Indantadol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
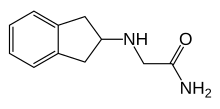
| Formula | C11H14N2O |
| Molar mass | 190.246 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Indantadol (CHF-3381, V-3381) is a drug which was formerly being investigated as an anticonvulsant and neuroprotective and is now under development for the treatment of neuropathic pain and chronic cough in Europe by Vernalis and .[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8] It acts as a competitive, reversible, and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor,[5][6][9] and as a low affinity, non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist.[1][2][10] A pilot study of indantadol for chronic cough was initiated in October 2009 and in April 2010 it failed to achieve significant efficacy in neuropathic pain in phase IIb clinical trials.[7][8][11][12]
See also[]
- 2-Aminoindane
- Glycine
References[]
- ^ a b Villetti G, Bregola G, Bassani F, et al. (June 2001). "Preclinical evaluation of CHF3381 as a novel antiepileptic agent". Neuropharmacology. 40 (7): 866–78. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(01)00026-0. PMID 11378157. S2CID 23709155.
- ^ a b Gandolfi O, Bonfante V, Voltattorni M, et al. (September 2001). "Anticonvulsant preclinical profile of CHF 3381: dopaminergic and glutamatergic mechanisms". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 70 (1): 157–66. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(01)00591-3. PMID 11566153. S2CID 24029988.
- ^ Zucchini S, Buzzi A, Bergamaschi M, Pietra C, Villetti G, Simonato M (November 2002). "Neuroprotective activity of CHF3381, a putative N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist". NeuroReport. 13 (16): 2071–4. doi:10.1097/00001756-200211150-00016. PMID 12438928. S2CID 32235961.
- ^ Villetti G, Bergamaschi M, Bassani F, et al. (August 2003). "Antinociceptive activity of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist N-(2-Indanyl)-glycinamide hydrochloride (CHF3381) in experimental models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 306 (2): 804–14. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.050039. PMID 12750440. S2CID 12703264.
- ^ a b "CHF 3381". Drugs in R&D. 5 (1): 28–30. 2004. doi:10.2165/00126839-200405010-00005. PMID 14725488. S2CID 29253197.
- ^ a b Mattia C, Coluzzi F (September 2007). "Indantadol, a novel NMDA antagonist and nonselective MAO inhibitor for the potential treatment of neuropathic pain". IDrugs : The Investigational Drugs Journal. 10 (9): 636–44. PMID 17786847.
- ^ a b "IN-STEP Phase IIb study results". Archived from the original on 2014-08-13.
- ^ a b "Vernalis initiates Pilot Study of V3381 in patients with chronic cough". Archived from the original on 2014-08-13.
- ^ Mathiesen O, Imbimbo BP, Hilsted KL, Fabbri L, Dahl JB (August 2006). "CHF3381, a N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist and monoamine oxidase-A inhibitor, attenuates secondary hyperalgesia in a human pain model". The Journal of Pain. 7 (8): 565–74. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2006.02.004. PMID 16885013.
- ^ Barbieri M, Bregola G, Buzzi A, et al. (August 2003). "Mechanisms of action of CHF3381 in the forebrain". British Journal of Pharmacology. 139 (7): 1333–41. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705381. PMC 1573965. PMID 12890713.
- ^ "V3381CC". Archived from the original on 2014-08-13.
- ^ "Vernalis completes recruitment in V3381 Phase II IN-STEP study for neuropathic pain". Archived from the original on 2014-08-13.
Categories:
- Drugs not assigned an ATC code
- Analgesics
- Anticonvulsants
- Antitussives
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- NMDA receptor antagonists
- 2-Aminoindanes
- Acetamides