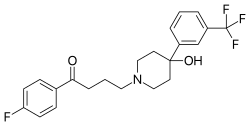
Trifluperidol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Triperidol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H23F4NO2 |
| Molar mass | 409.425 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
InChI
| |
Trifluperidol is a typical antipsychotic of the butyrophenone chemical class. It has general properties similar to those of haloperidol, but is considerably more potent by weight, and causes relatively more severe side effects, especially tardive dyskinesia and other extrapyramidal effects. It is used in the treatment of psychoses including mania and schizophrenia. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1959.[1][2]
Synthesis[]

See also[]
References[]
- ^ Gallant DM, Bishop MP, Timmons E, Steele CA (September 1963). "A controlled evaluation of Trifluperidol: a new potent psychopharmacologic agent". Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental. 5: 463–71. PMID 14065098.
- ^ Gallant DM, Bishop MP, Timmons E, Steele CA (November 1963). "Trifluperidol: a butyrophenone derivative". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 120 (5): 485–7. doi:10.1176/ajp.120.5.485. PMID 14051242.
Categories:
- 4-Phenylpiperidines
- Tertiary alcohols
- Aromatic ketones
- Belgian inventions
- Butyrophenone antipsychotics
- Janssen Pharmaceutica
- Trifluoromethyl compounds
- Typical antipsychotics
- Nervous system drug stubs