Republican reactions to Donald Trump's claims of 2020 election fraud
2020 U.S. presidential election | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Attempts to overturn | |
| Democratic Party | |
|
|
| Republican Party | |
|
|
| Third parties | |
|
|
| Related races | |
| |
| ||
|---|---|---|
Business and personal
45th president of the United States
Tenure
Policies
Appointments
Presidential campaigns
Impeachments
Interactions involving Russia
COVID-19 pandemic
 |
||
Members of the United States Republican Party have reacted differently to Republican President Donald Trump's false claims about the 2020 United States presidential election, with many publicly supporting them, many remaining silent, and a few publicly denouncing them.[1] Trump falsely claimed to have won the election,[2][3][4] and made many false and unsubstantiated claims of election fraud.[5] By December 11, 2020, 126 out of 196 Republican members of the House backed a lawsuit filed in the United States Supreme Court supported by nineteen Republican state attorneys general seeking to subvert the election and overturn the election results.[6] Multiple polls for months after the election found that majorities of Republicans believed the election was fraudulent and stolen, and that Trump remained president.[7] Drawing on the false allegations of voting fraud and a stolen election, by February 2021 Republican state legislatures had begun to implement new laws and rules to restrict voting access in ways that would favor Republican candidates.[8][9][10] In Arizona, the Republican-controlled government proceeded with legislation to allow the state attorney general, currently a Republican, to intervene in the voting certification process managed by the secretary of state, currently a Democrat.[11] Republican lawmakers in several states sought to seize control of the administrative management of elections.[12][13][14][15][16]
By December 30, 2020, Republican members of the House and Senate indicated their intent to object to the congressional certification of Electoral College results, to force both chambers to debate and vote on whether to accept the results.[17][18] Mike Pence, who as vice president would preside over the proceedings, signaled his endorsement of the effort, stating on January 4, "I promise you, come this Wednesday, we will have our day in Congress." Trump and some supporters promoted a false "Pence card" theory that the vice president has the authority to reject certified results.[19][20][21] However, Pence later reversed his endorsement of the effort, saying in a letter he would not reject certified results.[22] In the early hours of January 7, 2021, Pence (while performing his duties as President of the Senate, during the counting of electoral votes) conceded that Joe Biden and Kamala Harris had won.[23] On the evening of January 7, 2021, Trump tweeted a video in which he agreed to a peaceful transition on January 20.[24]
The insistence by Trump and his supporters throughout 2021 that the election had been stolen from him by fraud came to be characterized as an implementation of "the big lie" and was used by Republicans to justify efforts to impose new voting restrictions and to take control of the administrative management of elections at the state and local level.[25]
Timeline[]
Summary[]
From six months before,[26] during, and after the 2020 United States elections, most notably during a speech held late on November 5, President Donald Trump, who was running for re-election on the Republican Party ticket, suggested and claimed that large-scale electoral fraud would happen, was happening, or had happened, to the effect that it would make him lose his presidential re-election. In the days after Election Day (November 3, 2020), Trump also demanded that the vote counting be stopped in some swing states (Pennsylvania, Georgia, and North Carolina), where he was slowly losing his lead to Democratic presidential candidate Joe Biden, until Republican observers could meaningfully observe and challenge the vote counting process. Concurrently, Trump demanded that the vote counting be continued in the swing state of Arizona, where he was catching up on Biden. Several prominent members of his Republican Party, including recently elected or former officials, denounced Trump's claims of election fraud before, during, and after the 2020 United States elections as unsubstantiated, baseless or without evidence, as well as damaging to the election process, undermining democracy and dangerous to political stability.[27][28][29][30][31][32][33][34][35][excessive citations] In one case, a former Republican member of the U.S. House of Representatives referred to the totality of Trump's actions as an attempted coup d'état.[36]
Before Election Day[]
Months before Election Day, Democrats regularly condemned President Trump's suggestions that widespread electoral fraud would occur (especially through the use of mail-in ballots, a claim Trump first made on April 7, 2020),[37] but Republicans rarely did.[38] Attempts by Politico to obtain comments from prominent Republicans on the issue mostly failed; Miles Taylor (former Homeland Security chief of staff of Secretary and author of "I Am Part of the Resistance Inside the Trump Administration") and Michael Steele (former chairman of the Republican National Committee) were among the few they could find expressing serious concerns about Trump's comments.[38] Politico stated on the morning of November 3 that "[m]any Republicans insist they are disgusted by Trump's threats, they just aren't willing to say so publicly."[38]
November 4: Counting transparency[]
After Election Day (November 3, 2020), in the afternoon of November 4, the Trump campaign sued Michigan and Pennsylvania, alleging that they were not being given proper access to monitor the vote counting process, and demanded the counting stop. The Trump team declared that they had already won the state of Pennsylvania at a moment when Trump was leading by 320,000 votes, but only 85% of the votes had been counted, and it was known that the vote counting in the city of Philadelphia could still tip the balance in favor of Biden. Eric Trump alleged that "the Democrats" would try to "cheat in Pennsylvania."[39][40] However, Philadelphia City Commissioner Al Schmidt, who oversaw the city's counting and was himself a Republican, rejected claims that the process lacked transparency, as observers were able to see everything that was happening in the counting hall.[39]
November 5: Trump speech alleging electoral fraud[]
According to CNBC, there was mostly silence within the Republican Party shortly after Trump's speech from the White House late at night on November 5.[41] Rick Santorum, Ben Sasse, Mitt Romney, Larry Hogan, and Chris Christie were among the first Republicans to criticize the President's remarks as indefensible.[41][34] Combined with a statement from Nikki Haley that some deemed to concede Trump's defeat, several Republicans, including Trump's sons Donald Trump Jr. and Eric Trump, rebuked other Republicans for staying silent and not supporting the President's allegations of electoral fraud.[41][42] According to a Reuters/Ipsos poll conducted on November 5, only about 30% of Republican Americans believed that Trump had won the election; the vast majority of Americans, including most Republicans, believed Biden had.[43]
November 6: Critics and loyalists[]
Some Trump loyalists such as Lindsey Graham, Ted Cruz, Tom Cotton and Kevin McCarthy endorsed the false claims that Trump had actually won the election and that there was large-scale fraud, and called on Republicans to stay united behind Trump. Over 20 other leading Republicans denounced Trump's accusations of voter fraud on November 6.[27][28][29][30][31][32][33][35][excessive citations] Some observers concluded that statements denouncing or supporting Trump's claims were also part of a conflict inside the Republican Party over who should be their nominee for the 2024 presidential election, and whether to continue Trumpist politics.[42][44] In March 2021, McCarthy denied he had supported Trump's false claims of election fraud, though he had supported Texas v. Pennsylvania that sought to overturn voting results in four states and voted in favor of a House resolution to overturn voting results in two states.[45]
November 7: Several Republicans congratulate Biden while others refuse[]
On November 7, most major American news networks called the election a victory for Biden when vote-counting in Pennsylvania and Nevada reached the point where he would certainly receive the 270 electors' votes needed for the presidency. The Trump campaign refused to concede defeat and instead asserted that "the election was far from over."[46] Several leading Republicans, including former 2012 Republican presidential candidate Mitt Romney, Larry Hogan, John Kasich, Phil Scott, Adam Kinzinger, Will Hurd, Paul Mitchell, Fred Upton, Lamar Alexander, Tom Reed, and Jeb Bush, proceeded to congratulate Biden as the new President-elect (and Kamala Harris as Vice President-elect) of the United States; others such as Josh Hawley and Paul Gosar insisted that the election was not over yet until "all lawful votes have been counted, recounts finished, and allegations of fraud addressed."[47][48][49]
Just before the media called the election, re-elected Texas Congressman Dan Crenshaw tweeted "If Trump loses, he loses. It was never an impossible outcome and we must accept the final results when it is over," to which newly elected Georgia Congresswoman Marjorie Taylor Greene (a QAnon conspiracy theory supporter) responded, "The time to STAND UP for (President Donald Trump) is RIGHT NOW. Republicans can't back down." Crenshaw criticized her for trying to "talk tough" and said: "You're a member of Congress now, Marjorie. Start acting like one," while stressing that any irregularity should be addressed.[50]
November 8: George W. Bush congratulates Biden and Harris[]

On November 8, former President George W. Bush (2001–2009), the previous Republican president, congratulated President-elect Joe Biden and Vice President-elect Kamala Harris by phone, and said in a statement: "The American people can have confidence that this election was fundamentally fair, its integrity will be upheld, and its outcome is clear." He further stated: "The President-elect reiterated that while he ran as a Democrat, he will govern for all Americans. I offered him the same thing I offered presidents Trump and Obama: my prayers for his success, and my pledge to help in any way I can." While congratulating Trump "on a hard-fought campaign" and saying he "has the right to request recounts and pursue legal challenges," Bush stated the election's outcome was clearly in Biden's favor.[51][52][53] According to Forbes, "most Trump allies and congressional Republicans" had by then either stayed silent or explicitly refused to congratulate Biden and Harris, but the number of Republicans who did was growing.[54] After Bush's declaration, Trump ally Chris Christie stepped up the pressure on Trump to provide evidence of electoral fraud if he wanted Republicans to support his cause: "If your basis for not conceding is [because] there was voter fraud, then show us. Because if you don't show us, we can't do this. We can't back you blindly without evidence."[55] CNN claimed two sources had said Trump's son-in-law and Director of the Office of American Innovation Jared Kushner had urged the President to accept the loss, while a third, separate source alleged that First Lady Melania Trump had tried to convince her husband as well.[56] Roy Blunt repeated his earlier statement that Trump had been making baseless claims and that "it's time for the president's lawyers to present the facts," but when asked by ABC's George Stephanopoulos, he refused to acknowledge for the time being that Biden had won; Pat Toomey took a similar but softer stance.[57] Kristi Noem, on the other hand, pushed the narrative of widespread fraud, but was unable to present evidence when pressed by Stephanopoulos.[57]
November 9: Trump campaign announces legal challenges[]
At the Four Seasons Total Landscaping press conference, the Trump campaign team had announced it would formally present several legal challenges against the election process and results on Monday, November 9, refusing to concede the Biden/Harris victory. Speaking on the condition of anonymity to the Associated Press, senior officials, campaign aides and allies said that "[t]he strategy to wage a legal fight against the votes tallied for Biden in Pennsylvania and other places is more to provide Trump with an off-ramp for a loss he can't quite grasp and less about changing the election's outcome." Some of them even had "deep reservations about the president's attempts to undermine faith in the vote."[58] Similarly, The Washington Post reported on Monday that "[b]ehind the scenes, Trump advisers and allies are increasingly resigned to a Biden victory, according to people familiar with internal discussions, who, like others interviewed for this report, spoke on the condition of anonymity to share private conversations."[59]
In response, Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell stated that "President Trump is 100% within his rights to look into allegations of irregularities and weigh his legal options."[60] Texas senator John Cornyn and Iowa senator Chuck Grassley were among the Republicans who said that they hadn't yet seen any evidence of widespread voting fraud that could change the election, while saying the President had the right to legally investigate allegations of fraud. Close Trump ally Graham also referred to minor incidents that he admitted wouldn't yet change the election result, and said he would accept a loss in the courts.[61]
That same day, ABC News noted that actually very few members of the Trump administration and White House staff itself had so far explicitly supported Trump's claims of electoral fraud, or asserted that he won the election; Vice President Mike Pence only went so far as tweeting he stood by President Trump in saying that every legal vote should be counted, and otherwise remained silent.[62] Lieutenant Governor Geoff Duncan of the key swing state of Georgia stated: "We've not had any sort of credible incidents [of widespread systemic voter fraud or irregularities] raised to our level yet."[63] At a press conference, White House press secretary Kayleigh McEnany accused Democrats of encouraging fraud and illegal voting. Notably, Fox News decided to cut away during her speech because host Neil Cavuto found it irresponsible to continue broadcasting such "an explosive charge." Previously, Fox News had continuously aired most of President Trump's press conferences and rallies, regardless of the false claims he made during his speeches.[64]
In a highly contentious move, U.S. Attorney General William Barr, who had previously supported Trump's unfounded claims about voter fraud, authorized the investigation of alleged voting irregularities before the states had certified the election results, prompting Richard Pilger, director of the elections crimes branch in the Justice Department, to resign in protest.[60] Pilger stated that Barr's action was "abrogating the forty-year-old Non-Interference Policy for ballot fraud investigations in the period prior to elections becoming certified and uncontested."[65]
Meanwhile, Republican senators David Perdue and Kelly Loeffler from Georgia demanded Georgia Secretary of State Brad Raffensperger to resign for "[failing] to deliver honest and transparent elections" after his voting system manager, Gabriel Sterling (a lifelong Republican), called the claims of electoral fraud "hoaxes and nonsense," "fake news" and "disinformation" in a Monday morning press conference, but Raffensperger (also a Republican) rejected the demand outright, adding that any incidents of voter fraud were unlikely to tip the balance of Biden's lead of more than 12,000 votes (0.25%) towards Trump for Georgia's 16 electors.[66] He called Perdue and Loeffler's claim of lack of transparency "laughable."[67]
November 10: Pompeo rejects Biden's victory while other Republicans privately acknowledge it[]

On November 10, Secretary of State Mike Pompeo sparked outrage among diplomats when he told journalists during a press conference that there would be a "smooth transition to a second Trump administration," because he was confident that the vote counting would still result in a Trump victory.[68] John Bolton, National Security Advisor in the Trump administration from 2018 to 2019, who had already denounced Trump's fraud claims days earlier,[32] was highly critical of Pompeo's remarks, saying he had "eviscerated his credibility" and was "delusional."[69] Meanwhile, Democratic Senator Chris Coons from Delaware told CNN that several Republican senators had privately acknowledged President-elect Joe Biden's victory to him in phone calls, asking him "to convey their well-wishes to the President-elect," but they weren't yet willing to do so publicly themselves. At that point, four Republican senators had publicly recognized Biden, and Coons expected others to follow that week.[70]
An inquiry from The New York Times showed that throughout the country, election officials representing both parties reported no evidence of significant voter fraud, even though some Republican candidates running for office were casting doubt on the results without proof.[67] Republican officials criticized unsupported allegations, with Ohio Secretary of State Frank LaRose stating: "There's a great human capacity for inventing things that aren't true about elections. The conspiracy theories and rumors and all those things run rampant."[67] Kansas Republican Secretary of State Scott Schwab wrote in an email: "Kansas did not experience any widespread, systematic issues with voter fraud, intimidation, irregularities or voting problems."[67] Republican Washington Secretary of State Kim Wyman determined the election was free of fraud. Her assessment was rebuked by Republican candidate Loren Culp, who lost his gubernatorial race against Democrat Jay Inslee by a large margin of 14%, leading Wyman to say: "It's just throwing grass at the fence at this point, see what sticks."[67] Republican Montana Secretary of State Corey Stapleton tweeted: "I have supported you, Mr. President. @realDonaldTrump accomplished some incredible things during your time in office! But that time is now over! Tip your hat, bite your lip, and congratulate @JoeBiden."[67]
November 11: Senior Republicans call on Trump to concede[]
On November 11, Arizona attorney general Mark Brnovich, a Republican, stated that he had not found any evidence of significant fraud that could change the outcome of that state's result. He said it was "very, highly unlikely" that Trump would receive enough votes from the last remaining uncounted ballots to beat Biden's 13,000 vote lead, and thus obtain Arizona's 11 electors. Even without these, Biden would still have 279 electors, enough to gain the presidency with a large margin.[71] Meanwhile, pressure was mounting on Trump to concede defeat: most foreign heads of state or government had already congratulated President-elect Biden, who a day earlier had labeled Trump's refusal to concede "an embarrassment." Senior Republicans who had already acknowledged the Democratic nominee's victory were publicly calling on the President to do the same, with former Defense Secretary and former US Senator from Maine William Cohen describing Trump's behavior as "more akin to a dictatorship than a democracy."[72] Former White House Chief of Staff Andrew Card said: "I think it's hyperbole beyond expectation or credibility to say that somebody 'stole the election'; they didn't." He said he was addressing the president, but also trying to give "Republicans who know this, but are afraid to say it, permission to say it," and urged people close to the President to "tell him the truth, polish our democracy, and polish his legacy," "recognize reality," and begin the transition to prevent security risks.[73]
Massachusetts governor Charlie Baker commented: "I'm dismayed to hear the baseless claims from the president, from his team, and from many other elected Republican officials in Washington. I can't think of a worse time to stall a transition than amid a deadly pandemic."[72] Maryland governor Larry Hogan added: "Most people realize that this election is over. It's really dangerous, I think, in the middle of this pandemic, this economic collapse, people dying across the country, to not know if we're going to have a transition."[72] An editorial in the Las Vegas Review-Journal, owned by Republican megadonor Sheldon Adelson who had supported the Trump campaign with over 75 million dollars, wrote: "The president does a disservice to his more rabid supporters by insisting that he would have won the Nov 3 election absent voter fraud. That's simply false."[74]
Senate Ethics Committee Chair James Lankford, a Republican Senator from Oklahoma, demanded the Trump administration to give President-elect Biden and Vice President-elect Harris access to the President's Daily Brief, the daily presidential intelligence briefings on national security issues. Lankford took the pragmatic position of not yet acknowledging Biden and Harris as elects while Trump's legal challenges were ongoing, but recognized they would form the next administration if the lawsuits failed, and said they needed to be informed about the country's pressing security issues to be prepared before taking office. This practice during the presidential lame duck period was long established, even during the contested 2000 presidential election, Lankford argued, warning he would intervene if the Trump administration would not grant Biden/Harris access by the end of the week.[75]
November 12: "Most secure election in American history"[]
On November 12, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), part of the Department of Homeland Security, published a statement saying "The November 3 election was the most secure in American history," and that it had found "no evidence that any voting system deleted or lost votes, changed votes, or was in any way compromised." It was the first time that an entire agency – one which Trump had in fact created in 2018 – within the Trump administration contradicted the President's claims of widespread fraud and irregularities.[78]
The Trump-appointed Director of CISA, Christopher C. Krebs, had already been at odds with President Trump over creating a website that sought to debunk election-related disinformation, while a lot of such disinformation was being spread by Trump himself and other Republican Party leaders. He therefore expected to be fired by the President soon for disloyalty, as many other officials had been in preceding days due to conflicts with Trump over the election and other issues. Nevertheless, he persisted in leading his agency's efforts in combating what he saw as dangerous nonsense, hoaxes and conspiracy theories such as "wild and baseless claims about voting machines, even if they're made by the president."[76] Trump fired Krebs on November 17.[79]
New Hampshire Governor Chris Sununu insisted there was no fraud in his state and congratulated Biden as President-elect, bringing the number of Republican governors denouncing Trump's claims to 5 out of 26.[80] Ohio Governor Mike DeWine then did the same, becoming the 6th.[81] That same day, 161 former national security officials, who served in Democratic or Republican administrations (including the Trump administration), signed a letter urging the General Services Administration (GSA) to recognize Joe Biden as president-elect, as further delaying the acknowledgement posed "serious risk to national security."[82]
November 13: Trump suffers legal setbacks[]
On November 13, the Trump campaign suffered three defeats in Arizona, Michigan and Pennsylvania related to his challenges against the electoral process. Spokesperson Tim Murtaugh repeated claims about voting machine irregularities in Maricopa County, but the Trump team dropped its lawsuit because Biden's overall lead in Arizona was too large for the disputed ballots to make a difference.[83] That same day, several law firms including Porter Wright Morris & Arthur, Jones Day (which had supported Trump in over 20 cases in 4 years) and Snell & Wilmer that had been representing the Trump campaign or the Republican Party in some of its legal complaints withdrew their support, commenting that the President's objections were pointless, and they did not wish to legitimize his arguments anymore. Jones Day lawyer Parker A. Rider-Longmaid stated: "I believe the question is whether this firm should lend its prestige and credibility to the project of an administration bent on undermining our democracy and our rule of law." The Lincoln Project, a group of anti-Trump Republicans, had been publicly urging employees of Jones Day and Porter Wright to resign in protest in the preceding days.[84] President Trump himself reportedly also came close to conceding defeat by admitting that he may not be leading the next administration, during an interview on the new COVID-19 surge, saying: "I will not go – this administration will not be going to a lockdown. Hopefully the – whatever happens in the future, who knows which administration will be. I guess time will tell. But I can tell you this administration will not go to a lockdown."[85]
November 14: Trump criticizes Republican officials dismissing fraud[]
On November 14, President Trump vehemently criticized Georgia Secretary of State Brad Raffensperger for dismissing claims of fraud, labeling him "a so-called Republican (RINO)", accusing him of obstructing investigations into fraud, even though Raffensperger said the investigations were still ongoing "but we have not seen something widespread." In response to pressure to follow Trump's narrative, Raffensperger stated: "People are just going to have to accept the results. I'm a Republican. I believe in fair and secure elections." His comments were supported by Republican Lieutenant Governor Geoff Duncan.[86] Trump also attacked Philadelphia City Commissioner Al Schmidt as a "so-called Republican (RINO)", alleging he "refused to look at a mountain of corruption & dishonesty." Schmidt had called some of Trump's claims "fantastical" and "completely ridiculous allegations that have no basis in fact at all."[86] Similarly, Republican election officials in the Dauphin and Cumberland counties refuted presidential claims of voter fraud.[86]
Meanwhile, Republican Kent County Clerk Lisa Posthumus Lyons rejected Trump's claims that the voting system was unreliable, saying it had been used before by the Michigan Republican Party; she added: "I am 100% confident in the results in Kent County, and I'm confident that our canvass, once its all concluded, will validate that."[86] Barbara Cegavske, the Nevada Secretary of State and also a Republican, declared that "[m]any voter fraud complaints lack any evidence and are more complaints about process or policy."[86]
November 15: Confusion about partial concession[]
On November 15, retweeting a Fox News video that claimed fraud, Trump wrote about Biden: "He won because the election was rigged," repeating a number of claims that have been generally dismissed as baseless. Nevertheless, several analysts and commentators regarded this statement as a partial concession or the start of a concession on the part of the incumbent president. While asserting Trump would remain influential within the Republican Party for some time, Republican Arkansas Governor Asa Hutchinson told NBC: "It was good actually to see President Trump tweet out that 'he won'. I think that's a start of an acknowledgment." Trump responded: "He only won in the eyes of the fake news media. I concede nothing!"[87]
November 19: Biden/Harris host bipartisan governor conference[]
Sixteen days into Trump's refusal to concede, the Biden/Harris Transitional Team hosted a conference call on how to deal with COVID-19 with ten governors, five of whom were Republicans: Alabama Governor Kay Ivey, Arkansas Governor Asa Hutchinson, Maryland Governor Larry Hogan, Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker, and Utah Governor Gary Herbert. President-elect Biden stressed the importance of bipartisanship, expressed hope for arriving at a consensus with "Republican colleagues," and criticized General Services Administrator Emily W. Murphy's decision to delay the transition process.[88]
November 19–22: Legal developments[]
The same day, Trump campaign attorneys Rudy Giuliani, Jenna Ellis, Joseph diGenova and Sidney Powell – who described themselves as Trump's "elite strike force team" – "spun a web of mistruths that made mention of the Clinton Foundation, liberal megadonor George Soros and the late Venezuelan strongman Hugo Chávez."[89] Powell referred to an alleged pro-Biden election-rigging software within polling machines issued by Dominion Voting Systems.[90][91] At no time did any of the lawyers give proof of their claims.[92] Trump cable news loyalist Tucker Carlson singled out the conspiratorial claims made by Powell, who alleged that Venezuela, Cuba and unidentified communist interests had used a secret algorithm to hack into voting machines and commit fraud, noting that "what Powell was describing would amount to the single greatest crime in American history."[93] He said Powell became "angry and told us to stop contacting her" when he asked for evidence of her claims.[93] On November 22, the Trump campaign distanced themselves from Powell, with Ellis saying "Sidney Powell is practicing law on her own. She is not a member of the Trump Legal Team. She is also not a lawyer for the President in his personal capacity."[94]
November 23: GSA ascertains Biden as apparent president-elect[]
General Services Administrator Emily Murphy formally sent the letter of ascertainment to Joe Biden on November 23. While Democrats and some Republicans had been pressuring her to make the ascertainment, and Trump loyalists not to do so, Murphy stated she made her own decision based on the official election results and developing circumstances of Trump's legal challenges: "Contrary to media reports and insinuations, my decision was not made out of fear or favoritism. Instead, I strongly believe that the statute requires that the GSA Administrator ascertain, not impose, the apparent president-elect."[95] Due to the ascertainment, the Biden/Harris transition team obtained funding and permission to start working with Trump administration officials across federal agencies to prepare for the Biden administration's succession in January 2021.[95] President Trump endorsed the GSA ascertainment "in the best interest of the Country," while vowing to continue his legal struggles, which several people close to Trump as well as external commentators interpreted as an indirect concession.[95][96]
December 2: Most Republican members of Congress still side with Trump[]
Over three weeks after Biden's victory speech, most Republican members of Congress who commented on the presidential election still sided with Trump.[97]
December 5: Few Republican members of Congress recognize Biden as the winner[]
Only 27 out of 249 Republicans in Congress had acknowledged Biden as the winner of the election.[98]
December 8: Texas v. Pennsylvania; rejected resolution to declare Biden president-elect[]
Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton, sues the state of Pennsylvania (Texas v. Pennsylvania) alleging that election results from Georgia, Michigan, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin were invalid. Within one day of Texas's filing, Trump, over 100 Republican Representatives, and 18 Republican state attorneys general filed motions to support the case.[99][100] Republican members of state legislatures also supported the assertions.[101]
During a meeting of the Joint Congressional Committee on Inaugural Ceremonies, Democrats proposed a resolution affirming Joe Biden to be president-elect, but Republicans voted it down. The vote was 3–3 along party lines.[102][103]
December 14: Counterfeit electors[]
On Fox News, Stephen Miller stated that failed Trump electors would meet and cast a set of "alternative votes."[104][105]
December 15: Electoral College votes to certify Biden's victory[]
After the electoral college vote to certify Biden's victory, more Republican senators begin to call Biden the president-elect.[106] Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell extended his congratulations for the first time on December 15, referring to Biden and Harris as "President-elect" and "vice president-elect" and stating: "The electoral college has spoken."[107] Nonetheless, in late December 2020, some Republican members in Congress[108] were reported to be considering challenging the results of the electoral college vote on January 6, 2021, in an attempt to overturn Trump's loss to Biden.[109][110][111][112]
December 28: Rep. Gohmert sues Vice President Pence[]
On December 28, 2020, Rep. Louis Gohmert (R-TX) challenged the constitutionality of the Electoral Count Act of 1887, claiming that the Vice President should have the power and ability to unilaterally decide which slates of electoral votes get counted. Vice President Pence was named as the defendant in the lawsuit.[113][114] Pence responded that he is "not the right person to sue," especially as Gohmert's lawsuit sought to expand Pence's powers, and he asked a judge to reject the lawsuit.[115] The Justice Department argued on Pence's behalf that the lawsuit would make more sense if Congress were the defendant. Congressional lawyers supported Pence's position as well.[116] The case was dismissed on January 1, 2021, for lack of both standing and jurisdiction.[117][118][119] The plaintiffs immediately filed an appeal to the United States Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit on the Order of Dismissal and the accompanying Final Judgment,[120] but the appeal was dismissed by a three-judge panel of the court on January 2.[121]
December 30: Senator Hawley asserts state law violations[]
Senator Josh Hawley stated "some states, particularly Pennsylvania, failed to follow their own state election laws," though multiple courts had rejected such claims.[122][123] Hawley repeated the false assertion about Pennsylvania in a February 2021 fundraising email, though the Pennsylvania Supreme Court had unanimously rejected the argument and the United States Supreme Court had declined to consider an appeal.[124][125] Steve Scalise, the #2 Republican in the House, continued to make the false assertion as late as October 2021, stating during a television appearance, "Those states that didn't follow the law, are they gonna keep doing that in the future or are we gonna get back to the what the Constitution calls out for electing our leaders?"[126][127][128]
January 2: Republican lawmakers object to the election outcome[]
On January 2, 2021, Vice President Pence reportedly welcomed Republican lawmakers' objections to the election outcome. (Senator Amy Klobuchar, the top Democrat of the committee with jurisdiction over federal elections, regarded the effort a "publicity stunt" that would fail eventually, and amounted to an attempt to "subvert the will of the voters.")[129]
January 5: Senators reveal whether they will support the vote count[]
Ahead of the electoral vote count on January 6, a number of senators declared their intention to oppose or support counting the electoral votes as submitted by the states.[130]
January 8: Nevada Republicans post manifesto predicting Trump will stay in office[]
The chairman of the Nye County Republican Party in Nevada posted a manifesto online that predicted two more weeks of national crisis with "high-profile arrests." It said that Trump would purge his Cabinet, replace his vice president, and ultimately remain in office. Michael Ahrens, RNC communications director, criticized it as sounding “deranged."[131]
January 9: Arizona Republicans draft resolution to censure Cindy McCain[]
Arizona Republicans drafted a resolution to censure Cindy McCain (the widow of the late Republican Senator John McCain) for supporting Joe Biden in the November election. RNC Chairwoman Ronna McDaniel disagreed with the effort, telling the Washington Post on January 11 that although "we are upset that a prominent Republican would support Joe Biden," nevertheless "the language in this resolution is abhorrent" and the Arizona Republican Party ought to disregard it if it is presented to them later in January.[131] McCain, noting that the GOP had also censured her husband, shrugged it off on January 14: "I'm in good company."[132]
January 12: Harvard Institute of Politics removes Rep. Elise Stefanik[]
The Harvard Institute of Politics senior advisory committee, expressing its disapproval of Representative Elise Stefanik's (R–N.Y.) false claims of election fraud, said she would no longer be allowed to participate on the committee.[133]
January 17: Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene suspended from Twitter for 12 hours[]
Twitter temporarily suspended the account of U.S. Representative Marjorie Taylor Greene, a Republican from Georgia, "for multiple violations of our civic integrity policy." Greene had tweeted that Americans should "mobilize...in opposition to these attacks on our liberties." The tweet was deleted, and the suspension was in effect for 12 hours.[134]
February 1: Sen. McConnell criticizes Rep. Greene[]
Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell said, "Loony lies and conspiracy theories are cancer for the Republican Party and our country." Though he did not name Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene, his comment was understood as a rebuke of her.[135]
Subsequent events[]
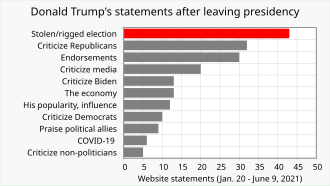
On April 10, 2021, the Nevada Republican Party voted 126–112 to censure the Nevada Secretary of State, Barbara Cegavske, a Republican, after her investigation concluded there had been no fraud in the state's 2020 election.[137] Similarly, the Georgia Republican Convention censured Secretary of State Brad Raffensperger on June 5, 2021.[138]
In April and May 2021, the Arizona Senate Republican Caucus was still conducting an audit of November 2020 election results in Maricopa County, even though the results were previously audited several times with the same outcome, and state officials had long since finalized certification. Republican state Sen. Paul Boyer said the audit "makes us look like idiots". The federal Department of Justice warned the methods being used might violate federal election and civil rights laws, and that the chain of custody had not been maintained.[139] In response to a conspiracy theory promoted by a conservative radio show, ballots were examined for bamboo content (in a way experts said would not accurately detect bamboo) on the implausible theory that ballots were secretly imported from South Korea.[140][141] Maricopa County sheriff Paul Penzone criticized as "mind-numbingly reckless and irresponsible" a demand by state Senate Republicans for routers, which he asserted could compromise confidential, sensitive and highly classified law enforcement data and equipment.[142]
In a May post on his blog, Trump amplified a false assertion by Arizona senate president Karen Fann that an "entire database" of Maricopa County voter information had been deleted. Maricopa County recorder Stephen Richer, a Republican who oversees elections, tweeted that Trump's post was "unhinged," noting he was looking at the database on his computer at that moment. Richer added, "We can't indulge these insane lies any longer. As a party. As a state. As a country."[143] The Maricopa county Twitter account later tweeted a lengthy thread with the hashtag #RealAuditorsDont, citing examples including "Release false 'conclusions' without understanding what they are looking at" and "Hire known conspiracy theorists."[144][145]
During a May 17 meeting of the Maricopa County Board of Supervisors, Republicans who dominate the board sharply objected to the audit, with chairman Jack Sellers chastising Fann's "attempt at legitimatizing a grift disguised as an audit." That day, the county sent a twelve-page letter to dispute Fann's earlier allegations of wrongdoing by county officials, and Sellers stated the allegations were actually due to the incompetence of the auditors. Board members asked party and business leaders to speak out against the audit, noting they had received death threats.[146][147]
While Senator Lindsey Graham said on May 6 that the party "can't grow without" Trump,[148] on May 17 he said "I accept the results of the election," adding, "2020 is over for me."[149]
Fulton County, Georgia, which includes most of Atlanta and is dominated by Democrats, was also the focus of election conspiracy theories. In May 2021, a county judge granted a request to unseal 147,000 mail-in ballots so they could be examined to determine if they are counterfeit. Georgia had already conducted three audits, including a hand recount, during the weeks after the election. The court case and ballot review were led by a man who has promoted various political conspiracy theories for decades. His effort has been supported by some leading Georgia Republicans, including former senator Kelly Loeffler.[150][151][152]
The insistence by Trump and his supporters throughout 2021 that the election had been stolen from him by fraud came to be characterized as an implementation of "the big lie." Despite no evidence of election fraud surfacing after more than a year since the election, Trump and his supporters continued to insist he won and inverted the narrative to insist that saying he lost was the real big lie. Polls indicated a large majority of Republicans continued to agree that Trump's false assertions were valid, leading to efforts they characterized as bolstering "election integrity" to restrict voting and take control of the administrative management of elections. Trump ally Steve Bannon said in December 2021 that "we are going to take over the election apparatus." January 2022 analysis conducted by NPR found that at least fifteen Republicans who denied Biden's victory were candidates for secretary of state in the 2022 elections.[153] Fascism scholar Timothy Snyder observed: "The lie is so big that it reorders the world. And so part of telling the big lie is that you immediately say it's the other side that tells the big lie. Sadly, but it's just a matter of record, all of that is in Mein Kampf."[154]
Denounced election fraud claims[]
These Republican officials have either explicitly and publicly denounced Donald Trump's election fraud claims, acknowledged Joe Biden as President-elect, or both.
Federal executive officials[]
Current[]
- Christopher A. Wray, Director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (2017–present)[155]
Former[]
- Kay Bailey Hutchison, United States Permanent Representative to NATO (2017–2021)[156]
- James Baker, White House Chief of Staff (1981–1985, 1992–1993), United States Secretary of State (1989–1992), United States Secretary of the Treasury (1985–1988)[157]
- John Bolton, National Security Advisor (2018–2019), United States Ambassador to the United Nations (2005–2006)[32][69]
- George W. Bush, President of the United States (2001–2009)[51][52][53]
- Andrew Card, White House Chief of Staff (2001–2006)[73]
- Michael Chertoff, United States Secretary of Homeland Security (2005–2009)[158]
- Dick Cheney, Vice President of the United States (2001–2009), United States Secretary of Defense (1989–1993)[159][160]
- William Cohen, United States Secretary of Defense (1997–2001), Senator from Maine (1979–1997), Representative from Maine (1973–1979)[72]
- Dan Coats, Director of National Intelligence (2017–2019)[158]
- James Comey, Director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (2013-2017)[161]
- Ari Fleischer, White House Press Secretary (2001–2003)[74]
- Chuck Hagel, Senator from Nebraska (1997–2009); United States Secretary of Defense (2013–2015)[26]
- Gina Haspel, Director of the Central Intelligence Agency (2018-2021)[162]
- Christopher C. Krebs, Director of the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (2018–2020)[78][76][77]
- Ray LaHood, United States Secretary of Transportation (2009–2013), Representative from Illinois, 18th district (1995–2009) & 27 district (1982–1983)[163]
- H. R. McMaster, Assistant to the President for National Security Affairs (2017–2018)[164]
- Connie Morella, United States Ambassador to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (2003–2007)[163]
- Richard Painter, Republican until 2018 then independent; chief White House ethics lawyer (2005–2007)[165]
- Dan Quayle, Vice President of the United States (1989–1993)[166]
- Condoleezza Rice, National Security Advisor (2001–2005), United States Secretary of State (2005–2009)[167]
- Donald Rumsfeld, United States Secretary of Defense (1975-1977;2001-2006)[159]
- Tom Ridge, United States Secretary of Homeland Security (2003–2005)[33]
- Jeffrey A. Rosen, United States Attorney General (2020-2021)[168]
- Karl Rove, White House Deputy Chief of Staff (2005–2007)[27]
- Stephen A. Schwarzman, advisor to President Trump (2017)[169]
- Miles Taylor, Chief of Staff to the United States Secretary of Homeland Security (2019)[38]
Supreme Court Justices Appointed by Republicans[]
- Amy Coney Barrett, Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States (2020–present)[170]
- Brett Kavanaugh, Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States (2018–present)[170]
- John Roberts, Chief Justice of the United States, (2005–present)[170]
Federal legislative officials[]
Senators[]
Current[]


- Roy Blunt, Senator from Missouri (2011–present)[30]
- Richard Burr, Senator from North Carolina (2005–present)
- Shelley Moore Capito, Senator from West Virginia (2015–present)
- Bill Cassidy, Senator from Louisiana (2015–present)[171]
- Susan Collins, Senator from Maine (1997–present)[30]
- John Cornyn, Senator from Texas (2002–present)
- Kevin Cramer, Senator from North Dakota (2019–present)
- Deb Fischer, Senator from Nebraska (2013–present)[172]
- John Hoeven, Senator from North Dakota (2011–present)[30]
- Jerry Moran, Senator from Kansas (2011–present)
- Lisa Murkowski, Senator from Alaska (2002–present)[28]
- Rob Portman, Senator from Ohio (2011–present)[35]
- Mitt Romney, Senator from Utah (2019–present)[28][29][30][32][33][34]
- Mike Rounds, Senator from South Dakota (2015–present)[173]
- Marco Rubio, Senator from Florida (2011–present)[28][32][33]
- Ben Sasse, Senator from Nebraska (2015–present)[30]
- Richard Shelby, Senator from Alabama (1986–present)
- John Thune, Senator from South Dakota (2005–present)
- Pat Toomey, Senator from Pennsylvania (2011–present)[28][30][32][33]
All these senators counted electoral votes as submitted by the states on January 6, 2021.[174]
Former[]

- Lamar Alexander, Senator from Tennessee (2003–2021)[47][176]
- Bob Corker, Senator from Tennessee (2007–2019)[177]
- Bob Dole, Senator from Kansas (1969–1996)[178]
- David Durenberger, Senator from Minnesota (1978–1995)[163] (Independent)
- Jeff Flake, Senator from Arizona (2013–2019)[29]
- Bill Frist, Senate Majority Leader (2003–2007); Senator from Tennessee (1995–2007)[158]
- Rick Santorum, Senator from Pennsylvania (1995–2007)[175][34]
- Gordon Smith, Senator from Oregon (1997–2009)[179]
- Olympia Snowe, Senator from Maine (1995–2013)[180]
House Representatives[]
Current[]


- Liz Cheney, WY-AL (2017–present)[30]
- John Curtis, UT-03 (2017–present)[182]
- Anthony Gonzalez, OH-16 (2019–present)[183]
- Jenniffer González, Resident Commissioner of Puerto Rico (2017–present)[184]
- John Katko, NY-24 (2015–present)[185]
- Adam Kinzinger, IL-16 (2011–present)[27][28][29][32][33]
- Nancy Mace, SC-1 (2021–present)[186]
- Peter Meijer, MI-3 (2021–present)
- Mariannette Miller-Meeks, IA-02 (2021–present)[187]
- Tom Reed, NY-23 (2010–present)[54]
- Fred Upton, MI-06 (1987–present)[54][188]
- Don Young, AK-AL (1973–present)[54]
Former[]
- Justin Amash, MI-3 (2011-2021) (Libertarian)[189]
- Steve Bartlett, TX-3 (1983–1991)[163]
- Robert Bauman, MD-1 (1973–1981)[163]
- Doug Bereuter, NE-1 (1979–2004)[163]
- Charles Boustany, LA-3 (2005–2017)[158]
- Mike Coffman, CO-6 (2009–2019)[190]
- Tom Coleman, MO-6 (1976–1993)[163]
- Barbara Comstock, VA-10 (2015–2019)[163]
- Carlos Curbelo, FL-26 (2015–2019)[27]
- Charlie Dent, PA-15 (2005–2018)[31][163]
- Charles Djou, HI-1 (2010–2011)[163]
- Mickey Edwards, OK-5 (1977–1993)[163]
- Wayne Gilchrest, MD-1 (1991–2009)[163]
- James C. Greenwood, PA-8 (1993–2005)[163]
- Steve Gunderson, WI-3 (1981–1997)[158]
- Bob Inglis, SC-4 (2005–2011)[163]
- Peter T. King, NY-02 (1993–2021)[188]
- Scott L. Klug, WI-2 (1991–1999)[163]
- Jim Kolbe, AZ-5 (1985–2003) and AZ-8 (2003–2007)[163]
- Steven T. Kuykendall, CA-36 (1991–2001)[163]
- Jim Leach, IA-1 (1977–2003) and IA-2 (2003–2007)[163]
- John LeBoutillier, NY-6 (1981–1983)[163]
- Paul Mitchell, MI-10 (2017–2021)[27][29][30]
- Susan Molinari, NY-14 (1990–1993) and NY-13 (1993–1997)[163]
- Mike Parker, MS-4 (1989–1999)[163]
- Tom Petri, WI-6 (1979–2015)[163]
- Deborah Pryce, OH-15 (1993–2009)[163]
- Jack Quinn, NY-30 (1990–1993) and NY-27 (2003–2005)[163]
- Jim Renacci, OH-16 (2011–2019)[158]
- Denver Riggleman, VA-05 (2019–2021)[30][33]
- Mike Rogers, MI-8 (2001–2015)[191]
- Francis Rooney, FL-19 (2017–2021)[191][188]
- Paul Ryan, WI-1 (1999–2019), Speaker of the House of Representatives (2015–2019)[181][192]
- Joe Scarborough, FL-1 (1995–2001)—now a cable news host for MSNBC and since 2017 identifies as Independent;[193] on December 1, 2020, characterized the actions of Trump et al as an attempted coup d'état, using the legal term "four corners" for the degree to which the combined activities fit the definition of a coup[36]
- Chris Shays, CT-4 (1987–2009)[163]
- Peter Plympton Smith, VT-AL (1989–1991)[163]
- Alan Steelman, TX-5 (1973–1977)[163]
- James T. Walsh, NY-25 (1993–2009) and NY-27 (1983–1993)[163]
- Dick Zimmer, NJ-12 (1991–1997)[163]
Federal judicial officials[]
Current[]
- Stephanos Bibas, Judge on the United States Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit (2017–present)[194]
- Matthew W. Brann, Judge on the United States District Court for the Middle District of Pennsylvania (2012–present)[195]
- Brett H. Ludwig, Judge on the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Wisconsin (2020–present), Judge on the United States bankruptcy court for the Eastern District of Wisconsin (2017–2020)[196]
State and territory executive officials[]
Governors[]
Current[]


- Charlie Baker, Governor of Massachusetts (2015–present)[54]
- Spencer Cox, Governor of Utah (2021–present)[32][33]
- Mike DeWine, Governor of Ohio (2019–present)[81][191]
- Doug Ducey, Governor of Arizona (2015–present)[33]
- Larry Hogan, Governor of Maryland (2015–present)[28][29][32][33]
- Asa Hutchinson, Governor of Arkansas (2015–present)[87]
- Kay Ivey, Governor of Alabama (2017–present)[88]
- Brian Kemp, Governor of Georgia (2019–present)[197]
- Phil Scott, Governor of Vermont (2017–present)[32]
- Kevin Stitt, Governor of Oklahoma (2019–present)[198]
- Chris Sununu, Governor of New Hampshire (2017–present)[80]
- Ralph Torres, Governor of the Northern Mariana Islands (2015–present)[199]
Former[]

- Jeb Bush, Governor of Florida (1999–2007)[47]
- Chris Christie, Governor of New Jersey (2010–2018)[28][33][34][55][200]
- Wanda Vázquez Garced, Governor of Puerto Rico (2019–2021)[201]
- Bill Haslam, Governor of Tennessee (2011–2019)[158]
- Gary Herbert, Governor of Utah (2009–2021)[88]
- John Kasich, Governor of Ohio (2011–2019)[54]
- Mark Sanford, Governor of South Carolina (2003–2011)[202]
- Arnold Schwarzenegger, Governor of California (2003–2011)[203]
Lieutenant governors[]
Current[]
- Geoff Duncan, Lieutenant Governor of Georgia (2019–present)[63]
- Kevin Meyer, Lieutenant Governor of Alaska (2018–present)[204]
- Arnold Palacios, Lieutenant Governor of the Northern Mariana Islands (2019–present)[199]
- Karyn Polito, Lieutenant Governor of Massachusetts (2015–present)[205]
- Boyd Rutherford, Lieutenant Governor of Maryland (2015–present)[206]
Former[]
- Kim Guadagno, Lieutenant Governor of New Jersey (2010–2018)[207]
- Michael Steele, Lieutenant Governor of Maryland (2003–2007); Chairman of the Republican National Committee (2009–2011)[38]
Other executive officials[]
Current[]
- Mark Brnovich, Arizona Attorney General (2015–present)[71]
- Barbara Cegavske, Nevada Secretary of State (2015–present)[86]
- Frank LaRose, Ohio Secretary of State (2019–present)[67]
- Brad Raffensperger, Georgia Secretary of State (2019–present)[66][67]
- Scott Schwab, Kansas Secretary of State (2019–present)[67]
- Kim Wyman, Washington Secretary of State (2013–present)[67]
Former[]
- Trey Grayson, Secretary of State of Kentucky (2004–2011)[158]
- Corey Stapleton, Montana Secretary of State (2017–2021)[67]
State Legislators[]
Senators[]
- Jake Corman, Majority Leader of the Pennsylvania State Senate (2015–present)[208]
Representatives[]
- Jon Bramnick, New Jersey State Assemblymember from District 21 (2003–present)[209]
- Bryan Cutler, Speaker of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives (2020–present)[208]
Election officials[]
- Aaron Van Langevelde, vice-chair of Michigans State Board of Canvassers[210]
- Gabriel Sterling, Manager of Georgia's voting system[66][210]
- Al Schmidt, City Commissioner of Philadelphia[39][210]
Others[]
- Bret Baier, Fox News host[211]
- Cindy McCain, widow of 2008 Republican presidential nominee John McCain[212]
- Meghan McCain, daughter of 2008 Republican presidential nominee John McCain[212][213]
- Frank Luntz, Republican Party strategist[214]
- Alyssa Farah, former White House communications director for Trump[215]
- Ann Romney, wife of Mitt Romney, First Lady of Massachusetts (2003–2007)[216]
Supported Donald Trump's claims of election fraud[]
These Republican officials have either explicitly publicly supported Donald Trump's election fraud claims, refused to acknowledge Joe Biden as President-elect, or both. (Note: this excludes Republicans who have only supported Trump's right to legally challenge the election results without explicitly supporting his election fraud claims;[59] some Republicans who have denounced his claims or recognized Biden have also supported Trump's right to challenge the results[50][51]).
Federal executive officials[]
Former[]
- Steve Bannon, Counselor to the President (2017)[217]
- William Barr, U.S. Attorney General (1991-1993;2019-2020) (Changed Position)[218][219]
- Gary Bauer, Assistant to the President for Policy Development (1987–1988), United States Under Secretary of Education (1985–1987) and United States Deputy Under Secretary of Education for Planning and Budget (1982–1985)[220]
- Jeffrey Clark, United States Assistant Attorney General for the United States Department of Justice Environment and Natural Resources Division (2018-2021)[221]
- William Boykin, Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence (2002–2007)[220]
- Boris Epshteyn, Strategic Advisor on the Trump 2020 Campaign (2017)[222]
- Michael Flynn, 25th United States National Security Advisor (2017)[223]
- John Lott, former Trump Administration official[224]
- Kayleigh McEnany, White House Press Secretary (2020–2021)[64][210]
- Linda McMahon, Administrator of the Small Business Administration (2017–2019)[225]
- Mark Meadows, White House Chief Of Staff (2020-2021)[155]
- Stephen Miller, Senior Advisor to the President of the United States (2017–2021)[226]
- Emily W. Murphy, Administrator of General Services (2017–2021) (Changed Position)[227]
- Peter Navarro, Director of the Office of Trade and Manufacturing Policy (2017–2021)[228]
- Mike Pence, Vice President of the United States (2017–2021)[229][230][231]
- Tony Perkins, Chair of the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (2019–2020)[220]
- John Poindexter, National Security Advisor (1985–1986) and Deputy National Security Advisor (1983–1985)[232]
- Mike Pompeo, United States Secretary of State (2018–2021)[68]
- John Ratcliffe, Director of National Intelligence (2020–2021)[233]
- Alfred S. Regnery, Deputy Assistant Attorney General of the Land and Natural Resources Division (1981–1986)[220]
- Dan Scavino, White House Deputy Chief of Staff for Communications (2019–2021)[234]
- Ken Starr, former United States Solicitor General (1989–1993)[235]
- James Stewart, Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and Readiness (2018–2019) and Assistant Secretary of Defense for Manpower and Reserve Affairs (2018–2019)[232]
Nominated[]
- Scott O'Grady, nominee for the Assistant Secretary of Defense for International Security Affairs[236]
Members of the U.S. Congress[]
Members of the U. S. Senate[]
Current[]

- John Barrasso, Senator from Wyoming (2007–present) (In December 2020 he said he accepted the results)[237][238]
- Marsha Blackburn, Senator from Tennessee (2019–present)[239]
- Mike Braun, Senator from Indiana (2019–present)
- Tom Cotton, Senator from Arkansas (2015–present)[32][33][44][240]
- Ted Cruz, Senator from Texas (2013–present)[33][44]
- Steve Daines, Senator from Montana (2015–present)
- Lindsey Graham, Senator from South Carolina (2003–present); chairman of the United States Senate Committee on the Judiciary (2019–2021)[28][44][241] (In May 2021, he said he accepted the election results[149])
- Chuck Grassley, Senator from Iowa (1981–present)[242]
- Bill Hagerty, Senator from Tennessee (2021–present)
- Josh Hawley, Senator from Missouri (2019–present)[237]
- Cindy Hyde-Smith, Senator from Mississippi (2018–present)[239]
- Jim Inhofe, Senator from Oklahoma (1994–present)[239]
- Ron Johnson, Senator from Wisconsin (2011–present)[243]
- John Neely Kennedy, Senator from Louisiana (2017–present)
- Mike Lee, Senator from Utah (2011–present)[244]
- Cynthia Lummis, Senator from Wyoming (2021–present)
- James Lankford, Senator from Oklahoma (2014–present)[245]
- Roger Marshall, Senator from Kansas (2021–present)[246]
- Rand Paul, Senator from Kentucky (2011–present)[239]
- Rick Scott, Senator from Florida (2019–present) (Changed Position)[174][247]
- Tommy Tuberville, Senator from Alabama (2021–present)
- Roger Wicker, Senator from Mississippi (2007–present) (In January 2021 he said he accepted the results)[239][248]
Senators in bold italics opposed counting some of Biden's electoral votes on January 6, 2021.[174]
Former[]
- Jim DeMint, Senator from South Carolina (2005–2013)[220]
- David Perdue, Senator from Georgia (2015–2021)[66][249]
- Kelly Loeffler, Senator from Georgia (2020–2021)[66]
Members of the U.S. House of Representatives[]
Current[]

- Mark Amodei, NV-2 (2011–present)[239]
- Robert Aderholt, AL-4 (1997–present)[174]
- Kelly Armstrong, ND-AL (2019–present)[239]
- Brian Babin, TX-36 (2015–present)[239]
- Jim Banks, IN–3 (2017–present)[237][239][174]
- Andy Barr, KY-6 (2013–present)[239]
- Andy Biggs, AZ–5 (2017–present)[239]
- Dan Bishop, NC-9 (2019–present)[239]
- Mo Brooks, AL–5 (2011–present)[250]
- Lauren Boebert, CO-3 (2021–present)[251]
- Ted Budd, NC-13 (2017–present)[239]
- Ken Buck, CO-4 (2015–present)[252]
- Tim Burchett, TN-2 (2019–present)[239]
- Ken Calvert, CA-42(1993-present)[253]
- Madison Cawthorn, NC-11(2021–present)[254][255]
- Ben Cline, VA–6 (2019–present)[239]
- Michael Cloud, TX-27 (2018–present)[256]
- James Comer, KY-1 (2015–present)[239]
- Dan Crenshaw, TX-2 (2019–present)(Changed Position)[257][258]
- Mario Díaz-Balart, FL–25 (2003–2011; 2013–present); FL–21 (2011–2013)[239]
- Jeff Van Drew, NJ-2 (2019–present)[174]
- Byron Donalds, FL-19 (2021–present)[174]
- Jeff Duncan, SC-3 (2011–present)[239]
- Beth Van Duyne, TX-24 (2021–present)[174]
- Tom Emmer, MN-6 (2015–present)[239]
- Pat Fallon, TX-30 (2021–present)[174]
- Drew Ferguson, GA–03 (2017–present)[239]
- Chuck Fleischmann, TN-3 (2011–present)[174]
- Michelle Fischbach, MN-7 (2021–present)[259]
- Virginia Foxx, NC-5 (2005–present)[174]
- Matt Gaetz, FL-1 (2017–present)[260]
- Mike Garcia, CA-25 (2020–present)[174]
- Louie Gohmert, TX–1 (2005–present)[239]
- Lance Gooden, TX–5 (2019–present)[239]
- Paul Gosar, AZ–4 (2013–present); AZ–1 (2011–2013)[239]
- Sam Graves, MO-6 (2001–present)[239]
- Marjorie Taylor Greene, GA–14 (2021–present)[50]
- Michael Guest, MS-3 (2019–present)[239]
- Jim Hagedorn, MN-1 (2019–present)[239]
- Andy Harris, MD-1 (2011–present)[239]
- Jody Hice, GA-10 (2015–present)[174]
- Richard Hudson, NC-8 (2013–present)[239]
- Darrell Issa, CA-50(2021-present)[261]
- Bill Huizenga, MI-2 (2011–present)[239]
- Ronny Jackson, TX-13 (2021–present)[174]
- Mike Johnson, LA-4 (2017–present)[239]
- Jim Jordan, OH-4 (2007–present)[239][262]
- Dave Joyce, OH-14 (2013–present)[239]
- Fred Keller, PA–12 (2019–present)[54]
- Mike Kelly, PA-16 (2011–present)[239]
- Trent Kelly, MS-1 (2015–present)[239]
- Barry Loudermilk, GA-11 (2015–present)[239]
- Doug LaMalfa, CA–1 (2013–present)[239]
- Debbie Lesko, AZ–8 (2018–present)[239]
- Blaine Luetkemeyer, MO-3 (2009–present)[239]
- Thomas Massie, KY-4 (2012–present)[239]
- Brian Mast, FL-18 (2017–present)[174]
- Kevin McCarthy, CA–23 (2013–present), House Minority Leader (2019–present)[28][42][263]
- Tom McClintock, CA–4 (2009–present)[239]
- Carol Miller, WV-3 (2019–present)[264]
- Mary Miller, Il-15 (2021–present)[265]
- John Moolenaar, MI-4 (2015–present)[239]
- Markwayne Mullin, OK-2 (2013–present)[239]
- Ralph Norman, SC-5 (2017–present)[239]
- Devin Nunes, CA–22 (2013–present); California–21 (2003–2013)[239]
- Steven Palazzo, MS-4 (2011–present)[239]
- Gary Palmer, AL–6 (2015–present)[239]
- Scott Perry, PA-10 (2013–present)[239]
- Greg Pence, IN-6 (2019–present)[264]
- Bill Posey, FL-8 (2009–present)[266][267]
- Guy Reschenthaler, PA-14 (2019–present)[239]
- Tom Rice, SC-7 (2013–present)[264]
- Cathy McMorris Rodgers, WA-5 (2021–present)[268]
- David Rouzer, NC-7 (2015–present)[254]
- Chip Roy, TX-21 (2019–present)[269]
- Steve Scalise, LA–1 (2008–present), House Minority Whip (2019–present)[237]
- Pete Sessions, TX-17 (2021–present)[270]
- Jason Smith, MO-8 (2013–present)[239]
- Lloyd Smucker, PA-11 (2013–present)[239]
- Elise Stefanik, NY-21 (2015–present)[239]
- Greg Steube, FL–17 (2019–present)[239]
- Glenn Thompson, PA-15 (2017–present)[239]
- Tom Tiffany, WI–7 (2020–present)[239]
- William Timmons, SC-4 (2019–present)[239]
- Tim Walberg, MI-9 (2007–2009, 2011–present)[239]
- Michael Waltz, FL-6 (2019–present)[271]
- Bruce Westerman, AR–4 (2015–present)[239]
- Roger Williams, TX-25 (2015–present)[239]
- Joe Wilson, SC-2 (2011–present)[239]
- Lee Zeldin, NY-1 (2015–present)[174]
Representatives in bold italics objected to some of Biden's electoral votes on January 6, 2021.[264]
Former[]
- Ralph Abraham, LA-5 (2015–2021)[239]
- Lou Barletta, PA–11 (2011–2019)[272]
- Bradley Byrne, AL–1 (2014–2021)[239]
- Doug Collins, GA-9 (2013–2021)[239]
- Ron Paul, TX-14 (1997–2013)[273]
- Newt Gingrich, GA–06 (1979–1999), Speaker of the House of Representatives (1995–1999)[274][44]
- Steve King, IA-4 (2013–2021); IA-5 (2003-2013)[239]
- Bob McEwen, OH-6 (1981–1993)[220]
- Dana Rohrabacher, CA-48 (2013–2019), CA-46 (2003–2013), CA-45 (1993–2003), CA-42 (1989–1993)[275]
- Ron Wright, TX-6 (2019–2021)[239]
State executive officials[]
Governors[]
Current[]
- Greg Abbott, Governor of Texas (2015–present)[276][277]
- Ron DeSantis, Governor of Florida (2019–present)[44]
- Mike Dunleavy, Governor of Alaska (2018–present)[278]
- Greg Gianforte, Governor of Montana (2021–present)[279]
- Bill Lee, Governor of Tennessee (2019–present)[280][281]
- Kristi Noem, Governor of South Dakota (2019–present)[282]
- Tate Reeves, Governor of Mississippi (2020–present)[283] [284]
- Kim Reynolds, Governor of Iowa (2017–present)[285]
Former[]
- Sarah Palin, former Governor of Alaska (2006-2009)[286]
Lieutenant governors[]
Current[]
- Dan Patrick, Lieutenant Governor of Texas (2015–present)[287]
Attorneys general[]
Current[]
- Daniel Cameron, Kentucky Attorney General (2020–present)[288]
- Lynn Fitch, Mississippi Attorney General (2020–present)[288]
- Michael J. Hunter, Oklahoma Attorney General (2017–present)[288]
- Jeff Landry, Louisiana Attorney General (2016–present)[288]
- Steve Marshall, Alabama Attorney General (2017–present)[288]
- Ashley Moody, Florida Attorney General (2019–present)[288]
- Ken Paxton, Texas Attorney General (2015–present)[289]
- Doug Peterson, Nebraska Attorney General (2015–present)[290]
- Jason Ravnsborg, South Dakota Attorney General[288]
- Sean Reyes, Utah Attorney General (2013–present)[291]
- Leslie Rutledge, Arkansas Attorney General (2015–present)[288]
- Derek Schmidt, Kansas Attorney General (2011–present)[292]
- Eric Schmitt, Missouri Attorney General(2019–present)[293]
- Herbert Slatery, Attorney General of Tennessee (2014–present)[290]
- Wayne Stenehjem, North Dakota Attorney General (2000–present)[290]
- Alan Wilson, South Carolina Attorney General (2011–present)[288]
- Patrick Morrisey, West Virginia Attorney General (2013–present)[290]
Former[]

- Pam Bondi, Florida Attorney General (2011–2019)[295]
- Tim Fox, Montana Attorney General (2013-2021)
- Curtis Hill, Indiana Attorney General (2017-2021)[290]
- Adam Laxalt, Nevada Attorney General (2015–2019)[182]
Attorney generals in bold italics supported Texas v. Pennsylvania
Secretary of State[]
Former[]
- Ken Blackwell, Secretary of State of Ohio (1999–2007)[220]
State Legislators[]
Arizona House[]
- Nancy Barto, District 15[296]
- Brenda Barton, District 6 (Rep. Elect)[296]
- Shawnna Bolick, District 20[296]
- John Fillmore, District 16[296]
- Mark Finchem, District 11[296]
- Travis Grantham, District 12[296]
- Gail Griffin, District 14[296]
- Steve Kaiser, District 15 (Rep. Elect)[296]
- Anthony Kern, District 20[296]
- Kevin Payne, District 21[296]
- Warren Petersen, District 12[296]
- Justin Wilmeth, District 15 (Rep. Elect)[296]
Arizona Senate[]
- Sonny Borrelli, District 5[296]
- David Gowan, District 14[296]
- Steve Montenegro, District 13[296]
- Kelly Townsend, District 16 (Sen. Elect)[296]
Georgia House[]
- Timothy Barr, District 103[296]
- David Clark, District 98[296]
- Emory Dunahoo, District 30[296]
- Sheri Gilligan, District 24[296]
- Matt Gurtler, District 8[296]
- Jeff Jones, District 167[296]
- Ken Pullin, District 131[296]
- Philip Singleton, District 71[296]
Georgia Senate[]
- Jason Anavitarte, District 31 (Sen. Elect)[101]
- Brandon Beach, District 21[297][298][101]
- Greg Dolezal, District 27[298][101]
- Steve Gooch, District 51[101]
- Marty Harbin, District 16[101]
- Tyler Harper, District 7[101]
- Billy Hickman, District 4[101]
- Burt Jones, District 25[297][298][101]
- William Ligon, District 3[298][101]
- Sheila McNeill, District 3 (Sen. Elect)[101]
- Jeff Mullis, District 53[101]
- Carden Summers, District 13[101]
- Blake Tillery, District 19[101]
- Bruce Thompson, District 14[101]
- Renee Unterman, District 45[101]
Michigan House[]
- Julie Alexander, District 64[296]
- Ken Borton, District 105 (Rep. Elect)[296]
- Steve Carra, District 59[296]
- Gary Eisen, District 81[296]
- Beth Griffin, District 66[296]
- Matt Maddock, District 44[296]
- Luke Meerman, District 88[296]
- John Reilly, District 46[296]
- Daire Rendon, District 103[296]
- Mary Whiteford, District 80[296]
- Doug Wozniak, District 36[296]
Texas Senate[]
Oklahoma House[]
- Cleta Mitchell, District 44[300]
Pennsylvania House[]
- Aaron Bernstine, District 10[296]
- Stephanie Borowicz, District 76[296]
- Robert Brooks, District 54[296]
- Bud Cook, District 49[296]
- Jim Cox, District 129[296]
- Eric Davanzo, District 58[296]
- Russ Diamond, District 102[296]
- Barbara Gleim, District 199[296]
- Mike Jones, District 93[296]
- Rob Kauffman, District 89[296]
- Dawn Keefer, District 92[296]
- David Maloney, District 130[296]
- Daryl Metcalfe, District 12[296]
- Dan Moul, District 91[296]
- Eric Nelson, District 57[296]
- Michael Puskaric, District 39[296]
- Kathy Rapp, District 65[296]
- Jim Rigby, District 71[296]
- Brad Roae, District 6[296]
- David Rowe, District 85[296]
- Francis Ryan, District 101[296]
- Jason Silvis, District 55[296]
- Brian Smith, District 66[296]
- David Zimmerman, District 99[296]
Pennsylvania Senate[]
- Dave Argall, District 29[296]
- Cris Dush, District 25 (Sen. Elect)[296]
- Wayne Langerholc, District 35[296]
- Doug Mastriano, District 33[296]
- Kristin Phillips-Hill, District 28[296]
- Joe Pittman, District 41[296]
- Mike Regan, District 31[296]
- Judy Ward, District 30[296]
- Kim Ward, District 39[296]
Wisconsin Assembly[]
- Janel Bradtjen, District 22[296]
- Robert Brooks, District 60[296]
- Rick Gundrum, District 58[296]
- Cody Horlacher, District 33[296]
- Dan Knodl, District 24[296]
- Gae Magnifici, District 28[296]
- Dave Murphy, District 56[296]
- Jeff Mursau, District 36[296]
- Timothy Ramthun, District 59[296]
- Joe Sanfelippo, District 15[296]
- Michael Schraa, District 53[296]
- Shae Sortwell, District 2[296]
- Jeremy Thiesfeldt, District 52[296]
- Chuck Wichgers, District 83[296]
Wisconsin Senate[]
Municipal executive officials[]
Party officials[]
Current[]

- David Bossie, National Committeeman of the Republican National Committee in Maryland (2016–present)[220]
- Ronna McDaniel, Chairperson of the Republican National Committee (2017–present)[301][210]
- Kelli Ward, Chair of the Arizona Republican Party (2019–present)[302]
Former[]
- Saul Anuzis, Chair of the Michigan Republican Party (2005–2009)[220]
- Chad Connelly, Chair of the South Carolina Republican Party (2011–2013)[220]
- Ed Martin, Chair of the Missouri Republican Party (2013–2015)[220]
Trump's legal team[]
- Joseph diGenova, former United States Attorney for the District of Columbia (1983 to 1988)[303]
- Jenna Ellis, former deputy district attorney of Weld County, Colorado[304]
- Rudy Giuliani, former Mayor of New York City (1994-2001)[305]
Election officials[]
- Joyce Dombroski-Gebhardt, board of elections member, Pennsylvania[210]
- Joe Gale, board of elections member, Pennsylvania[210]
- Keith Gould, board of elections member, Pennsylvania[210]
- William Hartmann, electoral official, Michigan[210]
- Monica Palmer, electoral official, Michigan[210]
Military[]
- Joseph Anderson, U.S. Marine Corps Major General (1968–2001)[232]
- Donald Bolduc, U.S. Army Brigadier General (1981–2017)[232]
- Patrick Henry Brady, U.S. Army Major General (1959–1993) and Medal of Honor recipient[232]
- Edward Briggs, U.S. Navy Vice Admiral (1949–1984)[232]
- John Closner, U.S. Air Force Major General (1962–1996)[232]
- John Cotton, U.S. Navy Vice Admiral (1969–2008)[232]
- Timothy Ghormley, U.S. Marine Corps Major General (1967–2008)[232]
- William Hancock, U.S. Navy Vice Admiral (1965–1998)[232]
- Murray Hansen, U.S. Air Force Brigadier General (1987–2019)[232]
- Gary Harrell, U.S. Army Major General (1973–2008)[232]
- Henry Hatch, U.S. Army Lieutenant General (1957–1992) and Chief of Engineers (1988–1992)[232]
- Thomas Hayward, U.S. Navy Admiral (1942–1982) and Chief of Naval Operations (1978–1982)[232]
- Larry Hereth, U.S. Coast Guard Rear Admiral (1973–2007)[232]
- Gregory Horn, U.S. Navy Rear Admiral (1988–2013)[232]
- William James, U.S. Air Force Major General (1959–1993) and Director of the Defense Mapping Agency (1990–1993)[232]
- James Johnson, U.S. Army Lieutenant General (1960–1993)[232]
- Jerome Johnson, U.S. Navy Admiral (1956–1992) and Vice Chief of Naval Operations (1990–1992)[232]
- James Livingston, U.S. Marine Corps Major General (1962–1995) and Medal of Honor recipient[232]
- John Logeman, U.S. Air Force Major General (1961–1995)[232]
- Jarvis Lynch, U.S. Marine Corps Major General (1956–1991)[232]
- Ronald Magnum, U.S. Army Brigadier General (1969–2004)[232]
- Thomas McInerney, U.S. Air Force Lieutenant General (1959–1994)[232]
- James Mukoyama, U.S. Army Major General (1965–1995)[232]
- Raymund O'Mara, U.S. Air Force Major General (1963–1994) and Director of the Defense Mapping Agency (1993–1994)[232]
- Garry Parks, U.S. Marine Corps Lieutenant General (1969–2004)[232]
- Richard Secord, U.S. Air Force Major General (1955–1983)[232]
- Richard Severson, U.S. Air Force Brigadier General (1972–2008)[232]
- Perry Smith Sr, U.S. Army Major General (1973–2008) and Adjutant General of Alabama (2011–2017)[232]
- William Streeter, U.S. Army Major General (1959–1990)[232]
- Howard Thorsen, U.S. Coast Guard Vice Admiral (1955–1991)[232]
- Nils Thunman, U.S. Navy Vice Admiral (1954–1998)[232]
- William Thurman, U.S. Air Force Lieutenant General (1954–1988)[232]
- Robert Wetzel, U.S. Army Lieutenant General (1952–1986)[232]
- Paul Vallely, U.S. Army Major General (1961–1993)[232]
- Albert Zapanta, U.S. Army Major General (1964–1996)[232]
Others[]
- Kirstie Alley, American actress[306]
- Sharyl Attkisson, former CBS journalist[307]
- Maria Bartiromo, Fox Business host[308]
- Glenn Beck, founder of TheBlaze radio network[309]
- Dan Bongino, conservative commentator and radio host[310]
- L. Brent Bozell III, founder of Media Research Center[220]
- Patrick M. Byrne, former CEO of Overstock.com[311]
- Tucker Carlson, Fox News host[312]
- Kenneth Copeland, televangelist and megachurch pastor[313]
- Steven Crowder, conservative commentator and Fox News contributor[314]
- Loren Culp, 2020 Washington gubernatorial candidate[67]
- Diamond and Silk, Newsmax hosts[315]
- Lou Dobbs, former Fox Business host[308]
- Dinesh D'Souza, American author and filmmaker[316]
- Tom Fitton, president of Judicial Watch[317]
- Kimberly Guilfoyle, news anchor and Trump advisor[318]
- Greg Gutfeld, Fox News host[319]
- Sean Hannity, Fox News host[320]
- Pete Hegseth, Fox News host[321]
- Steve Hilton, Fox News commentator[322]
- Laura Ingraham, Fox News host[319]
- Alex Jones, political commentator and radio host[323]
- Gary Jones, President of the Louisiana Board of Elementary and Secondary Education (2017–present)[232]
- Andrew Klavan, Daily Wire conservative commentator and writer[324]
- Michael J. Knowles, Daily Wire conservative commentator[325]
- Tomi Lahren, political commentator and Fox News television host[326]
- Chris Langan, horse rancher and high IQ test scorer[327]
- Mark Levin, Fox News radio host[328]
- Rush Limbaugh, radio host[329]
- Mike Lindell, CEO of My Pillow[330]
- Jenny Beth Martin, co-founder of the Tea Party Patriots[220]
- James O'Keefe, founder of Project Veritas[331]
- Candace Owens, Daily Wire news pundit and conservative commentator[332]
- George Papadopoulos, Trump campaigner and official
- Frank Pavone, Catholic priest and anti-abortion activist[220]
- Katrina Pierson, Tea Party activist and spokesperson[333]
- Jeanine Pirro, Fox News host[308]
- Sidney Powell, former federal prosecutor[334]
- Pat Robertson, televangelist and Christian Broadcasting Network CEO[335]
- Rick Scarborough, former Southern Baptist pastor[220]
- Norm Shinkle, member, Michigan Board of Canvassers[210]
- Roger Stone, Trump campaigner[336]
- Dave Rubin, conservative commentator and podcaster[337]
- Christopher Ruddy, founder and CEO of Newsmax Media (Changed Position)[315]
- Enrique Tarrio, leader of the Proud Boys[338]
- Virginia Thomas, wife of Clarence Thomas[339]
- Donald Trump Jr., son of Donald Trump[41][42]
- Lara Trump, daughter in law of Donald Trump
- Eric Trump, son of Donald Trump[41][42]
- Jon Voight, American actor[340]
- Herschel Walker, former NFL player[341]
- Matt Walsh, Daily Wire conservative commentator[342]
- Jesse Watters, Fox News host[343]
- Ron Watkins, 8kun administrator[344][345]
- James Woods, American actor[346]
- L. Lin Wood,attorney[347]
See also[]
- Big lie – Gross distortion of the truth
- Attempts to overturn the 2020 United States presidential election
- Expulsion from the United States Congress
- International reactions to the 2020 United States presidential election
- List of Donald Trump 2020 presidential campaign endorsements
- List of federal political scandals in the United States
- List of former Trump administration officials who endorsed Joe Biden
- List of lawsuits involving Donald Trump
- List of Republicans who opposed the Donald Trump 2020 presidential campaign
- List of United States representatives expelled, censured, or reprimanded
- List of United States senators expelled or censured
- Stop the Steal
- Texas v. Pennsylvania
- Sedition Caucus
- Republican efforts to make voting laws more restrictive following the 2020 presidential election
References[]
- ^ McCarthy, Tom (December 25, 2020). "The Republican heroes and villains of Trump's attempt to steal the election - As Donald Trump peddled baseless claims of vote fraud after 3 November, democracy found out who its friends were". The Guardian. Archived from the original on December 25, 2020. Retrieved December 25, 2020.
- ^ Wilkie, Christina (November 4, 2020). "Trump tries to claim victory even as ballots are being counted in several states – NBC has not made a call". CNBC. Archived from the original on November 4, 2020. Retrieved November 4, 2020.
- ^ Bomey, Nathan (November 4, 2020). "Facebook, Twitter label Trump claims over 'stealing the election' as potentially misleading". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 5, 2020. Retrieved November 4, 2020.
- ^ Burns, Alexander; Martin, Jonathan (November 4, 2020). "As America Awaits a Winner, Trump Falsely Claims He Prevailed". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on November 4, 2020. Retrieved November 4, 2020.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Young, Ashley (September 23, 2016). "A Complete Guide To Early And Absentee Voting". Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Farley, Robert (April 10, 2020). "Trump's Latest Voter Fraud Misinformation". FactCheck.org. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved June 19, 2020.
- "Donald Trump suggests delay to 2020 US presidential election". BBC News. July 30, 2020. Archived from the original on July 30, 2020. Retrieved July 31, 2020.
- Morello, Carol (November 4, 2020). "European election observers decry Trump's 'baseless allegations' of voter fraud". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on November 5, 2020. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- Cillizza, Chris (May 26, 2020). "Here's the *real* reason Donald Trump is attacking mail-in ballots". CNN. Archived from the original on July 30, 2020. Retrieved June 29, 2020.
- Haberman, Maggie; Corasaniti, Nick; Qiu, Linda (June 24, 2020). "Trump's False Attacks on Voting by Mail Stir Broad Concern". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on July 29, 2020. Retrieved June 29, 2020.
- ^ Solender, Andrew. "126 House Republicans Now Support Lawsuit To Overturn Election in Updated Brief". Forbes. Archived from the original on December 12, 2020. Retrieved December 11, 2020.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Folley, Aris (December 13, 2020). "Majority in Fox News poll says Trump disputing results is weakening democracy". The Hill. Archived from the original on December 14, 2020. Retrieved December 13, 2020.
- "Quinnipiac Poll: 77% of Republicans believe there was widespread fraud in the presidential election; 60% overall consider Joe Biden's victory legitimate". Yahoo!. December 10, 2020. Archived from the original on December 14, 2020. Retrieved December 14, 2020.
- Enten, Harry (April 11, 2021). "Polls show majority of Republicans mistakenly think the 2020 election wasn't legitimate". CNN. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- "Over half of Republicans believe Donald Trump is the actual President of the United States". Ipsos. May 21, 2021. Archived from the original on May 22, 2021. Retrieved May 23, 2021.
- ^ Wines, Michael (February 27, 2021). "In Statehouses, Stolen-Election Myth Fuels a G.O.P. Drive to Rewrite Rules". The New York Times.
- ^ Kelly Mena. "More than 100 bills that would restrict voting are moving through state legislatures". CNN. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ Gardner, Amy (March 26, 2021). "After Trump tried to intervene in the 2020 vote, state Republicans are moving to take more control of elections". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Arizona GOP Bill Would Allow GOP-Controlled State Legislature to Strip Key Election Powers from Democratic Secretary of State". May 26, 2021.
- ^ Corasaniti, Nick (March 24, 2021). "Republicans Aim to Seize More Power Over How Elections Are Run". The New York Times.
- ^ "GOP lawmakers seek greater control over local elections". AP NEWS. April 20, 2021.
- ^ Reid, Tim; Layne, Nathan; Lange, Jason (September 22, 2021). "Special Report: Backers of Trump's false fraud claims seek to control next elections". Reuters – via www.reuters.com.
- ^ Epstein, Reid J. (November 19, 2021). "Wisconsin Republicans Push to Take Over the State's Elections". The New York Times.
- ^ Amy Gardner; Tom Hamburger; Josh Dawsey (November 29, 2021). "Trump allies work to place supporters in key election posts across the country, spurring fears about future vote challenges". The Washington Post.
- ^ Jeremy Herb, Phil Mattingly and Lauren Fox. "GOP senator to delay affirming Biden victory". CNN. Archived from the original on January 8, 2021. Retrieved December 30, 2020.
- ^ Wagner, John. "Sen. Hawley announces he will contest certification of electoral college vote". Archived from the original on January 15, 2021. Retrieved December 30, 2020 – via www.washingtonpost.com.
- ^ Broadwater, Luke (January 2, 2021). "Pence Welcomes Futile Bid by G.O.P. Lawmakers to Overturn Election". The New York Times. Archived from the original on January 2, 2021. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ Karni, Annie (January 4, 2021). "Pence's Choice: Side With the Constitution or His Boss". The New York Times. Archived from the original on January 5, 2021. Retrieved January 5, 2021.
- ^ Jalonick, Mary Clare (January 3, 2021). "EXPLAINER: How Congress will count Electoral College votes". Associated Press. Archived from the original on January 9, 2021. Retrieved January 5, 2021.
- ^ "Read: Vice President Mike Pence's statement breaking with Trump on Electoral College vote count". CNN. Archived from the original on January 7, 2021. Retrieved January 8, 2021.
- ^ "Congress Affirms Biden As President After Completing Electoral Vote Count". YouTube. MSNBC. Archived from the original on January 18, 2021. Retrieved September 17, 2021.
- ^ Kevin Liptak, Veronica Stracqualursi and Allie Malloy. "Trump publicly acknowledges he won't serve a second term day after inciting mob". CNN. Archived from the original on January 7, 2021. Retrieved January 8, 2021.
- ^ Riccardi, Nicholas (December 29, 2021). "'Slow-motion insurrection': How GOP seizes election power". Associated Press.
- ^ a b Farivar, Masood (November 6, 2020). "Trump's Claims of Voter Fraud Draw Criticism from Both Parties". Voice of America. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f Perkins, Tom (November 6, 2020). "Donald Trump's baseless vote fraud claim opens cracks in Republican ranks". The Guardian. Archived from the original on November 6, 2020. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Daly, Matthew (November 6, 2020). "GOP divided over Trump's baseless claims of election fraud". Associated Press. Archived from the original on November 6, 2020. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Hayes, Christal (November 5, 2020). "'This is getting insane': Republicans say Trump's attacks on election integrity are dangerous". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 6, 2020. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Everett, Burgess; Zanona, Melanie (November 6, 2020). "GOP begins pushing back against Trump's false election claims". Politico. Archived from the original on November 6, 2020. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- ^ a b c Gregorian, Dareh (November 6, 2020). "'This is getting insane': Republicans push back against Trump's false election claims". NBC News. Archived from the original on November 6, 2020. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Crowley, Michael (November 6, 2020). "Trump's False Election Fraud Claims Split Republicans". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Shepherd, Katie (November 6, 2020). "GOP splits over Trump's false election claims, unfounded fraud allegations". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e "Republicans react to Trump's election fraud claims". Reuters. November 6, 2020. Archived from the original on November 7, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b c Daly, Matthew (November 5, 2020). "Some in GOP break with Trump over baseless vote-fraud claims". Star Tribune. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b Scarborough, Charles Joseph (December 1, 2020). "Morning Joe" (Interview). Interviewed by Scarborough, Mika Emilie Leonia Brzezinski. MSNBC.
Just so people who think this, to call this a coup is hyperbolic, or an attempted coup, you just look at the definition in Wikipedia: it says, "Typically, it's an illegal, unconstitutional attempt to seize power by a political faction". Definition of a coup. Of course, if he's already in power, it'd be an "autocoup". But at the same time, you look at the definition, and if... I guess I would just say to Trump defenders, if it's not an attempted coup, if it's not an "illegal unconstitutional attempt to seize power by a political faction" when he's trying to call people to the White House to get them to change their votes, trying to call the Governor of Arizona to try to stop him from doing legally what he has to do which is to certify the election results, trying to get those in Michigan and Wayne County to illegally not certify the votes there... if Republicans don't think it's a coup or doesn't fit this definition of a coup in all four corners then I'd love to hear what they would call it.
- ^ Timm, Jane C. (April 10, 2020). "Trump pushes false claims about mail-in vote fraud. Here are the facts". NBC News. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 9, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Lizza, Ryan (November 3, 2020). "Republicans publicly silent, privately disgusted by Trump's election threats". Politico. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b c Petrillo, Matt (November 4, 2020). "Trump Campaign Says It's Suing To Stop Pennsylvania's Vote Count Over Lack Of 'Transparency'". CBS Philly. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ Argos, Greg (November 4, 2020). "Trump Campaign Declaring Pennsylvania Win For President Despite Hundreds Of Thousands Of Outstanding Ballots". CBS Philly. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Jackson, Hallie; Smith, Shep (November 5, 2020). "There's silence in the Republican Party after Donald Trump's press conference, except for a few". CNBC. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f "US results: Trump sons attack Republicans for 'weak' backing". BBC News. November 6, 2020. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ Cowan, Richard (November 6, 2020). "U.S. Republicans divided over Trump's election-fraud claims". Reuters. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f Luscombe, Richard (November 7, 2020). "After Trump: first shots fired in battle for Republican party's future". The Guardian. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ Grayer, Annie (March 19, 2021). "McCarthy tries to rewrite history by claiming that he didn't back Trump's efforts to overturn the election". CNN.
- ^ Krueger, Hanna (November 7, 2020). "Trump's next move? He declares he'll sue but grounds are still unclear". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c Smith, Allan (November 7, 2020). "Democrats congratulate Biden; many Republicans haven't extended their hands". NBC News. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ Dennis, Steven T. (November 7, 2020). "GOP's silence leaves Trump raging mostly alone". BNN Bloomberg. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ Solender, Andrew (November 7, 2020). "President-Elect Biden, Long A Bridge-Builder, Congratulated By Prominent Republicans". Forbes. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c Elbeshbishi, Sarah (November 7, 2020). "GOP Rep. Dan Crenshaw tells Marjorie Taylor Greene to 'start acting like a member of Congress'". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c d Bradner, Eric (November 8, 2020). "Bush congratulates Biden, says election was 'fundamentally fair' and 'its outcome is clear'". CNN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b Baker, Peter (November 8, 2020). "George W. Bush congratulates Biden on his victory". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b Subramanian, Courtney; Collins, Michael (November 8, 2020). "Former President George W. Bush extends 'warm congratulations' to President-elect Joe Biden". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g Solender, Andrew (November 8, 2020). "These Are The Republicans Who Have Acknowledged Biden's Victory". Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c Zappone, Chris (November 8, 2020). "Chris Christie on Trump's election claim: if 'there was voter fraud, then show us'". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ Collins, Kaitlan; Bennett, Kate; Diamond, Jeremy; Liptak, Kevin (November 8, 2020). "Jared Kushner, Melania Trump advise Trump to accept election loss". CNN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 9, 2020.
- ^ a b Burns, Katelyn (November 8, 2020). "GOP lawmakers are refusing to acknowledge the reality that Biden won the election". Vox. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 9, 2020.
- ^ Long, Colleen; Miller, Zeke (November 9, 2020). "Fraud claims aimed in part at keeping Trump base loyal". Associated Press. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 9, 2020.
- ^ a b Gardner, Amy; Parker, Ashley; Dawsey, Josh; Brown, Emma (November 10, 2020). "Top Republicans back Trump's efforts to challenge election results". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
Mr. McConnell and many other Republicans were keeping alive the possibility that Mr. Trump might have legitimate claims. Their approaches were consistent with the way Republicans in Congress have handled Mr. Trump for the last four years, declining to explicitly challenge or contradict the president's false claims, without necessarily echoing them either.
- ^ a b Kim, John (April 16, 2019). "ED-2 vs. ED-2.1 vs ED-2.2". dx.doi.org. doi:10.5194/gmd-2019-45-sc1. S2CID 242160626. Retrieved February 21, 2021.
- ^ Foran, Clare; Raju, Manu; Barrett, Ted (November 10, 2020). "Top Republicans skeptical court challenges will change election, even as many defend Trump". CNN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ Gittleson, Ben (November 9, 2020). "Trump's White House largely silent as he refuses to concede". ABC News. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 9, 2020.
- ^ a b Duster, Chandelis (November 9, 2020). "Georgia GOP lieutenant governor says 'no credible examples' of voter fraud". KTEN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 9, 2020.
- ^ a b Chalfant, Morgan (November 9, 2020). "Fox cuts away from McEnany press conference". The Hill. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ Perez, Evan (November 10, 2020). "DOJ's top election crimes prosecutor quits in protest after Barr tells federal attorneys to probe unsupported allegations of voting irregularities". CNN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Jarvie, Jenny; Mehta, Seema (November 9, 2020). "'Hoaxes and nonsense': GOP election officials in Georgia reject Trump's unfounded fraud claims". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Corasaniti, Nick; Epstein, Reid J.; Rutenberg, Jim (November 10, 2020). "The Times Called Officials in Every State: No Evidence of Voter Fraud". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 12, 2020.
- ^ a b c Gaouette, Nicole; Hansler, Jennifer; Atwood, Kylie (November 10, 2020). "Pompeo refuses to acknowledge Biden has won election, sparking furor and 'disgust' among diplomats". CNN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ a b Blitzer, Wolf (November 10, 2020). "Mike Pompeo 'has eviscerated his credibility': Bolton". CNN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ "Senator: Some Republicans are privately acknowledging Biden's win". CNN. November 10, 2020. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ a b Mangan, Dan (November 11, 2020). "'Very, highly unlikely' Trump wins Arizona, no evidence of fraud, Republican state attorney general says". CNBC. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 11, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Luscombe, Richard; Greve, Joan E (November 11, 2020). "Pressure builds on Trump to concede as Biden pushes ahead with transition plan". The Guardian. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 12, 2020.
- ^ a b DeCiccio, Emily (November 11, 2020). "Former Bush chief of staff cites 9/11 Commission, warns about slow transition". CNBC. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 14, 2020.
- ^ a b Goldmacher, Shane; Cochrane, Emily (November 12, 2020). "Small Cracks Emerge in G.O.P. Support for Trump's Baseless Fraud Claims". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ Main, Alison; Kelly, Caroline (November 11, 2020). "Republican senator says he will step in if Biden doesn't have access to intelligence briefings by Friday". CNN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 12, 2020.
- ^ a b c Geller, Eric; Bertrand, Natasha (November 12, 2020). "Top cyber official expecting to be fired as White House frustrations hit agency protecting elections". Politico. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ a b Kaitlan Collins; Paul LeBlanc. "Trump fires director of Homeland Security agency who had rejected President's election conspiracy theories". CNN. Archived from the original on November 18, 2020. Retrieved November 18, 2020.
- ^ a b Al-Arshani, Sarah (November 12, 2020). "The Department of Homeland Security breaks from Trump and his baseless claims of election fraud, calling this year's presidential race 'the most secure in American history'". Business Insider. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ Sanger, David E. (November 18, 2020). "Trump fires Christopher Krebs, whose agency disputed president's false claims of election fraud". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on November 18, 2020. Retrieved November 18, 2020.
- ^ a b Peoples, Steve; Mascaro, Lisa; McCormack, Kathy (November 12, 2020). "Sununu on board with Biden's win, calling him the president-elect". Concord Monitor. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 12, 2020.
- ^ a b Greve, Joan E. (November 12, 2020). "Nancy Pelosi tells Republicans to 'stop the circus' as Trump still refuses to concede – live". The Guardian. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 12, 2020.
- ^ Bertrand, Natasha (November 12, 2020). "Ex-national security officials warn of risks in Biden transition delay". Politico. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2020.
- ^ Mangan, Dan; Breuninger, Kevin (November 13, 2020). "Trump strikes out in Arizona, Michigan, Pennsylvania ballot challenges, Biden's lead more secure". CNBC. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ Abrams, Rachel; Enrich, David; Silver-Greenberg, Jessica (November 13, 2020). "Once Loyal to Trump, Law Firms Pull Back From His Election Fight". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ Smith, David (November 13, 2020). "Trump comes close to admitting defeat but stops short of formal concession". The Guardian. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 14, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f Behrmann, Savannah (November 14, 2020). "Trump says the battleground states saw election fraud. Republican officials running those states disagree". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2020.
- ^ a b Pengelly, Martin (November 15, 2020). "Trump tweets that Biden 'won' – but repeats baseless vote fraud claim". The Guardian. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 16, 2020.
- ^ a b c Quinn, Melissa; Segers, Grace (November 19, 2020). "Biden says Trump delay on transition is 'hard to fathom'". CBS News. Archived from the original on November 20, 2020. Retrieved November 20, 2020.
- ^ Forgey, Quint; Isenstadt, Alex (November 19, 2020). "Giuliani and fellow Trump lawyers crank out conspiracies as legal challenges implode". Politico. Archived from the original on November 22, 2020. Retrieved November 23, 2020.
- ^ Peters, Jeremy W.; Feuer, Alan (November 23, 2020). "What We Know About Sidney Powell, the Lawyer Behind Wild Voting Conspiracy Theories". The New York Times.
- ^ McCarthy, Andrew C. (November 23, 2020). "About That 'Broken Algorithm'". National Review.
- ^ Subramaniam, Tara; Lybrand, Holmes (November 20, 2020). "Fact-checking Giuliani and the Trump legal team's wild, fact-free press conference". CNN. Archived from the original on November 23, 2020. Retrieved November 23, 2020.
- ^ a b Peters, Jeremy W. (November 20, 2020). "Tucker Carlson Dared Question a Trump Lawyer. The Backlash Was Quick". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 21, 2020. Retrieved November 23, 2020.
- ^ Schorr, Isaac (November 22, 2020). "Sidney Powell Dropped from Trump Team". National Review.
- ^ a b c Kirby, Jen (November 23, 2020). "The presidential transition begins as the GSA formally recognizes Biden's victory". Vox. Archived from the original on November 24, 2020. Retrieved November 24, 2020.
- ^ Holmes, Kristen; Herb, Jeremy (November 24, 2020). "First on CNN: Key government agency acknowledges Biden's win and begins formal transition". CNN. Archived from the original on January 19, 2021. Retrieved November 24, 2020.
- ^ Solender, Andrew (November 23, 2020). "These Are The Republicans Who Have Acknowledged Biden's Victory". Forbes. Retrieved December 1, 2020.
- ^ "Just 27 congressional Republicans acknowledge Biden's win, Washington Post survey finds". The Washington Post. 2020. Archived from the original on December 5, 2020. Retrieved December 5, 2020.
- ^ "17 states and Trump join Texas request for Supreme Court to overturn Biden wins in four states". Dallas News. December 10, 2020. Archived from the original on December 9, 2020. Retrieved January 16, 2021.
- ^ Liptak, Adam (December 8, 2020). "Texas files an audacious suit with the Supreme Court challenging the election results". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on December 9, 2020. Retrieved January 16, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Miller, Dave. "GA Senators applaud Texas election challenge". www.walb.com. Retrieved January 16, 2021.
- ^ Ferris, Sarah (December 8, 2020). "GOP leaders block measure affirming Biden as president-elect". Politico. Retrieved December 8, 2020.
- ^ Fox, Lauren, Manu Raju and Daniella Diaz (December 8, 2020). "GOP leadership rejects resolution acknowledging Biden as President-elect". CNN. Retrieved December 8, 2020.
- ^ Samuels, Brett. "Stephen Miller: 'Alternate' electors will keep Trump election challenge alive". The Hill. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
- ^ Pierce, Charles P. (December 14, 2020). "The Electoral College Isn't Festival Seating". Esquire. Retrieved December 17, 2020.
- ^ "'Time for everybody to move on': Senate GOP accepts Biden's win". POLITICO. Retrieved December 15, 2020.
- ^ Zaslav, Ali; Raju, Manu; Barrett, Ted (December 15, 2020). "McConnell for the first time recognizes Biden as President-elect". CNN. Archived from the original on December 15, 2020. Retrieved December 15, 2020.
- ^ Brockell, Gillian (January 5, 2021). "The senators who were expelled after refusing to accept Lincoln's election". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 5, 2021. Retrieved January 5, 2021.
- ^ Sonmez, Felicia (December 20, 2020). "Trump says he spoke with Sen.-elect Tuberville, who has hinted at backing electoral college challenge next month". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 7, 2021. Retrieved December 25, 2020.
- ^ Kim, Seung Min; Dawsey, Josh; Olorunnipa, Toluse (December 22, 2020). "Republicans plunge into open battle over attempts to overturn Trump's loss to Biden". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 25, 2020.
- ^ Itkowitz, Colby; Dawsey, Josh (December 24, 2020). "Pence under pressure as the final step nears in formalizing Biden's win". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 25, 2020.
- ^ Colarossi, Natalie (December 26, 2020). "GOP Lawmaker Accuses Trump and 'Grifters' of Pushing Electoral Challenge to Raise Funds". Newsweek. Retrieved December 26, 2020.
- ^ Cheney, Kyle. "Gohmert suit may force Pence's hand in effort to overturn Trump's defeat". POLITICO. Archived from the original on December 30, 2020. Retrieved January 1, 2021.
- ^ Breuninger, Kevin (December 28, 2020). "Congressman, other Republicans sue Vice President Pence in last-ditch effort to overturn Biden win". CNBC. Archived from the original on December 30, 2020. Retrieved January 1, 2021.
- ^ Helderman, Rosalind S.; Wagner, John (December 31, 2020). "Pence seeks rejection of lawsuit that aimed to expand his power to overturn the election". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on December 31, 2020. Retrieved January 1, 2021.
- ^ Barrett, Devlin (January 1, 2021). "Gohmert court filing claims Pence is not a 'glorified envelope-opener'". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 6, 2021. Retrieved January 1, 2021.
- ^ "Dismissal" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 6, 2021. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Edmondson, Catie; Haberman, Maggie (January 1, 2021). "Federal Judge Dismisses Election Lawsuit Against Pence - President Trump's congressional allies had hoped to give the vice president the power to reject electoral votes that were cast for Joseph R. Biden Jr". The New York Times. Archived from the original on January 2, 2021. Retrieved January 2, 2021.
- ^ Barrett, Devlin (January 1, 2021). "Judge dismisses Gohmert lawsuit seeking to stymie Biden electoral college count". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 6, 2021. Retrieved January 2, 2021.
- ^ "Gohmert v. Pence - Notice of Appeal — Document #39". Court Listener. Archived from the original on January 15, 2021. Retrieved January 2, 2021.
- ^ Vella, Lauren (January 2, 2021). "Appeals court dismisses Gohmert's election suit against Pence". The Hill. Archived from the original on January 3, 2021. Retrieved January 2, 2021.
- ^ Alba, Davey (January 6, 2021). "Watch out for this misinformation when Congress meets to certify the election". The New York Times.
- ^ Canipe, Chris (February 4, 2021). "The Republicans who voted to overturn the election". Reuters.
- ^ Corn, David (February 23, 2021). "Josh Hawley Is Fundraising Off Lies About the Big Lie". Mother Jones.
- ^ Sprunt, Barbara (December 8, 2020). "Supreme Court Rejects GOP Bid To Reverse Pennsylvania Election Results". NPR.
- ^ Naranjo, Jesse (February 21, 2021). "Rep. Scalise: Don't pinpoint blame on Trump". Politico.
- ^ "No. 2 House Republican refuses to say election wasn't stolen". PBS NewsHour. October 10, 2021. Retrieved October 11, 2021.
- ^ Meyer, Ken (February 21, 2021). "ABC's Jon Karl Repeatedly Grills Steve Scalise: Does Trump Bear Responsibility for Capitol Riots?". Mediaite.
- ^ Broadwater, Luke (January 2, 2021). "Pence Welcomes Bid to Overturn Biden's Election as Republican Senators Join - The vice president's office said he welcomed the efforts of a group of Republican lawmakers who plan to object to the outcome of the election". The New York Times. Archived from the original on January 2, 2021. Retrieved January 2, 2021.
- ^ Uhrmacher, Kevin; Muyskens, John (January 5, 2021). "Where Senate Republicans stand on counting the electoral college vote". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 11, 2021. Retrieved January 5, 2021.
- ^ a b Scherer, Michael (January 11, 2021). "'War for the soul': Capitol riot elevates GOP power struggle between pro-Trump conspiracy theorists and party establishment". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Williams, Jordan (January 14, 2021). "Cindy McCain on possible GOP censure: 'I think I'm going to make T-shirts'". TheHill. Retrieved January 15, 2021.
- ^ Bendery, Jennifer (January 12, 2021). "GOP Rep. Elise Stefanik Loses Harvard Post For Lying About Election Fraud". HuffPost. Retrieved January 13, 2021.
- ^ Karanth, Sanjana (January 17, 2021). "Twitter Temporarily Suspends QAnon Rep. For Election Disinformation, Inciting Violence". HuffPost. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ Dean, Jessica; Kelly, Caroline (February 2, 2021). "McConnell: Marjorie Taylor Greene's views are a 'cancer' for the GOP". CNN. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- ^ Dale, Daniel (June 12, 2021). "Trump is doing more lying about the election than talking about any other subject". CNN. Archived from the original on June 16, 2021. Similar graphic in source attributed to Janie Boschma, CNN.
- ^ Scherer, Michael (May 25, 2021). "Nevada GOP thrown into turmoil after avowed Proud Boys member said he participated in censure vote of state official". Washington Post. Retrieved May 26, 2021.
- ^ Janfaza, Rachel; Hackney, Deanna (June 5, 2021). "Kemp booed and Raffensperger censured at Georgia GOP convention". CNN. Retrieved June 6, 2021.
- ^ Schnell, Mychael (May 10, 2021). "Republican says 'embarrassing' Arizona recount 'makes us look like idiots'". TheHill.
- ^ The great bamboo hunt: Arizona's bizarre vote-examination effort gets more bizarre
- ^ "Inside Arizona's election audit, GOP fraud fantasies live on". AP NEWS. May 10, 2021.
- ^ Fifield, Jen. "Maricopa County Sheriff Paul Penzone blasts Arizona Senate's election audit demand as a risk to law enforcement". The Arizona Republic.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Neff, Terri Jo (May 13, 2021). "Deleted Election Files And Ballot Handling Concerns Prompt Senate President To Beckon Maricopa County Officials To State Capitol".
- "Republican Arizona election official says Trump "unhinged"". AP NEWS. May 16, 2021.
- Roberts, Laurie. "Trump says Arizona auditors have found 'unbelievable election crime'? This is nonsense". The Arizona Republic.
- ^ Fifield, Jen. "Maricopa County supervisors holding meeting Monday to refute election auditors' claims". The Arizona Republic.
- ^ Bump, Philip (May 17, 2021). "The fight that encapsulates the GOP's struggle is happening in Arizona, not Washington". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Arizona Republicans fight back against election fraud claims". Star Tribune.
- ^ Wines, Michael (May 17, 2021). "Arizona G.O.P. Is Split on Vote Review: 'We Can't Indulge These Insane Lies'". The New York Times.
- ^ Shabad, Rebecca (May 7, 2021). "Sen. Lindsey Graham says the GOP can't move forward without Trump". NBC News. Retrieved May 18, 2021.
- ^ a b Dicker, Ron (May 18, 2021). "Lindsey Graham: 'I Accept The Results Of The Election'". HuffPost. Retrieved May 18, 2021.
- ^ "Judge rules Fulton County absentee ballots to be unsealed, reviewed after fraud claims". NBC News. May 21, 2021.
- ^ Eric Bradner (May 24, 2021). "Arizona and Georgia audits move forward as Republicans continue to push election fraud lies". CNN.
- ^ Epstein, Reid J.; Corasaniti, Nick (May 24, 2021). "Long After Trump's Loss, a Push to Inspect Ballots Persists". The New York Times.
- ^ Parks, Miles (January 4, 2022). "Here's where election-denying candidates are running to control voting". NPR.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Block, Melissa (December 23, 2021). "The clear and present danger of Trump's enduring 'Big Lie'". National Public Radio. Retrieved December 23, 2021.
- Corasaniti, Nick (March 24, 2021). "Republicans Aim to Seize More Power Over How Elections Are Run". The New York Times.
- Tim Reid; Nathan Layne; Jason Lange. "Special Report: Backers of Trump's false fraud claims seek to control next elections". September 22, 2021. Reuters.
- Epstein, Reid J. (November 9, 2021). "Wisconsin Republicans Push to Take Over the State's Elections". The New York Times.
- Amy Gardner; Tom Hamburger; Josh Dawsey (November 29, 2021). "Trump allies work to place supporters in key election posts across the country, spurring fears about future vote challenges". The Washington Post.
- Collinson, Stephen (September 16, 2021). "Trump's Big Lie is changing the face of American politics". CNN.
- Graziosi, Graig (December 21, 2021). "'Evil takes no breaks': Warnings as Steve Bannon vows to take over America's entire 'election apparatus'". The Independent.
- ^ a b Segers, Grace. "White House chief of staff Mark Meadows contradicts FBI Director Christopher Wray on voter fraud". CBS News. Retrieved January 10, 2021.
- ^ Solender, Andrew. "Ohio Congressman Is Latest Republican To Acknowledge Biden's Victory – The Full List". Forbes. Archived from the original on December 7, 2020. Retrieved December 8, 2020.
- ^ Williams, Jordan. "James Baker says White House should stop trying to end vote counting". Archived from the original on November 16, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Solender, Andrew (November 13, 2020). "Ex-Trump Intelligence Chief Dan Coats Among 20 New Republicans Calling Biden President-Elect". Forbes. Archived from the original on November 13, 2020. Retrieved November 21, 2020.
- ^ a b Priggge, Matt (January 4, 2021). "Dick Cheney, Donald Rumsfeld, And More Did Not Mince Words When They Demanded Trump Finally Admit He Lost The Election". uproxx.com.
- ^ Cillizza, Chris (January 7, 2022). "Analysis: Dick Cheney just spoke a hard truth to his fellow Republicans about January 6". CNN. Retrieved January 8, 2022.
- ^ Castronuovo, Celine. "Comey: 'Republican Party has to be burned to the ground'". msn.com. Archived from the original on January 23, 2021. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- ^ McLaughlin, Jenna. "CIA's Gina Haspel, who quietly resisted some Trump moves, outlasted many in administration". news.yahoo.com. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac Garrison, Joey. "31 former GOP House members urge Donald Trump to accept Joe Biden election win". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 20, 2020. Retrieved November 17, 2020.
- ^ Fuchs, Hailey; Delkic, Melina; Cameron, Chris (November 15, 2020). "Presidential Transition: As More Republicans Break With Trump, He Refuses to Budge". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2020.
- ^ Painter, Richard; Finkelstein, Claire (November 24, 2020). "Senate Republicans' Georgia bullying failed. But Lindsey Graham's ethics violations stand out". NBC News. Archived from the original on November 25, 2020. Retrieved November 25, 2020.
- ^ Coleman, Justine (November 9, 2020). "Former Vice President Dan Quayle: It is time for Trump to 'move on'". The Hill. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ Langlois, Shawn (November 9, 2020). "Condoleezza Rice calls for 'respect' and 'empathy' from both sides – and gets the exact opposite". MarketWatch. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ Benner, Katie (January 25, 2021). "The Justice Dept.'s inspector general opens an investigation into any efforts to overturn the election". The New York Times. Archived from the original on January 28, 2021. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- ^ Diamond, Jeremy. "Trump friend and adviser Steve Schwarzman recognizes Biden as President-elect". CNN. Retrieved December 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c Olson, Tyler (December 11, 2020). "Supreme Court declines to hear Trump-supported Texas case over election results in four other states". foxnews.com. Archived from the original on January 23, 2021. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ Cassidy, Bill. "With Michigan's certifying it's results, Joe Biden has over 270 electoral college votes. President Trump's legal team has not presented evidence of the massive fraud which would have had to be present to overturn the election. I voted for President Trump but Joe Biden won. (1/2)". Archived from the original on November 23, 2020. Retrieved November 23, 2020 – via Twitter.
- ^ Kane, Paul (December 5, 2020). "220 congressional Republicans won't say whether Biden or Trump won the election, Washington Post survey finds". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on December 5, 2020. Retrieved December 13, 2020.
- ^ Cillizza, Chris (January 10, 2022). "Analysis: This Republican senator just admitted the 2020 election wasn't rigged". CNN. Retrieved January 10, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Chang, Alvin (January 7, 2021). "The long list of Republicans who voted to reject election results". theguardian.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2021. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ a b "Santorum: 'Shocking' to hear Trump say these things". CNN. November 6, 2020. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- ^ "GOP's silence leaves Trump raging mostly alone". BNN. November 7, 2020. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ "Republicans who have broken with Trump to congratulate Biden on his win". NBC News. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 11, 2020.
- ^ Janfaza, Rachel (July 22, 2021). "Bob Dole says he's still 'a Trumper' but 'sort of Trumped out'". CNN. Retrieved December 6, 2021.
- ^ "NAB Head, Former Senator Calls For Trump To Concede". the HOT List. November 8, 2020.
- ^ "Congratulations to @JoeBiden and @KamalaHarris. The President-elect's speech reflects the opportunity we now have to heal our nation. We can also celebrate the historic election of VP-elect Kamala Harris who has proven there are no boundaries to what is possible for all women". Archived from the original on November 29, 2020. Retrieved December 12, 2020 – via Twitter.
- ^ a b Hayes, Christal. "Paul Ryan excoriates planned GOP effort to challenge Biden's Electoral College win as 'anti-democratic and anti-conservative'". USA Today. Archived from the original on January 3, 2021. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ a b Romboy, Dennis (November 9, 2020). "Utah AG Sean Reyes gives statement after volunteering in Nevada to review election results". KSL.com. Deseret Digital Media. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ Rowland, Darrel (December 13, 2020). "Capitol Insider: Just two of Ohio's 13 Republicans in Congress will publicly say that Joe Biden won election". The Columbus Dispatch.
- ^ Jarvis, Jacob (November 17, 2020). "The Republicans calling on Trump to concede, congratulating Biden". Newsweek. Archived from the original on November 19, 2020. Retrieved November 19, 2020.
- ^ "Katko responds to Trump's election claims: 'There has been no evidence of fraud'". syracuse. November 6, 2020. Archived from the original on December 3, 2020. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
- ^ https://www.thestate.com/news/politics-government/article248343115.html
- ^ "Mariannette Miller-Meeks says she didn't agree to letter calling for investigation of presidential election". The Gazette. Archived from the original on December 17, 2020. Retrieved December 17, 2020.
- ^ a b c Fandos, Nicholas; Edmonson, Catie (November 19, 2020). "'Absolutely outrageous.' Joni Ernst bristles at Trump team's groundless claims about election results". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 22, 2020. Retrieved November 20, 2020.
- ^ "While Trump Clings to Power, Justin Amash Has Left the Building". January 4, 2021.
- ^ "Colorado leaders react to projections of Biden-Harris election win". KUSA.com. November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b c Via y Rada, Nicole (November 10, 2020). "Republicans who have broken with Trump to congratulate Biden on his win". NBC News. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ Harvey, Josephine (August 31, 2021). "Paul Ryan Says It's 'Really Clear' Biden Won The Election: 'It Was Not Rigged'". HuffPost. Retrieved September 1, 2021.
- ^ Cummings, William (July 11, 2017). "'Morning Joe' Scarborough is leaving the Republican Party". USA Today. Archived from the original on June 12, 2020. Retrieved December 11, 2020.
- ^ "Trump-Appointed Judges Balk at President's Efforts to Overturn Election". Voice of America. Archived from the original on December 30, 2020. Retrieved December 4, 2020.
- ^ Hals, Jan Wolfe, Tom (November 23, 2020). "U.S. judge calls Trump claim challenging Biden win in Pennsylvania 'Frankenstein's Monster'". Reuters. Archived from the original on December 12, 2020. Retrieved December 18, 2020 – via www.reuters.com.
- ^ "Federal judge casts doubt on Trump's Wisconsin lawsuit". AP NEWS. December 10, 2020. Archived from the original on December 30, 2020. Retrieved December 18, 2020.
- ^ Greenwood, Max (December 30, 2020). "Trump calls on Georgia Gov. Kemp to resign". thehill.com. Archived from the original on January 27, 2021. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ Rojas, Rick; Robertson, Campbell; Wright, Will (November 18, 2020). "Many G.O.P. Governors Avoid Stating Plainly That Biden Won". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 20, 2020. Retrieved November 21, 2020.
- ^ a b "Torres congratulates Biden, thanks Trump". Saipan Tribune. November 9, 2020. Retrieved November 17, 2020.
- ^ Reston, Maeve (November 6, 2021). "Chris Christie delivers tough message to Republican audience, saying GOP gains hinge on moving on from 2020". CNN. Retrieved November 7, 2021.
- ^ "Wanda Vázquez congratulates Biden and demands statehood – PR Headline News". puertoricoheadlinenews.com. Archived from the original on January 9, 2021. Retrieved December 6, 2020.
- ^ "Former SC Gov. Sanford calls on Republicans to condemn Trump's 'dangerous cling to power'". abcnews4.com. November 12, 2020.
- ^ Schwarzenegger, Arnold (January 5, 2021). "Judgment Day: Arnold Schwarzenegger on why Republicans must stop Trump". The Economist. Archived from the original on January 5, 2021. Retrieved January 5, 2021.
- ^ Brooks, James (November 18, 2020). "Lt. Gov. Meyer says no fraud found in election but he will seek an audit of voting on Ballot Measure 2 to reassure Alaskans". Anchorage Daily News. Archived from the original on November 20, 2020. Retrieved November 21, 2020.
- ^ Dwyer, Dialynn (November 4, 2020). "Charlie Baker, Karyn Polito issue statement on presidential election". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2020.
- ^ Shwe, Elizabeth (November 10, 2020). "Leading Md. Republicans Largely Align With Trump on Election Outcome". Maryland Matters. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2020.
- ^ Columnist, Star-Ledger Guest (November 22, 2020). "GOP's Guadagno: It's time for Trump to move on | Opinion". nj. Archived from the original on December 9, 2020. Retrieved December 8, 2020.
- ^ a b Siegel, Benjamin (November 7, 2020). "Pennsylvania Republicans leaders dismiss Trump fraud claims, but call for audit". ABC News. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ "Trump GOP in New Jersey won't have moderate run for governor". Northjersey.com. December 10, 2020. Archived from the original on December 28, 2020. Retrieved December 13, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k McCarthy, Tom (December 25, 2020). "The Republican heroes and villains of Trump's attempt to steal the election". Archived from the original on December 25, 2020. Retrieved December 25, 2020 – via www.theguardian.com.
- ^ "Fox News host confronts GOP chair over fraud allegations: "It doesn't pan out"". Newsweek. November 6, 2020.
- ^ a b Mastrangelo, Dominick (November 7, 2020). "Cindy, Meghan McCain celebrate Biden win". The Hill. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 9, 2020.
- ^ Mastrangelo, Dominick. "Meghan McCain responds to Katie Couric: 'I don't need to be deprogrammed'". msn.com. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved January 26, 2021.
- ^ "Pollster Frank Luntz: Trump's 'Big Lie' is working, may cost GOP votes". MSN.
- ^ Stracqualursi, Veronica (January 8, 2021). "Former Trump communications director says President lied about 2020 election and should consider resigning". CNN. Retrieved December 20, 2021.
- ^ Imlay, Ashley (November 7, 2020). "Utah leaders share hope of 'healing wounds' after Joe Biden wins presidential race". Deseret News. Archived from the original on November 14, 2020. Retrieved November 17, 2020.
- ^ Dean, Grace (November 10, 2020). "Facebook shut down a network of Steve Bannon-linked pages for spreading election misinformation – but unlike Twitter, it hasn't banned Trump's former chief strategist". Business Insider. Archived from the original on November 10, 2020. Retrieved November 28, 2020.
- ^ Cobler, Paul (September 4, 2020). "AG Barr's claim of 1,700 fraudulent ballots in 2017 Dallas City Council race not true, prosecutor says". dallasnews.com.
- ^ "Trump is said to be livid at Barr, with one official suggesting termination possible". washingtonpost.com.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "Conservatives Call on State Legislators to Appoint New Electors, in Accordance with the Constitution". Conservative Action Project. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ Benner, Katie (January 25, 2021). "The Justice Dept.'s inspector general opens an investigation into any efforts to overturn the election". The New York Times. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- ^ Woodward, Alex (November 25, 2020). "Trump adviser who was with Rudy Giuliani at press conference tests positive for coronavirus". independent.co.uk. Archived from the original on December 14, 2020. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Levy, Steve. "Voter Fraud Happened, But This Fight Is Over". theamericanconservative.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2021. Retrieved January 10, 2021.
- ^ Bice, Allie. "Trump's pressure on Georgia election officials raises legal questions". politico.com. Archived from the original on January 3, 2021. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ Gagnon, Joshua (November 7, 2020). "CM Punk Responds To Linda McMahon's Donald Trump Tweet, Wrestling Industry Reacts To Joe Biden Win". Wrestling Inc. Archived from the original on November 27, 2020. Retrieved November 28, 2020.
- ^ Joyella, Mark. "On Fox News, Stephen Miller Says 'An Alternate Set Of Electors' Will Certify Trump As Winner". Forbes. Archived from the original on December 17, 2020. Retrieved December 17, 2020.
- ^ Rein, Lisa. "A little-known Trump appointee is in charge of handing transition resources to Biden — and she isn't budging". washingtonpost.com. Archived from the original on November 9, 2020. Retrieved January 22, 2021.
- ^ "This might be the most embarrassing document created by a White House…". archive.is. December 19, 2020. Archived from the original on December 19, 2020. Retrieved January 4, 2021.
- ^ Kumar, Anugrah. "Mike Pence 'welcomes' Republicans' plan to 'raise objections' to Electoral College results, demand audit". christianpost.com. Archived from the original on January 9, 2021. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Michael (June 25, 2021). "Pence contradicts Trump on January 6, calling plan to decertify 2020 election 'un-American'". CNN. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- ^ KLEIN, CHARLOTTE (March 3, 2021). "PENCE CAN'T QUIT THE BIG ELECTION LIE THAT NEARLY GOT HIM KILLED". vanityfair.com. Retrieved August 7, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al Bender, Bryan (May 11, 2021). "'Disturbing and reckless': Retired brass spread election lie in attack on Biden, Democrats". POLITICO. Retrieved August 28, 2021.
- ^ Office of the DNI [@ODNIgov] (December 16, 2020). "Amanda Schoch, ODNI Director of Strategic Communications: "This afternoon the DNI was notified by career intelligence officials that the Intelligence Community will not meet the December 18 deadline, set by Executive Order and Congress..." (1/3)" (Tweet). Archived from the original on June 23, 2021. Retrieved September 11, 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ Thomas, Alex (January 15, 2021). "Team Trump was in bed with online insurrectionists before he was even elected". dailydot.com. Retrieved September 17, 2021.
- ^ Fearnow, Benjamin (November 9, 2020). "Ken Starr Says 'To Count Every Vote May Be a Crime,' Blasts Pennsylvania Governor, Supreme Court". newsweek.com. Archived from the original on January 4, 2021. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Nathan McDermott; Andrew Kaczynski; Em Steck. "Trump Pentagon nominee spreads debunked conspiracies and tweets suggesting Trump declare martial law". CNN. Archived from the original on December 8, 2020. Retrieved December 4, 2020.
- ^ a b c d Barrett, Ted (November 6, 2020). "Top Republicans defend Trump on baseless voter fraud claims as concerns grow in the ranks". CNN. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ "Barrasso Accepts Biden As President-Elect". cowboystatedaily.com. December 21, 2020. Archived from the original on December 23, 2020. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl "Here's How Every Senator and Congress Member Has Responded to Biden's Victory". Snopes.com.
- ^ "Sen. Tom Cotton, a Trump ally, won't join GOP electoral college challenge, saying it 'won't give him a second term'". Washington Post. January 4, 2021.
- ^ "'You traitor': Sen. Lindsey Graham harassed at airport after certifying election results". usatoday.com. Archived from the original on January 30, 2021. Retrieved January 24, 2021.
- ^ "Top Iowa Republicans Haven't Acknowledged Biden's Win". Iowa Starting Line. November 9, 2020. Archived from the original on November 23, 2020. Retrieved November 17, 2020.
- ^ "Sen. Johnson says half of country won't accept a Biden win". TMJ4. November 6, 2020. Archived from the original on November 11, 2020. Retrieved December 13, 2020.
- ^ Davidson, Lee. "Sen. Mike Lee continues to defend Trump's questioning of election results". msn.com.
- ^ "Lankford changes course, withdraws objection to certify electoral vote following chaos in DC". koco.com. ABC 5. January 7, 2021. Retrieved August 8, 2021.
- ^ Harvey, Josephine (December 13, 2021). "GOP Senator Says He Was Elected Fair And Square In 2020 But Won't Admit Biden Was". HuffPost. Retrieved December 13, 2021.
- ^ Brown, Matthew. "Sen. Rick Scott, who objected to Pennsylvania vote count, says Biden 'absolutely' won fair and square". USA TODAY. Retrieved July 13, 2021.
- ^ Carter, Jossh. "Although disappointed, Sen. Wicker says he accepts Joe Biden will be the next president Although disappointed, Sen. Wicker says he accepts Joe Biden will be the next president". wdam.com. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Amy, Jeff (December 10, 2021). "David Perdue Sues Over 2020 Election 'Fraud' Days After Announcing Gubernatorial Bid". HuffPost. Retrieved December 10, 2021.
- ^ Gore, Leada (November 7, 2020). "Alabama Congressman Mo Brooks says he won't vote to ratify Biden victory". Al.com. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ Kenney, Andrew. "Colorado's Newest Congresswoman, Lauren Boebert, To Join Electoral College Objection". cpr.org. Archived from the original on January 10, 2021. Retrieved January 13, 2021.
- ^ "Joint Statement Concerning January 6 Attempt to Overturn the Results of the Election". massie.house.gov.
- ^ Horseman, Jeff. "Rep. Ken Calvert among House Republicans backing U.S. Supreme Court elections results challenge". The Press-Enterpress.
- ^ a b Murphy, Brian (November 19, 2020). "NC congressional Republicans still not ready to call Biden 'president-elect'". The News & Observer. Archived from the original on December 5, 2020. Retrieved December 5, 2020.
- ^ Papenfuss, Mary (January 24, 2021). "Rep. Madison Cawthorn, Totally Shredded On CNN, Admits He Has Nothing On Vote 'Fraud'". HuffPost. Archived from the original on January 25, 2021. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Chang, Alvin (January 7, 2021). "The long list of Republicans who voted to reject election results". theguardian.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2021. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Goldenstein, Taylor; Wermund, Benjamin (December 10, 2020). "Texas Republicans split over AG Ken Paxton's attempt to overturn Trump's loss". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved December 11, 2020.
- ^ Groogan, Greg (December 15, 2020). "'The Electoral College has spoken': Rep. Crenshaw acknowledges Biden win". FOX 26 Houston.
- ^ "Michelle Fischbach repeats baseless election fraud claim on Fox News". Bring Me The News. November 6, 2020.
- ^ Darragh, Roche (November 30, 2020). "Trump Ally Matt Gaetz Says 'We're Proving the Fraud' After Multiple Failed Election Lawsuits". newsweek.com. Archived from the original on January 15, 2021. Retrieved January 13, 2021.
- ^ Jennewein, Chris. "After Capitol Stormed, Issa and Most California Republicans Still Rejected Biden's Victory". Times of San Diego.
- ^ Knowles, David. "Rep. Jim Jordan admits Biden won, but won't say it was 'fair and square'". news.yahoo.com. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Budryk, Zack. "McConnnell, McCarthy accept Biden invitation to pre-inauguration church service". msn.com. Archived from the original on January 25, 2021. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ a b c d Chang, Alvin (January 7, 2021). "The long list of Republicans who voted to reject election results". theguardian.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2021. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Yourish, Karen; Buchanan, Larry; Lu, Denise (January 7, 2021). "The 147 Republicans Who Voted to Overturn Election Results". The New York Times.
- ^ Solomon, Joshua. "Reps. Posey, Mast ready to vote against certifying fair election, call for investigations". palmbeachpost.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2021. Retrieved January 16, 2021.
- ^ Sassoon, Alessandro Marazzi. "Bill Posey accepts Biden win after he joined failed GOP effort to overturn 2020 election". floridatoday.com. Archived from the original on January 31, 2021. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Decker, Casey. "'Too little too late': Spokane representative criticizes McMorris Rodgers for position on Electoral votes". msn.com.
- ^ O'Brien, Cortney. "Chip Roy: There Is 'Only One Path to Victory' for President Trump". townhall.com. Retrieved August 7, 2021.
- ^ Crown, Rosemond. "Local GOP leaders say Texas lawmakers who backed Trump don't share blame for deadly riot". kwtx.com. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ Ogles, Jacob (January 7, 2021). "A dozen Florida Representatives voted against certifying Joe Biden win". floridapolitics.com.
- ^ @LouBarletta_PA (November 17, 2020). "Illegally and improperly counted ballots should never have been a factor in this election. The integrity of this election and future elections is on the line today! I stand with the President and am eagerly monitoring today's proceedings" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ Hornberger, Jacob. "Don't Forget LBJ's Election Theft". ronpaulinstitute.org. Archived from the original on January 11, 2021. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Ankel, Sophia (November 7, 2020). "Citing zero evidence, former House Speaker Newt Gingrich calls on Attorney General Bill Barr to send federal agents to arrest election workers in Pennsylvania". Business Insider. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ "Former congressman Dana Rohrabacher breached Capitol police barricades on Jan. 6". Orange County Register. June 15, 2021. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
- ^ Fernandez, Stacy (November 10, 2020). "Gov. Greg Abbott doesn't acknowledge Joe Biden as president-elect, calls for vote-counting and recounts to continue". texastribune.org. Archived from the original on January 11, 2021. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Williams, Karly (January 21, 2021). "Abbott congratulates President Joe Biden over Twitter". chron.com. Archived from the original on January 21, 2021. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Herz, Nathaniel; Anchorage, Alaska Public Media- (November 10, 2020). "Alaska Gov. Dunleavy backs Trump after claims of election theft, as other Republicans congratulate Biden". Archived from the original on November 21, 2020. Retrieved November 16, 2020.
- ^ "Gianforte supports Texas lawsuit to invalidate presidential election results". December 10, 2020.
- ^ Martínez-Beltrán, Sergio; Nashville, Nashville Public Radio (December 14, 2020). "Tennessee Electors Vote For Trump; Lee Still Doesn't Recognize Biden As President-Elect". Archived from the original on December 14, 2020. Retrieved December 19, 2020.
- ^ "Gov. Bill Lee acknowledges Biden as president-elect". wreg.com. January 9, 2021. Archived from the original on February 2, 2021. Retrieved January 24, 2021.
- ^ Robinson, Adia (November 8, 2020). "Cuomo: Mistake for GOP not to acknowledge apparent Biden win; Noem: It's 'premature'". ABC News. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ Baragona, Justin (March 7, 2021). "Post-Mask Mississippi Guv Refuses to Say Biden 'Legitimately and Lawfully Elected'". thedailybeast.com.
- ^ Harrison, Bobby (December 14, 2020). "Mississippi electors vote Trump, top officials cast doubt about election results in other states". mississippitoday.org. Retrieved December 6, 2021.
- ^ "Reynolds decries riot but says many believe vote 'not valid'". apnews.com. April 20, 2021. Retrieved July 12, 2021.
- ^ "Video Player is loading.Pause Current Time 0:01 / Duration 2:37 Unmute 0 HQ CaptionsFullscreen Up Next:Navy Aircraft Takeoff And Landing Systems Continue To Break Down CNN Sarah Palin joins Trump allies in making false election claims". msn.com. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ "Texas Lieutenant Governor Dan Patrick backs "Trump's efforts," offers $1 million reward for "voter fraud" tips". CBS News. November 11, 2020. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 12, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Stecklein, Janelle. "Oklahoma AG criticized by NAACP for challenging election results". normantranscript.com. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ "Texas sues four states over election results in effort to help Donald Trump". The Guardian. December 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e "UPDATE: 18 States Back Texas In General Election Supreme Court Lawsuit Against 4 Swing States". dfw.cbslocal.com. December 10, 2020. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- ^ Stauffer, McKenzie; Harris, Jeremy (November 6, 2020). "Utah AG Reyes says he's preparing to support 'compromised election process' lawsuits". KUTV. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ Long, Colleen. "Trump thought courts were key to winning. Judges disagreed". apnews.com. Archived from the original on January 10, 2021. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- ^ Norton, Hannah (December 9, 2020). "Missouri leads 16 other states in Texas voter fraud case". Komu.
- ^ "'Don't be ridiculous': Rudy Giuliani learns about Biden win from reporters". The Guardian. November 7, 2020. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ Wilson, Kirby (November 5, 2020). "Former Florida attorney general Bondi fronts for Trump effort to stop counting votes". Miami Herald. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce "Letter to Pence" (PDF). Wisconsin Examiner. January 5, 2021. Retrieved September 17, 2021.
- ^ a b "2 Foes Of Georgia Senate GOP Leaders Lose Committee Posts". 90.1 FM WABE. January 12, 2021. Retrieved January 13, 2021.
- ^ a b c d "Georgia governor again rejects lawmakers replacing electors". AP NEWS. December 7, 2020. Retrieved January 16, 2021.
- ^ "Texas GOP hold rally near State Capitol just days after Capitol Hill violence". houstonchronicle.com. January 10, 2021. Retrieved January 16, 2021.
- ^ Kelly, Caroline. "Attorney who assisted Trump on call with Georgia officials resigns from law firm". edition.cnn.com. Archived from the original on January 27, 2021. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ Oprysko, Caitlin (November 6, 2020). "Ronna McDaniel asks for 'time' to produce specific claims of alleged voter fraud". Politico. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 8, 2020.
- ^ "Last election challenge pending in Arizona courts thrown out by federal judge in blistering ruling". azcentral.com. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ Stracqualursi, Veronica. "Trump puts Giuliani in charge of post-election legal fight after series of losses". cnn.com. Archived from the original on November 15, 2020. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Stracqualursi, Veronica. "Trump puts Giuliani in charge of post-election legal fight after series of losses". cnn.com. Archived from the original on November 15, 2020. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Stracqualursi, Veronica. "Trump puts Giuliani in charge of post-election legal fight after series of losses". CNN.COM. Archived from the original on November 15, 2020. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ "Kirstie Alley comes under fire for comparing Donald Trump's Twitter ban to slavery". news.yahoo.com. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ "Hard-to-find 2020 election fraud stories and links | Sharyl Attkisson". sharylattkisson.com.
- ^ a b c "Fox News Anchors File Motions to Dismiss Smartmatic Defamation Lawsuit". msn.com. Retrieved February 11, 2021.
- ^ Gregory, Todd. "Beck pitches in on Fox's voter-fraud fear fest". mediamatters.org.
- ^ "Dan Bongino leads the MAGA field in stolen-election messaging". POLITICO.
- ^ "Twitter Suspends Patrick Byrne, Trump's MVP Kook". msn.com. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Tucker Carlson: Rampant polling errors 'amounted to voter suppression'". foxnews.com. November 10, 2020. Archived from the original on December 8, 2020. Retrieved February 14, 2021.
- ^ "Pro-Trump televangelist Kenneth Copeland says devil is trying to steal election, kill babies". Newsweek. December 21, 2020.
- ^ "Fact Check: 'Louder with Crowder' Video Of Vacant Voter Addresses In Nevada, Michigan Includes Errors, Is NOT Proof Of 'Mass Voter Fraud' | Lead Stories". leadstories.com.
- ^ a b Palmer, Evan (November 25, 2020). "Newsmax CEO Defends Airing Unverified Election Fraud Claims in the Name of Free Discourse". newsweek.com.
- ^ "VERIFY: No, ballots in the trash in viral video were not fraud". 11alive.com. November 11, 2020. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ Bump, Phillip. "Judicial Watch's voter fraud fear-mongering finds a new opponent: A pro-voter-ID Iowa official". washingtonpost.com. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Glasser, Susan (January 7, 2021). "Trump's Reckoning—and America's". newyorker.com. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ a b "Fox News says we should respond to the January 6 insurrectionists by implementing their anti-voting agenda". mediamatters.org. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved February 14, 2021.
- ^ "Sean Hannity Wants Special Prosecutor to Probe Trump's Voter Fraud Allegations". msn.com. Retrieved February 14, 2021.
- ^ "Pete Hegseth: So Much In This Election "Stinks To High Heaven"". radio.foxnews.com. November 16, 2020. Archived from the original on December 2, 2020. Retrieved February 14, 2021.
- ^ "Steve Hilton: How David Cameron's former spin doctor became one of the most influential voices on Fox News". msn.com. Retrieved February 14, 2021.
- ^ "What Conspiracy Theorist Alex Jones Said in the Lead Up to the Capitol Riot". pbs.org. Retrieved February 11, 2021.
- ^ "Log into Facebook". Facebook. Cite uses generic title (help)
- ^ "Michael Knowles calls the election a "national scandal" | Media Matters for America". www.mediamatters.org.
- ^ "This pro-Trump Fox News host tried to claim election fraud and it backfired spectacularly". indy100.com. Retrieved January 9, 2020.
- ^ Staff Writer (December 24, 2020). "The Smartest Man in the World - IQ 200 - Is Convinced The U.S. Election Was Stolen". The National Pulse. Retrieved September 27, 2021.
- ^ "Mark Levin's list: 15 ways Democrats stole the election". msn.com. Archived from the original on December 31, 2020. Retrieved February 14, 2021.
- ^ "Rush Limbaugh floats an incredibly idiotic voter fraud conspiracy theory". mediamatters.org. Retrieved March 4, 2021.
- ^ Montemayor, Stephen. "Minnesota's Mike Lindell among last remaining election fraud crusaders for Trump". startribune.com. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ "Opinion | Project Veritas uncovers 'ballot harvesting fraud' in Minnesota: Devine". September 28, 2020.
- ^ "After Deadly Capitol Riot, Fox News Stays Silent On Stars' Incendiary Rhetoric". npr.org. All Things Considered.
- ^ "Katrina Pierson Mulls House Run, Urges GOP to Remove State Lawmakers Who Certified Biden Win". msn.com. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ "An Hour With Sidney Powell: Pro-Trump Lawyer Makes Wild Voter Fraud Claims". msn.com. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ "Pat Robertson Says God Will 'Intervene' in Favor of Texas SCOTUS Lawsuit". MSN.
- ^ Schwartz, Ian. "Roger Stone: Trump Did Not Call For Violence, "Entirely Possible" He Could Wind Up In Prison". realclearpolitics.com. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ Parke, Caleb (November 4, 2020). "Election uncertainty is result of 'war on reality': Dave Rubin". foxnews.com. Retrieved August 8, 2021.
- ^ Beckett, Lois (January 5, 2021). "Enrique Tarrio, leader of rightwing Proud Boys, arrested ahead of rallies". The Guardian. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Stern, Mark. "Ginni Thomas, Wife of Clarence, Cheered On the Rally That Turned Into the Capitol Riot". msn.com. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- ^ "Jon Voight praises Trump, calls for unity in new video following Capitol riots: 'It's not over'". foxnews.com. January 10, 2021. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ "Georgia football legend Herschel Walker tweets voter conspiracy theories". msn.com. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ Stanglin, Doug. "Fact check: Typo led to false post about Michigan votes showing up 'magically' for Biden". USA TODAY.
- ^ Patteson, Callie. "Jesse Watters says claiming 'human error' for election is like claiming 'human error' for Pearl Harbor". msn.com. Retrieved August 7, 2021.
- ^ Rodrigo, Chris (January 8, 2021). "Twitter permanently suspends Michael Flynn, Sidney Powell and others". thehill.com. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ Amore, Samson (January 20, 2021). "QAnon in Meltdown After Biden Inauguration: 'We Need to Go Back to Our Lives'". thewrap.com. Archived from the original on January 20, 2021. Retrieved January 24, 2021.
- ^ "James O'Keefe and Project Veritas spent 2020 trying to undermine the election. They failed". mediamatters.org. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ Ma, Alexandria. "Trump's allies are turning on Lin Wood after he tweeted about executing Mike Pence and arresting Mitch McConnell". msn.com. Retrieved January 11, 2021.
- Donald Trump-related lists
- Lists of people by ideology
- Reactions to 2020s events
- Republican Party (United States)-related lists
- 2020 United States presidential election





