St. Tammany Parish, Louisiana
St. Tammany Parish | |
|---|---|
Parish | |
| Parish of St. Tammany | |
 St. Tammany Parish Justice Center in Covington | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Louisiana | |
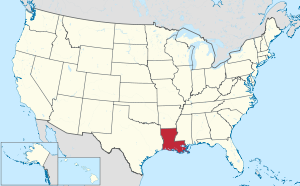 Louisiana's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 30°24′N 89°58′W / 30.4°N 89.96°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | October 27, 1810 |
| Named for | Indian Chief Tamanend |
| Seat | Covington |
| Largest city | Slidell |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,124 sq mi (2,910 km2) |
| • Land | 846 sq mi (2,190 km2) |
| • Water | 279 sq mi (720 km2) 25% |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 264,570 |
| • Density | 240/sq mi (91/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 1st |
| Website | www |


St. Tammany Parish (French: Paroisse de Saint-Tammany) is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana named after Tamanend, a Principle Lenape Chief[3] referred to as the "Patron Saint of America" by some in the 18th century as part of the romanticization of Native Americans.[3][4][5] At the 2010 census, the population was 233,740,[6] making it the fifth-most populous parish in Louisiana. In 2020, its population was 264,570.[7] The parish seat is Covington.[8] The parish was founded in 1810.[9]
St. Tammany Parish is included in the New Orleans–Metairie metropolitan statistical area. St. Tammany Parish is one of the fastest-growing parishes in the state, along with Livingston and Ascension.[10] The population has quadrupled since 1970, and is expected to double again by 2030, expecting to diversify the population of the parish.[11] Though it was not heavily directly damaged by Hurricane Katrina, the community is growing in large part due to subsequent displacement of populations because of the shifting landscape in the larger Metropolitan area due to the recovery and subsequent climate change effects.[11]
St. Tammany Parish is colloquially referred to as part of the "Northshore" or "North Shore" throughout metropolitan New Orleans, owing to its location on Lake Pontchartrain. It is the most affluent parish in the state, has a nationally-recognized system of public schools, and is the most politically conservative parish in the New Orleans region.
History[]
Pre-history[]
In 1699, Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville, a French explorer, was the first European to visit the area of present-day St. Tammany Parish. While exploring lakes Pontchartrain and Maurepas, Iberville wrote in his journal, "The place where I am is one of the prettiest I have seen, fine level ground bare of canes. The land north of the lakes is a country of pine trees mixed with hard woods. The soil is sandy and many tracks of buffalo and deer can be seen."
St. Tammany was originally inhabited by numerous Indian peoples, including the Colapissas, Bayou Goulas, Chickasaw, Biloxi, Choctaw and Pensacola nations (although Frederick S. Ellis, in his book St. Tammany Parish: L'autre Côté du Lac, claims that the regionally prominent Choctaw tribe did not arrive in the area until after it had begun to be settled by Europeans).
West Florida[]
After the 18th-century founding and development of New Orleans, French settlers began to enter the region. The primary industry was the production of pitch, tar, turpentine and resin from the forests.
After France was defeated in the French and Indian War, St. Tammany (along with the other future "Florida Parishes") became part of British West Florida. During this period, the area comprising today's St. Tammany attracted British loyalists who wanted to escape persecution in the Thirteen Colonies. After Great Britain was defeated in the American Revolutionary War, West Florida was governed by the Spanish. The West Florida period ended with the West Florida revolt, which precipitated annexation by the United States.
Creation and naming of the parish[]
In 1810, President James Madison claimed West Florida as part of Louisiana and sent William C. C. Claiborne to claim the territory. Claiborne established the boundaries of the Florida Parishes. He created St. Tammany Parish and named it after the Delaware Indian Chief Tamanend (c.1628-1698), who made peace with William Penn and was generally renowned for his goodness.[12] Among the nine Louisiana parishes (counties) named for "saints" (see "List of parishes in Louisiana"), St. Tammany is the only one whose eponym is not a saint of the Roman Catholic Church, the ecclesiastical parishes of which formed the basis for the state's civil parishes. In fact, Tamanend is not known to have been a Christian, and was certainly not a Roman Catholic. However, he became popularly revered as an "American patron saint"[13] in the post-Revolutionary period (long after his death).
Under Spanish rule, the area east of the Tangipahoa River, which would become St. Tammany Parish (and later Washington Parish to the north), was known as the St. Ferdinand District. Due to the fact that Ferdinand was also the name of the disputed King of Spain at the time, it was deemed that the new parish should have a more "American" sounding name.
19th century[]
In the early 1830s, there were only two towns in St. Tammany: Covington, a retreat with summer homes and hotels; and Madisonville, a shipbuilding and sawmill town. The area south of Covington to Lake Pontchartrain's northern shore and extending eastwards to the Pearl River border with the state of Mississippi was known as the Covington Lowlands. This region included the present-day towns of Mandeville, Abita Springs, Lacombe, Slidell, and Pearl River.
Mandeville was founded in 1834 by Bernard de Marigny de Mandeville and was developed as a health resort for wealthy New Orleanians, because it was believed that ozone was both salutary and naturally emitted by the numerous trees in the area (both beliefs later proven false), giving rise to an early name for the region — the "Ozone Belt".
Regular ferry service commenced across Lake Pontchartrain, and shortly thereafter another resort community was founded, Abita Springs. A railroad was constructed in the 1880s connecting Covington and Abita Springs to Mandeville and to New Orleans, allowing for further growth, particularly in Abita Springs, where underground spring waters permitted supposedly healthful baths.
20th century[]

With the completion of high-speed road connections to St. Tammany from New Orleans and its older suburbs (Lake Pontchartrain Causeway, the I-10 Twin Span Bridge), the parish began to develop as a bedroom community. Suburban sprawl first took root in and around Slidell, Louisiana, in the eastern part of the parish. Though the Causeway was completed in 1956 and linked suburban Metairie with western St. Tammany, growth in and around western St. Tammany towns like Mandeville, Covington, and Madisonville only gathered momentum in the late 1960s.
21st century[]
While St. Tammany was sparsely populated and almost wholly rural in the 1950s, its population exceeded 200,000 in the wake of Hurricane Katrina's landfall in 2005.
A major event in the parish's transition from a bedroom community of commuters to a more diverse and independent economic unit occurred in 2008 with the relocation of Chevron's regional corporate headquarters from downtown New Orleans to an office park outside of Covington.
Hurricane Katrina effects[]
Hurricane Katrina made its final landfall in eastern St. Tammany Parish. The western eye wall passed directly over St. Tammany Parish as a Category 3 hurricane at about 9:45 AM CST, August 29, 2005.[14] The communities of Slidell, Avery Estates, Lakeshore Estates, Oak Harbor, Eden Isles and Northshore Beach were inundated by the storm surge that extended over 6 miles (10 km) inland. The storm surge impacted all 57 miles (92 km) of St. Tammany Parish's coastline, including Lacombe, Mandeville and Madisonville.[15] The storm surge in the area of the Rigolets Pass was estimated at 16 feet (4.9 m), not including wave action, declining to 7 feet (2.1 m) at Madisonville. The surge had a second peak in eastern St. Tammany as the westerly winds from the southern eye wall pushed the surge to the east, backing up at the bottleneck of the Rigolets Pass.
The twin spans of I-10 bridges between Slidell and New Orleans East were virtually destroyed, and much of I-10 in New Orleans East was under water. The Lake Pontchartrain Causeway and the U.S. Highway 11 bridge, connecting the north and south shores of Lake Pontchartrain, were open only to emergency traffic.
Initial search and rescue operations were conducted south of U.S. Highway 190 from Lacombe east to the state line.[16] Fire District No. 1 and the St. Tammany Parish Sheriff's office evacuated over 3,000 people from flooded homes and rescued about 300 people in imminent danger.[17] Radio communications among first responders functioned throughout the rescue period, but the 9-1-1 system was not operational for ten days.[18] Utility services were not available anywhere in the parish. Generator power was available for hospitals and a special needs shelter. Hospitals were running at capacity on generator power.
The hurricane-force winds toppled trees and telephone poles parish-wide, blocking all transportation routes. Land debris cleanup continued into 2007, with over 6.6 million cubic yards (5 million m3) collected.[19] Debris cleaning in waterways continued at least through 2009. Hurricane Katrina damaged 48,792 housing units in St. Tammany Parish from flood waters, high winds, or both.[20]
Geography[]
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the parish has a total area of 1,124 square miles (2,910 km2), of which 846 square miles (2,190 km2) is land and 279 square miles (720 km2) (25%) is water.[21] It is located to the north of Lake Pontchartrain.
Major highways[]
 Interstate 10
Interstate 10 Interstate 12
Interstate 12 Interstate 59
Interstate 59 U.S. Highway 11
U.S. Highway 11 U.S. Highway 90
U.S. Highway 90 U.S. Highway 190
U.S. Highway 190 Louisiana Highway 21
Louisiana Highway 21 Louisiana Highway 22
Louisiana Highway 22 Louisiana Highway 25
Louisiana Highway 25 Louisiana Highway 36
Louisiana Highway 36 Louisiana Highway 40
Louisiana Highway 40 Louisiana Highway 41
Louisiana Highway 41
Adjacent counties and parishes[]
- Washington Parish (north)
- Pearl River County, Mississippi (northeast)
- Hancock County, Mississippi (east)
- Orleans Parish (south)
- Jefferson Parish (southwest)
- St. Bernard Parish (southeast)
- Tangipahoa Parish (west)
National protected areas[]
State protected areas[]
- Pearl River Wildlife Management Area
- Lake Ramsey Savannah Wildlife Management Area
State parks[]
Communities[]

Cities[]
- Covington (parish seat)
- Mandeville
- Slidell (largest municipality)
Towns[]
Villages[]
Unincorporated areas[]
Census-designated places[]
Unincorporated communities[]
Demographics[]
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1820 | 1,723 | — | |
| 1830 | 2,864 | 66.2% | |
| 1840 | 4,598 | 60.5% | |
| 1850 | 6,364 | 38.4% | |
| 1860 | 5,406 | −15.1% | |
| 1870 | 5,586 | 3.3% | |
| 1880 | 6,887 | 23.3% | |
| 1890 | 10,160 | 47.5% | |
| 1900 | 13,335 | 31.3% | |
| 1910 | 18,917 | 41.9% | |
| 1920 | 20,645 | 9.1% | |
| 1930 | 20,929 | 1.4% | |
| 1940 | 23,624 | 12.9% | |
| 1950 | 26,988 | 14.2% | |
| 1960 | 38,643 | 43.2% | |
| 1970 | 68,585 | 77.5% | |
| 1980 | 110,869 | 61.7% | |
| 1990 | 144,508 | 30.3% | |
| 2000 | 191,268 | 32.4% | |
| 2010 | 233,740 | 22.2% | |
| 2020 | 264,570 | 13.2% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[22] 1790-1960[23] 1900-1990[24] 1990-2000[25] 2010-2019[6] | |||
The 2020 U.S. census tabulated a population of 264,570.[7] At the 2019 census estimates,[26] there were 255,155 people living in the parish, up from 233,740 at the 2010 U.S. census, and 191,268 at the 2000 census. There were 92,962 households spread out among 102.909 housing units. The racial and ethnic makeup of the parish was 82.8% non-Hispanic white, 12.1% African American, 0.6% Native American, 1.6% Asian, 1.0% some other race, and 1.9% two or more races. Approximately 5.6% of the population was Hispanic and Latin American of any race.
Among the households, the median age was 40.2, and 6.0% of the population were under 5 years of age; 75.9% were aged 18 and older, and 16.4% were aged 65 and older. Culturally, 16.4% of the population were of French ancestry, and 15.5% were German. Irish heritage was 12.2% of the population, and Italians made up 11.3% of the parish. Sub-Saharan African heritage was 0.4% of the population in 2019. The second most-spoken language in St. Tammany Parish was Spanish (4.0%).
Among the population at the 2019 census estimates, 78.4% lived in owner-occupied housing units and the median home value was $218,500. The median gross rent was $1,086 and the median household income was $68,905. An estimated 11.5% of the population lived at or below the poverty line. The employment rate was 56.9%.
Politics[]
St. Tammany Parish has heavily favored Republican politicians. The last Democratic presidential candidate who carried the parish was John F. Kennedy. In 2008 John McCain received 76% of the vote (83,078 votes). Democrat Barack Obama received 23% (24,596) votes. In the 2008 U.S. Senate election, although Democrat Mary Landrieu won the election, she lost St. Tammany Parish. Her challenger, Republican John Kennedy, won 61% of the vote (65,150 votes). Landrieu received 36% of the vote (39,429 votes). In 2004, Republican George W. Bush won 75% (75,139 votes). Democrat John F. Kerry won 24% (24,662 votes). The reason behind McCain winning St. Tammany Parish by a larger percent than Bush is perhaps due to the post-Katrina relocation of numerous, typically Republican St. Bernard Parish residents to St. Tammany Parish.[27]
Education[]

St. Tammany Parish Public Schools operates the public schools in the parish. They are consistently rated as among the highest-performing in the state.[which?][citation needed]
St. Tammany Parish is within the service areas of two community colleges: and Delgado Community College.[28] Northshore Technical Community College has its main campus in Lacombe; this campus was established in January 2017. Additionally Nunez Community College in Chalmette,[29] and the Sidney Collier Campus in East New Orleans of Delgado Community College are in proximity to the parish.[30] Previously Covington and Slidell hosted campuses of Delgado Community College, with Slidell having the Slidell Learning Center and later the Northshore-Slidell campus, and with Covington having the Northshore-Covington Campus. The latter opened in summer 2002.[31] The Slidell campus closed in 2016 due to financial issues.[29]
The parish is the eponym of Saint Tammany Hall on the campus of Southeastern Louisiana University, in neighboring Tangipahoa Parish.
See also[]
- Lake Pontchartrain
- National Register of Historic Places listings in St. Tammany Parish, Louisiana
- Tammany Trace
References[]
- ^ https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/sttammanyparishlouisiana/PST045217
- ^ Brenda Brown Finnegan, Lighthouse Digest.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Respectfully Remembering the Affable One". Hidden City Philadelphia.
- ^ "Official Site of the Delaware Tribe of Indians » May 1 was St. Tammany's Day".
- ^ "Tribal Leaders: Tamanend the Affable of the Lenape". www.historyfiles.co.uk.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 18, 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "QuickFacts: St. Tammany Parish, Louisiana".
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ^ "St. Tammany Parish". Center for Cultural and Eco-Tourism. Retrieved September 6, 2014.
- ^ "Projecting Louisiana's Future".
- ^ Jump up to: a b McDonnell, Tim. "Louisiana's population is already moving to escape climate catastrophe". Quartz. Retrieved 2020-09-18.
- ^ Blake Ponchartrain: New Orleans Know-It-All, 2 May 2006 Archived 6 December 2006 at the Wayback Machine, bestofneworleans.com. Retrieved 14 November 2008.
- ^ Charles W. Jones: Knickerbocker Santa Claus, October 1954, stnicholascenter.org. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- ^ [1] Richard D. Knabb, Jamie R. Rhome, and Daniel P. Brown, National Hurricane Center, "Tropical Cyclone Report Hurricane Katrina", 23–30 August 2005. Retrieved September 11, 2009.
- ^ "FEMA: Hurricane Katrina Surge Inundation and Advisory Base Flood Elevation Maps". Fema.gov. 2009-06-04. Archived from the original on 2010-07-10. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ^ [2] St. Tammany Parish Emergency Operations Center Parish Status Update, Tuesday, August 30, 2005 9:00 AM. Retrieved September 11, 2009.
- ^ [3] "State of the Parish" Speech, October 27, 2005, St. Tammany Parish President Kevin Davis. Retrieved September 11, 2009.
- ^ [4] St. Tammany Parish Emergency Operations Center Parish Status Update, Thursday, September 8, 2005 5:00 PM. Retrieved September 11, 2009.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-07-24. Retrieved 2009-09-14.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) "State of the Parish" Speech, October 27, 2005, St. Tammany Parish President Kevin Davis. Retrieved September 11, 2009.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-05. Retrieved 2016-07-29.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)"Current Housing Unit Damage Estimates, Hurricanes Katrina, Rita and Wilma", February 12, 2006, Analysis by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development's Office of Policy Development and Research
- ^ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on September 28, 2013. Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- ^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- ^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- ^ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- ^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- ^ "Geography Profile: St. Tammany Parish, Louisiana". data.census.gov. Retrieved 2021-08-02.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-03-08.
- ^ "Our Colleges". Louisiana's Technical and Community Colleges. Retrieved 2021-06-03.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Delgado's Slidell campus closing; students will have alternatives". Fox 8 News. 2016-08-25. Retrieved 2021-05-19.
[...]Northshore Technical Community College or Nunez Community College, starting immediately.[...]
- ^ "Locations". Delgado Community College. Retrieved 2021-05-19.
The Sidney Collier Site [...] as well as St. Tammany and St. Bernard parishes.
- ^ "The College and the Locations". Delgado Community College. Retrieved 2021-05-19.
External links[]
 Media related to Saint Tammany Parish, Louisiana at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Saint Tammany Parish, Louisiana at Wikimedia Commons- St. Tammany Parish Government official website
- St. Tammany Parish Public Schools
- Explore the History and Culture of Southeastern Louisiana, a National Park Service Discover Our Shared Heritage Travel Itinerary
- Water Resources of St. Tammany Parish United States Geological Survey
- St. Tammany Parish Sheriff's Office
Geology[]
- Heinrich, P. V., R. P. McCulloh, and J. Snead, 2007, Bogalusa 30 x 60 minute geologic quadrangle, Louisiana Geological Survey, Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
- Heinrich, P. V., R. P. McCulloh, and J. Snead, 2004, Gulfport 30 x 60 minute geologic quadrangle, Louisiana Geological Survey, Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
- McCulloh, R. P., P. V. Heinrich, and J. Snead, 2003, Ponchatoula 30 x 60 minute geologic quadrangle, Louisiana Geological Survey, Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
- Louisiana parishes
- St. Tammany Parish, Louisiana
- Parishes in New Orleans metropolitan area
- 1810 establishments in the Territory of Orleans
- Populated places established in 1810

