AlphaFold
AlphaFold is an artificial intelligence (AI) program developed by Alphabets's/Google's DeepMind which performs predictions of protein structure.[1] The program is designed as a deep learning system.[2]
AlphaFold AI software has had two major versions. A team of researchers that used AlphaFold 1 (2018) placed first in the overall rankings of the 13th Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction (CASP) in December 2018. The program was particularly successful at predicting the most accurate structure for targets rated as the most difficult by the competition organisers, where no existing template structures were available from proteins with a partially similar sequence.
A team that used AlphaFold 2 (2020) repeated the placement in the CASP competition in November 2020.[3] The team achieved a level of accuracy much higher than any other group.[2] It scored above 90 for around two-thirds of the proteins in CASP's global distance test (GDT), a test that measures the degree to which a computational program predicted structure is similar to the lab experiment determined structure, with 100 being a complete match, within the distance cutoff used for calculating GDT.[2][4]
AlphaFold 2's results at CASP were described as "astounding"[5] and transformational.[6] Some researchers noted that the accuracy is not high enough for a third of its predictions, and that it does not reveal the mechanism or rules of protein folding for the protein folding problem to be considered solved.[7][8] Nevertheless, there has been widespread respect for the technical achievement.
On 15 July 2021 the AlphaFold2 paper was published at Nature as an advance access publication alongside open source software and a searchable database of species proteomes.[9][10][11]
Protein folding problem[]
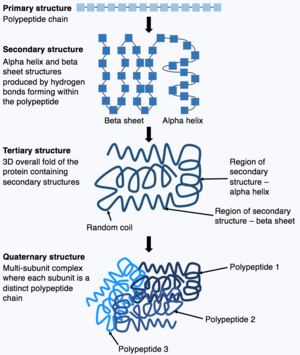
Proteins consist of chains of amino acids which spontaneously fold, in a process called protein folding, to form the three dimensional (3-D) structures of the proteins. The 3-D structure is crucial to the biological function of the protein. However, understanding how the amino acid sequence can determine the 3-D structure is highly challenging, and this is called the "protein folding problem".[12] The "protein folding problem" involves understanding the thermodynamics of the interatomic forces that determine the folded stable structure, the mechanism and pathway through which a protein can reach its final folded state with extreme rapidity, and how the native structure of a protein can be predicted from its amino acid sequence.[13]
Protein structures are currently determined experimentally by means of techniques such as X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance, techniques which are both expensive and time-consuming.[12] Such efforts have identified the structures of about 170,000 proteins over the last 60 years, while there are over 200 million known proteins across all life forms.[4] If it is possible to predict protein structure from the amino-acid sequence alone, it would greatly help to advance scientific research. However, the Levinthal's paradox shows that while a protein can fold in milliseconds, the time it takes to calculate all the possible structures randomly to determine the true native structure is longer than the age of the known universe, which made predicting protein structures a grand challenge in biology for scientists.[12]
Over the years, researchers have applied numerous computational methods to resolve the issue of protein structure prediction, but their accuracy has not been close to experimental techniques except for small simple proteins, thus limiting their value. CASP, which was launched in 1994 to challenge the scientific community to produce their best protein structure predictions, found that GDT scores of only about 40 out of 100 can be achieved for the most difficult proteins by 2016.[4] AlphaFold started competing in the 2018 CASP using an artificial intelligence (AI) deep learning technique.[12]
Algorithm[]
DeepMind is known to have trained the program on over 170,000 proteins from a public repository of protein sequences and structures. The program uses a form of attention network, a deep learning technique that focuses on having the AI algorithm identify parts of a larger problem, then piece it together to obtain the overall solution.[2] The overall training was conducted on processing power between 100 and 200 GPUs.[2] Training the system on this hardware took "a few weeks", after which the program would take "a matter of days" to converge for each structure.[14]
AlphaFold 1, 2018[]
AlphaFold 1 (2018) was built on work developed by various teams in the 2010s, work that looked at the large databanks of related DNA sequences now available from many different organisms (most without known 3D structures), to try to find changes at different residues that appeared to be correlated, even though the residues were not consecutive in the main chain. Such correlations suggest that the residues may be close to each other physically, even though not close in the sequence, allowing a contact map to be estimated. Building on recent work prior to 2018, AlphaFold 1 extended this to estimate a probability distribution for just how close the residues might be likely to be—turning the contact map into a likely distance map. It also used more advanced learning methods than previously to develop the inference. Combining a statistical potential based on this probability distribution with the calculated local free-energy of the configuration, the team was then able to use gradient descent to a solution that best fitted both.[clarification needed][15][16]
More technically, Torrisi et al summarised in 2019 the approach of AlphaFold version 1 as follows:[17]
Central to AlphaFold is a distance map predictor implemented as a very deep residual neural networks with 220 residual blocks processing a representation of dimensionality 64×64×128 – corresponding to input features calculated from two 64 amino acid fragments. Each residual block has three layers including a 3×3 dilated convolutional layer – the blocks cycle through dilation of values 1, 2, 4, and 8. In total the model has 21 million parameters. The network uses a combination of 1D and 2D inputs, including evolutionary profiles from different sources and co-evolution features. Alongside a distance map in the form of a very finely-grained histogram of distances, AlphaFold predicts Φ and Ψ angles for each residue which are used to create the initial predicted 3D structure. The AlphaFold authors concluded that the depth of the model, its large crop size, the large training set of roughly 29,000 proteins, modern Deep Learning techniques, and the richness of information from the predicted histogram of distances helped AlphaFold achieve a high contact map prediction precision.
AlphaFold 2, 2020[]
This section is missing information about AlphaFold-multimer expansion. (October 2021) |

The 2020 version of the program (AlphaFold 2, 2020) is significantly different from the original version that won CASP 13 in 2018, according to the team at DeepMind.[18][19]
The DeepMind team had identified that its previous approach, combining local physics with a guide potential derived from pattern recognition, had a tendency to over-account for interactions between residues that were nearby in the sequence compared to interactions between residues further apart along the chain. As a result, AlphaFold 1 had a tendency to prefer models with slightly more secondary structure (alpha helices and beta sheets) than was the case in reality (a form of overfitting).[20]
The software design used in AlphaFold 1 contained a number of modules, each trained separately, that were used to produce the guide potential that was then combined with the physics-based energy potential. AlphaFold 2 replaced this with a system of sub-networks coupled together into a single differentiable end-to-end model, based entirely on pattern recognition, which was trained in an integrated way as a single integrated structure.[19][21] Local physics, in the form of energy refinement based on the AMBER model, is applied only as a final refinement step once the neural network prediction has converged, and only slightly adjusts the predicted structure.[20]
A key part of the 2020 system are two modules, believed to be based on a transformer design, which are used to progressively refine a vector of information for each relationship (or "edge" in graph-theory terminology) between an amino acid residue of the protein and another amino acid residue (these relationships are represented by the array shown in green); and between each amino acid position and each different sequences in the input sequence alignment (these relationships are represented by the array shown in red).[21] Internally these refinement transformations contain layers that have the effect of bringing relevant data together and filtering out irrelevant data (the "attention mechanism") for these relationships, in a context-dependent way, learnt from training data. These transformations are iterated, the updated information output by one step becoming the input of the next, with the sharpened residue/residue information feeding into the update of the residue/sequence information, and then the improved residue/sequence information feeding into the update of the residue/residue information.[21] As the iteration progresses, according to one report, the "attention algorithm ... mimics the way a person might assemble a jigsaw puzzle: first connecting pieces in small clumps—in this case clusters of amino acids—and then searching for ways to join the clumps in a larger whole."[4]
The output of these iterations then informs the final structure prediction module,[21] which also uses transformers,[22] and is itself then iterated. In an example presented by DeepMind, the structure prediction module achieved a correct topology for the target protein on its first iteration, scored as having a GDT_TS of 78, but with a large number (90%) of stereochemical violations – i.e. unphysical bond angles or lengths. With subsequent iterations the number of stereochemical violations fell. By the third iteration the GDT_TS of the prediction was approaching 90, and by the eighth iteration the number of stereochemical violations was approaching zero.[23]
The AlphaFold team stated in November 2020 that they believe AlphaFold can be further developed, with room for further improvements in accuracy.[18]
Competitions[]

The crimson trend-line shows how a handful of models including AlphaFold 1 achieved a significant step-change in 2018 over the rate of progress that had previously been achieved, particularly in respect of the protein sequences considered the most difficult to predict.
(Qualitative improvement had been made in earlier years, but it is only as changes bring structures within 8 Å of their experimental positions that they start to affect the CASP GDS-TS measure).
The orange trend-line shows that by 2020 online prediction servers had been able to learn from and match this performance, while the best other groups (green curve) had on average been able to make some improvements on it. However, the black trend curve shows the degree to which AlphaFold 2 had surpassed this again in 2020, across the board.
The detailed spread of data points indicates the degree of consistency or variation achieved by AlphaFold. Outliers represent the handful of sequences for which it did not make such a successful prediction.
CASP13[]
In December 2018, DeepMind's AlphaFold placed first in the overall rankings of the 13th Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction (CASP).[25][26]
The program was particularly successfully predicting the most accurate structure for targets rated as the most difficult by the competition organisers, where no existing template structures were available from proteins with a partially similar sequence. AlphaFold gave the best prediction for 25 out of 43 protein targets in this class,[26][27][28] achieving a median score of 58.9 on the CASP's global distance test (GDT) score, ahead of 52.5 and 52.4 by the two next best-placed teams,[29] who were also using deep learning to estimate contact distances.[30][31] Overall, across all targets, the program achieved a GDT score of 68.5.[32]
In January 2020, implementations and illustrative code of AlphaFold 1 was released open-source on GitHub.[33][12] but, as stated in the "Read Me" file on that website: "This code can't be used to predict structure of an arbitrary protein sequence. It can be used to predict structure only on the CASP13 dataset (links below). The feature generation code is tightly coupled to our internal infrastructure as well as external tools, hence we are unable to open-source it." Therefore, in essence, the code deposited is not suitable for general use but only for the CASP13 proteins. The company has not announced plans to make their code publicly available as of 5 March 2021.
CASP14[]
In November 2020, DeepMind's new version, AlphaFold 2, won CASP14.[14][34] Overall, AlphaFold 2 made the best prediction for 88 out of the 97 targets.[5]
On the competition's preferred global distance test (GDT) measure of accuracy, the program achieved a median score of 92.4 (out of 100), meaning that more than half of its predictions were scored at better than 92.4% for having their atoms in more-or-less the right place,[35][36] a level of accuracy reported to be comparable to experimental techniques like X-ray crystallography.[18][6][32] In 2018 AlphaFold 1 had only reached this level of accuracy in two of all of its predictions.[5] 88% of predictions in the 2020 competition had a GDT_TS score of more than 80.[37]: slide 3 On the group of targets classed as the most difficult, AlphaFold 2 achieved a median score of 87.
Measured by the root-mean-square deviation (RMS-D) of the placement of the alpha-carbon atoms of the protein backbone chain, which tends to be dominated by the performance of the worst-fitted outliers, 88% of AlphaFold 2's predictions had an RMS deviation of less than 4 Å for the set of overlapped C-alpha atoms.[5] 76% of predictions achieved better than 3 Å, and 46% had a C-alpha atom RMS accuracy better than 2 Å.,[5] with a median RMS deviation in its predictions of 2.1 Å for a set of overlapped CA atoms.[5] AlphaFold 2 also achieved an accuracy in modelling surface side chains described as "really really extraordinary".[24]: at 0:31:50
To additionally verify AlphaFold-2 the conference organisers approached four leading experimental groups for structures they were finding particularly challenging and had been unable to determine.[37] In all four cases the three-dimensional models produced by AlphaFold 2 were sufficiently accurate to determine structures of these proteins by molecular replacement.[37] These included target T1100 (Af1503), a small membrane protein studied by experimentalists for ten years.[4]
Of the three structures that AlphaFold 2 had the least success in predicting, two had been obtained by protein NMR methods,[24]: at 0:30:30 which define protein structure directly in aqueous solution, whereas AlphaFold was mostly trained on protein structures in crystals. The third exists in nature as a multidomain complex consisting of 52 identical copies of the same domain,[24]: at 0:30:30 a situation AlphaFold was not programmed to consider. For all targets with a single domain, excluding only one very large protein and the two structures determined by NMR, AlphaFold 2 achieved a GDT_TS score of over 80.[38]
Responses[]
AlphaFold 2 scoring more than 90 in CASP's global distance test (GDT) is considered a significant achievement in computational biology[4] and great progress towards a decades-old grand challenge of biology.[6] Nobel Prize winner and structural biologist Venki Ramakrishnan called the result "a stunning advance on the protein folding problem",[4] adding that "It has occurred decades before many people in the field would have predicted. It will be exciting to see the many ways in which it will fundamentally change biological research."[14]
Propelled by press releases from CASP and DeepMind,[39][14] AlphaFold 2's success received wide media attention.[40] As well as news pieces in the specialist science press, such as Nature,[6] Science,[4] MIT Technology Review,[2] and New Scientist,[41][42] the story was widely covered by major national newspapers,[43][44][45][46] as well as general news-services and weekly publications, such as Fortune,[47][19] The Economist,[18] Bloomberg,[32] Der Spiegel,[48] and The Spectator.[49] In London The Times made the story its front-page photo lead, with two further pages of inside coverage and an editorial.[50][51] A frequent theme was that ability to predict protein structures accurately based on the constituent amino acid sequence is expected to have a wide variety of benefits in the life sciences space including accelerating advanced drug discovery and enabling better understanding of diseases.[6][52] Writing about the event, the MIT Technology Review noted that the AI had "solved a fifty-year old grand challenge of biology."[2] The same article went on to note that the AI algorithm could "predict the shape of proteins to within the width of an atom."[2]
As summed up by Der Spiegel reservations about this coverage have focussed in two main areas: "There is still a lot to be done" and: "We don't even know how they do it".[53]
Although a 30-minute presentation about AlphaFold 2 was given on the second day of the CASP conference (December 1) by project leader John Jumper,[54] it has been described as "exceedingly high-level, heavy on ideas and insinuations, but almost entirely devoid of detail".[55][unreliable source?] Unlike other research groups presenting at CASP14, DeepMind's presentation was not recorded and is not publicly available.[56] DeepMind are expected to publish a scientific paper giving an account of AlphaFold 2 in the proceedings volume[when?] of the CASP conference; but it is not known whether it will go beyond what was said in the presentation.
Speaking to El País, researcher Alfonso Valencia said "The most important thing that this advance leaves us is knowing that this problem has a solution, that it is possible to solve it... We only know the result. Google does not provide the software and this is the frustrating part of the achievement because it will not directly benefit science."[46] Nevertheless, as much as Google and DeepMind do release may help other teams develop similar AI systems, an "indirect" benefit.[46] In late 2019 DeepMind released much of the code of the first version of AlphaFold as open source; but only when work was well underway on the much more radical AlphaFold 2. Another option it could take might be to make AlphaFold 2 structure prediction available as an online black-box subscription service. Convergence for a single sequence has been estimated to require on the order of $10,000 worth of wholesale compute time.[57] But this would deny researchers access to the internal states of the system, the chance to learn more qualitatively what gives rise to AlphaFold 2's success, and the potential for new algorithms that could be lighter and more efficient yet still achieve such results. Fears of potential for a lack of transparency by DeepMind have been contrasted with five decades of heavy public investment into the open Protein Data Bank and then also into open DNA sequence repositories, without which the data to train AlphaFold 2 would not have existed.[58][59][60]
Of note, on June 18th, 2021 Demis Hassabis tweeted: "Brief update on some exciting progress on #AlphaFold! We’ve been heads down working flat out on our full methods paper (currently under review) with accompanying open source code and on providing broad free access to AlphaFold for the scientific community. More very soon!"[61]
However it is not yet clear to what extent structure predictions made by AlphaFold 2 will hold up for proteins bound into complexes with other proteins and other molecules.[62] This was not a part of the CASP competition which AlphaFold entered, and not an eventuality it was internally designed to expect. Where structures that AlphaFold 2 did predict were for proteins that had strong interactions either with other copies of themselves, or with other structures, these were the cases where AlphaFold 2's predictions tended to be least refined and least reliable. As a large fraction of the most important biological machines in a cell comprise such complexes, or relate to how protein structures become modified when in contact with other molecules, this is an area that will continue to be the focus of considerable experimental attention.[62]
With so little yet known about the internal patterns that AlphaFold 2 learns to make its predictions, it is not yet clear to what extent the program may be impaired in its ability to identify novel folds, if such folds are not well represented in the existing protein structures known in structure databases.[7][62] It is also not well known the extent to which protein structures in such databases, overwhelmingly of proteins that it has been possible to crystallise to X-ray, are representative of typical proteins that have not yet been crystallised. And it is also unclear how representative the frozen protein structures in crystals are of the dynamic structures found in the cells in vivo. AlphaFold 2's difficulties with structures obtained by protein NMR methods may not be a good sign.
On its potential as a tool for drug discovery, Stephen Curry notes that while the resolution of AlphaFold 2's structures may be very good, the accuracy with which binding sites are modelled needs to be even higher: typically molecular docking studies require the atomic positions to be accurate within a 0.3 Å margin, but the predicted protein structure only have at best an RMSD of 0.9 Å for all atoms. So AlphaFold 2's structures may only be a limited help in such contexts.[7][62] Moreover, according to Science columnist Derek Lowe, because the prediction of small-molecule binding even then is still not very good, computational prediction of drug targets is simply not in a position to take over as the "backbone" of corporate drug discovery—so "protein structure determination simply isn’t a rate-limiting step in drug discovery in general".[63] It has also been noted that even with a structure for a protein, to then understand how it functions, what it does, and how that fits within wider biological processes can still be very challenging.[64] Nevertheless, if better knowledge of protein structure could lead to better understanding of individual disease mechanisms and ultimately to better drug targets, or better understanding of the differences between human and animal models, ultimately that could lead to improvements.[65]
Also, because AlphaFold processes protein-only sequences by design, other associated biomolecules are not considered. On the impact of absent metals, co-factors and, most visibly, co- and post-translational modifications such as protein glycosylation from AlphaFold models, Elisa Fadda (Maynooth University, Ireland) and Jon Agirre (University of York, UK) highlighted the need for scientists to check databases such as UniProt-KB for likely missing components, as these can play an important role not just in folding but in protein function.[66] However, the authors highlighted that many AlphaFold models were accurate enough to allow for the introduction of post-predictional modifications.[67]
Finally, some have noted that even a perfect answer to the protein prediction problem would still leave questions about the protein folding problem—understanding in detail how the folding process actually occurs in nature (and how sometimes they can also misfold).[68]
But even with such caveats, AlphaFold 2 was described as a huge technical step forward and intellectual achievement.[69][70]
Protein Structure Database[]
| Content | |
|---|---|
| Data types captured | protein structure prediction |
| Organisms | humans; model organisms |
| Contact | |
| Research center | EMBL-EBI |
| Primary citation | [9] |
| Access | |
| Website | https://www.alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/ |
| Download URL | yes |
| Tools | |
| Web | yes |
| Miscellaneous | |
| License | CC-BY 4.0 |
| Curation policy | automatic |
The AlphaFold Protein Structure Database was launched on July 22, 2021 as a joint effort between AlphaFold and EMBL-EBI. At launch the database contains AlphaFold-predicted models of protein structures of nearly the full UniProt proteome of humans and 20 model organisms, amounting to over 365,000 proteins. AlphaFold plans to add more sequences to the collection. As of July 2021, UniProt-KB and InterPro[71] has been updated to show AlphaFold predictions when available.[72] The database does not include proteins with fewer than 16 or more than 2700 amino acid residues,[73] but for humans they are available in the whole batch file.[74] In October 2021, it was suggested that the database could be progressively completed with the structures of missing co-factors, metals, and co- and post-translational modifications,[75] particularly as between 50% and 70% of the structures of the human proteome are incomplete without covalently-attached glycans.[76]
Applications[]
SARS-CoV-2[]
AlphaFold has been used to predict structures of proteins of SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19. The structures of these proteins were pending experimental detection in early 2020.[77][6] Results were examined by the scientists at the Francis Crick Institute in the United Kingdom before release into the larger research community. The team also confirmed accurate prediction against the experimentally determined SARS-CoV-2 spike protein that was shared in the Protein Data Bank, an international open-access database, before releasing the computationally determined structures of the under-studied protein molecules.[78] The team acknowledged that although these protein structures might not be the subject of ongoing therapeutical research efforts, they will add to the community's understanding of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.[78] Specifically, AlphaFold 2's prediction of the structure of the ORF3a protein was very similar to the structure determined by researchers at University of California, Berkeley using cryo-electron microscopy. This specific protein is believed to assist the virus in breaking out of the host cell once it replicates. This protein is also believed to play a role in triggering the inflammatory response to the infection.[79]
Published works[]
AlphaFold research[]
- Andrew W. Senior et al. (December 2019), "Protein structure prediction using multiple deep neural networks in the 13th Critical Assessment of Protein Structure Prediction (CASP13)", Proteins: Structure, Function, Bioinformatics 87(12) 1141–1148 doi:10.1002/prot.25834
- Andrew W. Senior et al. (15 January 2020), "Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning", Nature 577 706–710 doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1923-7
- John Jumper et al. (December 2020), "High Accuracy Protein Structure Prediction Using Deep Learning", in Fourteenth Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction (Abstract Book), pp. 22–24
- John Jumper et al. (December 2020), "AlphaFold2". Presentation given at CASP 14.
Derivative research[]
- Yang, Jianyi; Anishchenko, Ivan; Park, Hahnbeom; Peng, Zhenling; Ovchinnikov, Sergey; Baker, David (21 January 2020). "Improved protein structure prediction using predicted inter-residue orientations". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (3): 1496–1503. bioRxiv 10.1101/846279. doi:10.1073/pnas.1914677117. PMC 6983395. PMID 31896580.
- Billings, Wendy M.; Hedelius, Bryce; Millecam, Todd; Wingate, David; Corte, Dennis Della (2019-11-04). "ProSPr: Democratized Implementation of Alphafold Protein Distance Prediction Network". p. 830273. bioRxiv 10.1101/830273.S2CID 209578310
- Baek, Minkyung; DiMaio, Frank; Anishchenko, Ivan; Dauparas, Justas; Ovchinnikov, Sergey; Lee, Gyu Rie; Wang, Jue; Cong, Qian; Kinch, Lisa N.; Schaeffer, R. Dustin; Millán, Claudia; Park, Hahnbeom; Adams, Carson; Glassman, Caleb R.; DeGiovanni, Andy; Pereira, Jose H.; Rodrigues, Andria V.; van Dijk, Alberdina A.; Ebrecht, Ana C.; Opperman, Diederik J.; Sagmeister, Theo; Buhlheller, Christoph; Pavkov-Keller, Tea; Rathinaswamy, Manoj K.; Dalwadi, Udit; Yip, Calvin K.; Burke, John E.; Garcia, K. Christopher; Grishin, Nick V.; Adams, Paul D.; Read, Randy J.; Baker, David (15 July 2021). "Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network". Science. 373 (6557): 871–876. Bibcode:2021Sci...373..871B. doi:10.1126/science.abj8754. PMID 34282049.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "AlphaFold". Deepmind. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "DeepMind's protein-folding AI has solved a 50-year-old grand challenge of biology". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 2020-11-30.
- ^ Shead, Sam (2020-11-30). "DeepMind solves 50-year-old 'grand challenge' with protein folding A.I." CNBC. Retrieved 2020-11-30.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Robert F. Service, ‘The game has changed.’ AI triumphs at solving protein structures, Science, 30 November 2020
- ^ a b c d e f Mohammed AlQuraishi, CASP14 scores just came out and they’re astounding, Twitter, 30 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f Callaway, Ewen (2020-11-30). "'It will change everything': DeepMind's AI makes gigantic leap in solving protein structures". Nature. 588 (7837): 203–204. Bibcode:2020Natur.588..203C. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03348-4. PMID 33257889.
- ^ a b c Stephen Curry, No, DeepMind has not solved protein folding, Reciprocal Space (blog), 2 December 2020
- ^ Balls, Phillip (9 December 2020). "Behind the screens of AlphaFold". Chemistry World.
- ^ a b Jumper, John; Evans, Richard; Pritzel, Alexander; Green, Tim; Figurnov, Michael; Ronneberger, Olaf; Tunyasuvunakool, Kathryn; Bates, Russ; Žídek, Augustin; Potapenko, Anna; Bridgland, Alex; Meyer, Clemens; Kohl, Simon A A; Ballard, Andrew J; Cowie, Andrew; Romera-Paredes, Bernardino; Nikolov, Stanislav; Jain, Rishub; Adler, Jonas; Back, Trevor; Petersen, Stig; Reiman, David; Clancy, Ellen; Zielinski, Michal; Steinegger, Martin; Pacholska, Michalina; Berghammer, Tamas; Bodenstein, Sebastian; Silver, David; Vinyals, Oriol; Senior, Andrew W; Kavukcuoglu, Koray; Kohli, Pushmeet; Hassabis, Demis (2021-07-15). "Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold". Nature. 596 (7873): 583–589. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2. PMC 8371605. PMID 34265844.
- ^ "GitHub - deepmind/alphafold: Open source code for AlphaFold". GitHub. Retrieved 2021-07-24.
- ^ "AlphaFold Protein Structure Database". alphafold.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2021-07-24.
- ^ a b c d e "AlphaFold: Using AI for scientific discovery". Deepmind. Retrieved 2020-11-30.
- ^ Ken A. Dill, S. Banu Ozkan, M. Scott Shell, and Thomas R. Weikl (2008). "The Protein Folding Problem". Annual Review of Biophysics. 37: 289–316. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.092707.153558. PMC 2443096. PMID 18573083.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ a b c d e "AlphaFold: a solution to a 50-year-old grand challenge in biology". Deepmind. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ (May 2019), AlphaFold at CASP13, Bioinformatics, 35(22), 4862–4865 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btz422. See also Mohammed AlQuraishi (December 9, 2018), AlphaFold @ CASP13: "What just happened?" (blog post).
Mohammed AlQuraishi (15 January 2020), A watershed moment for protein structure prediction, Nature 577, 627–628 doi:10.1038/d41586-019-03951-0 - ^ AlphaFold: Machine learning for protein structure prediction, Foldit, 31 January 2020
- ^ Torrisi, Mirko et al. (22 Jan. 2020), Deep learning methods in protein structure prediction. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal vol. 18 1301–1310. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2019.12.011 (CC-BY-4.0)
- ^ a b c d "DeepMind is answering one of biology's biggest challenges". The Economist. 2020-11-30. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 2020-11-30.
- ^ a b c Jeremy Kahn, Lessons from DeepMind's breakthrough in protein-folding A.I., Fortune, 1 December 2020
- ^ a b John Jumper et al., conference abstract (December 2020)
- ^ a b c d See block diagram. Also John Jumper et al. (1 December 2020), AlphaFold2 presentation, slide 10
- ^ The structure module is stated to use a "3-d equivariant transformer architecture" (John Jumper et al. (1 December 2020), AlphaFold2 presentation, slide 12).
One design for a transformer network with SE(3)-equivariance was proposed in Fabian Fuchs et al SE(3)-Transformers: 3D Roto-Translation Equivariant Attention Networks, NeurIPS 2020; also website. It is not known how similar this may or may not be to what was used in AlphaFold.
See also the blog post by AlQuaraishi on this, or the more detailed post by Fabian Fuchs - ^ John Jumper et al. (1 December 2020), AlphaFold2 presentation, slides 12 to 20
- ^ a b c d John Moult (30 November 2020), CASP 14 introductory presentation, slide 19. See also CASP 14 video stream day 1 part 1, from 00:22:46
- ^ Group performance based on combined z-scores, CASP 13, December 2018. (AlphaFold = Team 043: A7D)
- ^ a b Sample, Ian (2 December 2018). "Google's DeepMind predicts 3D shapes of proteins". The Guardian. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ "AlphaFold: Using AI for scientific discovery". Deepmind. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ Singh, Arunima (2020). "Deep learning 3D structures". Nature Methods. 17 (3): 249. doi:10.1038/s41592-020-0779-y. ISSN 1548-7105. PMID 32132733. S2CID 212403708.
- ^ See CASP 13 data tables for 043 A7D, 322 Zhang, and 089 MULTICOM
- ^ Wei Zheng et al,Deep-learning contact-map guided protein structure prediction in CASP13, Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 87(12) 1149–1164 doi:10.1002/prot.25792; and slides
- ^ Hou, Jie; Wu, Tianqi; Cao, Renzhi; Cheng, Jianlin (2019-04-25). "Protein tertiary structure modeling driven by deep learning and contact distance prediction in CASP13". Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics. Wiley. 87 (12): 1165–1178. bioRxiv 10.1101/552422. doi:10.1002/prot.25697. ISSN 0887-3585. PMC 6800999.
- ^ a b c "DeepMind Breakthrough Helps to Solve How Diseases Invade Cells". Bloomberg.com. 2020-11-30. Retrieved 2020-11-30.
- ^ "deepmind/deepmind-research". GitHub. Retrieved 2020-11-30.
- ^ "DeepMind's protein-folding AI has solved a 50-year-old grand challenge of biology". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ For the GDT_TS measure used, each atom in the prediction scores a quarter of a point if it is within 8 Å (0.80 nm) of the experimental position; half a point if it is within 4 Å, three-quarters of a point if it is within 2 Å, and a whole point if it is within 1 Å.
- ^ To achieve a GDT_TS score of 92.5, mathematically at least 70% of the structure must be accurate to within 1 Å, and at least 85% must be accurate to within 2 Å.
- ^ a b c Andriy Kryshtafovych (30 November 2020), Experimentalists: Are models useful? CASP 14 presentation. See also CASP 14 video stream day 1 part 1, from 0:34:30
- ^ Lisa Kinch et al, CASP14 Tertiary Structure Prediction Assessment:Topology (FM) Category (CASP 14 presentation), slide 11. See also CASP 14 video stream day 1 part 3, from 0:18:25
- ^ Artificial intelligence solution to a 50-year-old science challenge could ‘revolutionise’ medical research (press release), CASP organising committee, 30 November 2020
- ^ Brigitte Nerlich, Protein folding and science communication: Between hype and humility, University of Nottingham blog, 4 December 2020
- ^ Michael Le Page, DeepMind's AI biologist can decipher secrets of the machinery of life, New Scientist, 30 November 2020
- ^ The predictions of DeepMind’s latest AI could revolutionise medicine, New Scientist, 2 December 2020
- ^ , London A.I. Lab Claims Breakthrough That Could Accelerate Drug Discovery, New York Times, 30 November 2020
- ^ Ian Sample,DeepMind AI cracks 50-year-old problem of protein folding, The Guardian, 30 November 2020
- ^ Lizzie Roberts, 'Once in a generation advance' as Google AI researchers crack 50-year-old biological challenge. Daily Telegraph, 30 November 2020
- ^ a b c Nuño Dominguez, La inteligencia artificial arrasa en uno de los problemas más importantes de la biología (Artificial intelligence takes out one of the most important problems in biology), El País, 2 December 2020
- ^ Jeremy Kahn, In a major scientific breakthrough, A.I. predicts the exact shape of proteins, Fortune, 30 November 2020
- ^ Julia Merlot, Forscher hoffen auf Durchbruch für die Medikamentenforschung (Researchers hope for a breakthrough for drug research), Der Spiegel, 2 December 2020
- ^ Bissan Al-Lazikani, The solving of a biological mystery, The Spectator, 1 December 2020
- ^ Tom Whipple, "Deepmind computer solves new puzzle: life", The Times, 1 December 2020. front page image, via Twitter.
- ^ Tom Whipple, Deepmind finds biology’s ‘holy grail’ with answer to protein problem, The Times (online), 30 November 2020.
In all science editor Tom Whipple wrote six articles on the subject for The Times on the day the news broke. (thread). - ^ Tim Hubbard, The secret of life, part 2: the solution of the protein folding problem., medium.com, 30 November 2020
- ^ Christian Stöcker, Google greift nach dem Leben selbst (Google is reaching for life itself), Der Spiegel, 6 December 2020
- ^ John Jumper et al. (1 December 2020), AlphaFold2. Presentation given at CASP 14.
- ^ AlQuraishi, Mohammed (2020-12-08). "AlphaFold2 @ CASP14: "It feels like one's child has left home." The Method". Some Thoughts on a Mysterious Universe. Retrieved 2020-12-15.
- ^ "CASP14_recordings - Google Drive". drive.google.com. Retrieved 28 April 2021.
- ^ Carlos Outeiral, CASP14: what Google DeepMind’s AlphaFold 2 really achieved, and what it means for protein folding, biology and bioinformatics, Oxford Protein Informatics Group. (3 December)
- ^ Aled Edwards, The AlphaFold2 success: It took a village, via medium.com, 5 December 2020
- ^ David Briggs, If Google’s Alphafold2 really has solved the protein folding problem, they need to show their working, The Skeptic, 4 December 2020
- ^ The Guardian view on DeepMind’s brain: the shape of things to come, The Guardian, 6 December 2020
- ^ Demis Hassabis, "Brief update on some exciting progress on #AlphaFold!" (tweet), via twitter, 18 June 2021
- ^ a b c d Tom Ireland, How will AlphaFold change bioscience research?, The Biologist, 4 December 2020
- ^ Derek Lowe, In the Pipeline: What’s Crucial And What Isn’t, Science Translational Medicine, 25 September 2019
- ^ Philip Ball, Behind the Screens of AlphaFold, Chemistry World, 9 December 2020. See also tweets, 1 December
- ^ Derek Lowe, In the Pipeline: The Big Problems, Science Translational Medicine, 1 December 2020
- ^ Bagdonas, Haroldas; Fogarty, Carl A.; Fadda, Elisa; Agirre, Jon (2021-10-29). "The case for post-predictional modifications in the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: 1–2. doi:10.1038/s41594-021-00680-9. ISSN 1545-9985.
- ^ Bagdonas, Haroldas; Fogarty, Carl A.; Fadda, Elisa; Agirre, Jon (2021-10-29). "The case for post-predictional modifications in the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: 1–2. doi:10.1038/s41594-021-00680-9. ISSN 1545-9985.
- ^ e.g. Greg Bowman, Protein folding and related problems remain unsolved despite AlphaFold's advance, Folding@home blog, 8 December 2020
- ^ Cristina Sáez, El último avance fundamental de la biología se basa en la investigación de un científico español, La Vanguardia, 2 December 2020. (Alfonso Valencia overall view)
- ^ Zero Gravitas and Jacky Liang, DeepMind’s AlphaFold 2—An Impressive Advance With Hyperbolic Coverage, Skynet today (blog), Stanford, 9 December 2020
- ^ InterPro. "Alphafold Structure Predictions Available In Interpro". proteinswebteam.github.io. Retrieved 2021-07-29.
- ^ "Putting the power of AlphaFold into the world's hands". Deepmind.
- ^ "AlphaFold Protein Structure Database". alphafold.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2021-07-29.
- ^ "AlphaFold Protein Structure Database". alphafold.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 27 July 2021.
- ^ Bagdonas, Haroldas; Fogarty, Carl A.; Fadda, Elisa; Agirre, Jon (2021-10-29). "The case for post-predictional modifications in the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: 1–2. doi:10.1038/s41594-021-00680-9. ISSN 1545-9985.
- ^ An, Hyun Joo; Froehlich, John W; Lebrilla, Carlito B (2009-10-01). "Determination of glycosylation sites and site-specific heterogeneity in glycoproteins". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. Analytical Techniques/Mechanisms. 13 (4): 421–426. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.07.022. ISSN 1367-5931. PMC 2749913.
- ^ "AI Can Help Scientists Find a Covid-19 Vaccine". Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- ^ a b "Computational predictions of protein structures associated with COVID-19". Deepmind. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- ^ "How DeepMind's new protein-folding A.I. is already helping to combat the coronavirus pandemic". Fortune. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
Further reading[]
- Carlos Outeiral, CASP14: what Google DeepMind’s AlphaFold 2 really achieved, and what it means for protein folding, biology and bioinformatics, Oxford Protein Informatics Group. (3 December)
- Mohammed AlQuraishi, AlphaFold2 @ CASP14: "It feels like one’s child has left home." (blog), 8 December 2020
- Mohammed AlQuraishi, The AlphaFold2 Method Paper: A Fount of Good Ideas (blog), 25 July 2021
External links[]
AlphaFold 1[]
- Senior, Andrew (August 23, 2019). "AlphaFold: improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning". Institute for Protein Design – via YouTube.
- AlphaFold code used at CASP13 on GitHub
- Open source community implementation – ProSPr on GitHub
AlphaFold 2[]
- AlphaFold v2.1 code and links to model on GitHub
- Open access to protein structure predictions for the human proteome and 20 other key organisms at European Bioinformatics Institute
- CASP 14 website
- AlphaFold: The making of a scientific breakthrough, DeepMind, via YouTube.
- ColabFold (Mirdita, Milot; Ovchinnikov, Sergey; Steinegger, Martin (2021-08-15). "ColabFold - Making protein folding accessible to all". bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.08.15.456425. ), version for homooligomeric prediction and complexes
- Software
- Artificial intelligence applications
- Applied machine learning
- Protein folding
- Deep learning