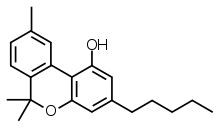
Cannabinol
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral, inhaled |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
show
IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.216.772 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 310.437 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 77 °C (171 °F) [1] |
| Solubility in water | insoluble in water[2] soluble in methanol[3] and ethanol[4] mg/mL (20 °C) |
show
SMILES | |
show
InChI | |
| | |
Cannabinol (CBN) is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid found in trace amounts from Cannabis.[5] CBN is mostly found in cannabis that is aged and stored, and is derived from the plant's main psychoactive chemical, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).[6][7]
It was the first cannabis compound to be isolated from cannabis extract in the late 1800s. Then by the 1930s, the first to have its structure determined and in 1940, to have scientists achieve its chemical synthesis.[8]
Formation[]
There is usually little CBN in a fresh plant. However, if cannabis is exposed to air or ultraviolet light (for example, in sunlight) for a prolonged period of time, THCA will convert to (CBNA). CBN is then formed by decarboxylation of CBNA.[citation needed]
Pharmacology[]
CBN acts as a partial agonist at the CB1 receptors, but has a higher affinity to CB2 receptors; however, it has lower affinities relative to THC.[9][10][11] Both THC and CBN activate the CB1 (Ki = 211.2 nM) and CB2 (Ki = 126.4 nM) receptors.[12]
Chemistry[]
In contrast to THC, CBN has no double bond isomers nor stereoisomers.
Legal status[]
CBN is not listed in the schedules set out by the United Nations' Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs from 1961 nor their Convention on Psychotropic Substances from 1971,[13] so the signatory countries to these international drug control treaties are not required by these treaties to control CBN.
United States[]

As of 2021 in the United States, CBN and other cannabis extracts remain illegal under federal law to prescribe for medical use or to use as an ingredient in dietary supplements or other foods,[14][15][16][17] and sales or possession of CBN could potentially be prosecuted under the Federal Analogue Act.[18] In December 2016, the Drug Enforcement Administration added marijuana extracts, which are defined as any "extract containing one or more cannabinoids that has been derived from any plant of the genus Cannabis, other than the separated resin", to Schedule I.[19]
References[]
- ^ Cannabinol in the ChemIDplus database.
- ^ David R. Lide (2012). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC Press. pp. 3–90. ISBN 978-1-43988049-4.
- ^ Sigma-Aldrich Co., Cannabinol solution, 1.0 mg/mL in methanol, analytical standard, for drug analysis.
- ^ Biotrend: Cannabinol Archived 2016-05-22 at the Wayback Machine (PDF: 21 kB)
- ^ Karniol IG, Shirakawa I, Takahashi RN, Knobel E, Musty RE (1975). "Effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol in man". Pharmacology. 13 (6): 502–12. doi:10.1159/000136944. PMID 1221432.
- ^ Kroner GM, Johnson-Davis KL, Doyle K, McMillin GA (May 2020). "Cannabinol (CBN) Cross-Reacts with Two Urine Immunoassays Designed to Detect Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Metabolite". The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine. 5 (3): 569–574. doi:10.1093/jalm/jfaa020. PMID 32445358.
- ^ Andre CM, Hausman JF, Guerriero G (2016-02-04). "Cannabis sativa: The Plant of the Thousand and One Molecules". Frontiers in Plant Science. 7: 19. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00019. PMC 4740396. PMID 26870049.
- ^ Pertwee RG (January 2006). "Cannabinoid pharmacology: the first 66 years". British Journal of Pharmacology. 147 (Suppl 1): S163-71. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706406. PMC 1760722. PMID 16402100.
Cannabinol (CBN; Figure 1), much of which is thought to be formed from THC during the storage of harvested cannabis, was the first of the plant cannabinoids (phytocannabinoids) to be isolated, from a red oil extract of cannabis, at the end of the 19th century. Its structure was elucidated in the early 1930s by R.S. Cahn, and its chemical synthesis first achieved in 1940 in the laboratories of R. Adams in the U.S.A. and Lord Todd in the U.K.
- ^ Mahadevan A, Siegel C, Martin BR, Abood ME, Beletskaya I, Razdan RK (October 2000). "Novel cannabinol probes for CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 43 (20): 3778–85. doi:10.1021/jm0001572. PMID 11020293.
- ^ Petitet F, Jeantaud B, Reibaud M, Imperato A, Dubroeucq MC (1998). "Complex pharmacology of natural cannabinoids: evidence for partial agonist activity of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and antagonist activity of cannabidiol on rat brain cannabinoid receptors". Life Sciences. 63 (1): PL1-6. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(98)00238-0. PMID 9667767.
- ^ "NIA National Cancer Institute; NCIthesaurus". Cannabinol (Code C84510).
- ^ Russo EB, Marcu J (2017). "Cannabis Pharmacology: The Usual Suspects and a Few Promising Leads". Advances in Pharmacology (San Diego, Calif.). 80: 67–134. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2017.03.004. PMID 28826544.
- ^ UN International Drug Control Conventions
- ^ Mead A (2019-06-14). "Legal and Regulatory Issues Governing Cannabis and Cannabis-Derived Products in the United States". Frontiers in Plant Science. 10: 697. doi:10.3389/fpls.2019.00697. PMC 6590107. PMID 31263468.
- ^ "FDA Regulation of Cannabis and Cannabis-Derived Products, Including Cannabidiol (CBD)". US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 1 October 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- ^ Mead A (May 2017). "The legal status of cannabis (marijuana) and cannabidiol (CBD) under U.S. law". Epilepsy & Behavior. 70 (Pt B): 288–291. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.11.021. PMID 28169144.
- ^ §1308.11 Schedule I.
- ^ Erowid Analog Law Vault : Federal Controlled Substance Analogue Act Summary
- ^ "Establishment of a New Drug Code for Marihuana Extract" (PDF). Federal Register, Vol. 81, No. 240. December 14, 2016.
External links[]
- Erowid Compounds found in Cannabis sativa
- Drugs not assigned an ATC code
- Cannabinoids
- Natural phenols
- Benzochromenes
- CB1 receptor agonists
- CB2 receptor agonists