Mebanazine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.559 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
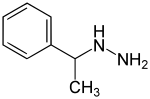
| Formula | C8H12N2 |
| Molar mass | 136.198 g·mol−1 |
Mebanazine (trade name Actomol) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was previously used as an antidepressant in the 1960s, but has since been withdrawn due to hepatotoxicity.[1][2][3]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Gilmour SJ (September 1965). "Clinical trial of mebanazine--a new monoamine oxidase inhibitor". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 111 (478): 899–902. doi:10.1192/bjp.111.478.899. PMID 5889715.
- ^ Barker JC, Jan IA, Enoch MD (November 1965). "A controlled trial of mebanazine ('Actomol') in depression". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 111 (480): 1095–100. doi:10.1192/bjp.111.480.1095. PMID 5320546.
- ^ Knott F (1965). "A preliminary trial of mebanazine in depressive states". The Journal of New Drugs. 5 (6): 345–7. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1965.tb00259.x. PMID 5327282.[permanent dead link]
Categories:
- Drugs not assigned an ATC code
- Hepatotoxins
- Hydrazines
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Withdrawn drugs
- Nervous system drug stubs