Al-Qubab
Al-Qubab
القباب Qubab | |
|---|---|
 Al-Qabab, aerial view 1948 | |
| Etymology: The domes[1] | |
 A series of historical maps of the area around Al-Qubab (click the buttons) | |
 Al-Qubab Location within Mandatory Palestine | |
| Coordinates: 31°52′00″N 34°57′15″E / 31.86667°N 34.95417°ECoordinates: 31°52′00″N 34°57′15″E / 31.86667°N 34.95417°E | |
| Palestine grid | 145/141 |
| Geopolitical entity | Mandatory Palestine |
| Subdistrict | Ramle |
| Date of depopulation | July 15, 1948[4] |
| Population (1945) | |
| • Total | 1,980[2][3] |
| Cause(s) of depopulation | Military assault by Yishuv forces |
| Current Localities | Gezer,[5] Kefar Bin-Nun,[5][6] Mishmar Ayyalon[5] |
Al-Qubab (Arabic: القباب) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict. It was depopulated in July 1948 during the Operation Dani led by the Yiftach Brigade.
History[]
Remains, possibly dating from the Roman era have been found here.[7] Archeological excavations have revealed tombs and cisterns dating to the Roman and Byzantine eras,[8][9] and addition to pottery remains from the same eras.[8]
Pottery remains from the early Islamic era, including a glazed bowl from the Abbasid period have also been found here.[8]
Mamluk era[]
During the late Mamluk era, Mujir al-Din wrote that al-Qubab was a village within the administrative jurisdiction of al-Ramla in 1483.[10] Mujir al-Din further noted that In 898 A. H., or 1492 C.E. the fellahin rebelled against the governor of Jerusalem. They were then caught between the governors of Gaza and Jerusalem, about in whose jurisdiction Al-Qubab was.[7]
Ceramics from the Mamluk era have also been excavated here.[8]
Ottoman era[]
In 1838, it was noted as a Muslim village, Beit Kubab, in the Ibn Humar area in the District of Er-Ramleh.[11]
Edward Robinson passed by the village in 1852 and described it as being of considerable size.[12]
In 1863, Victor Guérin found it to have at least five hundred inhabitants,[13] while an Ottoman village list from about 1870 found that Al-Qubab had a population of 381, in 114 houses, though the population count included men, only.[14][15]
In 1883, the PEF's Survey of Western Palestine (SWP) described it as "a small adobe village on rising ground, by the main road. It is surrounded with prickly-pear hedges and olives. The ground is rocky. The water-supply is from the fine spring of 'Ain Yerdeh. This spring is 1 1/4 miles from the village, yet is the only source whence water is obtained."[16]
British Mandate era[]
In the 1922 census of Palestine, conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Qubab had a population of 1,275 inhabitants, all Muslims,[17] increasing in the 1931 census to 1502 inhabitants, all Muslim, in 382 houses.[18]
It had a population of 1,980 Muslims in the 1945 statistics,[2] while the total land area was 13,918 dunams, according to an official land and population survey.[3] Of this, a total of 12,295 dunums were allocated to cereals, 238 dunums were irrigated or used for plantations,[19] while 54 dunams were classified as built-up urban areas.[20]

Al-Qubab 1942 1:20,000
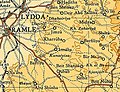
Al-Qubab 1945 Scale 1:250,000
Depopulated villages in the Ramle Subdistrict
1948, aftermath[]

On September 13, 1948, al-Qubab was mostly destroyed, although the school (founded in 1921) and few houses remain standing.
In 1992 the village site was so described:
"The part of the north side of the kibbutz is covered by woods. The only landmark that remains is the school; a number of stone houses that have rectangular doors and windows still stand, and some of them are used as Israeli residences. One is rectangular and has two doors, one high window and two very small windows, one on the side and another in the front. Another residential house is angular; there is a tall tree in the yard in front of it. One of the houses used for storing agricultural tools and equipment is rectangular, with four front entrances and a high window. Another house, used at present as a shop, has a stairway leading to a front porch that is enclosed by wire grillwork. A variety of trees and other types of vegetation grow on the site, including eucalyptus and carob trees, cactuses, and foxtail. The surrounding land is planted with almond and olive trees."[5]
On the ruins of the destroyed Palestinian village, in 2005 a monument to the Lechi fighters (the Stern Gang) has been erected.[21]

Road leading to Al-Qubab, 1948

Photo of al-Qubab from Palmach archives. Caption: "Operation Yoram. Conquest of Al-Qubab." 6 July 1948

Members of the 1st Battalion, Yiftach Brigade, in al-Qubab after the first truce. 1948
References[]
- ^ Palmer, 1881, p. 313
- ^ Jump up to: a b Department of Statistics, 1945, p. 30
- ^ Jump up to: a b Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 68
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. xix, village #240. Also gives cause of depopulation
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Khalidi, 1992, p. 407
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. xxi, settlement #84
- ^ Jump up to: a b Clermont-Ganneau, 1896, vol 2, pp. 83-85
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Lupu, 2010, El-Qubab
- ^ Shachar, 2019, El-Qubab
- ^ Khalidi, 1992, p. 406
- ^ Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p. 120
- ^ Robinson, 1856, pp. 143-144
- ^ Guérin, 1868, pp. 56-57, 314
- ^ Socin, 1879, p. 154
- ^ Hartmann, 1883, p. 140, also noted 114 houses
- ^ Conder and Kitchener, 1883, SWP III, p. 15
- ^ Barron, 1923, Table VII, Sub-district of Ramleh, p. 21
- ^ Mills, 1932, p. 22
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 116.
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 166
- ^ Israel and you
Bibliography[]
- Barron, J.B., ed. (1923). Palestine: Report and General Abstracts of the Census of 1922. Government of Palestine.
- Clermont-Ganneau, C.S. (1896). [ARP] Archaeological Researches in Palestine 1873-1874, translated from the French by J. McFarlane. 2. London: Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Conder, C.R.; Kitchener, H.H. (1883). The Survey of Western Palestine: Memoirs of the Topography, Orography, Hydrography, and Archaeology. 3. London: Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Department of Statistics (1945). Village Statistics, April, 1945. Government of Palestine.
- Glick, Alexander (2006-07-09). "Mishmar Ayyalon" (118). Hadashot Arkheologiyot – Excavations and Surveys in Israel. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Guérin, V. (1868). Description Géographique Historique et Archéologique de la Palestine (in French). 1: Judee, pt. 1. Paris: L'Imprimerie Nationale.
- Hadawi, S. (1970). Village Statistics of 1945: A Classification of Land and Area ownership in Palestine. Palestine Liberation Organization Research Center. Archived from the original on 2018-12-08. Retrieved 2009-08-18.
- Haiman, Mordechai (2014-07-21). "El-Qubab" (126). Hadashot Arkheologiyot – Excavations and Surveys in Israel. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Hartmann, M. (1883). "Die Ortschaftenliste des Liwa Jerusalem in dem türkischen Staatskalender für Syrien auf das Jahr 1288 der Flucht (1871)". Zeitschrift des Deutschen Palästina-Vereins. 6: 102–149.
- Khalidi, W. (1992). All That Remains: The Palestinian Villages Occupied and Depopulated by Israel in 1948. Washington D.C.: Institute for Palestine Studies. ISBN 0-88728-224-5.
- Lupu, Ronit (2010-09-12). "El-Qubab" (122). Hadashot Arkheologiyot – Excavations and Surveys in Israel. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Mills, E., ed. (1932). Census of Palestine 1931. Population of Villages, Towns and Administrative Areas. Jerusalem: Government of Palestine.
- Morris, B. (2004). The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-00967-6. (pp. 257, 346, 354, 376, 395)
- Palmer, E.H. (1881). The Survey of Western Palestine: Arabic and English Name Lists Collected During the Survey by Lieutenants Conder and Kitchener, R. E. Transliterated and Explained by E.H. Palmer. Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Robinson, E.; Smith, E. (1841). Biblical Researches in Palestine, Mount Sinai and Arabia Petraea: A Journal of Travels in the year 1838. 3. Boston: Crocker & Brewster.
- Robinson, E.; Smith, E. (1856). Later Biblical Researches in Palestine and adjacent regions: A Journal of Travels in the year 1852. London: John Murray.
- Saintine, P. G. (1860). Trois ans en Judée (in French). Hachette. (p. 31, quoted in Guérin, 1868, p. 57)
- Shachar, Dan (2019-07-23). "El-Qubab" (131). Hadashot Arkheologiyot – Excavations and Surveys in Israel. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Socin, A. (1879). "Alphabetisches Verzeichniss von Ortschaften des Paschalik Jerusalem". Zeitschrift des Deutschen Palästina-Vereins. 2: 135–163.
External links[]
- Welcome To al-Qubab
- al-Qubab, Zochrot
- Survey of Western Palestine, Map 17: IAA, Wikimedia commons
- al-Qubab from the Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center
- Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
- District of Ramla