Govia Thameslink Railway
 | |
 A Thameslink Class 700 at Shepreth Branch Junction, south of Cambridge in 2019 | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Franchise(s) | Thameslink, Southern and Great Northern 14 Sep 2014 – 31 March 2022[1] |
| Main region(s) | South East England, Greater London, East Anglia |
| Stations operated | 238 |
| Parent company | Govia (Go-Ahead Group 65%, Keolis 35%) |
| Reporting mark | GN, GX, SN, TL |
| Other | |
| Website | www |
Govia Thameslink Railway (GTR) is a train operating company that operates the Thameslink, Southern and Great Northern (TSGN) rail franchise in England. Within the franchise, GTR runs the Thameslink, Great Northern, Southern and Gatwick Express airport services.[2]
GTR is a subsidiary of Govia, which is itself a joint venture between the British Go-Ahead Group (65%) and French company Keolis (35%).
History[]
Thameslink and Great Northern services were merged into one franchise in 2006 due to the upcoming Thameslink Programme. In 2012, it was announced that services of First Capital Connect, Southern (with Gatwick Express) and some Southeastern routes would be merged into a single Thameslink, Southern and Great Northern franchise (TSGN).[3] The Invitation to Tender was to have been issued in October 2012, with the successful bidder announced in Spring 2013 and TSGN originally due to start in September 2013. However, due to the collapse of the InterCity West Coast re-franchising process, all franchising competitions were frozen until January 2013.[4] In January 2013 the government announced that it would extend the contract until March 2014, intending to negotiate with FirstGroup to operate the franchise on a management contract for up to two years.[5]
In March 2013 the Secretary of State for Transport announced that the franchise would again be extended, until 13 September 2014, and that the future franchise would be a management-style contract due to the level of investment and change on the route.[6] In September 2013 a revised invitation to tender was issued.[7] Govia Thameslink Railway was awarded the franchise on 23 May 2014.[8][9]
On 14 September 2014, Govia Thameslink Railway took over services from First Capital Connect, serving 122 stations and operating a fleet of 226 trains. In December 2014, full control was taken of the Sevenoaks Thameslink service (this service was previously jointly operated with Southeastern). The separate Thameslink and Great Northern were maintained upon the GTR takeover. Southern and Gatwick Express became part of GTR in July 2015, making it the largest rail franchise in terms of passengers, staff and fleet in the UK.[10][11]
The franchise has an unusual structure: it is a management contract where fare income does not go to GTR. Under their original contract, Department for Transport will pay GTR £8.9 billion over the first seven years and receive all revenue.[2] Consequently, the company carries less revenue risk. This form of franchise was chosen because of long-term engineering works anticipated around London, which would be a significant challenge to organise within the normal form of franchise.[12][13]
In June 2016, amongst criticism of the performance of its services, Go-Ahead warned of lower than anticipated profits on the franchises, leading to 18% drop in the Go-Ahead share price. Passengers had previously rated its Thameslink service as the worst in the country. Only 20% of Southern trains arrived on time in the year from April 2015 to March 2016, and there was an ongoing industrial dispute over driver-only operated trains.[14][15][16] On 12 July 2016, after 15% of Southern services were cancelled for a period of weeks to improve service reliability, Mayor of London Sadiq Khan called for GTR to be stripped of the franchise.[17] On 15 July 2016, Rail Minister Claire Perry resigned.[18]
Thameslink and Great Northern services[]

Govia Thameslink Railway has operated Thameslink and Great Northern services since 14 September 2014. Thameslink is a 68-station main-line route running 225 km (140 mi) north to south through London from Bedford to Brighton, serving both London Gatwick Airport and London Luton Airport, with a suburban loop serving Sutton, Mitcham and Wimbledon and on weekdays a suburban line via Catford and Bromley South to Sevenoaks. Great Northern is the name of the suburban rail services run on the southern end of Britain's East Coast Main Line and associated branches. Services operate to or from London King's Cross and London Moorgate. Destinations include Hertford North, Welwyn Garden City, Stevenage, Peterborough, Cambridge and King's Lynn.
In May 2018, the company introduced a new timetable which included the first regular services through the Canal Tunnels and to other new destinations previously not served by Thameslink. However, due to frequent disruption of services on the whole network, Govia decided to create a new interim timetable with a reduced number of trains; this came into operation in July 2018.[19]
Thameslink service pattern[]
The published Thameslink off-peak service pattern as of May 2020, with frequencies in trains per hour (tph), includes:[20]
| London Bridge routes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock |
| Cambridge to Brighton | 2 |
|
700 |
| Cambridge to London King's Cross | 2 | ||
| Peterborough to Horsham via Redhill | 2 |
| |
| Bedford to Brighton | 2 |
| |
| Bedford to Gatwick Airport via Redhill | 2 |
| |
| Luton to Rainham via Greenwich | 2 |
| |
| Elephant & Castle routes | |||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock |
| St Albans City to Sutton via Wimbledon (loop) | 2 |
|
700 |
| St Albans City to Sutton via Carshalton (loop) | 2 |
| |
| Kentish Town to Orpington via Catford (weekdays only) | 2 |
| |
| London Blackfriars to Sevenoaks via Catford and Otford | 2 |
| |
During peak hours, additional services run, including to East Grinstead[21] and Littlehampton.[22]
Great Northern service pattern[]

Since the introduction of regular services through the Canal Tunnels in May 2018, many GTR services on the East Coast Main Line were rebranded from Great Northern to Thameslink. Most of these services are now extended through central London and incorporated into the Thameslink network (as per above), although as of October 2019 some services are yet to be extended. The only services to retain the Great Northern brand (which will not become part of Thameslink) are those on the Northern City line and the express services to/from Cambridge, Ely and King's Lynn, as well as Peterborough at peak times.[23]
The Great Northern off-peak service pattern, with frequencies in trains per hour (tph), consists of the following:[24]
| Cambridge express & Fen line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock |
| London King's Cross to Ely | 1 | Cambridge, Cambridge North | 387 |
| London King's Cross to King's Lynn | 1 | Cambridge, Cambridge North, Waterbeach, Ely, Littleport, Downham Market, Watlington | |
| Northern City line | |||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock |
| Moorgate to Welwyn Garden City | 4 |
|
717 |
| Moorgate to Hertford North | 2 |
| |
| Moorgate to Stevenage | 2 |
| |
Southern and Gatwick Express services[]

The Southern and Gatwick Express brands joined Govia Thameslink Railway on 26 July 2015. Southern routes run from London Victoria and London Bridge through the South London suburbs of Battersea, Norbury, Peckham, Sydenham, Crystal Palace, Norwood, Croydon, Streatham, Purley and Sutton to towns surrounding London including Caterham, Epsom and Tadworth. Further afield, Southern also serve Redhill, Tonbridge, Uckfield, East Grinstead, Gatwick Airport, Brighton, Ashford (Kent), Worthing, Hastings, Portsmouth, Eastbourne, Horsham, Southampton, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis. Additionally, Southern run West London route services from Milton Keynes to South Croydon via Watford and Clapham Junction. Since 2008, Southern has operated the Gatwick Express service from London Victoria to Gatwick Airport and Brighton.
Gatwick Express[]
Gatwick Express services have been suspended from 30 March 2020 until further notice.[25] The Gatwick Express airport rail link from central London is to resume before Christmas after 21 months out of service during the pandemic.[26]
Southern[]
Details of each route, including maps and timetables, are on Southern's website (see External links below). As of May 2020, the off-peak Monday-Saturday service pattern, with frequencies in 'trains per hour' (tph), consists of:[27]
| Brighton Mainline | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock | |
| London Victoria – Littlehampton | 2 |
|
377 | |
| London Victoria – Eastbourne | 1 |
|
377 | |
| London Victoria – Ore | 1 |
|
377 | |
| London Victoria – Brighton | 2 |
|
| |
| Arun Valley | ||||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock | |
| London Victoria – Southampton Central and Bognor Regis via Crawley | 1 |
The two portions divide/attach at Horsham. |
377 | |
Southampton Central portion:
|
Bognor Regis portion:
| |||
| London Victoria – Portsmouth & Southsea and Bognor Regis via Crawley | 1 |
The two portions divide/attach at Horsham. |
377 | |
Portsmouth & Southsea portion:
|
Bognor Regis portion:
| |||
| Coastway East | ||||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock | |
| Brighton – Lewes | 2 |
|
313 | |
| Brighton – Seaford | 2 |
|
313 | |
| Brighton – Hastings | 1 |
|
| |
| Brighton – Ore | 1 |
| ||
| Eastbourne – Ashford International | 1 |
Three Oaks and Winchelsea are served by alternate trains. |
171 | |
| Coastway West | ||||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock | |
| Brighton – Hove | 2 | 313 | ||
| Brighton – West Worthing | 2 |
|
313 | |
| Brighton – Southampton Central | 1 | 377 | ||
| Brighton – Portsmouth Harbour | 1 |
|
| |
| Littlehampton – Portsmouth & Southsea | 1 |
|
313 | |
| Littlehampton – Bognor Regis | 1 |
|
313 | |
| Barnham – Bognor Regis | 1 | 313 | ||
| Oxted | ||||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock | |
| London Victoria – East Grinstead | 2 |
|
377 | |
| London Bridge – Uckfield | 1 |
|
171 | |
| Redhill | ||||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock | |
| London Victoria – Reigate | 2 | 377 | ||
| Redhill – Tonbridge | 1 | 377 | ||
| West London | ||||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock | |
| Milton Keynes Central – Clapham Junction | 1 |
|
| |
| Metro | ||||
| Route | tph | Calling at | Stock | |
| London Victoria – Dorking (and Horsham) via Carshalton | 2 |
|
377 | |
| London Victoria – Epsom via Carshalton | 2 |
|
377 | |
| London Victoria – Sutton (and Epsom Downs) via Norbury | 4 |
|
| |
| London Victoria – West Croydon via Gipsy Hill | 2 |
|
377 | |
| London Victoria – London Bridge via Gipsy Hill | 2 |
Services continue to London Bridge via Sydenham (see below). |
377 | |
| London Bridge – London Victoria via Sydenham | 2 |
Services continue to London Victoria via Gipsy Hill (see above). |
377 | |
| London Bridge – Coulsdon Town via Sydenham | 2 |
|
455 | |
| London Bridge – Epsom | 2 |
|
377 | |
| London Bridge – Caterham and Tattenham Corner | 2 |
The two portions divide/attach at Purley. |
377 | |
Caterham portion:
|
Tattenham Corner portion:
| |||
| London Bridge – Caterham via Peckham Rye and Norbury | 2 |
|
| |
| London Bridge – Beckenham Junction via Peckham Rye | 2 |
|
| |
Franchise commitments[]

This franchise is different from many other franchises let since privatisation in 1996. Now the operator, in this case Govia, gives all revenue to the government, rather than paying set premiums. The Department for Transport will pay Govia, totalling around £8.9bn over the franchise period of seven years, from the expected revenues of £12.4bn. With this Govia expects to make a 3% profit, and the risks on costs will be Govia's, while the DfT will profit or lose from fluctuations in revenue.[28]
Govia plans to invest £50m in all 239 stations it will manage. It plans to:[29]
- Enhance all 239 stations including improving access, replace electronic information screens and working with local authorities on the redevelopment of St Albans and Luton stations.
- Increase staffing hours at many stations, with the 100 busiest stations staffed from first to last train, like London Overground stations.
- Extension of 'the key' smartcard which Southern has been introducing.
- Provide 104 stations with free wifi.
- £1.5m on station access improvements including increased cycle storage and electrical vehicle charging points.
Other plans include:[30]
- Half-hourly King's Lynn to London services
- Direct Peterborough, Cambridge, Welwyn Garden City and Finsbury Park to Tattenham Corner, Caterham, Horsham services.[31]
- Increasing Great Northern suburban services to four trains per hour via Enfield Chase and New Barnet
- Great Northern suburban services to run to Moorgate at weekends and on weekday evenings
- 50% increase in capacity from Uckfield to London in the peaks.
- Doubling overnight Thameslink services
- Sevenoaks Thameslink services to run on Saturdays
- Working to extend Oyster to Epsom, Gatwick Airport, Luton Airport Parkway, Welwyn Garden City and Hertford North[32]
- Class 387 Electrostars for King's Lynn express services, releasing Class 317s, 321s and some Class 365s for newly electrified routes elsewhere.[33]
- Creating an with Network Rail in 2016, like South West Trains.[34]
Rolling stock[]


In 2011 the consortium Cross London Trains Ltd. consisting of Siemens Project Ventures, 3i Infrastructure plc and Innisfree Ltd was announced as preferred bidder with Siemens to manufacture and maintain the rolling stock to run on the Thameslink routes from 2016. This was a politically controversial decision as the competing bidder Bombardier Transportation had a train factory in the UK.[35] Both the procurement process and final close of contract were significantly delayed, resulting in the expected first delivery date moving from 2012 to 2016. The trains are known as Class 700s and the £1.6 billion contract to manufacture and provide service depots for the trains was finalised in mid 2013.[36] A fleet of 115 8- and 12-car trains is expected to enter service between 2016 and 2018. A new-build rolling stock depot was completed at Three Bridges in 2015,[37] and Hornsey depot was extended northwards and had several new buildings added in 2016.[38]
Because of the delay in procuring the Class 700 trains, 29 Class 387 trains were ordered for the Thameslink route, releasing the Class 319 trains to newly electrified routes. Delivery was completed in 2014 and the trains entered service later that year. The order includes provision for an extra 140 vehicles.[7][39] It was originally planned that once the Class 700s began entering service, the Class 387s would be transferred to Great Western Railway for use on routes in the Thames Valley.[40] However a change of plans saw GWR order an entirely new fleet of Class 387s, so the Thameslink units were cascaded to the Great Northern route following delivery of the Class 700s.[41][42]
In addition to the introduction of the new Class 700 units, GTR also ordered a further 25 new 6-car trains to replace the 40-year-old Class 313 units[28] on the Great Northern Moorgate suburban services. In December 2015, Siemens was selected to provide these as a follow-on to the Class 700 order.[43][44] They were designated as the Class 717 in June 2016, and were first introduced in September 2018.[45][46]
Current fleet[]
| Family | Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Cars | Number | Routes operated | Built | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | ||||||||
| Southern | |||||||||
| Bombardier Turbostar | 
|
DMU | 100 | 161 | 2 | 12 | Oxted line (Uckfield branch) Marshlink line |
2003–04 | |
| 4 | 8 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| BREL 1972 |
313 |

|
EMU | 75 | 120 | 3 | 19 | West Coastway line East Coastway line |
1976–77 |
| |||||||||
| Bombardier Electrostar |
377 |

|
EMU | 100 | 160 | 3 | 28 | Entire Southern network apart from Oxted to Uckfield and Ore to Ashford International lines | 2001–05 |
| 4 | 152 | ||||||||
| 5 | 34 | 2012–14 | |||||||
|
455 |

|
EMU | 75 | 120 | 4 | 46 | Metro and commuter services from London Victoria and London Bridge | 1982–84 | |
| Gatwick Express | |||||||||
| Bombardier Electrostar |
387/2 |

|
EMU | 110 | 177 | 4 | 27 | Express services between London Victoria and Gatwick Airport / Brighton | 2015–16 |
| Great Northern | |||||||||
| Bombardier Electrostar | 387 | 
|
EMU | 110 | 177 | 4 | 29 | Express services between London King's Cross and Peterborough / Ely / King's Lynn | 2014–15 |
| Siemens Desiro |
717 Desiro City[46] |

|
EMU | 85 | 137 | 6 | 25 | Northern City Line: Services between London Moorgate and Welwyn Garden City / Hertford North / Watton-at-Stone | 2018 |
| Thameslink | |||||||||
| Siemens Desiro | 700/0 & 700/1 Desiro City |  
|
EMU | 100 | 161 | 8 | 60 | All Thameslink services | 2015–18 |
| 12 | 55 | ||||||||
Past fleet[]
Former units operated by Thameslink and Great Northern include:
| Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Carriages | Number | Built | Routes | Withdrawn | Transferred to | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | |||||||||
| 365 Networker Express | 
|
EMU | 100 | 161 | 4 | 40 | 1994-95 | Express services between London King's Cross and Peterborough / Ely / King's Lynn | 2018-2021 | Abellio ScotRail and Storage |
| 313 | 
|
EMU | 75 | 121 | 3 | 44 | 1976-77 | Northern City Line | 2019 | Scrapped and replaced with Class 717 |
| 317 | 
|
EMU | 100 | 161 | 4 | 12 | 1981–82 | Express services between London King's Cross to Peterborough and Cambridge | 2017 | Greater Anglia |
| 319 | 
|
EMU | 100 | 161 | 4 | 86 | 1987–88 1990 |
All Thameslink services | 2015–17 | Arriva Rail North, London Midland, Northern Rail or stored. |
| 321 | 
|
EMU | 100 | 161 | 4 | 13 | 1989–90 | Express services between London King's Cross to Peterborough and Cambridge | 2016 | Greater Anglia, Abellio ScotRail (converted to Class 320/4s) |
| 377 Electrostar | 
|
26 | 2008–09 | Some Thameslink services | 2017 | Southeastern and Southern | ||||
Performance[]
In February 2015, Thameslink and Great Northern came at the bottom of Which? magazine's Best and worst UK train companies customer survey, scoring a customer satisfaction score of 43%. Thameslink and Great Northern were also scored 2/5 stars in each of the specific categories covered by the survey (including Reliability, Punctuality and Cleanliness of toilets) – which is the worst performance of any UK train operator. In the Which? 2017 survey Thameslink and Great Northern improved their performance slightly with a rating of 46% also, their position in the table was second to bottom[49](Southern were in bottom place, but had been subject huge disruption due to industrial action).
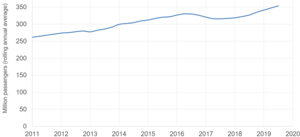
Passenger numbers on Govia Thameslink Railway (which also includes Southern and Gatwick Express) have risen from 262 million annually in 2010/11 to 327 million annually in 2015/16.[48]
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ "GTR contract extended to March 2022". The Go-Ahead Group. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ a b Topham, Gwyn (23 May 2014). "FirstGroup loses Thameslink franchise to Go-Ahead joint venture". The Guardian. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Consultation on the combined Thameslink, Southern and Great Northern franchise". Department for Transport. 26 September 2013. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Expanding and improving the rail network". Department for Transport. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ Rail franchising future programme. Department for Transport. 31 January 2013.
- ^ "Railway plan puts new focus on passengers". Secretary of State for Transport statement 26 March 2013.
- ^ a b Thameslink Southern & Great Northern Invitation to Tender. Department for Transport. 26 September 2013.
- ^ "Govia chosen for new Thameslink contract". Railnews. 23 May 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- ^ "Govia wins TSGN franchise, beating FirstGroup". Rail Technology. 23 May 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- ^ "New rail franchising deal set to transform passenger services across London and south east". Department for Transport (DfT). 23 May 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Govia wins Thameslink rail franchise". BBC News Online. 23 May 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ Ben James (18 June 2016). "Fines issued to rail provider GTR for poor performance slammed". The Argus. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Simon Usborne (8 July 2016). "All aboard the Southern chaos train: the commuters caught in a war on rails". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- ^ "Thameslink woes hit Go-Ahead shares". BBC News. 14 June 2016. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Craig Richard (17 June 2016). "Boss of Epsom's main train operator Govia Thameslink Railway takes home £2.1m paycheck despite "appalling service"". Your Local Guardian. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Joseph Watts (17 June 2016). "Govia Thameslink Railway boss refuses to defend CEO £2m pay". Evening Standard. London. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Gwyn Topham, Matthew Weaver (12 July 2016). "Take Southern rail franchise off operator, urges Sadiq Khan". The Guardian. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- ^ "Rail minister Claire Perry resigns". BBC News. 15 July 2016. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- ^ "Thameslink: Train Timetables". June 2018.
- ^ Table 25 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (ECML services)
Table 52 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Thameslink route services)
Table 52-MML National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Midland Main Line services)
Table 179 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Sutton loop)
Table 183 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Gatwick Airport and Horsham services)
Table 184 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Brighton Main Line services)
Table 196 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Catford Loop Line services)
Table 201 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (North Kent Line services) - ^ Table 182 National Rail timetable, May 2020
- ^ Table 188 National Rail timetable, May 2020
- ^ Train Routes - Great Northern
- ^ Table 24 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (commuter services)
Table 25 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (regional services) - ^ "Temporary suspension of Gatwick Express". Gatwick Express. 30 March 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ^ Ltd, Jacobs Media Group. "Gatwick Express reinstated after 21 months". Travel Weekly. Retrieved 5 December 2021.
- ^ Table 170 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (via Selhurst)
Table 171 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (via Gipsy Hill)
Table 172 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Sutton and Epsom Downs services)
Table 173 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (via Peckham Rye)
Table 176 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (West London Line services)
Table 177 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (via Sydenham)
Table 180 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Epsom, Dorking and Horsham services)
Table 181 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Tattenham Corner and Caterham services)
Table 182 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (via Oxted)
Table 183 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Redhill services)
Table 184 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Brighton Main Line services)
Table 186 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Arundel Line and via Chichester)
Table 188 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (West Coastway Line via Worthing)
Table 189 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Lewes and Seaford services)
Table 190 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Eastbourne and Ore services)
Table 192 National Rail timetable, May 2020 (Marshlink Line services) - ^ a b Topham, Gwyn (23 May 2014). "FirstGroup loses Thameslink franchise to Go-Ahead joint venture". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Govia awarded TSGN franchise" (Press release). Govia. 23 May 2014. Retrieved 9 September 2014.
- ^ "TSGN". Govia. Archived from the original on 25 May 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Proposed Thameslink service pattern" (PDF). Thameslink Programme. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 May 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Easier journeys and better information". Govia. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 11 July 2014.
- ^ "New Trains". Govia. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 11 July 2014.
- ^ "More reliable and faster services". Govia. Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 11 July 2014.
- ^ "Siemens beats Bombardier to Thameslink train order". BBC News. 16 June 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ Millward, David (13 June 2013). "Bombardier blow as Siemens wins £1.6bn Thameslink deal". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Three Bridges depot opens its doors". VolkerFitzpatrick. VolkerFitzpatrick. 15 October 2015. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ "Modernised depot to transform Great Northern rail services". VolkerFitzpatrick. VolkerFitzpatrick. 3 December 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ "Bombardier to manufacture 116 new train carriages for Thameslink rolling stock cascade" (Press release). Southern. 17 July 2013.
- ^ "First Great Western plans AT300s to Cornwall". Railway Gazette. 23 March 2015.
- ^ "Latest Class 387 Electrostar deal details". Rail. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Great Northern Class 700s to operate from next year". Rail. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Siemens selected to supply Moorgate suburban EMU fleet". Railway Gazette. London. 22 December 2015. Retrieved 22 December 2015.
- ^ Clinnick, Richard (22 December 2015). "Siemens favoured for new GN trains". Rail. Peterborough. Retrieved 22 December 2015.
- ^ "New Great Northern Class 717 carries first passengers". Rail. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ a b "New Govia Thameslink Railway trains to be Class 717s". Rail. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- ^ "Table 1223 - Passenger journeys by operator | ORR Data Portal". dataportal.orr.gov.uk. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Govia Thameslink Railway - Table 2.8". Archived from the original on 1 May 2017. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ "Best train companies overall". Which?. Archived from the original on 3 June 2017.
External links[]
![]() Media related to Govia Thameslink Railway at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Govia Thameslink Railway at Wikimedia Commons
- 2014 establishments in England
- Airport rail links in London
- Go-Ahead Group companies
- Keolis
- Rail transport in East Sussex
- Rail transport in Hampshire
- Rail transport in Kent
- Rail transport in Surrey
- Rail transport in West Sussex
- Railway operators in London
- Thameslink
- Train operating companies in the United Kingdom