Chanthaburi Province
Chanthaburi
จันทบุรี | |
|---|---|
 Chantaboon Community | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname(s): Mueang Chan | |
| Motto(s): "น้ำตกลือเลื่อง เมืองผลไม้ พริกไทยพันธุ์ดี อัญมณีมากเหลือ เสื่อจันทบูร สมบูรณ์ธรรมชาติ สมเด็จพระเจ้าตากสินมหาราช รวมญาติกู้ชาติที่จันทบุรี" ("Famous lue waterfall, Fruit town, Good pepper, Many jewels left, Chanthaboon Mat, Complete nature, King Taksin the Great and Including relatives in Chanthaburi") | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Chanthaburi Province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Chanthaburi |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Suthee Thongyam (since 2020) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,338 km2 (2,447 sq mi) |
| Area rank | Ranked 33rd |
| Population (2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 536,496 |
| • Rank | Ranked 49th |
| • Density | 84.6/km2 (219/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | Ranked 57th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
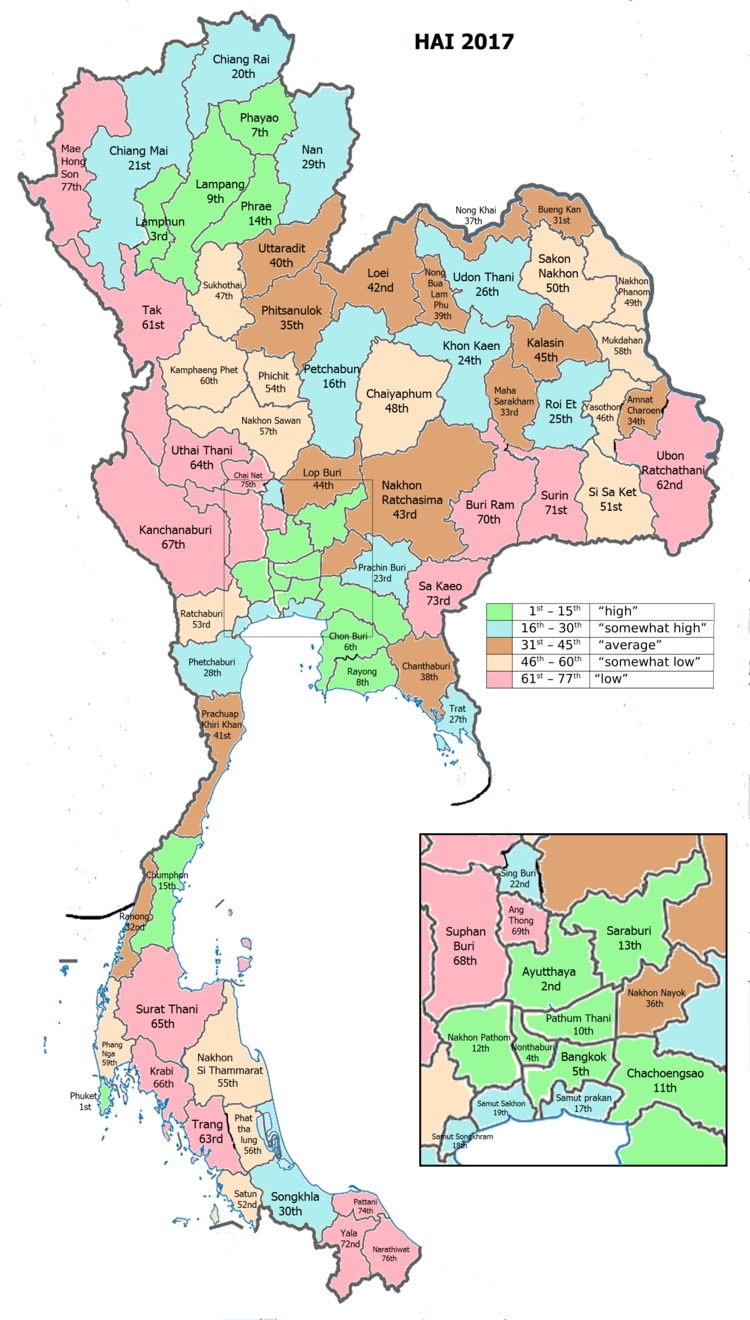
| • HAI (2017) | 0.5862 "average" Ranked 38th |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 22xxx |
| Calling code | 039 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-22 |
Chanthaburi (Thai: จันทบุรี, pronounced [tɕān.tʰá.bù.rīː]; Chong: จันกะบูย chankabui,[4] lit. 'Lady Chan, Who wears a pan on her head'[5]) is one of seventy-six provinces (changwat) in eastern Thailand, on the border with Battambang and Pailin of Cambodia, on the shore of the Gulf of Thailand. Neighbouring provinces are Trat in the east and Rayong, Chonburi, Chachoengsao, and Sa Kaeo to the west and north.
History[]

The indigenous people of the Chantaburi region are the Chong. The Chong have lived in the area since the Ayutthaya Kingdom, and are thought to have been early inhabitants of Cambodia, possibly pre-dating the Khmer. In Chantaburi Province, the Chong predominantly inhabit the districts of Khao Khitchakut, Pong Nam Ron, and Makham.[6]
After the Paknam crisis in 1893, French colonial troops occupied Chanthaburi, returning it in 1905 when Thailand gave up ownership of the western part of Cambodia. A significant minority of Chanthaburi citizens are native Vietnamese, who came there in three waves: first in the 19th century during anti-Catholic persecutions in Cochin China; a second wave in the 1920s to 1940s fleeing French Indochina; and a third wave after the communist victory in Vietnam in 1975.[citation needed] The town of Chanthaburi has been the seat of a Bishop of Chanthaburi since 1944.
Chanthaburi once used to be an important source of gemstones, especially rubies and sapphires. While the Chantaboon Waterfront Community, was developed over three centuries ago during the reign of King Narai along the banks of the River Mae Nam Chantaburi. It was an essential transportation and trade hub. Over the years, the Chantaboon Waterfront Community had lost its sheen. However, in the recent decade, the locals with the help of Thai officials have contributed to its revival as a major destination for cultural tourism.
Geography[]

While the southern part of the province is on the shore of the Gulf of Thailand and thus is mostly coastal alluvial plains, the interior of the province is mountainous. The Chanthaburi Mountains in the north has the highest elevation in the province, the 1,675 m high Khao Soi Dao Tai peak. The main river of the province is the Chanthaburi River. The total forest area is 2,076 km2 (802 sq mi) or 32.4 percent of provincial area.[7]
Together with the neighboring province, Trat, Chanthaburi is a center of gemstone mining, especially rubies and sapphires.[8] Tropical fruits are also among the main products of the province. In 2000, it produced nearly 380,000 tonnes of durian, which was 45.57 percent of Thailand's durian production, approximately 27 percent of the entire world's production.[9][10]
Within provincial boundaries lie three national parks: Namtok Phlio National Park,[11] Khao Khitchakut National Park,[12] and .[13] The province is also home to the Khao Soi Dao Wildlife Sanctuary.
Symbols[]
The provincial seal shows the moon surrounded by an aura. Inside the moon disc is a rabbit, as in Thai folklore the dark areas on the moon (maria) form the shape of a rabbit. The seal symbolizes the peace and tranquility of the province. The moon also refers to the meaning of the province, "City of Moon", from Chantha- (Thai: จันท-, lit. 'moon') and buri (Thai: บุรี, lit. 'city').
The flag of the province also shows the seal in the middle, a white rabbit on a yellow moon disc, on a blue disc. The background of the flag is red, with the name of province in yellow written below the seal.[14]
The provincial tree is Diospyros decandra. The provincial flower is an orchid (Dendrobium friedericksianum).[15] The brackish water fish flagfin prawn goby (Mahidolia mystacina) is the provincial fish.
The provincial slogan is "Magnificent waterfalls, fruit city, good breeding peppercorns, loads of gems, Chanthabun mat, fertile nature, gathering place of King Taksin the Great's Liberation Army".
Administrative divisions[]

Provincial government[]
The province is divided into 10 districts (amphoes). These are further subdivided into 76 subdistricts (tambons) and 690 villages (mubans).
- Mueang Chanthaburi
- Khlung
- Tha Mai
- Pong Nam Ron
- Makham
- Laem Sing
- Soi Dao
- Kaeng Hang Maeo
- Na Yai Am
- Khao Khitchakut
Local government[]
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[16] one Chanthaburi Provincial Administration Organisation (transl. tha – transl. ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 47 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Chanthaburi, Chanthanimit, Khlung, Tha Chang and Tha Mai have town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 42 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 34 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[2]
Transportation[]
Roads[]
Route 3 (Sukhumvit Road) passes near Chanthaburi and connects to Rayong, Pattaya, Chonburi, and Bangkok to the northwest and Trat to the southeast. Route 317 connects Chanthaburi to Sa Kaeo.[17]
Air[]
There is no airport in Chantaburi. The nearest airport is Trat Airport, 66 km from the center of Chanthaburi.
Human achievement index 2017[]
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 52 | 31 | 13 | 21 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |

|
 |

|
|
| 58 | 65 | 14 | 67 |
| Province Chanthaburi, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.5862 is "average", occupies place 38 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[3]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| showMap with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |

Local food[]
- Mu chamuang (หมูชะมวง): a curry is made from pork belly, herbs and sour grape apple shimba Chamuang (Garcinia cowa) leaves which is a popular dish of Chanthaburi and other provinces in eastern region.[18]
- Kuaytiew mu liang (ก๋วยเตี๋ยวหมูเลี้ยง): stewed pork noodles in Rĕw (Amomum villosum) herbal thicken soup which is unique local food.[19]
- Khanom khuai ling (ขนมควยลิง): traditional dessert of Chanthaburi with a long history, its name literally means "monkey's dick snack".[20]
- Kuaytiew sen chan pad pu (ก๋วยเตี๋ยวเส้นจันท์ผัดปู): a kind of Pad thai that uses Chanthaburi's rice noodles stir-fried with crab meat.[21]
References[]
- ^ Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.CS1 maint: postscript (link)[dead link]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "ร่ยงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior. stat.bora.dopa.go.th (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- ^ องค์ บรรจุน. สยามหลากเผ่าหลายพันธุ์. กรุงเทพฯ: มติชน, 2553, หน้า 128 (in Thai)
- ^ ชอง จันทะบูย ฤาลมหายใจเฮือกสุดท้าย. OK Nation (in Thai). 19 October 2012. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
- ^ Pholdhampalit, Khetsirin (22 June 2019). "Chantaburi on the table". The Nation. Retrieved 22 June 2019.
- ^ "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019CS1 maint: postscript (link)
- ^ Chao Khong Ran. "ตำนานพลอยเมืองจันท์" [Legend of Chan rubies]. luckyjewelista (in Thai).
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 March 2008. Retrieved 18 August 2008.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 March 2008. Retrieved 18 August 2008.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Namtok Phlio National Park". Department of National Parks (Thailand). Archived from the original on 22 May 2013. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
- ^ "Khao Khitchakut National Park". Department of National Parks (Thailand). Archived from the original on 22 May 2013. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
- ^ "Khao Sip Ha Chan National Park". Department of National Parks (Thailand). Archived from the original on 26 September 2015. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
- ^ "ตราประจำจังหวัดจันทบุรี" [Provincial seal]. M-culture.go.th (in Thai).
- ^ "ดอกเหลืองจันทบูร ดอกไม้ประจำจังหวัดจันทบุรี" [Yellow Chantaboon flower the provincial flower]. panmai.com (in Thai).
- ^ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
6 Chanthaburi: 1 PAO, 5 Town mun., 42 Subdistrict mun., 34 SAO.
- ^ "ประเภทของทางหลวง" [Types of highway]. Highwayweigh.go.th (in Thai).
- ^ "หมูชะมวง" [Mu chamuang]. RBRU e-Culture (in Thai).
- ^ "ก๋วยเตี๋ยวหมูเลียง" [Mu liang noodles]. RBRU e-Culture (in Thai).
- ^ "ไม่ได้ทะลึ่งนะ ชื่อแบบนี้จริงๆ 'ขนมxxxลิง' ไฮไลต์เด็ดขนมแปลกเมืองจันท์" [Not assuming a name like this 'Khanomxxxling' highlight of Chanthaburi's weird dessert]. Thai Rath (in Thai). 11 July 2017. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ "ก๋วยเตี๋ยวเส้นจันท์ผัดปู" [Kuaytiew sen chan pad pu]. RBRU e-Culture (in Thai).
External links[]
 Chanthaburi travel guide from Wikivoyage
Chanthaburi travel guide from Wikivoyage
Coordinates: 12°36′37″N 102°06′10″E / 12.61028°N 102.10278°E
- Chanthaburi Province
- Provinces of Thailand
- Gulf of Thailand