Bars County
| Bars County | |
|---|---|
| County of the Kingdom of Hungary | |
| 11th century–1920 | |
 Coat of arms
| |
 | |
| Capital | Bars; Léva (1321-1580); Kis-Tapolcsan (1580-1735) Aranyosmarót (1735-1920) |
| Area | |
| • Coordinates | 48°23′N 18°24′E / 48.383°N 18.400°ECoordinates: 48°23′N 18°24′E / 48.383°N 18.400°E |
• 1910 | 2,724 km2 (1,052 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1910 | 178500 |
| History | |
• Established | 11th century |
| 4 June 1920 | |
| Today part of | |
| Starý Tekov; Levice; Topoľčianky; Zlaté Moravce are the current name of the capital. | |
Bars (Latin: comitatus Barsiensis, Hungarian: Bars, Slovak: Tekov, German: Barsch) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in central and southern Slovakia. Today in Slovakia, Tekov is the informal designation of the corresponding territory.
Geography[]


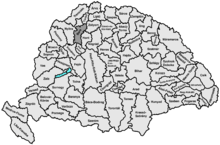
Bars County shared borders with the Hungarian counties of Nyitra, Turóc, Zólyom, Hont, Esztergom and Komárom. It was situated along the Garam river between Hont in the east, Körmöcbánya and Felsőbesenyő in the north (which were part of the county), the Zsitva river in the west, and Zsitvabesenyő and Bény in the south (which was not part of the county). The rivers Garam and Zsitva ran through the county. The county was characterised by mining. Around 1910, its area was 2,724 km2 (1,052 sq mi).
Capitals[]
The capital of the county was the Bars Castle, then the Léva Castle, then from the late 16th century Kistapolcsány and since the 18th century Aranyosmarót.
History[]
The county arose in the 11th century. The southern part of this county was occupied by Ottoman Empire between 1663 and 1685 and managed as Uyvar Eyalet by her. In the aftermath of World War I, the area became part of newly formed Czechoslovakia, as recognized by the concerned states in 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon.
Following the provisions of the First Vienna Award, the southern part of the area was returned to Hungary in November 1938. This was merged with the southern part of the former Hont county to form Bars-Hont county, with the capital Léva.
After World War II, the Trianon borders were restored and the area lay again completely in Czechoslovakia. In 1993, Czechoslovakia was split and Tekov became part of Slovakia.
Demographics[]
1900[]
In 1900, the county had a population of 165,122 people and was composed of the following linguistic communities:[1]
Total:
- Slovak: 94,879 (57.5%)
- Hungarian: 52,317 (31.7%)
- German: 17,325 (10.5%)
- Serbian: 19 (0.0%)
- Romanian: 12 (0.0%)
- Croatian: 5 (0.0%)
- Ruthenian: 0 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 565 (0.3%)
According to the census of 1900, the county was composed of the following religious communities:[2]
Total:
- Roman Catholic: 139,729 (84.6%)
- Calvinist: 17,018 (10.3%)
- Jewish: 5,191 (3.2%)
- Lutheran: 3,115 (1.9%)
- Greek Catholic: 46 (0.0%)
- Unitarian: 10 (0.0%)
- Greek Orthodox: 7 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 6 (0.0%)
1910[]

In 1910, the county had a population of 178,500 people and was composed of the following linguistic communities:[3]
Total:
- Slovak: 97,824 (54.8%)
- Hungarian: 62,022 (34.8%)
- German: 17,366 (9.7%)
- Ruthenian: 92 (0.0%)
- Croatian: 12 (0.0%)
- Romanian: 11 (0.0%)
- Serbian: 8 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 1,165 (0.7%)
According to the census of 1910, the county was composed of the following religious communities:[4]
Total:
- Roman Catholic: 153,286 (85.9%)
- Calvinist: 16,795 (9.4%)
- Jewish: 4,969 (2.8%)
- Lutheran: 3,253 (1.8%)
- Greek Catholic: 140 (0.1%)
- Greek Orthodox: 37 (0.0%)
- Unitarian: 12 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 8 (0.0%)
Subdivisions[]

In the early 20th century, the subdivisions of Bars county were:
| Districts (járás) | |
|---|---|
| District | Capital |
| Aranyosmarót | Aranyosmarót |
| Garamszentkereszt | Garamszentkereszt |
| Léva | Léva |
| Oszlány | Oszlány |
| Verebély | Verebély |
| Urban districts (rendezett tanácsú város) | |
| Körmöcbánya | |
| Léva | |
| Újbánya | |
References[]
- ^ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 24 June 2012.
- ^ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 24 June 2012.
- ^ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 24 June 2012.
- ^ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 24 June 2012.
- States and territories established in the 11th century
- States and territories disestablished in 1920
- Counties in the Kingdom of Hungary

