Methanethiol
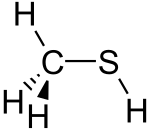
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methanethiol | |||
| Other names
Methyl mercaptan
Mercaptomethane Methiol Thiomethyl alcohol/Thiomethanol Methylthiol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.748 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1064 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH3SH | |||
| Molar mass | 48.11 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas[1] | ||
| Odor | Distinctive, like that of rotten cabbage or eggs | ||
| Density | 0.9 g/mL (liquid at 0°C)[1] | ||
| Melting point | −123 °C (−189 °F; 150 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 5.95 °C (42.71 °F; 279.10 K) | ||
| 2% | |||
| Solubility | alcohol, ether | ||
| Vapor pressure | 1.7 atm (20°C)[1] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | ~10.4 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements
|
H220, H331, H400, H410 | ||
| P210, P261, P271, P273, P304+340, P311, P321, P377, P381, P391, P403, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
4
4
1 | ||
| Flash point | −18 °C; 0 °F; 255 K [1] | ||
| Explosive limits | 3.9%-21.8%[1] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
60.67 mg/kg (mammal)[2] | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
3.3 ppm (mouse, 2 hr) 675 ppm (rat, 4 hr)[2] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
C 10 ppm (20 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
C 0.5 ppm (1 mg/m3) [15-minute][1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
150 ppm[1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Ethanethiol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methanethiol /ˈmɛθeɪnˈθaɪɒl/ (also known as methyl mercaptan) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH
3SH. It is a colorless gas with a distinctive putrid smell. It is a natural substance found in the blood, brain and feces of animals (including humans), as well as in plant tissues. It also occurs naturally in certain foods, such as some nuts and cheese. It is one of the chemical compounds responsible for bad breath and the smell of flatus. Methanethiol is the simplest thiol and is sometimes abbreviated as MeSH. It is very flammable.
Structure and reactions[]
The molecule is tetrahedral at carbon, like methanol. It is a weak acid, with a pKa of ~10.4, but is about a million times more acidic than methanol. The colorless salt can be obtained in this way:
- CH3SH + CH3ONa → CH3SNa + CH3OH
The resulting thiolate anion is a strong nucleophile.
It can be oxidized to dimethyl disulfide:
- 2CH3SH + [O] → CH3SSCH3 + H2O
Further oxidation takes the disulfide to two molecules of methanesulfonic acid, which is odorless. Bleach deodorizes methanethiol in this way.
Occurrence[]
Methanethiol (MeSH) is released as a by-product of kraft pulping in pulp mills. In kraft pulping, lignin is depolymerized by nucleophilic attack with the strongly nucleophilic hydrosulfide ion (HS−) in a highly alkaline medium. However, in a side reaction, HS− attacks methoxyl groups (OMe) in lignin, demethylating them to give free phenolate groups (PhO−) and releasing MeSH. Due to alkalinity, MeSH is readily deprotonated (MeSNa), and the formed MeS− ion is also a strong nucleophile, reacting further to dimethyl sulfide. The compounds remain in the liquor and are burned in the recovery boiler, where the sulfur is recovered as sodium sulfide.[3]
Methanethiol is released from decaying organic matter in marshes and is present in the natural gas of certain regions, in coal tar, and in some crude oils. It occurs in various plants and vegetables, such as radishes.
In surface seawater, methanethiol is the primary breakdown product of the algal metabolite dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP). Marine bacteria appear to obtain most of the sulfur in their proteins by the breakdown of DMSP and incorporation of methanethiol, despite the fact that methanethiol is present in seawater at much lower concentrations than sulfate (~0.3 nM vs. 28 mM). Bacteria in environments both with and without oxygen can also convert methanethiol to dimethyl sulfide (DMS), although most DMS in surface seawater is produced by a separate pathway.[citation needed] Both DMS and methanethiol can be used by certain microbes as substrates for methanogenesis in some anaerobic soils.
Methanethiol is a byproduct of the metabolism of asparagus.[4] The production of methanethiol in urine after eating asparagus was once thought to be a genetic trait. More recent research suggests that the peculiar odor is in fact produced by all humans after consuming asparagus, while the ability to detect it (methanethiol being one of many components in "asparagus pee") is in fact the genetic trait.[5] The chemical components responsible for the change in the odor of urine show as soon as 15 minutes after eating asparagus.[6]
Preparation[]
Methanethiol is prepared commercially by the reaction of methanol with hydrogen sulfide gas over an aluminum oxide catalyst:[7]
- CH3OH + H2S → CH3SH + H2O
Although impractical, it can be prepared by the reaction of methyl iodide with thiourea.[8]
Uses[]

Methanethiol is mainly used to produce the essential amino acid methionine, which is used as a dietary component in poultry and animal feed.[7] Methanethiol is also used in the plastic industry as a moderator for free-radical polymerizations[7] and as a precursor in the manufacture of pesticides.
This chemical is also used in the natural gas industry as an odorant, as it mixes well with methane. The characteristic "rotten eggs" smell of the mix is widely known by natural gas customers as an indicator of a possible gas leak, even a very minor one.[9]
Safety[]
The safety data sheet (SDS) lists methanethiol as a colorless, flammable gas with an extremely strong and repulsive smell. At very high concentrations it is highly toxic and affects the central nervous system. Its penetrating odor provides warning at dangerous concentrations. An odor threshold of 1 ppb has been reported.[10] The United States OSHA Ceiling Limit is listed as 10 ppm.
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0425". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Methyl mercaptan". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Sixta, H.; Potthast, A.; Krotschek, A. W., Chemical Pulping Processes. In Handbook of Pulp, Sixta, H., Ed. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, 2006; Vol. 1, p 169 (109-510).
- ^ Richer, Decker, Belin, Imbs, Montastruc, Giudicelli: "Odorous urine in man after asparagus", British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, May 1989
- ^ Lison M, Blondheim SH, Melmed RN (1980). "A polymorphism of the ability to smell urinary metabolites of asparagus". Br Med J. 281 (6256): 1676–8. doi:10.1136/bmj.281.6256.1676. PMC 1715705. PMID 7448566.
- ^ Skinny On: Discovery Channel Archived 2008-02-29 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Norell, John; Louthan, Rector P. (1988). "Thiols". Kirk-Othmer Concise Encylclopedia of Chemical Technology (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 946–963. ISBN 978-0471801047.
- ^ Reid, E. Emmet (1958). Organic Chemistry of Bivalent Sulfur. 1. New York: Chemical Publishing Company, Inc. pp. 32–33, 38.
- ^ SafeGase: About Natural Gas:
- ^ Devos, M; F. Patte; J. Rouault; P. Lafort; L. J. Van Gemert (1990). Standardized Human Olfactory Thresholds. Oxford: IRL Press. p. 101. ISBN 0199631468.
External links[]
- Thiols
- Flatulence
- Foul-smelling chemicals