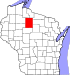
Price County, Wisconsin
Price County | |
|---|---|
U.S. county | |
 Price County courthouse | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Wisconsin | |
 Wisconsin's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 45°41′N 90°22′W / 45.68°N 90.36°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1882 |
| Named for | William T. Price |
| Seat | Phillips |
| Largest city | Park Falls |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,278 sq mi (3,310 km2) |
| • Land | 1,254 sq mi (3,250 km2) |
| • Water | 24 sq mi (60 km2) 1.9%% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 14,159 |
| • Estimate (2020) | 13,245 |
| • Density | 11/sq mi (4.3/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 7th |
| Website | www |

Price County is a county in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2010 census, the population was 14,159.[1] Its county seat is Phillips.[2]
History[]
Price County was created on March 3, 1879, when Wisconsin Governor William E. Smith signed legislation creating the county. The county was later organized in 1882.[3] William T. Price (1824–1886), for whom Price County was named,[4] was President of Wisconsin Senate and an early logger in Price County; he later was elected to the U.S. Congress.[5] The county was formed from portions of Chippewa and Lincoln counties.
The first white settler in what is now Price County was Major Isaac Stone, who located on the Spirit River in 1860 to engage in lumbering.[6] Price County continues today to be a large producer of raw timber.[7]
Geography[]
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,278 square miles (3,310 km2), of which 1,254 square miles (3,250 km2) is land and 24 square miles (62 km2) (1.9%) is water.[8] The highest natural point in Wisconsin, Timms Hill at 1,951 feet (595 m), is located in Price County.
Adjacent counties[]
- Ashland County - northwest
- Iron County - northeast
- Lincoln County - southeast
- Oneida County - east
- Rusk County - west
- Sawyer County - west
- Taylor County - south
- Vilas County - northeast
Major highways[]
 U.S. Highway 8
U.S. Highway 8 Highway 13 (Wisconsin)
Highway 13 (Wisconsin) Highway 70 (Wisconsin)
Highway 70 (Wisconsin) Highway 86 (Wisconsin)
Highway 86 (Wisconsin) Highway 102 (Wisconsin)
Highway 102 (Wisconsin) Highway 111 (Wisconsin)
Highway 111 (Wisconsin) Highway 182 (Wisconsin)
Highway 182 (Wisconsin)
Airports[]
- KPBH - Price County Airport
- KPKF - Park Falls Municipal Airport
- 5N2 - Prentice Airport
National protected area[]
- Chequamegon National Forest (part)
Demographics[]
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 785 | — | |
| 1890 | 5,258 | 569.8% | |
| 1900 | 9,106 | 73.2% | |
| 1910 | 13,795 | 51.5% | |
| 1920 | 18,517 | 34.2% | |
| 1930 | 17,284 | −6.7% | |
| 1940 | 18,467 | 6.8% | |
| 1950 | 16,344 | −11.5% | |
| 1960 | 14,370 | −12.1% | |
| 1970 | 14,520 | 1.0% | |
| 1980 | 15,788 | 8.7% | |
| 1990 | 15,600 | −1.2% | |
| 2000 | 15,822 | 1.4% | |
| 2010 | 14,159 | −10.5% | |
| 2020 (est.) | 13,245 | [9] | −6.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[10] 1790–1960[11] 1900–1990[12] 1990–2000[13] 2010–2020[1] | |||
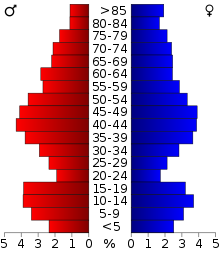
As of the census[14] of 2000, there were 15,822 people, 6,564 households, and 4,417 families residing in the county. The population density was 13 people per square mile (5/km2). There were 9,574 housing units at an average density of 8 per square mile (3/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 98.22% White, 0.10% Black or African American, 0.60% Native American, 0.30% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 0.15% from other races, and 0.60% from two or more races. 0.73% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 44.4% were of German, 6.5% Norwegian, 5.9% Swedish, 5.4% Polish, 5.2% Irish and 5.0% Czech ancestry.
There were 6,564 households, out of which 28.90% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 56.50% were married couples living together, 6.60% had a female householder with no husband present, and 32.70% were non-families. 28.50% of all households were made up of individuals, and 14.50% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.37 and the average family size was 2.91.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 23.80% under the age of 18, 5.80% from 18 to 24, 25.80% from 25 to 44, 25.70% from 45 to 64, and 18.80% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 42 years. For every 100 females there were 101.00 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 99.00 males.
In 2017, there were 127 births, giving a general fertility rate of 71.4 births per 1000 women aged 15–44, the 13th highest rate out of all 72 Wisconsin counties.[15] Additionally, there were fewer than five reported induced abortions performed on women of Price County residence in 2017.[16]
Communities[]

Cities[]
- Park Falls
- Phillips (county seat)
Villages[]
Towns[]
Census-designated place[]
- Ogema
Unincorporated communities[]
Ghost towns/neighborhoods[]
Politics[]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ^ "Wisconsin: Individual County Chronologies". Wisconsin Atlas of Historical County Boundaries. The Newberry Library. 2007. Archived from the original on April 14, 2017. Retrieved August 15, 2015.
- ^ "Here's How Iron Got Its Name". The Rhinelander Daily News. June 16, 1932. p. 2. Retrieved August 24, 2014 – via Newspapers.com.

- ^ William Thompson Price, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress.
- ^ Historical and Biographical Album of the Chippewa Valley, Wisconsin, A. Warner, 1891–1892, p. 353.
- ^ https://www.co.price.wi.us/188/Timber-Sales
- ^ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
- ^ "County Population Totals: 2010-2020". Retrieved June 20, 2021.
- ^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
- ^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
- ^ Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
- ^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- ^ "Annual Wisconsin Birth and Infant Mortality Report, 2017 P-01161-19 (June 2019): Detailed Tables". Archived from the original on June 19, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2019.
- ^ Reported Induced Abortions in Wisconsin, Office of Health Informatics, Division of Public Health, Wisconsin Department of Health Services. Section: Trend Information, 2013-2017, Table 18, pages 17-18
- ^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ The leading "other" candidate, Progressive Theodore Roosevelt, received 662 votes, while Socialist candidate Eugene Debs received 290 votes, Prohibition candidate Eugene Chafin received 75 votes, and Independent candidate Arthur Reimer received 3 votes.
External links[]
- Price County
- Price County map at Wisconsin Department of Transportation
- Price County Historical Society
- Wisconsin counties
- Price County, Wisconsin
- 1882 establishments in Wisconsin
- Populated places established in 1882