Laboratory Cabin Module
 A model of Tiangong-2, the prototype for the LCMs | |
| Module statistics | |
|---|---|
| Launch date | May–June 2022: Wentian August–September 2022: Mengtian |
| Launch vehicle | Long March 5B |
| Mass | 20,000 kg (44,000 lb) |
| Length | 17.9 m (59 ft) |
| Diameter | 4.2 m (14 ft) |
The Laboratory Cabin Modules (LCM), Wentian (simplified Chinese: 问天; traditional Chinese: 問天; pinyin: Wèn Tiān; lit. 'Quest for the Heavens[1]') and Mengtian (simplified Chinese: 梦天; traditional Chinese: 夢天; pinyin: Mèng Tiān; lit. 'Dreaming of the Heavens[1]'), are major components of the Chinese space station. Based on the Tiangong-2 experimental space module, the LCMs complete the third and final stage of Project 921, the CNSA's program to establish a permanent Chinese space station. While China's small unmanned spacecraft can provide platforms for zero gravity and exposure to space for scientific research, the LCMs offer a long term environment combined with ready access by human researchers over periods that far exceed the capabilities of Shenzhou spacecraft. Operations will be controlled from the Beijing Aerospace Command and Control Center in the People's Republic of China.
Purpose[]
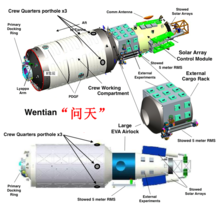

The first laboratory module will provide additional navigation avionics, propulsion and orientation control as backup functions for the Tianhe Core Module (TCM). Both LCMs provide a pressurized environment for researchers to conduct science experiments in freefall or zero gravity which could not be conducted on Earth for more than a few minutes. Experiments can also be placed on the outside of the modules, for exposure to the space environment, cosmic rays, vacuum, and solar winds.
The axial port of the LCMs will be fitted with rendezvous equipment and will first dock to the axial port of the CCM. A mechanical arm similar to the Russian Lyappa arm used on the Mir space station will then move the module to a radial port of the CCM.
Electrical power is provided by two steerable solar power arrays, which use photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electricity. Energy is stored to power the station when it passes into the Earth's shadow. Resupply ships will replenish fuel for LCM 1 for station-keeping, to counter the effects of atmospheric drag.
Dimensions[]
The length of each module is 17.9 m. They are cylindrical with a maximum diameter of 4.2 m and an on-orbit mass of approximately 20,000 kg (44,000 lb) apiece.[2][3]
Launch[]
Both modules are due for launch in 2022 on Long March 5B launch vehicles from Wenchang Satellite Launch Center. Wentian is scheduled to launch in May or June 2022,[4] while Mengtian is scheduled to launch in August or September.[5] They will be inserted into a low Earth orbit with an average altitude of 393 km (244 mi) at an orbital inclination of 42 degrees, centered in the Earth's thermosphere.[2][6]
References[]
- ^ a b "Planned space station details made public". China Daily. 2018-04-26.
The two space labs, Wentian, or Quest for Heavens, and Mengtian, or Dreaming of Heavens
- ^ a b Barbosa, Rui C. (1 March 2021). "China preparing to build Tiangong station in 2021, complete by 2022". NASASpaceFlight. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ 王, 翔; 王, 为 (2021). "天宫空间站关键技术特点综述". 中国科学: 技术科学 (in Chinese). 51 (11). Retrieved 2021-11-13.
- ^ "【22年待定】长征五号乙遥三火箭 • 中国空间站实验舱——问天 • LongMarch-5B Y3" [[2022 TBD] Long March 5B Y3 rocket • Chinese Space Station Laboratory Module—Wentian]. spaceflightfans.cn (in Chinese). 21 April 2021. Archived from the original on 4 August 2021. Retrieved 24 April 2021.
- ^ "【22年待定】长征五号乙遥四火箭 • 中国空间站实验舱——梦天 • LongMarch-5B Y4" [[2022 TBD] Long March 5B Y4 rocket • Chinese Space Station Laboratory Module—Mengtian]. spaceflightfans.cn (in Chinese). 21 April 2021. Archived from the original on 4 August 2021. Retrieved 24 April 2021.
- ^ David, Leonard (7 March 2011). "China Details Ambitious Space Station Goals". Space.com. Retrieved 23 February 2012.
External links[]
- Chinese space stations
- 2022 in spaceflight
- 2022 in China