2012 Japanese general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 480 seats in the House of Representatives of Japan 241 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 59.31% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 districts and PR districts won by respective parties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
General elections were held in Japan on 16 December 2012. Voters gave the Liberal Democratic Party a landslide victory, ejecting the Democratic Party from power after three years. It was the fourth worst defeat suffered by a ruling party in Japanese history.
Voting took place in all representatives' constituencies of Japan including proportional blocks, in order to appoint Members of Diet to seats in the House of Representatives, the lower house of the National Diet of Japan.
In July 2012, it was reported that the deputy prime minister Katsuya Okada had approached the Liberal Democratic Party to sound them out about dissolving the house of representatives and holding the election in January 2013.[1] An agreement was reached in August to dissolve the Diet and hold early elections "shortly" following the passage of a bill to raise the national consumption tax.[2] Some right-wing observers asserted that as the result of introducing the consumption tax to repay the Japan public debt,[3][4][5][6][7] the DPJ lost around 75% of its pre-election seats.[8][9]
Background[]
The LDP had governed Japan for all but three years since 1955. However, in the 2009 election, the LDP suffered the worst defeat of a sitting government in modern Japanese history. Due to the characteristics of the Japanese election system, DPJ candidates won 308 seats in the House of Representatives (64.2% of seats), enabling Yukio Hatoyama to become prime minister. Since then, Japan has had two other prime ministers, Naoto Kan and Yoshihiko Noda. On 16 November, Noda dissolved parliament, thus allowing for a new election in a month's time. He cited the lack of funds to carry on the functions of government and the need for an emergency budget.
Dissatisfaction with the DPJ-led government and the former LDP-led government led to the formation of several grassroots movements, collectively known as the "third pole," to counter the two major parties.[10] The former Governor of Tokyo Shintarō Ishihara announced the renamed and re-formed of the Sunrise Party on 14 November 2012 Ishihara co-leading with Takeo Hiranuma.[11] On 17 November 2012 Mayor of Osaka Tōru Hashimoto and former Tokyo Governor Shintarō Ishihara announced the merger of the Japan Restoration Party and the Sunrise Party as a third force to contend the 16 December 2012 general election.[12] It is Japan's first national political party that is based outside of Tokyo.[13]
On 23 November, Mayor of Nagoya Takashi Kawamura, former state minister Shizuka Kamei and former farm minister Masahiko Yamada joined forces together to launch Tax Cuts Japan – Oppose TPP – Zero Nuclear Party as another "third pole" national political party.[14] On 28 November, the Governor of Shiga Yukiko Kada in Ōtsu announced the establishment of an anti-nuclear and equal gender party known as the Tomorrow Party of Japan becoming the second national party based outside of Tokyo. Concurrent the DPJ splitter group, People's Life First president Ichirō Ozawa dissolved the party and merged into the Tomorrow Party. Tax Cuts Japan – Oppose TPP – Zero Nuclear Party and Japan Future Party are negotiating to merge parties to further counter the major parties and the pro-nuclear parties.[15] On 27 November Tax Cuts Japan – Oppose TPP – Zero Nuclear Party officially announced they would merge with Tomorrow, with party co-leader Mashahiko Yamada saying "We would also like to raise our hands in joining because our ways of thinking are the same."[16]
Opinion polls[]
| Graph of poll results since 2009 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
Democratic Liberal Democratic New Komeito Communist Social Democratic Your Party Others incl. NPN, PNP, NRP and SP No Party
| ||||
| Graph of the current Cabinet Approval/Disapproval Ratings | ||||
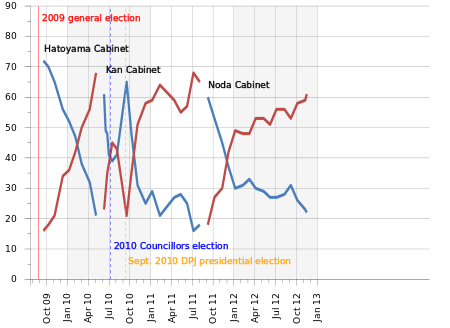 |
Party polling for the 180 proportional seats[]
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Undecided or declined | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPJ | LDP | JRP | LF ↓ TPJ |
NKP | JCP | YP | SDP | |||
| Asahi Shimbun | 15–16 November 2012 | 44% | 16% | 23% | 6% | 1% | 3% | 2% | 2% | 1% |
| Yomiuri Shimbun | 16–17 November 2012 | 43% | 13% | 22% | 13% | — | — | — | — | — |
| Asahi Shimbun | 17–18 November 2012 | 46% | 15% | 23% | 16% | — | 4% | — | — | — |
| Kyodo News | 17–18 November 2012 | 43% | 10.8% | 23% | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Yomiuri Shimbun | 23–25 November 2012 | — | 10% | 25% | 14% | 2% | 6% | — | 2% | — |
| Kyodo News [1] | 24–25 November 2012 | 45% | 8.4% | 18.7% | 10.3% | 2% | 4% | — | 3% | — |
| Asahi Shimbun | 24–25 November 2012 | 41% | 13% | 23% | 9% | 2% | 4% | — | 3% | — |
| Nikkei Business Daily | 28 November 2012 | — | 13% | 23% | 15% | 5% | 4% | — | — | — |
| Kyodo News | 1–2 December 2012 | — | 9.3% | 18.4% | 10.4% | 3.5% | 4.8% | — | — | — |
| Asahi Shimbun | 1–2 December 2012 | 41% | 15% | 20% | 9% | 3% | 4% | 3% | 3% | 1% |
| Yomiuri Shimbun | 30 Nov.-2 Dec 2012 | — | 13% | 19% | 13% | 5% | — | — | 5% | — |
| NHK | 7–9 December 2012 | — | 10% | 21% | 11% | — | — | — | — | — |
| Yomiuri Shimbun | 7–9 December 2012 | — | 12% | 29% | 11% | 3% | — | — | — | — |
| Asahi Shimbun | 8–9 December 2012 | 43% | 14% | 22% | 8% | 2% | 5% | 4% | 2% | — |
| Kyodo News | 12–13 December 2012 | 40% | 11% | 23% | 10% | — | — | — | — | — |
PM polling[]
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |

|

|

|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noda DPJ |
Abe LDP |
Ishihara JRP | ||
| Kyodo News | 3–4 November 2012 | 29.3% | 40% | — |
| Asahi Shimbun | 15–16 November 2012 | 31% | 33% | — |
| Yomiuri Shimbun | 16–17 November 2012 | 31% | 37% | — |
| Kyodo News | 17–18 November 2012 | 32.1% | 35% | — |
| Yomiuri Shimbun | 23–25 November 2012 | 19% | 29% | 22% |
| Kyodo News [2] | 24–25 November 2012 | 30% | 33.9% | — |
| Yomiuri Shimbun | 30 Nov.-2 Dec 2012 | 21% | 28% | — |
| NHK | 7–9 December 2012 | 19% | 28% | — |
| Kyodo News | 8–9 December 2012 | 31% | 39% | — |
| Kyodo News | 12–13 December 2012 | 29% | 34% | — |
Pre-election composition[]
As of official announcement (kōji [=deadline for candidate registration, legal campaign start, start of early voting on following day]) on 4 December[17] – note that the government had lost its majority, already slim at the time of dissolution of the House of Representatives (16 November), due to further defections during the positioning of candidates for the election.
| ↓ | |||
| 139 | 107 | 1 | 233 |
| LDP & NKP | Other opposition | V | Incumbent government (DPJ & PNP) |
Results[]
 | |||||||||
| Party | Proportional | Constituency | Total seats | +/– | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | ||||
| Liberal Democratic Party | 16,624,457 | 27.62 | 57 | 25,643,309 | 43.01 | 237 | 294 | +175 | |
| Japan Restoration Party | 12,262,228 | 20.38 | 40 | 6,942,354 | 11.64 | 14 | 54 | New | |
| Democratic Party of Japan | 9,628,653 | 16.00 | 30 | 13,598,774 | 22.81 | 27 | 57 | –251 | |
| New Komeito Party | 7,116,474 | 11.83 | 22 | 885,881 | 1.49 | 9 | 31 | +10 | |
| Your Party | 5,245,586 | 8.72 | 14 | 2,807,245 | 4.71 | 4 | 18 | +13 | |
| Japanese Communist Party | 3,689,159 | 6.13 | 8 | 4,700,290 | 7.88 | 0 | 8 | –1 | |
| Tomorrow Party of Japan | 3,423,915 | 5.69 | 7 | 2,992,366 | 5.02 | 2 | 9 | New | |
| Social Democratic Party | 1,420,790 | 2.36 | 1 | 451,762 | 0.76 | 1 | 2 | –5 | |
| New Party Daichi | 346,848 | 0.58 | 1 | 315,604 | 0.53 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Happiness Realization Party | 216,150 | 0.36 | 0 | 65,983 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| New Renaissance Party | 134,781 | 0.22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| People's New Party | 70,847 | 0.12 | 0 | 117,185 | 0.20 | 1 | 1 | –2 | |
| New Party Nippon | 62,697 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | –1 | ||||
| 21st Century Japan Restoration Party | 17,711 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | New | ||||
| Natural Party | 7,831 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | New | ||||
| Ainu Party | 7,495 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | New | ||||
| Euthanasia Party | 2,603 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | New | ||||
| World Economic Community Party | 1,011 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Independents | 1,006,468 | 1.69 | 5 | 5 | –1 | ||||
| Total | 60,179,888 | 100.00 | 180 | 59,626,569 | 100.00 | 300 | 480 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 60,179,888 | 97.60 | 59,626,568 | 96.69 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 1,480,081 | 2.40 | 2,040,970 | 3.31 | |||||
| Total votes | 61,659,969 | 100.00 | 61,667,538 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 103,959,866 | 59.31 | 103,959,866 | 59.32 | |||||
| Source: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, CLEA | |||||||||
Aftermath[]
As the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) won 294 seats and their allies the New Komeito Party won 31 seats, a coalition of the two parties would be able to form a two-thirds majority in the House of Representatives, enabling them to overrule the House of Councillors.[18][19] The significant swing back towards conservative politics was attributed to economic anxieties, including fear of falling behind China.[18] Despite this landslide victory, Shinzo Abe acknowledged that his party won mainly because of voter antipathy towards the Democratic Party and not due to a resurgence in popularity for the LDP.[20][21]
On the other hand, the election was an unmitigated disaster for the Democratic Party, which lost three-quarters[22] of its 230 seats in the lower house to finish with just 57. In addition, seven members of the Cabinet lost their seats, the most ever in an election. Naoto Kan, who preceded Noda as prime minister, lost his constituency as well.[23] Overall, this marked the worst performance by a ruling party in the post-World War II era. As a result, Yoshihiko Noda resigned from his post as party president.[22]
The Tomorrow Party of Japan, which formed shortly before the election, consisted mostly of incumbents defecting from the Democratic Party. Most of these incumbents were unseated, causing the party to lose 86% of its strength only weeks after forming. Both the Japan Restoration Party and Your Party emerged as viable players in the Diet, while the traditional left parties Social Democratic Party and Japanese Communist Party continued to decline in strength and relevance.
The voter turnout of 59.3% was the lowest since the Second World War.[22]
Reactions and analysis[]
The Liberal Democratic Party had campaigned on a tough stance on the Senkaku Islands dispute, leading to speculation as to how the new government would deal with the issue.[19] Abe made his party's position clear immediately following the election, stating that their "objective is to stop the challenge" from China with regards to ownership of the islands.[24] The re-election of the liberal conservative LDP has raised concern in foreign media that Japan's relations with its neighbours – China and South Korea — will become strained, given the past visits to the Yasukuni Shrine by LDP prime ministers, the party's perceived de-emphasization of Japan's war crimes committed during the Second World War and their intention to amend the country's pacifist constitution to give more power to the Self-Defense Forces.[25][26][27] Abe is also in favour of retaining nuclear energy in the country.[18]
In response to the election, the Nikkei 225 Index increased by 1%, while the yen fell to ¥84.48 against the US dollar, the lowest rate in 20 months.[28] Furthermore, the yield on 20-year Japanese government bonds (JCBs) rose to 1.710% a day after the election. This marked its highest level in nearly eight months.[29]
United States President Barack Obama spoke to Abe by telephone to congratulate him on the results of the general election, and discussed ongoing efforts to enhance bilateral security cooperation as well as deepening economic ties.[30]
Voiding of election[]
On 25 March 2013 the Hiroshima High Court ruled the election unconstitutional and the results void due to "the disparity in the value of one vote", which was up to 2.43 time the maximum constitutionally allowed disparity in some districts.[31][32] The decision is expected to be appealed to the Supreme Court,[33] and, if it's upheld, new elections must be held. The Supreme Court had previously ruled that the electoral system was unconstitutional without invalidating election results.[33] Foreign Minister Fumio Kishida said that government would give electoral reform new thought and examine the situation carefully in order to respond in the appropriate manner.[32]
See also[]
- List of Districts of the House of Representatives of Japan
References[]
- ^ "Okada eyes Jan. dissolution of lower house". Yomiuri Shimbun. Jiji Press. 30 July 2012. Retrieved 14 November 2012.
- ^ Harlan, Chico (18 August 2012). "In Japan, new taxes levy political toll on Prime Minister Yoshihiko Noda". The Washington Post. Retrieved 20 August 2012.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 5 January 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ http://www.nbr.org/research/activity.aspx?id=178
- ^ Schuman, Michael (6 April 2011). "A hard look at Japan's debt problem". Time. Retrieved 22 March 2018.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2 November 2012. Retrieved 30 December 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Japan's Debt Sustains a Deflationary Depression". Bloomberg.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 31 December 2012. Retrieved 28 December 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 March 2012. Retrieved 28 December 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Japan's 'third pole". Japantimes.co.jp. 16 November 2012. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ^ "New political party to be named 'Tachiagare Nippon' (Stand up Japan)" Archived 5 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Japan Today/Associated Press, "Ishihara, Hashimoto announce 'third force' in Japanese politics", Japan Today, 18 November 2012
- ^ Johnston, Eric, "Nippon Ishin no Kai: Local but with national outlook", Japan Times, 3 October 2012, p. 3
- ^ "New Kawamura-led party joins election fray". Yomiuri Shimbun. 24 November 2012. Retrieved 28 November 2012.
- ^ "Shiga's Kada readies party; Ozawa joins". Japantimes.co.jp. 28 November 2012. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ^ "2 Parties Merge With Japan Future". Ajw.asahi.com. Archived from the original on 30 November 2012. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ^ Yomiuri Shimbun: House of Representatives election 2012
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Nagano, Yuriko; Demick, Barbara (16 December 2012). "Japan conservatives win landslide election victory". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Japan election: LDP's Shinzo Abe vows tough China line". BBC. 16 December 2012. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ^ Fackler, Martin (16 December 2012). "Japan Election Returns Power to Old Guard". The New York Times. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ Yoshida, Reiji (17 December 2012). "LDP aware voters just punished DPJ". The Japan Times. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Brinsley, John; Reynolds, Isabel (17 December 2012). "Two-Party Japan Democracy Undone in 39 Months as DPJ Falls". Bloomberg. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ "LDP flattens DPJ in bruising return to power". The Japan Times. 17 December 2012. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ Ryall, Julian; Irvine, Chris (16 December 2012). "Japan election winner fires early warning to China". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ "'The Senkaku islands are our territory': Japanese nationalists return to power in a landslide victory". National Post. Associated Press. 16 December 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Dickie, Mure (16 December 2012). "Rightwing revival raises regional dilemmas". Financial Times. Retrieved 18 December 2012. (subscription required)
- ^ Nakamoto, Michiyo; Dickie, Mure; Soble, Jonathan (16 December 2012). "LDP crushes rivals in Japanese poll". Financial Times. Retrieved 18 December 2012. (subscription required)
- ^ "Japan elections: Shares rise and yen weakens on Abe win". BBC News. 17 December 2012. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ "JGB 20-year yield hits 8-month high after Japan election". Reuters. 16 December 2012. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ "Readout of the President's Call with Liberal Democratic Party President Shinzo Abe of Japan". whitehouse.gov. 17 December 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2012 – via National Archives.
- ^ Yomiuri: Court rules lower house poll invalid / Vote disparity in Hiroshima 'too wide' (english)
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Mainichi: Hiroshima court rules Dec. election invalid over vote disparity (english)". Archived from the original on 13 April 2013. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sekiguchi, Toko (25 March 2013). "Hiroshima Court Rules Election Invalid". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 22 March 2018.
External links[]
- 2012 elections in Asia
- General elections in Japan
- 2012 elections in Japan
- December 2012 events in Japan








