Elias James Corey
Elias James "E.J." Corey (born July 12, 1928) is an American organic chemist. In 1990, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for his development of the theory and methodology of organic synthesis",[3] specifically retrosynthetic analysis.[4][5] Regarded by many as one of the greatest living chemists, he has developed numerous synthetic reagents, methodologies and total syntheses and has advanced the science of organic synthesis considerably.
Biography[]
E.J. Corey (the surname was anglicized from the Lebanese Arabic Khoury, meaning priest) was born to Lebanese Greek Orthodox Christian immigrants in Methuen, Massachusetts, 50 km (31 mi) north of Boston.[6] His mother changed his name to "Elias" to honor his father, who died eighteen months after Corey's birth. His widowed mother, brother, two sisters, aunt and uncle all lived together in a spacious house, struggling through the Great Depression. As a young boy, Corey was independent and enjoyed sports such as baseball, football, and hiking. He attended a Catholic elementary school and Lawrence High School in Lawrence, Massachusetts.
At the age of 16 Corey entered MIT, where he earned both a bachelor's degree in 1948 and a Ph.D. under Professor John C. Sheehan in 1951. Upon entering MIT, Corey's only experience with science was in mathematics, and he began his college career pursuing a degree in engineering. After his first chemistry class in his sophomore year he began rethinking his long-term career plans and graduated with a bachelor's degree in chemistry. Immediately thereafter, at the invitation of Professor John C. Sheehan, Corey remained at MIT for his Ph.D. After his graduate career he was offered an appointment at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, where he became a full professor of chemistry in 1956 at the age of 27. He was initiated as a member of the Zeta chapter of Alpha Chi Sigma at the University of Illinois in 1952.[7] In 1959, he moved to Harvard University, where he is currently an emeritus professor of organic chemistry with an active Corey Group research program. He chose to work in organic chemistry because of "its intrinsic beauty and its great relevance to human health".[8] He has also been an advisor to Pfizer for more than 50 years.[9]
Among numerous honors, Corey was awarded the National Medal of Science in 1988,[10] the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1990,[5] and the American Chemical Society's greatest honor, the Priestley Medal, in 2004.[11]
Major contributions[]
Reagents[]
Corey has developed several new synthetic reagents:
- PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate), also referred to as the Corey-Suggs reagent, is widely used for the oxidation of alcohols to corresponding ketones and aldehydes.[12] PCC has several advantages over other commercial oxidants.

One of these advantages is that the compound is available as an air-stable yellow solid that is not very hygroscopic. Unlike other oxidizing agents, PCC can accomplish single oxidations with only about 1.5 equivalents (scheme 1). The alcohol performs nucleophilic attack to the electropositive chromium(VI) metal displacing chlorine. The chloride anion then acts as a base to afford the aldehyde product and chromium(IV). The slightly acidic character of PCC makes it useful for cyclization reactions with alcohols and alkenes (Scheme 2).[13]
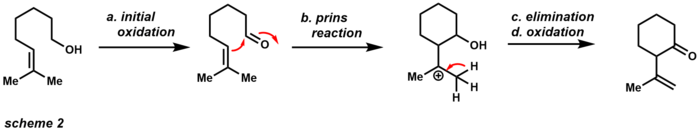
The initial oxidation yields the corresponding aldehyde, which can then undergo a Prins reaction with the neighboring alkene. After elimination and further oxidation, the product is a cyclic ketone. If this product is undesired, powdered sodium acetate can be used as a buffer to achieve only initial oxidation. The robustness of PCC as an oxidizing agent has also rendered it useful in the realm of total synthesis (Scheme 3). This example illustrates that PCC is capable of performing a Dauben oxidative rearrangement with tertiary alcohols through a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement.[14]
![[3,3] rearrangement with PCC](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/87/PCC_rearrangement3.png/700px-PCC_rearrangement3.png)
- t-Butyldimethylsilyl ether (TBS),[15] triisopropylsilyl ether (TIPS), and methoxyethoxymethyl (MEM): are popular alcohol protecting groups. The development of these protecting groups allowed the synthesis of several natural products that did not have the functional group compatibility to withstand standard chemical transformations. Although the synthetic community is now moving away from the use of protecting groups it is still rare that a published synthesis of a natural product omits them. Since 1972 the TBS group has become the most popular silicon protecting group. TBS is stable to chromatography and labile enough for cleavage under basic and acidic conditions. More importantly, TBS ethers are stable to some carbon nucleophiles such as Grignard reagents and enolates.[16][17][18]
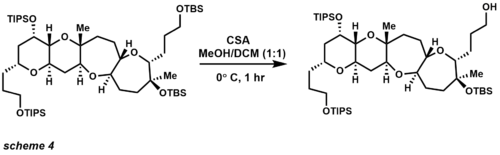
In the field of complex molecule synthesis, TBS has been widely used as one of the most versatile of the silicon-based protecting groups (scheme 4).[19][20] The use of CSA provides selective removal of a primary TBS ether in the presence of tertiary TBS ether and TIPS ethers. Other means of TBS deprotection include acids (also Lewis acids), and fluorides. TIPS protecting groups were also pioneered by Corey and provide increased selectivity of primary alcohol protection over secondary and tertiary alcohol protection. TIPS ethers are more stable under acidic and basic conditions, the disadvantage of this protecting group over TBS ethers being that the group is less labile for deprotection.[21] The most common reagents used for cleavage employ the same conditions as TBS ether, but longer reaction times are generally needed.

Usually TBS ethers are severed by TBAF, but the hindered TBS ether above survives the reaction conditions upon primary TIPS removal (scheme 5).[22] The MEM protecting group was first described by Corey in 1976.[23] This protecting group is similar in reactivity and stability to other alkoxy methyl ethers under acidic conditions. Cleavage of MEM protecting groups is usually accomplished under acidic conditions, but coordination with metal halides greatly enhances lability via assisted cleavage (scheme 6).[24]

- 1,3-Dithianes were pioneered by E.J. Corey in 1965 as a temporary modification of a carbonyl group in displacement and addition reactions. The formation of dithiane was the initial development that introduced Umpolung chemistry and is widely used for inversion of reactivity. The formations of dithianes can be accomplished with a Lewis acid (scheme 7) or directly from carbonyl compounds.[25]

The pKa of dithianes is approximately 30, allowing deprotonation with an alkyl lithium reagent, typically n-butyllithium. The reaction with dithianes and aldehydes is now known as the Corey-Seebach reaction. The dithiane once deprotonated serves as an acyl anion used to attack incoming electrophiles. After deprotection of the dithiane, usually with HgO, a ketone product is observed from the masked acyl dithiane anion. The utility of such reactions has expanded the field of organic synthesis by allowing synthetic chemists to use Umpolung disconnections in total synthesis (scheme 8).[26] 1,3-dithianes are also used as protecting groups for carbonyl compounds expressing the versatility and utility of this functional group.

- In addition, Corey commenced detailed studies on cationic polyolefin cyclizations utilized in enzymatic production of cholesterol from simpler plant terpenes.[27] Corey established the details of the remarkable cyclization process by first studying the biological synthesis of sterols from squalene.
Methodology[]
Several reactions developed in Corey's lab have become commonplace in modern synthetic organic chemistry. At least 302 methods have been developed in the Corey group since 1950.[28] Several reactions have been named after him:
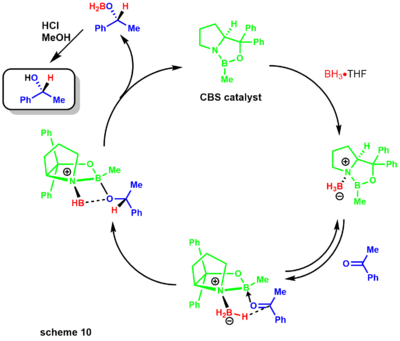
- Corey-Itsuno reduction, also known as the Corey-Bakshi-Shibata reduction, is an enantioselective reduction of ketones to alcohols utilizing an oxazaborolidine catalyst and various boranes as the stoichiometric reductant.[29] The Corey group first demonstrated the synthesis of the catalyst using borane and chiral aminoalcohols. The reaction uses the chiral amino acid proline and in the presence of borane leads to the CBS catalyst (scheme 9).[30][31]

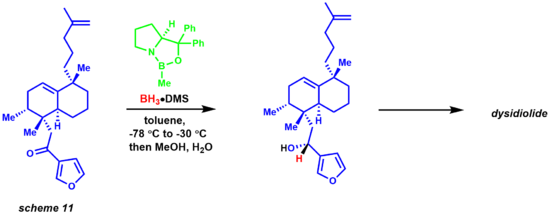
Later, Corey demonstrated that substituted boranes were easier to prepare and much more stable. The reduction mechanism begins with the oxazoborolidine being only slightly basic at [nitrogen], coordinating with the stoichiometric borane of the boron amine complex(scheme 10).[31] Lack of donation from the nitrogen to the boron increases its Lewis acidity, allowing coordination with the ketone substrate. The complexation of the substrate occurs from the most accessible lone pair of the oxygen leading to restricted rotation around the B-O bond due to the sterically neighboring phenyl group.[32]
Migration of the hydride from borane to the electrophilic ketone center occurs via a 6-membered ring transition state, leading to a four-membered ring intermediate ultimately providing the chiral product and regeneration of the catalyst. The reaction has also been of great use to natural products chemists (scheme 11).[33][34] The synthesis of dysidiolide by Corey and co-workers was achieved via an enantioselective CBS reduction using a borane-dimethylsulfide complex.
- Corey-Fuchs alkyne synthesis is the synthesis of terminal alkynes through a one-carbon homologation of aldehydes using triphenylphosphine and carbon tetrabromide.[30][35] The mechanism is similar to that of the Wittig reaction by the formation of a phosphorus ylide with triphenylphosphine and carbon tetrabromide. Reacting the phosphorus ylide with the aldehyde substrate yields a dibromoolefin.[36]

On treatment with two equivalents of n-buLi, lithium halogen exchange and deprotonation yields a lithium acetylide species that undergoes hydrolysis to yield the terminal alkyne product (scheme 12).[30] More recently, a one-pot synthesis using a modified procedure has been developed.[37] This synthetic transformation has been proven successful in the total synthesis (+)-taylorione by W.J. Kerr and co-workers (scheme 13).[38]

- The Corey–Kim oxidation was a newly developed transformation for the conversion of alcohols into corresponding aldehydes and ketones.[30][39] This process offers a less toxic alternative to chromium based oxidations with the use of N-chlorosuccinimidosulfonium chloride (NCS), dimethylsulfide (DMS), and triethylamine (TEA). The Corey-Kim reagent is formed in situ when NCS and DMS are reacted to form dimethylsuccinimidosulfonium chloride species (scheme 14).[30]

The alkoxy sulfonium salt is deprotonated at the alpha position with triethylamine to afford the oxidized product. The reaction accommodates a wide array of functional groups, but allylic and benzylic alcohols are typically transformed into allylic and benzylic chlorides. Its application in synthesis is based on the mild protocol conditions and functional and protecting group compatibility. In the total synthesis of ingenol, Kuwajima and co-workers exploited the Corey-Kim oxidation by selectively oxidizing the less hindered secondary alcohol(scheme 15).[40]

- Corey-Winter olefination is a stereospecific transformation of 1,2-diols to alkenes involving the diol substrate, thiocarbonyldiimidazole, and excess trialkylphosphite.[30][41] The mechanism has been narrowed down to two possible pathways, but the exact mechanism is unknown.[42] Specifically, the reaction between the thionocarbonate and the trialkylphosphite proceeds either through the formation of a phosphorus ylide species or a carbenoid intermediate. Nonetheless, the reaction is stereospecific for most substrates unless the product would lead to an exceedingly strained structure. The formation of sterically hindered trans alkenes present in 7-membered rings was attempted by Corey and coworkers, but was unsuccessful even when employing this new synthetic methodology incurring enormous ring strain. More importantly, stereospecfic alkenes are present in several natural products as the method continues to be exploited to yield a series of complex substrates. Professor T.K.M Shing et al used the Corey-Winter olefination reaction to synthesize (+)-Boesenoxide (scheme 16).[43]

- CBS enantioselective Diels-Alder reaction has been developed using a similar scaffold to the enantioselective CBS reduction.[31] After the development of this reaction the CBS reagent proved to be a very versatile reagent for a series of several powerful synthetic transformations. The use of a chiral Lewis acid such as the CBS catalyst includes a broad range of unsaturated enones substrates. The reaction likely proceeds via a highly organized 6-membered ring pre-transition state to deliver highly enantio-enriched products (scheme 17).[44]

This transition state likely occurs because of favorable pi-stacking with the phenyl substituent.[31][45] The enantioselectivity of the process is facilitated from the diene approaching the dienophile from the opposite face of the phenyl substituent. The Diels-Alder reaction is one of the most powerful transformations in synthetic chemistry. The synthesis of natural products using the Diels-Alder reaction as a transform has been applied especially to the formation of six-membered rings(scheme 18).[46]

- Corey-Nicolaou macrolactonization provides the first method for preparing medium to large sized lactones.[30][47] Previously, intermolecular outcompeted intramolecular lactonization even at low concentrations. One big advantage of this reaction is that it is performed under neutral conditions allowing the presence of acid and base-labile functional groups. To date rings of 7 to 48 members have been successfully synthesized using this method.[48]
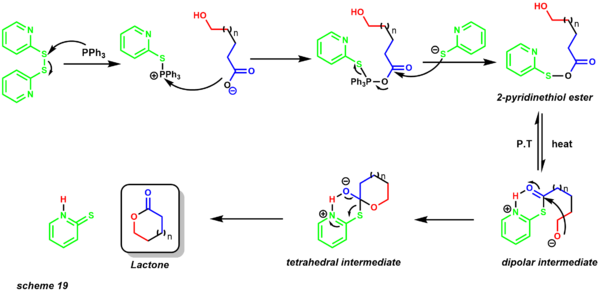
The reaction occurs in the presence of 2,2'-dipyridyl disulfide and triphenylphosphine. The reaction is generally refluxed in a nonpolar solvent such as benzene. The mechanism begins with formation of the 2-pyridinethiol ester (scheme 19). Proton-transfer provides a dipolar intermediate in which the alkoxide nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbonyl center, providing a tetrahedral intermediate that yields the macrolactone product. One of the first examples of this protocol was applied to the total synthesis of zearalenone (scheme 20).[49]

- Johnson-Corey-Chaykovsky reaction is useful for the synthesis of epoxides and cyclopropanes.[30] The reaction forms a sulfur ylide in situ that reacts with enones, ketones, aldehydes, and imines to form corresponding epoxides, cyclopropanes, and aziridines.[50] Two sulfur ylide variants have been employed that give different chemeoselective products (scheme 21).The dimethylsulfoxonium methylide provides epoxides from ketones, but yields the cyclopropanes when enones are employed. Dimethylsulfonium methylide transforms ketones and enones to the corresponding epoxides. Dimethylsulfonium methylide is much more reactive and less stable than dimethylsulfoxonium methylide, so it is generated at low temperatures.[51]

Based on their reactivity, another distinct advantage of these two variants is that kinetically they provide a difference in diastereoselectivity. The reaction is very well established, and enantioselective variants (catalytic and stoichiometric) have also been achieved. From a retrosynthetic analysis standpoint, this reaction provides a reasonable alternative to conventional epoxidation reactions with alkenes (scheme 22). Danishefsky utilized this methodology for the synthesis of taxol. Diastereoselectivity is established by 1,3 interactions in the transition state required for epoxide closure.[52]

Total syntheses[]
E. J. Corey and his research group have completed many total syntheses. At least 265 compounds have been synthesized in the Corey group since 1950.[53]
His 1969 total syntheses of several prostaglandins are considered classics.[54][55][56][57] Specifically the synthesis of Prostaglandin F2α presents several challenges. The presence of both cis and trans olefins as well as five asymmetric carbon atoms renders the molecule a desirable challenge for organic chemists. Corey's retrosynthetic analysis outlines a few key disconnections that lead to simplified precursors (scheme 23).

Molecular simplification began first by disconnecting both carbon chains with a Wittig reaction and Horner-Wadsworth Emmons modification. The Wittig reaction affords the cis product, while the Horner-Wadsworth Emmons produces the trans olefin. The published synthesis reveals a 1:1 diastereomeric mixture of the carbonyl reduction using zinc borohydride. However, years later Corey and co-workers established the CBS reduction. One of the examples that exemplified this protocol was an intermediate in the prostaglandin synthesis revealing a 9:1 mixture of the desired diastereomer (scheme 24).[33]
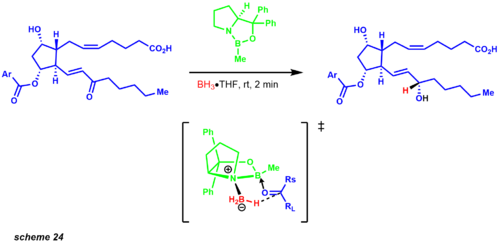
The iodolactonization transform affords an allylic alcohol leading to a key Baeyer-Villiger intermediate. This oxidation regioselectively inserts an oxygen atom between the ketone and the most electron-rich site. The pivotal intermediate leads to a straightforward conversion to the Diels-Alder structural goal, which provides the carbon framework for the functionalized cyclopentane ring. Later Corey developed an asymmetric Diels-Alder reaction employing a chiral oxazoborolidine, greatly simplifying the synthetic route to the prostaglandins.
Other notable syntheses:
- Longifolene[58][59]
- Ginkgolides A[60] and B[61][62]
- Lactacystin[63]
- Miroestrol[64]
- Ecteinascidin 743[65]
- Salinosporamide A[66]
Publications[]
E.J. Corey has more than 1100 publications.[67] In 2002, the American Chemical Society (ACS) recognized him as the "Most Cited Author in Chemistry". In 2007, he received the first ACS Publications Division "Cycle of Excellence High Impact Contributor Award"[68] and was ranked the number one chemist in terms of research impact by the Hirsch Index (h-index).[69] His books include:
- Corey, E. J. (2010). Enantioselective chemical synthesis : methods, logic and practice. Dallas, Texas: Direct Book Publishing. ISBN 978-0-615-39515-9. OCLC 868975499.
- Corey, E. J. (1995). The logic of chemical synthesis. New York: John Wiley. ISBN 0-471-11594-0. OCLC 45734016.
- Corey, E. J. (2007). Molecules and medicine. Hoboken, N.J: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-26096-8. OCLC 156819246.
- Li, Jie (2011). Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry II. Hoboken, N.J: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-08508-0. OCLC 761319808.
- Li, Jie (2007). Name reactions for functional group transformations. Hoboken, N.J: Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-74868-7. OCLC 85851580.
Altom suicide[]
Jason Altom, one of Corey's students, committed suicide in 1998.[70] Altom's suicide caused controversy because he explicitly blamed Corey, his research advisor, for his suicide.[71] Altom cited in his 1998 farewell note "abusive research supervisors" as one reason for taking his life. Altom's suicide note also contained explicit instructions on how to reform the relationship between students and their supervisors.
While Altom was the second suicide in as many years in Corey's lab,[72] Corey was devastated and bewildered by his student's death.[73] Corey said, "That letter doesn't make sense. At the end, Jason must have been delusional or irrational in the extreme." Corey also claimed he never questioned Altom's intellectual contributions. "I did my best to guide Jason as a mountain guide would to guide someone climbing a mountain. I did my best every step of the way," Corey states. "My conscience is clear. Everything Jason did came out of our partnership. We never had the slightest disagreement."[70] The American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP) cited The New York Times article on Altom's suicide as an example of problematic reporting, arguing that Altom presented warning signs of depression and suicidal ideation and that the article had scapegoated Corey despite a lack of secondary evidence that the advisor's behavior had contributed to Altom's distress.[74][75] According to The Boston Globe reporting, students and professors said Altom actually retained Corey's support.[73]
As a result of Altom's death, the Department of Chemistry accepted a proposal allowing graduate students to ask two additional faculty members to play a small advisory role in preparing a thesis.[76][71]
Corey Group members[]
As of 2010, approximately 700 people have been Corey Group members. A database of 580 former members and their current affiliation was developed for Corey's 80th birthday in July 2008.[77]
Woodward–Hoffmann rules[]
When awarded the Priestley Medal in 2004, E. J. Corey created a controversy with his claim to have inspired Robert Burns Woodward prior to the development of the Woodward–Hoffmann rules. Corey wrote:
"On May 4, 1964, I suggested to my colleague R. B. Woodward a simple explanation involving the symmetry of the perturbed (HOMO) molecular orbitals for the stereoselective cyclobutene → 1,3-butadiene and 1,3,5-hexatriene → cyclohexadiene conversions that provided the basis for the further development of these ideas into what became known as the Woodward–Hoffmann rules."[78]
This was Corey's first public statement on his claim that starting on May 5, 1964 Woodward put forth Corey's explanation as his own thought with no mention of Corey and the conversation of May 4. Corey had discussed his claim privately with Hoffmann and close colleagues since 1964. Corey mentions that he made the Priestley statement "so the historical record would be correct".[79]
Corey's claim and contribution were publicly rebutted by Roald Hoffmann in the journal Angewandte Chemie. In the rebuttal, Hoffmann states that he asked Corey over the course of their long discussion of the matter why Corey did not make the issue public. Corey responded that he thought such a public disagreement would hurt Harvard and that he would not "consider doing anything against Harvard, to which I was and am so devoted." Corey also hoped that Woodward himself would correct the historical record "as he grew older, more considerate, and more sensitive to his own conscience."[80] Woodward died suddenly of a heart attack in his sleep in 1979.
Awards and honors[]
E.J. Corey has received more than 40 major awards including the Linus Pauling Award (1973), Franklin Medal (1978), Tetrahedron Prize (1983), Wolf Prize in Chemistry (1986), National Medal of Science (1988), Japan Prize (1989), Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1990), Golden Plate Award of the American Academy of Achievement (1991),[81] Roger Adams Award (1993), and the Priestley Medal (2004).[11] He was inducted into the Alpha Chi Sigma Hall of Fame in 1998.[7] As of 2008, he has been awarded 19 honorary degrees from universities around the world including Oxford University (UK), Cambridge University (UK), and National Chung Cheng University.[82] In 2013, the E.J. Corey Institute of Biomedical Research (CIBR) opened in Jiangyin, Jiangsu Province, China.[83]
Corey was elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS) in 1998.[2]
References[]
- ^ Laureates of the Japan Prize Archived April 7, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. japanprize.jp
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Professor Elias Corey ForMemRS Foreign Member". London: Royal Society. Archived from the original on October 18, 2015.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1990". Nobelprize.org. Retrieved July 25, 2015.
- ^ E. J. Corey, X-M. Cheng, The Logic of Chemical Synthesis, Wiley, New York, 1995, ISBN 0-471-11594-0.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Corey, E.J. (1991). "The Logic of Chemical Synthesis: Multistep Synthesis of Complex Carbogenic Molecules (Nobel Lecture)". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 30 (5): 455–465. doi:10.1002/anie.199104553.
- ^ Elias James Corey – Autobiography Archived July 6, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. nobelprize.org
- ^ Jump up to: a b Fraternity – Awards – Hall of Fame – Alpha Chi Sigma Archived January 26, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Corey, E.J. (1990). "Nobel Prize Autobiography". Nobelprize.org: The Official Site of the Nobel Prize. Retrieved September 9, 2010.
- ^ "Compiled Works of Elias J. Corey, Notes, Pfizer, Celebrating your 80th birthday". June 27, 2008. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- ^ National Science Foundation – The President's National Medal of Science Archived October 15, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jump up to: a b See the E.J. Corey, About E.J. Corey, Major Awards tab "Compiled Works of Elias J. Corey". July 12, 2008. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- ^ Corey, E.J.; Suggs, W. (1975). "Pyridinium chlorochromate. An efficient reagent for oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carbonyl compounds". Tetrahedron Lett. 16 (31): 2647–2650. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)75204-x.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Boger, D. (1978). "Oxidative cationic cyclization reactions effected by pyridinium chlorochromate". Tetrahedron Lett. 19 (28): 2461–2464. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)94800-2.
- ^ Yang; et al. (2010). "Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Caribenol A". JACS. 132 (39): 13608–13609. doi:10.1021/ja106585n. PMID 20831198.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Venkateswarlu, A. (1972). "Protection of hydroxyl groups as tert-butyldimethylsilyl derivatives". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94 (17): 6190–6191. doi:10.1021/ja00772a043.
- ^ Kocienski, P.J. Protecting Groups; Georg Thieme Verlag: Germany, 2000
- ^ Friesen, R. W.; et al. (1991). "A highly stereoselective conversion of α-allenic alcohols to 1,2-syn amino alcohol derivatives via iodocarbamation". Tetrahedron Lett. 31 (30): 4249–4252. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)97592-0.
- ^ Imanieh; et al. (1992). "A facile generation of α-silyl carbanions". Tetrahedron Lett. 33 (4): 543–546. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)93991-1.
- ^ Mori; et al. (1998). "Formal Total Synthesis of Hemibrevetoxin B by an Oxiranyl Anion Strategy". J. Org. Chem. 63 (18): 6200–6209. doi:10.1021/jo980320p. PMID 11672250.
- ^ Furstner; et al. (2001). "Alkyne Metathesis: Development of a Novel Molybdenum-Based Catalyst System and Its Application to the Total Synthesis of Epothilone A and C". Chem. Eur. J. 7 (24): 5299–5317. doi:10.1002/1521-3765(20011217)7:24<5299::aid-chem5299>3.0.co;2-x. PMID 11822430.
- ^ Ogilvie; et al. (1974). "Selective protection of hydroxyl groups in deoxynucleosides using alkylsilyl reagents". Tetrahedron Lett. 116 (33): 2865–2868. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)91764-2.
- ^ Kadota; et al. (1998). "Stereocontrolled Total Synthesis of Hemibrevetoxin B". J. Org. Chem. 63 (19): 6597–6606. doi:10.1021/jo9807619.
- ^ Corey; et al. (1976). "A new general method for protection of the hydroxyl function". Tetrahedron Lett. 17 (11): 809–812. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)92890-9.
- ^ Chiang; et al. (1989). "Total synthesis of L-659,699, a novel inhibitor of cholesterol biosynthesis". J. Org. Chem. 54 (24): 5708–5712. doi:10.1021/jo00285a017.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Seebach, D. (1965). "Synthesis of 1,n-Dicarbonyl Derivates Using Carbanions from 1,3-Dithianes". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 4 (12): 1077–1078. doi:10.1002/anie.196510771.
- ^ Corey; et al. (1982). "Total synthesis of aplasmomycin". JACS. 104 (24): 6818–6820. doi:10.1021/ja00388a074.
- ^ Wendt, K.U.; Schulz, G.E.; Liu, D.R.; Corey, E.J. (2000). "Enzyme Mechanisms for Polycyclic Triterpene Formation". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 39 (16): 2812–2833. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20000818)39:16<2812::aid-anie2812>3.3.co;2-r. PMID 11027983.
- ^ See the Methods tab"Compiled Works of Elias J. Corey". July 12, 2008. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; et al. (1998). "Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds with Chiral Oxazaborolidine Catalysts: A New Paradigm for Enantioselective Catalysis and a Powerful New Synthetic Method". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37 (15): 1986–2012. doi:10.1002/(sici)1521-3773(19980817)37:15<1986::aid-anie1986>3.0.co;2-z. PMID 29711061.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h Kürti, L.; Czakó, B. Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis; Elsevier: Burlington, 2005.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Corey, E.J.; Kürti, L. Enantioselective Chemical Synthesis; Direct Book Publishing: Dallas, 2010
- ^ Corey, E.J.; Bakshi, R.K.; Shibata, S. (1987). "Highly enantioselective borane reduction of ketones catalyzed by chiral oxazaborolidines. Mechanism and synthetic implications". JACS. 109 (18): 5551–5553. doi:10.1021/ja00252a056.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Corey; et al. (1987). "A stable and easily prepared catalyst for the enantioselective reduction of ketones. Applications to multistep syntheses". JACS. 109 (25): 7925–7926. doi:10.1021/ja00259a075.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Roberts, B. E. (1997). "Total Synthesis of Dysidiolide". JACS. 119 (51): 12425–12431. doi:10.1021/ja973023v.
- ^ Corey, E.J.; Fuch, P.L. Tetrahedron Lett. 1972, 3769
- ^ Eymery et al Synthesis 2000, 185
- ^ Michel; et al. (1999). "A one-pot procedure for the synthesis of alkynes and bromoalkynes from aldehydes". Tetrahedron Lett. 40 (49): 8575–8578. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(99)01830-4.
- ^ Donkervoot; et al. (1996). "Development of modified Pauson-Khand reactions with ethylene and utilisation in the total synthesis of (+)-taylorione". Tetrahedron. 52 (21): 7391–7420. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(96)00259-1.
- ^ Corey, E.J.; Kim, C. U. (1972). "New and highly effective method for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carbonyl compounds". JACS. 94 (21): 7586–7587. doi:10.1021/ja00776a056.
- ^ Kuwajima; et al. (2003). "Total Synthesis of Ingenol". JACS. 125 (6): 1498–1500. doi:10.1021/ja029226n. PMID 12568608.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Winter, A. E. (1963). "A New, Stereospecific Olefin Synthesis from 1,2-Diols". JACS. 85 (17): 2677–2678. doi:10.1021/ja00900a043.
- ^ Block; et al. (1984). "Olefin Synthesis by Deoxygenation of Vicinal Diols". Organic Reactions. Org. React. 30. p. 457. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or030.02. ISBN 978-0-471-26418-7.
- ^ Shing; et al. (1998). "Enantiospecific Syntheses of (+)-Crotepoxide, (+)-Boesenoxide, (+)-β-Senepoxide, (+)-Pipoxide Acetate, (−)- iso -Crotepoxide, (−)-Senepoxide, and (−)-Tingtanoxide from (−)-Quinic Acid 1". J. Org. Chem. 63 (5): 1547–1554. doi:10.1021/jo970907o.
- ^ Nair; et al. (2007). "Intramolecular 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions in targeted syntheses". Tetrahedron. 63 (50): 12247–12275. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2007.09.065.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; et al. (2004). "Enantioselective and Structure-Selective Diels−Alder Reactions of Unsymmetrical Quinones Catalyzed by a Chiral Oxazaborolidinium Cation. Predictive Selection Rules". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126 (15): 4800–4802. doi:10.1021/ja049323b. PMID 15080683.
- ^ Corey; et al. (1994). "Demonstration of the Synthetic Power of Oxazaborolidine-Catalyzed Enantioselective Diels-Alder Reactions by Very Efficient Routes to Cassiol and Gibberellic Acid". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116 (8): 3611–3612. doi:10.1021/ja00087a062.
- ^ Corey; et al. (1975). "Synthesis of novel macrocyclic lactones in the prostaglandin and polyether antibiotic series". JACS. 97 (3): 653–654. doi:10.1021/ja00836a036. PMID 1133366.
- ^ Nicolaou, K. C. (1977). "Synthesis of macrolides". Tetrahedron. 33 (7): 683–710. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(77)80180-4.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Nicolaou, K. C. (1974). "Efficient and mild lactonization method for the synthesis of macrolides". JACS. 96 (17): 5614–5616. doi:10.1021/ja00824a073.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Chaykovsky (1962). "Dimethylsulfoxonium Methylide". JACS. 84 (5): 867–868. doi:10.1021/ja00864a040.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Chaykovsky (1965). "Dimethyloxosulfonium Methylide ((CH3)2SOCH2) and Dimethylsulfonium Methylide ((CH3)2SCH2). Formation and Application to Organic Synthesis". JACS. 87 (6): 1353–1364. doi:10.1021/ja01084a034.
- ^ Danishefsky; et al. (1996). "Total Synthesis of Baccatin III and Taxol". JACS. 118 (12): 2843–2859. doi:10.1021/ja952692a.
- ^ See the Syntheses tab"Compiled Works of Elias J. Corey". ejcorey.org. July 12, 2008. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Weinshenker, N. M.; Schaaf, T. K.; Huber, W. (1969). "Stereo-controlled synthesis of dl-prostaglandins F2.alpha. and E2". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 91 (20): 5675–5677. doi:10.1021/ja01048a062. PMID 5808505.
- ^ K. C. Nicolaou, E. J. Sorensen, Classics in Total Synthesis, VCH, New York, 1996, ISBN 3-527-29231-4.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Schaaf, T. K.; Huber, W.; Koelliker,V.; Weinshenker, N. M. (1970). "Total Synthesis of Prostaglandins F2α and E2 as the Naturally Occurring Forms". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 92 (2): 397–8. doi:10.1021/ja00705a609. PMID 5411057.
- ^ For a review see Axen, U.; Pike, J. E.; and Schneider, W. P. (1973) p. 81 in The Total Synthesis of Natural Products, Vol. 1, ApSimon, J. W. (ed.) Wiley, New York.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Ohno, M.; Vatakencherry, P. A.; Mitra, R. B. (1961). "TOTAL SYNTHESIS OF d,l-LONGIFOLENE". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83 (5): 1251–1253. doi:10.1021/ja01466a056.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Ohno, M.; Mitra, R. B.; Vatakencherry, P. A. (1964). "Total Synthesis of Longifolene". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86 (3): 478–485. doi:10.1021/ja01057a039.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Ghosh, A. K. (1988). "Total synthesis of ginkgolide a". Tetrahedron Lett. 29 (26): 3205–3206. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(88)85122-0. PMC 6781876. PMID 31595095.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Kang, M.; Desai, M. C.; Ghosh, A. K.; Houpis, I. N. (1988). "Total synthesis of (.+-.)-ginkgolide B". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110 (2): 649–651. doi:10.1021/ja00210a083. PMC 6746322. PMID 31527923.
- ^ Corey, E. J. (1988). "Robert Robinson Lecture. Retrosynthetic thinking?essentials and examples". Chem. Soc. Rev. 17: 111–133. doi:10.1039/cs9881700111.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Reichard, G. A. (1992). "Total Synthesis of Lactacystin". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114 (26): 10677–10678. doi:10.1021/ja00052a096.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Wu, L. I. (1993). "Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Miroestrol". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115 (20): 9327–9328. doi:10.1021/ja00073a074.
- ^ Corey, E. J.; Gin, D. Y.; Kania, R. S. (1996). "Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Ecteinascidin 743". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 (38): 9202–9203. doi:10.1021/ja962480t.
- ^ Reddy Leleti, Rajender; Corey, E. J. (2004). "A Simple Stereocontrolled Synthesis of Salinosporamide A". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126 (20): 6230–6232. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.472.2554. doi:10.1021/ja048613p. PMID 15149210.
- ^ See Publications in "Compiled Works of Elias J. Corey". ejcorey.org. November 15, 2013. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- ^ Baum, Rudy (August 21, 2007). "E.J. Corey: Chemist Extraordinaire". C&EN Meeting Weblog, 234th ACS National Meeting &Exposition, August 19–23, 2007, Boston, Massachusetts. Retrieved September 8, 2010.
- ^ Van Noorden, Richard (April 23, 2007). "Hirsch index ranks top chemists". RSC: Advancing the Chemical Sciences, Chemistry World. Retrieved September 9, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Schneider, Alison (1998). "Harvard Faces the Aftermath of a Graduate Student's Suicide". The Chronicle of Higher Education. Retrieved August 21, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hall, Stephen S. (November 29, 1998). "Lethal Chemistry at Harvard". The New York Times.
- ^ Hall, Stephen (December 29, 1998). "Lethal Chemistry at Harvard". New York Times. Retrieved September 26, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b English, Bella. "Grad-student suicides spur big changes at Harvard chem labs". Archived from the original on January 24, 2001. Retrieved November 24, 2010.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link), The Boston Globe via Archive.org (January 2, 2001).
- ^ "For the Media: Examples of Good and Problematic Reporting, Scapegoating, New York Times Magazine: Lethal Chemistry at Harvard". American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP). 2010. Archived from the original on September 25, 2006. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ The AFSP incorrectly identifies the author and date of The New York Times article as Keith B. Richburg and November 28, 1998. The author was Stephen S. Hall and the date of publication was November 29, 1998.H, H; M.A. (2010). "For the Media: Problematic Reporting, Scapegoating". American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP). Archived from the original on September 25, 2006. Retrieved August 21, 2010.
- ^ Disciplined Minds A Critical Look at Salaried Professionals and Soul-Battering System that Shapes Their Lives. Rowman and Littlefield Publishers, Inc. 2000.
- ^ "Group Members: Elias James Corey". ejcorey.org. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- ^ See the E. J. Corey, Impossible Dreams tabCorey, E.J. (April 30, 2004). "Impossible Dreams". 69 (9). JOC Perspective. pp. 2917–2919. Retrieved September 10, 2010.
- ^ Johnson, Carolyn Y. (March 1, 2005). "Whose idea was it?". Boston Globe. Archived from the original on January 11, 2012. Retrieved September 10, 2010.
- ^ Hoffman, Roald (December 10, 2004). "A Claim on the Development of the Frontier Orbital Explanation Electrocyclic Reactions". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 43 (48): 6586–6590. doi:10.1002/anie.200461440. PMID 15558636.
- ^ "Golden Plate Awardees of the American Academy of Achievement". www.achievement.org. American Academy of Achievement.
- ^ See the E.J. Corey, About E.J. Corey, Honorary Degrees tab"Compiled Works of Elias J. Corey". July 12, 2008. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- ^ "The grand opening ceremony of E.J. Corey Institute of Biomedical Research (CIBR)". E.J. Corey Institute of Biomedical Research. June 29, 2013. Archived from the original on June 20, 2015. Retrieved August 26, 2013.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to E.J. Corey. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Elias James Corey |
- 1928 births
- Living people
- Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences
- 20th-century American chemists
- 21st-century American chemists
- Organic chemists
- American people of Lebanese descent
- Nobel laureates in Chemistry
- American Nobel laureates
- Harvard University faculty
- Wolf Prize in Chemistry laureates
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology School of Science alumni
- National Medal of Science laureates
- Foreign Members of the Royal Society
- University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign faculty
- People from Methuen, Massachusetts
- Lawrence High School (Massachusetts) alumni


