | 0 | John Anthony Quitman | Mississippi | 0 |
| Other | 277 | 0.00% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 3,161,830 | 100% | 296 | 296 | ||||
| Needed to win | 149 | 149 | ||||||
Source (Popular Vote): Leip, David. "1852 Presidential Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved July 27, 2005.
Source (Electoral Vote): "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved July 31, 2005.
- The leading candidates for vice president were both born in North Carolina and in fact both attended the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, albeit two decades apart. While there, they were members of opposing debate societies: the Dialectic and Philanthropic Societies. Both also served in North Carolina politics: King was a representative from North Carolina before he moved to Alabama, and Graham was a governor of North Carolina.
Geography of results[]
Cartographic gallery[]

Map of presidential election results by county

Map of Democratic presidential election results by county

Map of Whig presidential election results by county

Map of Free Soil presidential election results by county

Map of "Other" presidential election results by county
Results by state[]
Source: Data from Walter Dean Burnham, Presidential ballots, 1836–1892 (Johns Hopkins University Press, 1955) pp 247–57.
| States/districts won by Pierce/King |
| States/districts won by Scott/Graham |
| Franklin Pierce Democratic |
Winfield Scott Whig |
John P. Hale Free Soil |
Margin | State Total | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | # | |||||
| Alabama | 9 | 26,881 | 60.89 | 9 | 15,061 | 34.12 | - | no ballots | 11,280 | 26.77 | 44,147 | AL | ||||||
| Arkansas | 4 | 12,173 | 62.18 | 4 | 7,404 | 37.82 | - | no ballots | 4,769 | 24.36 | 19,577 | AR | ||||||
| California | 4 | 40,721 | 53.02 | 4 | 35,972 | 46.83 | - | 61 | 0.08 | - | 4,749 | 6.19 | 76,810 | CA | ||||
| Connecticut | 6 | 33,249 | 49.79 | 6 | 30,359 | 45.56 | - | 3,161 | 4.73 | - | 2,890 | 4.23 | 66,781 | CT | ||||
| Delaware | 3 | 6,318 | 49.85 | 3 | 6,293 | 49.66 | - | 62 | 0.49 | - | 25 | 0.19 | 12,673 | DE | ||||
| Florida | 3 | 4,318 | 60.03 | 3 | 2,875 | 39.97 | - | no ballots | 1,443 | 20.06 | 7,193 | FL | ||||||
| Georgia | 10 | 40,516 | 64.70 | 10 | 16,660 | 26.60 | - | no ballots | 23,856 | 38.10 | 62,626 | GA | ||||||
| Illinois | 11 | 80,378 | 51.87 | 11 | 64,733 | 41.77 | - | 9,863 | 6.36 | - | 15,645 | 10.10 | 154,974 | IL | ||||
| Indiana | 13 | 95,340 | 52.05 | 13 | 80,901 | 44.17 | - | 6,929 | 3.78 | - | 14,439 | 7.88 | 183,170 | IN | ||||
| Iowa | 4 | 17,763 | 50.23 | 4 | 15,856 | 44.84 | - | 1,606 | 4.54 | - | 1,907 | 5.39 | 35,364 | IA | ||||
| Kentucky | 12 | 53,494 | 48.32 | - | 57,428 | 51.44 | 12 | 266 | 0.24 | - | -3,934 | -3.12 | 111,643 | KY | ||||
| Louisiana | 6 | 18,647 | 51.94 | 6 | 17,255 | 48.06 | - | no ballots | 1,392 | 3.88 | 35,902 | LA | ||||||
| Maine | 8 | 41,609 | 50.63 | 8 | 32,543 | 39.60 | - | 8,030 | 9.77 | - | 9,066 | 11.03 | 82,182 | ME | ||||
| Maryland | 8 | 40,022 | 53.28 | 8 | 35,077 | 46.69 | - | 21 | 0.03 | - | 4,945 | 6.59 | 75,120 | MD | ||||
| Massachusetts | 13 | 44,569 | 35.07 | - | 52,683 | 41.45 | 13 | 28,203 | 22.19 | - | -8,114 | -6.38 | 127,103 | MA | ||||
| Michigan | 6 | 41,842 | 50.45 | 6 | 33,860 | 40.83 | - | 7,237 | 8.73 | - | 7,982 | 9.62 | 82,939 | MI | ||||
| Mississippi | 7 | 26,896 | 60.50 | 7 | 17,558 | 39.50 | - | no ballots | 9,338 | 21.00 | 44,454 | MS | ||||||
| Missouri | 9 | 38,817 | 56.42 | 9 | 29,984 | 43.58 | - | no ballots | 8,833 | 12.84 | 68,801 | MO | ||||||
| New Hampshire | 5 | 28,503 | 56.40 | 5 | 15,486 | 30.64 | - | 6,546 | 12.95 | - | 13,017 | 25.76 | 50,535 | NH | ||||
| New Jersey | 7 | 44,305 | 53.24 | 7 | 38,556 | 46.33 | - | 359 | 0.43 | - | 5,749 | 6.91 | 83,220 | NJ | ||||
| New York | 35 | 262,083 | 50.18 | 35 | 234,882 | 44.97 | - | 25,329 | 4.85 | - | 27,201 | 5.21 | 522,294 | NY | ||||
| North Carolina | 10 | 39,778 | 50.43 | 10 | 39,043 | 49.49 | - | no ballots | 735 | 0.94 | 78,891 | NC | ||||||
| Ohio | 23 | 168,933 | 47.83 | 23 | 152,523 | 43.18 | - | 31,732 | 8.98 | - | 16,410 | 4.65 | 353,188 | OH | ||||
| Pennsylvania | 27 | 198,562 | 51.20 | 27 | 179,104 | 46.18 | - | 8,495 | 2.19 | - | 19,458 | 5.02 | 387,389 | PA | ||||
| Rhode Island | 4 | 8,735 | 51.37 | 4 | 7,626 | 44.85 | - | 644 | 3.79 | - | 1,109 | 6.52 | 17,005 | RI | ||||
| South Carolina | 8 | no popular vote | 8 | no popular vote | no popular vote | - | - | - | SC | |||||||||
| Tennessee | 12 | 56,900 | 49.27 | - | 58,586 | 50.73 | 12 | no ballots | -1,686 | -1.46 | 115,486 | TN | ||||||
| Texas | 4 | 13,552 | 73.07 | 4 | 4,995 | 26.93 | - | no ballots | 8,557 | 46.14 | 18,547 | TX | ||||||
| Vermont | 5 | 13,044 | 29.72 | - | 22,173 | 50.52 | 5 | 8,621 | 19.64 | - | -9,129 | -20.80 | 43,890 | VT | ||||
| Virginia | 15 | 73,872 | 55.71 | 15 | 58,732 | 44.29 | - | no ballots | 15,140 | 11.42 | 132,604 | VA | ||||||
| Wisconsin | 5 | 33,658 | 52.04 | 5 | 22,210 | 34.34 | - | 8,814 | 13.63 | - | 11,448 | 17.70 | 64,682 | WI | ||||
| TOTALS: | 296 | 1,605,943 | 50.83 | 254 | 1,386,418 | 43.88 | 42 | 155,799 | 4.93 | - | 3,159,640 | the US | ||||||
| TO WIN: | 149 | |||||||||||||||||
Close states[]
States where the margin of victory was under 1%:
- Delaware 0.19% (25 votes)
- North Carolina 0.90% (735 votes)
States where the margin of victory was under 5%:
- Tennessee 1.46% (1,686 votes)
- Kentucky 3.12% (3,934 votes)
- Louisiana 3.88% (1,392 votes)
- Connecticut 4.23% (2,890 votes)
- Ohio 4.65% (16,410 votes)
States where the margin of victory was under 10%:
- Pennsylvania 5.02% (19,458 votes)
- New York 5.21% (27,201 votes) (tipping point state)
- Iowa 5.39% (1,907 votes)
- California 6.19% (4,749 votes)
- Massachusetts 6.38% (8,114 votes)
- Rhode Island 6.52% (1,109 votes)
- Maryland 6.59% (4,945 votes)
- New Jersey 6.91% (5,749 votes)
- Indiana 7.88% (14,439 votes)
- Michigan 9.62% (7,982 votes)
Electoral college selection[]
| Method of choosing electors | State(s) |
|---|---|
| Each Elector appointed by state legislature | South Carolina |
| Each Elector chosen by voters statewide | (all other States)
|
See also[]
- History of the United States (1849–65)
- Inauguration of Franklin Pierce
- Second Party System
- 1852 United States House of Representatives elections
- 1852 and 1853 United States Senate elections
Notes[]
- ^ In 1892 Democrat Grover Cleveland did win one electoral vote from each of five Michigan congressional districts he carried despite losing the state
- ^ In 1892 the direct election of Presidential electors meant Grover Cleveland received one Ohio electoral vote
- ^ Constitutional Union Party candidate John Bell won Kentucky in 1860; however, Bell was surpassed in the popular vote by two Democratic factions and Republican Abraham Lincoln. Apart from this, the Democrats won Kentucky in all ten elections between 1856 and 1892.
- ^ The popular vote figures exclude South Carolina where the Electors were chosen by the state legislature rather than by popular vote.
- ^ Daniel Webster died on October 24, 1852, one week before the election. However, his name remained on the ballot in Massachusetts and Georgia, and he still managed to poll nearly seven thousand votes. He was also the original candidate of the Native American Party but was replaced on his death by Jacob Broom.
- ^ For a detailed discussion of the Union Party formed by Pro-Union Whigs, see Michael F. Holt, The Rise and Fall of the Whig Party: Jacksonian Politics and the Onset of the Civil War (New York: Oxford University Press, 1999), Chapters 19 and 20.
References[]
- ^ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara.
- ^ William DeGregorio, The Complete Book of U.S. Presidents, Gramercy 1997
- ^ "Franklin Pierce". whitehouse.gov. December 29, 2014 – via National Archives.
- ^ "Democratic Rallying Song for 1852". The Mountain Sentinel. Ebensburg, PA: 1. October 7, 1852.
- ^ Counting the Votes; Kentucky Archived November 20, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
Further reading[]
- Beeler, Dale. "The Election of 1852 in Indiana." Indiana Magazine of History (1915): 301–323. online
- Blue, Frederick J. The Free Soilers: Third-Party Politics, 1848-54 (U of Illinois Press, 1973).
- Gara, Larry. The Presidency of Franklin Pierce (UP of Kansas, 1991).
- Holt, Michael F. The Rise and Fall of the American Whig Party: Jacksonian Politics and the Onset of the Civil War. (Oxford University Press, 1999).
- Morrison, Michael A. "The Election of 1852." American Presidential Campaigns and Elections (Routledge, 2020) pp. 349–366.
- Morrill, James R. "The Presidential Election of 1852: Death Knell of the Whig Party of North Carolina." North Carolina Historical Review 44.4 (1967): 342-359 online.
- Nevins, Allan. Ordeal of the Union: A house dividing, 1852-1857. Vol. 2 (1947) pp 3–42.
- Nichols, Roy Franklin. The Democratic Machine, 1850–1854 (1923) online
- Wilentz, Sean. The rise of American democracy: Jefferson to Lincoln (2006) pp 659–667.
Primary sources[]
- Chester, Edward W A guide to political platforms (1977) online
- Porter, Kirk H. and Donald Bruce Johnson, eds. National party platforms, 1840-1964 (1965) online 1840-1956
Web sites[]
- "A Historical Analysis of the Electoral College". The Green Papers. Retrieved September 17, 2005.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to United States presidential election, 1852. |
- Presidential Election of 1852: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- 1852 popular vote by counties
- 1852 state-by-state popular vote
- Democratic National Convention overview
- Whig National Convention overview
- Native American National Convention overview
- How close was the 1852 election? — Michael Sheppard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Election of 1852 in Counting the Votes Archived October 23, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- 1852 United States presidential election
- Presidency of Franklin Pierce
- Franklin Pierce
- November 1852 events

















