French Island (Victoria)
| French Island Victoria | |
|---|---|
 Looking west over Western Port to Mornington Peninsula from the coast road | |
 French Island | |
| Coordinates | 38°21′00″S 145°22′12″E / 38.35000°S 145.37000°ECoordinates: 38°21′00″S 145°22′12″E / 38.35000°S 145.37000°E |
| Population | 116 (2011 census)[1] |
| • Density | 0.682/km2 (1.77/sq mi) |
| Postcode(s) | 3921 |
| Area | 170 km2 (65.6 sq mi) |
| LGA(s) | Unincorporated area |
| State electorate(s) | Hastings[2] |
| Federal Division(s) | Flinders |
French Island (Boonwurrung: Bellarmarin, Bawal, Woone, or Jouap)[3] is the largest coastal island of Victoria, Australia, located in Western Port, 61 km (38 mi) southeast of Melbourne. In 1997, about 70% of the island was declared the French Island National Park, administered by Parks Victoria, and was listed in the former Register of the National Estate in 1984.[4] The island is an unincorporated area, which means that it is not part of any municipal council, and is a declared locality of Victoria having its own postcode. Community issues are dealt by the French Island Community Association. The island is otherwise administered by Department of Infrastructure. The population of the island in 2011 was around 116 people,[1] of which about 60 were permanent residents.
French Island is relatively isolated and undeveloped. There are no mains water, mains electricity, or medical services on the island. There is one small general store and post office located on Tankerton Road about 3 km (1.9 mi) from Tankerton Jetty. Many of the locals actively promote environmental tourism. Visitor accommodation includes camping, bed and breakfast, guesthouse and farmstay.
History[]
According to the French Island Community Association, prior to European settlement, French Island was a hunting ground of the Bunurong people. They lived on the mainland and travelled to French Island to collect shellfish and swan eggs. There are several registered sites on the island that consist of shell middens and stone scatters they left behind.
In April 1802, a French expedition ship Naturaliste under Jacques Hamelin explored the area, as part of the Baudin expedition to Australia. He named the island Île de Françoise , which has since been Anglicised as French Island.[5]
The first European settlers on the island were William and John Gardiner in 1847. They had the first pastoral lease and grazed 8,000 sheep. The first land subdivision was in 1867 when 4733 acres were divided into 14 allotments. The first land sales took place in 1873 with the minimum price £1 per acre. In the 1880s, koalas were introduced to the island.
During the depression of the 1890s the government of the day encouraged settlement of the area and established seven village settlements on French Island under the Village Settlement Scheme. These were called Energy, Star of Hope, Callanan's, Perseverance, Industrial, Kiernan's and Grant Homestead Association. Altogether about 200 people made up these settlements. Tankerton Post Office opened on 3 September 1890 and remained open until 1994. It reopened in 2001 under the name French Island. A Fairhaven post office was also open from 1911 until 1957.[6] [7]Four schools were built of which the Perseverance Primary School, established in 1896, is the only one remaining and now caters for only a small number of primary school children.
The Phillip Island chicory industry started in 1878 and John Ratford spent a season there in 1895 to learn about it. He then introduced it to French Island where it became the main source of income for over 70 years. The Bayview chicory kiln was built in 1896-97 and was the second kiln built on the Island. In the 1890s, there was chicory planting and some 30 chicory kilns were established. The Bayview chicory kiln is now the oldest one remaining, and is currently an operating cafe and museum.
The McLeod prison farm occupies 222 hectares and opened on 17 July 1916 as an Alcatraz-style penitentiary. Timber cabins housed the prisoners until 1946 when concrete cells were built. It operated as a self-sustaining farm. The prison closed in 1975 and was used as a holiday camp facility until 1995. Most recently it operated as an eco-village until it was bought in 2017 for $4 million by a Chinese-based company with plans to turn it into a major tourism operation.
In 1967, at the request of then state Premier Henry Bolte[8] the State Electricity Commission of Victoria proposed the island as the site of the first nuclear power plant in Australia, but the plans were abandoned. During the 1960s and 1970s BHP, Hooker Rex and the State Electricity Commission paid inflated prices for land, inducing land owners to sell up and move off the island.[9]
In July 1997, 11,050 hectares (27,300 acres), about 70%, of the island was declared French Island National Park, and in May 2002 the waters directly north of French Island were declared the French Island Marine National Park.
Access and transport[]
Access to the island is by the Western Port Ferries passenger ferry running daily from Stony Point pier to Tankerton Jetty. Metro Trains run a service to Frankston with an additional diesel service to Stony Point railway station for the cost of a standard metro ticket. Some trains arriving at Stony Point connect with the ferry service to both French Island and Phillip Island throughout the day. The ferry does not carry vehicles; however, ample parking is provided at the Stony Point Foreshore. The crossing takes about 15 minutes. Western Port Ferries also provide a passenger ferry service to French Island from Cowes on Phillip Island.
There is no airport on the island, although a few properties have private landing strips.
There are more than 40 km of unsealed gravel roads and tracks on the island, which are quiet and ideal for mountain bikes. They are affected by rain and can become dangerous for the inexperienced. The island is generally flat or mildly undulating with the highest point being Mount Wellington (96 m above sea level). Bicycles can be hired from the general store. There is an abundance of walking tracks. Active pursuits include bushwalking, bird watching, horse riding, geocaching and cycling. There is one tour operator on the island, French Island Tours.
The French Island Barge Company operates a vehicular ferry from Corinella on the eastern side of Western Port to the barge landing on French Island. It accommodates two standard size cars or a larger truck. Tourists are always welcome.[10] All supplies to the island come by the French Island Barge, which runs every day of the year, depending on tide and appointments.
Geography[]
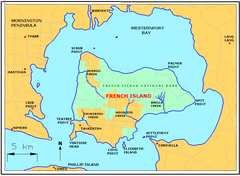
French Island has a few notable landforms, including:
- Mount Wellington – highest point on the island at about 96 m
- The Pinnacles – 66 m
- Harrop Hill
- Tortoise Head
Watercourses on the island include:
- Tankerton Creek
- Redbill Creek
- Mosquito Creek
- Brella Creek
There are no towns on the island.
Population[]
At the 2016 census the French Island population consisted of 119 people, 53% of which were male and 47% of which were female. The median age was 56.[1]
The island has a Primary School, on The Centre Way. In 2003 ten students were enrolled at the Perseverance Primary School. In 2009 five students were enrolled at the primary school.[11] According to ACARA, in 2011 there were nine enrolments[12] In 2018, Perseverance Primary had seven students taught by one teacher and a teacher's aide.[13]
Natural environment[]
Habitats range from coastal mangroves, swamps, heath, grasslands and blue gum forests. Most koala populations on the mainland of Australia are affected by the chlamydia disease; however French Island provides the world's densest and most disease-free population of koalas, with regular transfer of excess koalas to repopulate diseased areas on the mainland. Shelter is provided for more than 100 species of bush orchids, and 260 species of birds. Significant species on the island include: king quail, the critically endangered orange-bellied parrot, fairy tern, white-bellied sea eagle, , long-nosed potoroo.
The island is one of only two places in Victoria where the invasive red fox is not present, which has enabled the island to maintain a variety of indigenous species which have been devastated by the predator elsewhere including Phillip Island. However rabbits, feral cats, feral goats, feral pigs, Indian mynahs and starlings pose a threat to the island's biodiversity.
Camping[]
There is one free camping site in the National Park at Fairhaven, 4 km up the coast road from Tankerton Jetty, where the ferry arrives from Stony Point. The camp site is set among trees near the beach, with one public toilet and a water tank.[14] Other camping is available at "private sites" at French Island Eco Inn and through the local French Island tour operator.

Proposed nuclear power plant site[]
In mid 1967, the State Electricity Commission of Victoria applied to the Lands Department for the reservation of 400 acres (1.6 km2) of French Island for future construction of a nuclear power plant. The plant was speculated to have 350-500MW generator capacity and would likely have been built during the 1970s. Other plants around Australia were also envisioned after the construction of a successful, fully operational plant in Victoria. If the SEC did decide to construct a nuclear power station, it would have continued to construct brown coal power stations as well for some considerable time.[15]
Due to the low cost of brown coal in Victoria and mounting pressure from the anti-nuclear movement, the SEC subsequently decided against commissioning a nuclear plant and instead continued the commissioning of brown coal plants. These included the Hazelwood Power Station, which was completed in 1971. Nuclear plants were not constructed in NSW as access to black coal allowed for bigger generators. The declaration of various areas of many Australian states as nuclear free zones was a key factor in the selection of coal plants over nuclear plants.
The land acquired by the State Electrical Commission in the 1960s was subsequently subdivided and sold off in the 1990s during a time when ferry services to the island had become unreliable, with the two small vessels (King Fisher and Port Hunter) breaking down regularly.[citation needed] This drove the government to sell the land for significantly less than they had purchased it for in the 1960s, with land being sold in 60 and 90 acre allotments for just $1,000 per acre.[citation needed]
See also[]
- Elizabeth Island (Victoria)
- Sandstone Island
- Mornington Peninsula and Western Port Biosphere Reserve
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Australian Bureau of Statistics (31 October 2012). "French Island (Statistical Local Area)". 2011 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 17 October 2012.

- ^ "Hastings District Profile". Victorian Electoral Commission. Retrieved 15 June 2018.
- ^ Clark, Ian D, 2014, Ch 13. Multiple Aboriginal placenames in western and central Victoria in Indigenous and Minority Placenames Australian and International Perspectives, ANU Press Library, Canberra, http://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/p286811/html/ch13.xhtml
- ^ "French Island and Environs, Tankerton, VIC, Australia - listing on the now-defunct Register of the National Estate (Place ID 3504)". Australian Heritage Database. Department of the Environment. 27 March 1984. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- ^ Scott, Ernest (5 May 2011). Terre Napoléon: A History of French Explorations and Projects in Australia. Cambridge University Press. p. 191. ISBN 9781108030786.
- ^ Phoenix Auctions History. "Post Office List Tankerton". Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- ^ Phoenix Auctions History. "Post Office List Fairhaven". Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- ^ Hall, Stephen. "How Victoria's N-power future became its past". The Age.
- ^ French Island. Victoria Places. 2015. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- ^ "Transport - Off Island". French Island Community Association. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
- ^ "Primary School Class Sizes". The Age. 28 April 2003. Archived from the original on 10 December 2017. Retrieved 9 October 2008.
- ^ "School Profile". myschool.edu.au. Retrieved 17 October 2012.
- ^ Educating Anita: One teacher. Seven students. Welcome to one of Victoria’s tiniest schools., Jane Cowan, ABC News Online, 2018-11-15
- ^ Fairhaven Campground Parks Victoria
- ^ "Our N-Power, Stephen Hall, The Age, 4 October 1967". Archived from the original on 17 March 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to French Island (Victoria). |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for French Island. |
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Islands of Victoria (Australia)
- Towns in Victoria (Australia)
- Western Port
- Mornington Peninsula
- Victorian places listed on the defunct Register of the National Estate
