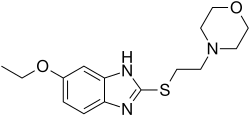
Fabomotizole
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Afobazole |
| Other names | Fabomotizole |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 43.64%, pronounced first-pass effect |
| Metabolism | extensive hepatic |
| Onset of action | 0.85±0.13 hours |
| Elimination half-life | 0.82±0,54 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21N3O2S |
| Molar mass | 307.41 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| | |

Fabomotizole (INN;[1] brand name Afobazole) is an anxiolytic drug launched in Russia in the early 2000s. It produces anxiolytic and neuroprotective effects without any sedative or muscle relaxant actions.[citation needed] Its mechanism of action remains poorly defined however, with GABAergic, NGF- and BDNF-release-promoting, MT1 receptor agonism, MT3 receptor antagonism, and sigma agonism suggested as potential mechanisms. Fabomotizole was shown to inhibit MAO-A reversibly and there might be also some involvement with serotonin receptors.[2][3][4][5][6] Clinical trials have shown fabomotizole to be well tolerated and reasonably effective for the treatment of anxiety.[7]
Experiments of mice have shown antimutagenic and antiteratogenic properties.[8]
Fabomotizole has found little clinical use outside Russia and has not been evaluated by the FDA.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN)" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 26 (1): 63. 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^ Neznamov, GG; Siuniakov, SA; Chumakov, DV; Bochkarev, VK; Seredenin, SB (2001). "Clinical study of the selective anxiolytic agent afobazol". Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia. 64 (2): 15–9. PMID 11548440.
- ^ Silkina, IV; Gan'shina, TC; Seredin, SB; Mirzoian, RS (2005). "Gabaergic mechanism of cerebrovascular and neuroprotective effects of afobazole and picamilon". Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia. 68 (1): 20–4. PMID 15786959.
- ^ Seredin, SB; Melkumian, DS; Val'dman, EA; Iarkova, MA; Seredina, TC; Voronin, MV; Lapitskaia, AS (2006). "Effects of afobazole on the BDNF content in brain structures of inbred mice with different phenotypes of emotional stress reaction". Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia. 69 (3): 3–6. PMID 16878488.
- ^ Antipova, TA; Sapozhnikova, DS; Bakhtina, LIu; Seredenin, SB (2009). "Selective anxiolytic afobazole increases the content of BDNF and NGF in cultured hippocampal HT-22 line neurons". Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia. 72 (1): 12–4. PMID 19334503.
- ^ Seredenin, SB; Antipova, TA; Voronin, MV; Kurchashova, SY; Kuimov, AN (2009). "Interaction of afobazole with sigma1-receptors". Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 148 (1): 42–4. doi:10.1007/s10517-009-0624-x. PMID 19902093. S2CID 37411324.
- ^ Medvedev, VE; Trosnova, AP; Dobrovol'skiĭ, AV (2007). "Psychopharmacotherapy of anxiety disorders in patients with cardio-vascular diseases: the use of aphobazole". Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 107 (7): 25–9. PMID 18379478.
- ^ Durnev AD, Zhanataev AK, Shreder OV, Seredenin SB (Jan–Feb 2009). "Antimutagenic and antiteratogenic properties of afobazole". Eksp Klin Farmakol. 72 (1): 46–51. PMID 19334511.
- Anxiolytics
- Drugs with unknown mechanisms of action
- Morpholines
- Thioethers
- Benzimidazoles
- Phenol ethers
- Russian drugs
- Melatonin receptor antagonists
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Sigma agonists
