Poulx
Poulx | |
|---|---|
 The church in Poulx | |
show Location of Poulx | |
 Poulx | |
| Coordinates: 43°54′41″N 4°25′27″E / 43.9114°N 4.4242°ECoordinates: 43°54′41″N 4°25′27″E / 43.9114°N 4.4242°E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Occitanie |
| Department | Gard |
| Arrondissement | Nîmes |
| Canton | Marguerittes |
| Intercommunality | CA Nîmes Métropole |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Patrice Quittard |
| Area 1 | 14.8 km2 (5.7 sq mi) |
| Population (Jan. 2018)[1] | 4,032 |
| • Density | 270/km2 (710/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 30206 /30320 |
| Elevation | 34–213 m (112–699 ft) (avg. 200 m or 660 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Poulx (French pronunciation: [pulks][2][3]) is a commune in the Gard department in southern France. Between the years of 1943 and 1945, it served as a secret meeting place for French resistance fighters.
History[]
World War II[]
The small size of the commune made Poulx a relatively inconspicuous hideout during the occupation years of France. Its proximity to the southern coast allowed communications to be secretly brought into and out of France via undercover ocean transport. The headquarters for the resistance fighters was built underneath the church; a fake furnace was installed to cover up the entrance.
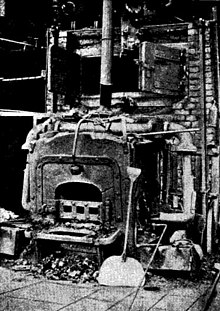
In August 1943, with news of Soviet counter-offensives in the East, the resistance improvised a system to take advantage of Germany's loosening grip on France. With many Nazis leaving their patrol duties to head to the Eastern front, smaller communes like Poulx were left almost unguarded. This allowed messages to reach Poulx from the southern coast, where the US navy was using captured German fishing boats to approach the shore without having their cover blown. Trained birds were then used to cover the remaining distance from the shore to Poulx. In Poulx, the birds would land on top of the church, where they would wait until a resistance member went under cover of darkness to retrieve the message and reward the bird with food.
The communication line stayed open until the liberation of France, and helped organize the resistance that aided in Operation Dragoon.
Post-war referendum[]
In 1962, a referendum was held in the commune of Poulx to determine whether the church, with its pivotal role in the resistance in the south, should be made into a museum. Almost unanimously (151 versus 9), the population declined the offer, giving the reason that the increased tourism to the location would be a disruption to their rural lives. The church is still in use to this day.
Population[]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1962 | 160 | — |
| 1968 | 190 | +18.8% |
| 1975 | 382 | +101.1% |
| 1982 | 723 | +89.3% |
| 1990 | 1,630 | +125.4% |
| 1999 | 3,148 | +93.1% |
| 2008 | 4,068 | +29.2% |
See also[]
- Communes of the Gard department
- Operation Dragoon
- French Resistance
References[]
- ^ "Populations légales 2018". INSEE. 28 December 2020.
- ^ "Poulx TV Émission Spéciale Bien vivre le déconfinement - YouTube". www.youtube.com. Retrieved 2021-02-03.
- ^ "La pinède centenaire de Poulx près de Nîmes détruite à cause d'un champignon - YouTube". www.youtube.com. Retrieved 2021-02-03.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Poulx. |
- Communes of Gard
- Gard geography stubs


