Khon Kaen Province
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2018) |
Khon Kaen
ขอนแก่น | |
|---|---|
From left to right, top to bottom : Phra That Kham Kaen, Nam Phong National Park, Ubol Ratana Dam, Phra Mahathat Kaen Nakhon, Khon Kaen City Pillar Shrine, Khon Kaen University | |
 Flag  Seal | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Khon Kaen Province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Khon Kaen |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Somsak Jangtrakul |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10,659 km2 (4,115 sq mi) |
| Area rank | Ranked 14th |
| Population (2019)[2] | |
| • Total | 1,802,872 |
| • Rank | Ranked 4th |
| • Density | 169/km2 (440/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | Ranked 19th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
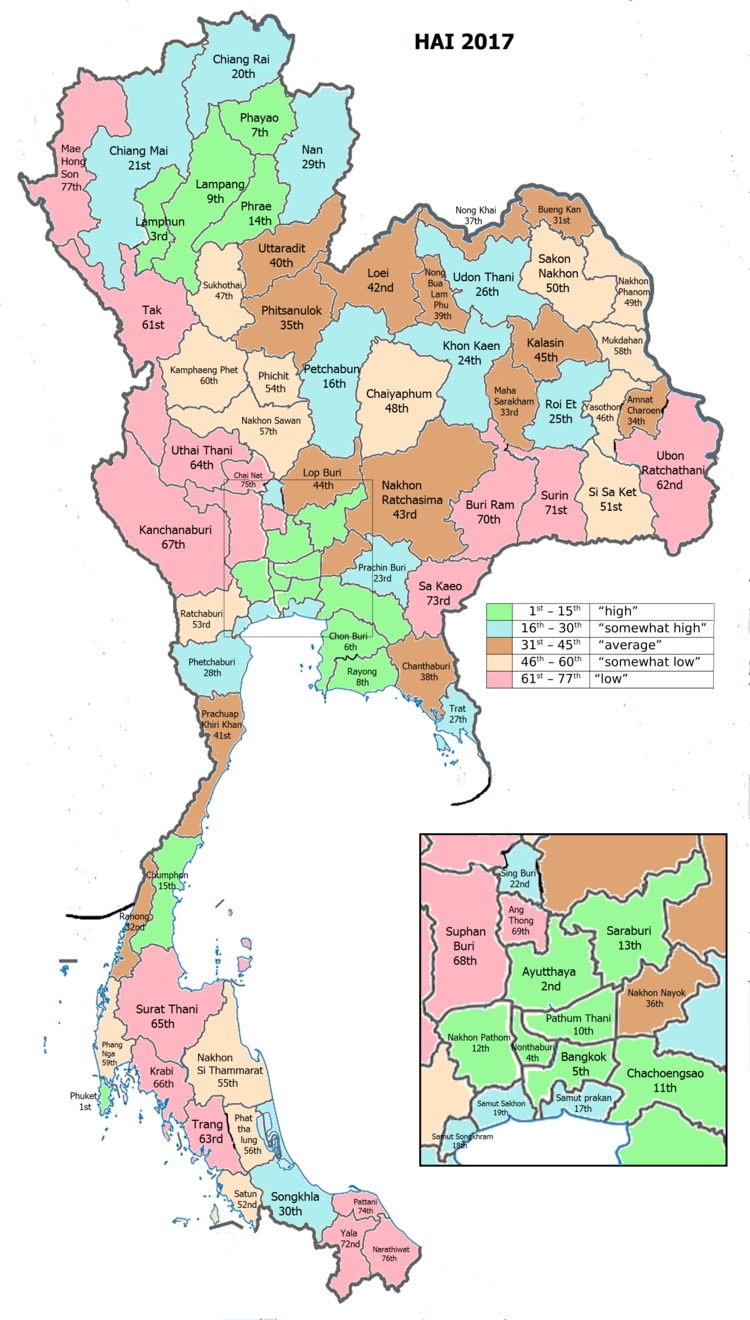
| • HAI (2017) | 0.6090 "somewhat high" Ranked 24th |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 40xxx |
| Calling code | 043 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-40 |
| Vehicle registration | ขอนแก่น |
| Website | www |
Khon Kaen (Thai: ขอนแก่น, pronounced [kʰɔ̌(ː)n kɛ̀n]) is one of Thailand's seventy-six provinces (changwat) lies in central northeastern Thailand also called Isan. Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Nong Bua Lamphu, Udon Thani, Kalasin, Maha Sarakham, Buriram, Nakhon Ratchasima, Chaiyaphum, Phetchabun, and Loei.
History[]
The first city of the area was established in 1783 when Rajakruluang settled there with 330 people. King Rama I made Rajakruluang the first governor of the area when establishing tighter connections with the Isan area. The main city was moved six times until in 1879 it reached its present-day location at Nuang Kaw. Khon Kaen was under the governance of Udon in the early period of Rattanakosin, c. 2450 BCE. The Integrated Opisthorchiasis Control Program, also known as the Lawa Project, an internationally recognized liver fluke control program, has its offices in the Ban Phai and Ban Haet Districts south of Khon Kaen city.
In 1789, Thao Pia Mueang Pan has taken children with around 330 families evacuated from Ban Chee Lon to be located at Ban Bueng Bon. King Rama I ordered to raised the status of Ban Bueng Bon to be the city of "Khon Kaen" in 1797.
All immigration[]
In 1896, during the reign of King Rama V, the government changed the rule of distant districts. By changing to the northern Lao districts to be a Lao Phuan city, Khon Kaen city is under the rule of Udon Thani city or Monthon Udon with Krom Luang Prajak Silapakhom as the governor of the county. Udon Thani center Krom Luang Prajak Silapakhom (Provincial governor of Udon Thani at that time), thought that Khon Kaen political office located at Ban Don Bom not convenient for the government and ordered to moved Khon Kaen city to be located at Ban Thum (Mueang Khon Kaen District at present) in late 1896.
In 1899, Khon Kaen was moved from Ban Thum back to Ban Muang Kao as it was.
In 1901, the government has required labor to help build a flood barrier to form a road around the old city marsh to hold water for use in the dry season, because this pond is an important water source for people of Khon Kaen.
Later on May 19, 1916, the county system in the country was abolished and the word "city" was changed to "province" instead. Since that time, Khon Kaen has become "Khon Kaen province".
Geography[]
Khon Kaen occupies part of the Khorat Plateau. The Chi and Phong Rivers flow through the province. The total forest area is 1,222 km2 (472 sq mi) or 11.5 percent of provincial area.[1]
Symbols[]
| The seal of the province shows the stupa (tower) of Phra That Kham Kaen, which is believed to contain relics of Buddha. A tree is depicted on each side. One is a banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis), the other a Golden Shower Tree (Cassia fistula). The Thai name of the golden shower means 'providing support and preventing a decline', and it is also the provincial flower. The provincial tree is the pink shower tree (), the Thai name of which translates as 'wishing tree'. |
Culture[]
Sinxay[]
The mayor of Khon Kaen in 2005 chose Sinxay to be the new identity of the Khon Kaen and had finials designed representing Sinxay and his two brothers, Siho and Sangthong. The story of Sang Sinxay, one of the masterpieces of Lao literature written by Pang Kham in 1649, during the Lan Xang period.[4]
Administrative divisions[]
Provincial government[]

The province is divided into 26 districts (amphoes). The districts are further divided into 198 subdistricts (tambons) and 2,139 villages (mubans).
- The numbers 26 to 28 were reserved for three other planned (minor) districts: Phu Kham Noi, Nong Kae, and Non Han.
There are plans to split off the northwestern part of the province to form a new province centered at Phu Wiang. The other districts which will belong to this new province are Nong Ruea, Chum Phae, Si Chomphu, Phu Pha Man, Nong Na Kham, and Wiang Kao.[5]
Local government[]
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[6] one Khon Kaen Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 84 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Khon Kaen has city (thesaban nakhon) status. Ban Phai, Ban Thum, Chum Pae, Kranuan, Mueang Phon and Sila have town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 77 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 140 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[2]
Education[]
- Universities
- Schools
Health[]
Khon Kaen has hospitals operated by both the public and private sectors. Its main hospital operated by the Ministry of Public Health is Khon Kaen Hospital. The province also has a university hospital, Srinagarind Hospital of the Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University.
Transport[]
- Air

- Rail
The railway system in Khon Kaen is on both northeastern routes from Bangkok Railway Station. Khon Kaen Province's main railway stations was Khon Kaen Railway Station. In 2017, a 60 kilometre dual-track line will connect Khon Kaen to Nakhon Ratchasima Province. It is the first segment of a dual track network that will connect Isan with the Laem Chabang seaport.[7]
- Road
The city is bisected by Mittraphap Road, also known as "Friendship Highway", or Asian Highway 2 (AH2), the road linking Bangkok to the Thai-Lao Friendship Bridge. A multi-lane by-pass enables through-traffic to avoid the city centre to the west, and connects to the airport and to the main roads to Kalasin Province and Maha Sarakham Province in the east, and Udon Thani Province in the north.
Sport[]
The sports teams listed below are based in Khon Kaen.
- Football
- Khon Kaen (Thai League 2)—Khon Kaen Provincial Stadium
- Khon Kaen United (Thai League 2)—Khon Kaen Provincial Stadium
- Volleyball
- Khonkaen Star (Women's Volleyball Thailand League)—Khonkaen International Convention and Exhibition Center
Human achievement index 2017[]
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 37 | 34 | 32 | 51 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |

|
 |

|
|
| 50 | 3 | 21 | 52 |
| Province Khon Kaen, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.6090 is "somewhat high", occupies place 24 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[3]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| showMap with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
Sister cities[]
Notable residents[]
- Paradorn Srichaphan, tennis player, the first Asian to reach top ten of the ATP rankings
- Somluck Kamsing, boxer, the first Thai athlete to win a gold medal at the Olympics
- Nadech Kugimiya, actor
- Sukollawat Kanarot, actor
- Peechaya Wattanamontree, actress
- Apichatpong Weerasethakul, filmmaker
Gallery[]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019, Thailand boundary from Department of Provincial Administration in 2013CS1 maint: postscript (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ส.2562 [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2019]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior. stat.bora.dopa.go.th (in Thai). 31 December 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- ^ "ฐานที่มั่นทางวัฒนธรรมของชาวลาวอีสาน-4-5600-107946-1.html "สินไซ - "ฐานที่มั่นทางวัฒนธรรม" ของชาวลาว-อีสาน".
- ^ "ที่เที่ยวขอนแก่น -10 เที่ยวหลากสไตล์ ท่องไปในขอนแก่น".
- ^ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
5 Khon Kaen: 1 PAO, 1 City mun., 6 Town mun., 77 Subdistrict mun., 140 SAO.
- ^ Janssen, Peter (2 November 2016). "Thailand takes a long-term gamble on Isaan region". Nikkei Asian Review. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
External links[]
 Khon Kaen travel guide from Wikivoyage
Khon Kaen travel guide from Wikivoyage- Province page from the Tourist Authority of Thailand
- Official website of province (Thai only)
Coordinates: 16°26′41″N 102°50′1″E / 16.44472°N 102.83361°E
- Khon Kaen Province
- Isan
- Provinces of Thailand