Europium(III) oxide

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.787 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Eu2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 351.926 g/mol |
| Appearance | white to light-pink solid powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 7.42 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2,350 °C (4,260 °F; 2,620 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 4,118 °C (7,444 °F; 4,391 K) |
| Negligible | |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
|
+10,100·10−6 cm3/mol |
| Thermal conductivity | 2.45 W/(m K) |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, Cubic | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
5000 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Europium(III) chloride |
Other cations
|
Samarium(III) oxide, Gadolinium(III) oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Europium(III) oxide (Eu2O3), is a chemical compound of europium and oxygen. It is widely used as a red or blue phosphor in television sets and fluorescent lamps, and as an activator for yttrium-based phosphors. It is also an agent for the manufacture of fluorescent glass. Europium fluorescence is used in the anti-counterfeiting phosphors in Euro banknotes.[2]
Europium oxide has two common structures: Monoclinic (mS30, space group C2/m, No. 12) and cubic (cI80, space group Ia3, No. 206). The cubic structure is similar to that of manganese(III) oxide.
It may be formed by ignition of europium metal.
It can react with acids to form the corresponding europium(III) salts.
Gallery[]
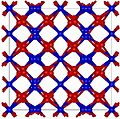
Cubic Eu2O3

Monoclinic Eu2O3
References[]
Categories:
- Inorganic compound stubs
- Europium compounds
- Glass engineering and science
- Sesquioxides

