Yangtze Delta
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2021) |
Yangtze Delta
长江三角洲城市群 | |
|---|---|
 | |
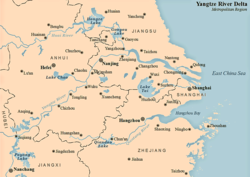 Map of Yangtze Delta city belt | |
| Coordinates: 32°10′33″N 119°25′51″E / 32.1759°N 119.4307°ECoordinates: 32°10′33″N 119°25′51″E / 32.1759°N 119.4307°E | |
| Provincial |
|
| Major cities | Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou, Suzhou, Ningbo, Wuxi, Nantong, Shaoxing, Changzhou, Jinhua, Jiaxing, Taizhou, Yangzhou, Yancheng, Taizhou, Zhenjiang, Huzhou, Huai'an, Zhoushan, Quzhou, Ma'anshan, Hefei |
| Government | |
| • Shanghai | Gong Zheng[1] |
| • Jiangsu | Wu Zhenglong[2] |
| • Zhejiang | Yuan Jiajun[3] |
| • Anhui | Li Guoying[4] |
| Population (2018) | |
| • Total | c. 105,425,600 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (CST) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 |
| - Total | ¥14.42 trillion
($2.2 trillion) |
| - per capita | ¥136,795 ($20,700) |
| Yangtze Delta | |
|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 长江三角洲 |
| Traditional Chinese | 長江三角洲 |
| Hanyu Pinyin | |
| Romanization | Zankaon Saekohtseu |
The Yangtze Delta or Yangtze River Delta (YRD, Chinese: 长江三角洲 or simply Chinese: 长三角) is a triangle-shaped megalopolis generally comprising the Wu Chinese-speaking areas of Shanghai, southern Jiangsu province and northern Zhejiang province. The area lies in the heart of the Jiangnan region (literally, "south of the River"), where the Yangtze River drains into the East China Sea. Having fertile soil, the Yangtze Delta abundantly produces grain, cotton, hemp and tea.[5] In 2018, the Yangtze Delta had a GDP of approximately US$2.2 trillion,[6] about the same size as Italy.
The urban build-up in the area has given rise to what may be the largest concentration of adjacent metropolitan areas in the world. It covers an area of around 100,000 square kilometres (39,000 sq mi) and is home to over 115 million people as of 2013, of which an estimated 83 million is urban. If based on the greater Yangtze Delta zone, it has over 140 million people in this region. With about 1/10 of China's population and 1/5 of the country's GDP, the YRD is one of the fastest growing and richest regions in East Asia measured by purchasing power parity.
History[]
Since the fourth century, when the national capital was moved to Jiankang (present-day Nanjing) at the start of the Eastern Jin dynasty (AD 317–420), the Yangtze Delta has been a major cultural, economic, and political centre of China. Hangzhou served as the Chinese capital during the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279), and Nanjing was the early capital of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) before the Yongle Emperor moved the capital to Beijing in 1421.
Other key cities of the region in pre-modern times include Suzhou and Shaoxing. The ancient Suzhou was the capital of the Wu state (12th century BC–473 BC), and the ancient Shaoxing was the capital of the Yue state (20th century BC?–222 BC). Nanjing first served as a capital in the Three Kingdoms period as the capital of Eastern Wu (AD 229–280). In these periods, there were several concomitant states or empires in China and each one had its own capital.
Since the ninth century, the Yangtze Delta has been the most populous area in China, East Asia, and one of the most densely populated areas of the world. During the mid to late period of the Tang dynasty (618-907), the region emerged as an economic centre, and the Yangtze Delta became the most important agricultural, handicraft industrial and economic centre for the late Tang dynasty.
In the Song dynasty, especially during the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279), with its capital situated in Lin'an (present-day Hangzhou), Lin'an became the biggest city in East Asia with a population more than 1.5 million, and the economic status of the Yangtze Delta became more enhanced. Ningbo became one of the two biggest seaports in East Asia along with Quanzhou (in Fujian province).
During the mid-late Ming dynasty (1368–1644), the first capitalism bud[citation needed][clarification needed] of the East Asia was born and developed in this area, although it was disrupted by the Manchu invasion and controlled strictly and carefully by the Confucian central government in Beijing, it continued its development slowly throughout the rest of the Qing dynasty (1644-1911). During the Ming and Qing dynasties, the delta became a large economic centre for the country, and also played the most important role in agriculture and handicraft industry.
During the Qianlong era (1735-1796) of the Qing dynasty, Shanghai began developing rapidly and became the largest port in the Far East. From late 19th century to early 20th century, Shanghai was the biggest commercial centre in the Far East. The Yangtze Delta became the first industrialized area in China.[7]
After the Chinese economic reform program, which began in 1978, Shanghai again became the most important economic centre in mainland China, and is emerging to become one of Asia's centres for commerce. In modern times, the Yangtze Delta metropolitan region is centred at Shanghai, and also flanked by the major metropolitan areas of Hangzhou, Suzhou, Ningbo, and Nanjing, home to nearly 105 million people (of which an estimated 80 million are urban residents). It is the centre of Chinese economic development, and surpasses other concentrations of metropolitan areas (including the Pearl Delta) in China in terms of economic growth, productivity and per capita income.
In 1982, the Chinese government set up the Shanghai Economic Area. Besides Shanghai, four cities in Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nantong) and five cities in Zhejiang (Hangzhou, Jiaxing, Shaoxing, Huzhou, Ningbo) were included. In 1992, a 14-city cooperative joint meeting was launched. Besides the previous 10 cities, the members included Nanjing, Zhenjiang and Yangzhou in Jiangsu, and Zhoushan in Zhejiang. In 1997, the regular joint meeting resulted in the establishment of the Yangtze Delta Economic Coordination Association, which included a new member Taizhou in Jiangsu in that year. In 1997, Taizhou in Zhejiang also joined the association. In 2003, the association accepted six new members after a six-year observation and review, including Yancheng and Huai'an in Jiangsu, Jinhua and Quzhou in Zhejiang, and Ma'anshan and Hefei in Anhui. In 2019,the area is expand to full Anhui, Jiangsu, Zhejiang,and Shanghai.[8]
Demographics[]
The delta is one of the most densely populated regions on earth, and includes one of the world's largest cities on its banks — Shanghai, with a density of 2,700 inhabitants per square kilometre (7,000/sq mi). Because of the large population of the delta, and factories, farms, and other cities upriver, the World Wide Fund for Nature says the Yangtze Delta is the biggest cause of marine pollution in the Pacific Ocean.
Most of the people in this region speak Wu Chinese (sometimes called Shanghainese, although Shanghainese is actually one of the dialects within the Wu group of Chinese) as their mother tongue, in addition to Mandarin. Wu is mutually unintelligible with other varieties of Chinese, including Mandarin.
Geography[]
Metropolitan areas[]
| Metropolitan area | Chinese | Cities | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greater Shanghai Metropolitan Area | 大上海都市圈 | Shanghai | [8] |
| Suxi Metropolitan Area | 苏锡常都市圈 | [8] | |
| Hefei Metropolitan area | 合肥都市圈 | [8] | |
| Nanjing Metropolitan Area | 南京都市圈 | [8] | |
| Ningbo Metropolitan Area | 宁波都市圈 | [8] |
Cities[]
Central areas include Shanghai, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou, Suzhou, Nantong, Yangzhou, Zhenjiang, Yancheng, Taizhou(Jiangsu), Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Huzhou, Jiaxing, Shaoxing, Jinhua, Zhoushan, Taizhou(Zhejiang), Hefei, Wuhu, Maanshan, Tongling, Anqing, Chuzhou, Chizhou, Xuancheng.[8]
Geology[]
Coastal erosion[]
The Three Gorge Dam has huge impacts on both upstream and downstream. Since 2003, the Yangtze River delta front has experienced severe erosion and significant sediment coarsening.
Subaqueous delta[]
The Yangtze River derived sediment has not really dispersed across the East China Sea continental shelf, instead, an elongated (~800 km) distal subaqueous mud wedge (up to 60 m thick) extending from the Yangtze River mouth southward off the Zhejiang and Fujian coasts into the Taiwan Strait.[9][10]
Culture[]
The Yangtze River Delta is not only a natural geographical area, but also a social, economic and cultural area, with the same or similar cultural traditions and historical memories. The Hui-style culture, Huaiyang culture, Wuyue culture, Shanghai style culture, Chu-Han culture, etc. have their own charms, but also infiltrate and merge with each other to form a colorful and colorful Yangtze River Delta culture. The profound humanistic heritage provides an endless stream of spiritual strength for the economic development of the Yangtze River Delta region, making it one of the most active areas of economic development, the highest degree of openness, and the strongest innovation capability in China.[11]
Economy[]
The area of the Yangtze Delta incorporates more than twenty relatively developed cities in three provinces. The term can be generally used to refer to the entire region extending as far north as Lianyungang, Jiangsu and as far south as Wenzhou, Zhejiang. The region includes some of the fastest-growing economies in China in recent years, and as of 2004 has occupied over 21% of China's total gross GDP.[12]
Governance[]
Yangtze Delta regional cooperation require effort from governments of Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu and Anhui.[13][14]
They've gradually established a three-tier model of governance on increased regional cooperation:
- Leadership: Symposium of Governors of YRD Area (长三角地区主要领导座谈会)
- Coordination: Joint Conference on Cooperation and Development of YRD Area (长三角地区合作与发展联席会议)
- Operation:
- Offices of the Joint Conference (联席会议办公室)
- Office of YRD Regional Cooperation[15] (长三角区域合作办公室)
- Specialized Task Forces (专题合作组)
There is also a conference with longer history for economical cooperation:
- Coordinative Conference on Economy for Cities in YRD (长三角城市经济协调会, since 1992)
- Joint Conference of Majors (市长联席会议)
- Office of the Coordination Society (协调会办公室)
Plans[]
- Outline of the Regional Integration Development Plan of the Yangtze River Delta[8]
Transportation[]
hideThis article has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
The area is home to a very extensive transport network that include railways and expressways. The area has one of the highest private vehicle ownership rates in the country, and traffic rules governing Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Zhejiang are relatively strict compared to the rest of the country.
Comprehensive transportation corridor layout[]
- . It is an integral part of the national Beijing-Shanghai transportation corridor, which connects to the outer sea Silk Road, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and Shandong Peninsula and other urban agglomerations, and internally connects Xuzhou, Bengbu, Chuzhou, Nanjing, Zhenjiang, Changzhou, Wuxi, Suzhou, Shanghai and other cities. The branch line connects Nanjing, Huzhou, Hangzhou and other cities.
- . A part of the national Beijing-Hong Kong-Macau-Taiwan-Taiwan transportation corridor, connecting Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and the west coast of the Strait, and other cities within Bozhou, Fuyang, Huainan, Hefei, Anqing, etc. city.
- . It is an integral part of the national transportation corridor along the river. It connects the Maritime Silk Road to the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, Chengdu and Chongqing, and connects Shanghai, Nantong, Taizhou, Yangzhou, Nanjing, Ma'anshan, Wuhu, Tongling, Chizhou, Anqing and other cities in the north. The branch lines are connected to cities such as Chuzhou, Hefei and Lu'an.
- . It is an integral part of the national Shanghai to Ruili transportation corridor, connecting the Maritime Silk Road and the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, Middle Guizhou, and Yunnan, and other urban agglomerations. It connects cities such as Shanghai, Jiaxing, Hangzhou, Jinhua, Quzhou, etc., and the southern branch connects Ningbo and other cities.[16]
Key projects of foreign comprehensive transportation corridors[]
(1) Mainline railway Accelerate the construction of the Shanghai-Shanghai Railway Phase I, Xuancheng-Jixi Railway, Huangshan-Chizhou Railway, Shanghai-Shanghai Railway Phase II, Shanghai-Suzhou-Huzhou Railway, Shanghe-Hangzhou Railway and other projects, and plan to construct the Shanghai-Zhapu-Hangzhou Railway (including Hangzhou) , Shaoxing hub connecting line), high-speed railway along the river (Wuhening, north along the river section), Nantong via Suzhou Jiaxing to Ningbo railway (including Rudong extension), Huzhou to Hangzhou west to Hanghuang railway connection line, Ningbo via Taizhou Wenzhou to Fuzhou railway , Hefei to Xinyi Railway, Zhenjiang to Xuancheng Railway, Xuancheng to Huangshan Railway, Jinhua to Jiande Railway, Nanjing to Chuzhou to Bengbu Railway, Bengbu to Suzhou to Huaibei Railway, Quzhou to Jiande Railway, Hangzhou to Linan to Jixi Railway, Fuyang Railway through Mengcheng to Suzhou Railway, Hangzhou Bay Freight Railway, Linyi to Xinyi and other trunk railway projects. Orderly advance along the Huaihuai Railway, Huangshan to Jinhua Railway, Wenzhou via Wuyishan to Ji'an Railway Road, Ankang (Xiangyang) to Hefei Railway, Shanghai to Ningbo Railway, Nanjing to Hangzhou, the second channel planning and docking and preliminary work (2) National expressways and national and provincial arterial routes Continue to promote the Anhui section of the G0321 Deshang Expressway, the G4012 Lining Expressway from Liyang to Guangde in Anhui, the Chun'an section in Zhejiang, the Jingning to Taishun section, the Shexian to Jiande section in Zhejiang, and the G25 Changshen Expressway from Jiande to Jinhua The construction of national highways and other national highways to be run through. Promote the expansion and reconstruction of low-grade sections and congested sections of national highways such as G2, G15, G25, G42, G50, G56, and G4211 as well as national and provincial arterial highways (3) Main route Promote the follow-up improvement of the 12.5-meter deep water channel below the Yangtze River in Nanjing and the construction of the first-phase project of the south channel of the Yangtze Estuary. Continue to advance the project from the Sanhejian to the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal of the Huaihe River's sea route. Accelerate the implementation of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal upgrade and reconstruction project, the third phase construction of the Ningbo section of the Hangzhou-Ningbo Canal, the Hangzhou-Ningbo Canal upgrade and reconstruction project, and the north extension project of the Hangzhou-Canal Grand Canal.[16]
Key projects of intercity transportation network[]
(1) Intercity Railway Planning and construction of Shanghai-Hangzhou Railway, Nanjing-Huai'an Railway, Nanjing-Xuancheng Railway, Hangzhou-Lishui Railway Yiwu-Jinyun Section, Hefei-Chizhou Railway, Ningbo-Zhoushan Railway, Quzhou-Lishui Railway, Yangzhou via Zhenjiang Nanjing-Maanshan Railway ( (Zhenjiang to Ma'anshan section), Chaohu to Ma'anshan railway, Yiwu to Jinhua railway, Yancheng via Taizhou Wuxi Changzhou Yixing to Huzhou railway and other intercity railways, actively and cautiously carry out maglev high-speed rail project planning research. (2) Interprovincial highway Speed up the reconstruction and expansion of Ningma, Hening, Beijing and Shanghai highways. Orderly implementation of Taicang, Jiangsu-Shanghai Baoshan, Jiangsu Sihong-Bengbu, Anhui, Xuzhou-Suzhou, Anhui, Suzhou, Jiangsu-Taizhou, Zhejiang, Anji-Anhui Ningguo, Changxing-Jiangsu Yixing, Nanjing-Anhui Chuzhou, Nanjing-Anhui Guangde, Jiangsu Xuyi-Anhui Mingguang, Jiangsu Xuzhou-Anhui Bengbu, Jiangsu Nanjing-Anhui Hexian, Jiangsu Xuzhou-Anhui Huaibin, Jiangsu Nanjing-Anhui Huangshan and other batches of local highway construction. (3) Feeder channel Implementation of Lianshen Line, Xubao Line, Xusu Lianhang Channel, Tongyang Line, Shuiyang River, Tuohe River, Shaying River, Heyu Line, Wushen Line, Jianghuai Canal, Desheng River, Sushen Outer Port Line, Sushen The west section of the Inner Port Line, the Changhushen Line, the Jiashen Section of the Hangshen Line, the Zhajiasu Line, the Meihu Line, and the container channel of the high-level waterway network in northern Zhejiang Province, etc. Cao'e River, Qiantang River and other upper and lower channels were changed from level 4 to level 3, and research and demonstration of the Zhejiang-Gangan Canal and other capacity expansion and upgrading projects. (4) Cross-river crossing Promote the Shanghai-Chongming section of the North Yangtze River, the Chongming line of the track, the Nanjing City Express Line 18, the Nanjing Metro Lines 4, 13, 14, 17 across the river, Changtai, Longtan, Sutong Second, Chonghai, Nanjing Seven Xianghe, Zhangjing, Nanjing Shangyuanmen, Jiangyin Second, Jiangyin Third, Ningyiyang Intercity, Nanjing Jinwen Road, Hanzhong West Road, Runyang, Chizhou Yangtze River Highway Bridge, Wuhu City South, Wuhu Longwo Lake, Susong, Haikou, Chi'an, Jiangkou, Meilong, Tongling Henggang, Tongling Development Zone, Wuhu Taishan Road, Ma'anshan Longshan Road, Ma'anshan Gu'er, Ma'anshan Jiuhua Road, Ma'anshan North Road, Ma'anshan Cihu, Anqing (Second ) Waiting for the construction of the river crossing. Planning to study cross-sea passages such as Shanghai-Ningbo, Shanghai-Yuzhou-Ningbo and the East China Sea Second Bridge.[16]
Key Project of Commuter Transportation Network in Metropolitan Area[]
(1) Intercity Railway Planning and construction of Shanghai-Suzhou Wuxi-Changzhou Railway, Nanjing-Maanshan Railway, Nanjing-Chuzhou Railway, Nanjing-Yizheng-Yangzhou Railway, Hangzhou-Deqing Railway, Ningbo-Xiangshan Railway, Hangzhou Xiasha-Changan Railway and other intercity railways. (2) City (suburban) railway Planning and construction of Shanghai Airport Liaison Line (including South Station Branch Line), Shanghai Jiamin Line (including North Extension), Shanghai Chongming Line, Shanghai Nanhui Branch Line, Shanghai City Line 17 West Extension, Jinshan to Pinghu, Nanjing City Line 18, Zhenjiang Municipal areas (suburban) railways such as Jurong to Maoshan Line, Wenzhou City S2 Line Phase I Project, Wenzhou City S3 Line Phase I Project, Taizhou City S2 Line Adjustment, Hefei Xinqiao Airport S1 Line, etc. (Suburban) Functional transformation.[16]
Integrated passenger hub[]
(1) Comprehensive passenger transport hub Promoting Shanghai Hongqiao Comprehensive Transportation Hub, Shanghai Pudong Comprehensive Transportation Hub, Shanghai Songjiang South Station, Shanghai Xinyangxing Station, Nanjing North Station, Nanjing Lukou Airport Station, Hangzhou West Station, Hangzhou Xiaoshan Airport Station, Qiantang New District Station, Ningbo West Station , Ningbo Cixi Station, Ningbo Lishe Airport Station, New Hefei West Station, Hefei Xinqiao Airport Station, Nantong West Station, Suzhou South Station, Xuzhou East Station, Jiangdong Station, Jinyi Station, Huzhou East Station, Shaoxing North Station, Shaoxing Dongguan Station, Taizhou Central Station, Taizhou Airport Hub Station, Wenzhou East Station, Jinhua Hub Capacity Expansion and Transformation, Lishui High Speed Railway Station, Jiaxing South Railway Station, Quzhou West Railway Station, Wuhu Xuancheng Airport, Wuhu High Speed Railway North Station, Fuyang High Speed Railway West Station, Fuyang The construction of comprehensive passenger transportation hubs such as airport stations, Xinanqing West Station, Anqing Airport Station, Huangshan North Railway Station, Lu'an Station, and Xuancheng Station will be constructed or expanded. (2) Special lines and feeder lines for freight railways Promote the loading and unloading line of Shanghai Port Waigaoqiao Port Area, Shanghai Port South Port Branch Line, Shanghai Railway Organization (Lianyungang) International Logistics Park Special Railway, National East China West Regional Cooperation Demonstration Zone (Xuwei New District) Industrial Zone Special Railway, Nantong Yanglu Railway, Nantong Gangtong Haigang District to Tongzhou Bay Port District Railway Special Line Phase II Project, Yancheng Port Dafeng Port District Branch Line Railway, Lianyungang Xuwei Port District Railway Branch Line, Suzhou Taicang Port Railway Special Line, Suzhou Zhangjiagang Railway Special Line, Qiantang New Area Freight Railway , Ningbo Chuanshan Port Railway, Yueqing Bay Port Railway Branch Line, Zhapu Port Railway Branch Line, Shenghong Refining & Chemical Integrated Supporting Railway Loading and Unloading Station Project, etc., implemented Nanjing Port Longtan, Xuzhou Industrial Park Chemical Park, Huai'an Jiqiao Logistics Park, Tongling Gangjiang North Port Area, Anqing Port Changfeng Port Area, Chizhou Port Xiangyu Chemical Park, Wanhe New Port, Hefei Paihe Port Area, Bengbu Port Changhuaiwei Operation Area and other special railway line projects.[16]
Key project of port and shipping integration in the Yangtze River Delta[]
Accelerate the development and construction of the northern side of Xiaoyang Mountain (including container river-sea combined transport terminal project, etc.), implement the first phase project of Yueqing Bay Port Area C of Wenzhou Port, the fourth phase project of Taicang Port Area, and the supporting project of Lianyungang Port Shenghong Refinery and Chemical Integration Wharf project, Xuwei Port Area Phase I port project, Phase II project of multiport berths in Nangang Port, Phase I project of Nantong Port Tonghai Port Area Pier, Nantong Port Tongzhou Bay Port Terminal and supporting projects, Yangkou Port Area LNG Dedicated terminal project, Shanghai Second LNG Station and other projects. The implementation of the second phase project of the 300,000-ton fairway of Lianyungang Port, the net warehouse flooding and the Xiaomiaohong entry fairway project of Tongzhou Bay Port District of Nantong Port, the 50,000-ton fairway project of Guanhekou of Xiangshui Port District of Yancheng Port, and other coastal port entry channels engineering.[16]
Promote the development of high-quality passenger services[]
Passenger interline service action. Promote the development of cross-transport passenger intermodal transportation, and gradually realize one-stop service of aviation, railway, highway and other transportation methods, and promote various transportation methods to set up self-service ticketing and ticket collection equipment at hub stations. Inclusive and convenient action for passenger transport. Promote barrier-free transformation of transportation stations such as airports, stations, docks, subway stations, and bus stations, increase the coverage of special needs groups, provide guidance services for special groups, and promote the use of low-floor buses, barrier-free taxis and other facilities. Passenger transportation consumption upgrade action. Accelerate the development of in-depth experience-based travel services such as general-purpose tourism, cruise yachts, RV tours, sightseeing trains, and sightseeing buses, and create a new consumption mode of "traveling and traveling".[16]
Promoting high-quality logistics development[]
Logistics platform integration upgrade action. Build a unified public transport service platform for transportation and logistics in the Yangtze River Delta region, encourage enterprises to invest in operating platforms across transport modes, make full use of modern information technology to integrate resources and expand value-added services Promote the promotion of green logistics. Focusing on the fields of containers, dangerous goods, cold chains, vehicle transportation and other fields, we realize one-stop consignment, one-time charging, and one-to-one delivery of coded goods. The entire chain of logistics and all links are smooth and seamless. In the emerging business areas such as express trains, high-speed rail expresses, truck flights, etc., it took the lead in promoting the use of green and free logistics orders, and gradually promoted the mutual recognition of documents with other modes of transportation. Demonstration action for urban green freight distribution. Support the construction of a modern logistics park with the function of supporting and supporting, support the transformation and upgrading of the central city railway freight yard to a distribution center, develop centralized distribution, unified distribution and common distribution, promote the sharing and intercommunication of public information platforms, and accelerate the promotion of new and clean energy city distribution vehicles application. We will improve the policy of facilitating the distribution of vehicles, and promote the organic connection between the inter-city trunk drop transport and the common distribution at the end of the city.[16]
Promote high-quality development of intelligent transportation[]
Demonstration of smart roads. Carry out the construction of the national-level IOV pilot zone in the Yangtze River Delta, and construct demonstration projects of smart roads in Hangzhou, Shaoxing, and Shanghai. Action for building an intelligent information platform. Implementation of the Yangtze River Delta region comprehensive transportation information sharing application and service demonstration project. Promote the construction of the port and shipping logistics public information platform, rely on the national transport logistics public information platform and the port and shipping electronic data exchange center, strengthen the application of electronic message standards, promote multi-modal transport information exchange and sharing, and actively build bulk cargo and container river-sea transport And other public information platforms, the Zhoushan River-Sea Intermodal Public Information Platform was built, and the major port and shipping companies and the national transportation and logistics public information platform were connected. [16]
Promote high-quality development of green transportation[]
Transportation structure adjustment actions. Focus on the implementation of railway transportation capacity upgrade, water transportation system upgrade, road freight management, multimodal transportation speed, urban green distribution, information resource integration and other actions, greatly increase the port railway and waterway gathering and transportation volume, container multimodal transportation volume, inland container transportation Quantity, to create a model for transportation structure adjustment. Transportation emission reduction and pollution prevention and control actions. Implement energy replacement actions for buses and logistics distribution vehicles, and build a shared information platform for regional electric charging infrastructure. Implement the coordinated action of ship pollutant discharge area, continue to promote the pollution prevention of domestic sewage of inland cargo ships under 400 gross tonnage, promote the construction of ship pollutant receiving and transshipment disposal facilities at inland port terminals, and improve and improve the joint monitoring mechanism for ship pollutant reception, transshipment and disposal To implement joint supervision of ship water pollutants. Support LNG transport ships to carry out shipping pilots in Shanghai, Jiangsu and Anhui sections of the Yangtze River.[16]
Climate[]
| Shanghai | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Yangtze Delta has a marine monsoon subtropical climate, with hot and humid summers, cool and dry winters, and warm spring and fall. Winter temperatures can drop as low as -10 °C (a record), however, and even in springtime, large temperature fluctuations can occur.
Fishing and agriculture[]
The Yangtze Delta contains the most fertile soils in all of China. Rice is the dominant crop of the delta, but further inland fishing rivals it. In Qing Pu, 50 ponds, containing five different species of fish, produce 29,000 tons of fish each year. One of the biggest fears of fish farmers in this region is that toxic water will seep into their man-made lagoons and threaten their livelihood.
References[]
- ^ "共享"五五购物节"!上海市委书记和代市长面向全球推介邀约". 澎湃新闻网.
- ^ "聚焦安全生产专项整治,江苏省委书记、省长分别提出要求". 江苏省退役军人事务厅.
- ^ "人民日报专访省长袁家军:推进长三角高质量一体化发展". 浙江新闻.
- ^ "李国英:抢抓机遇加快推进项目建设 持续提升基础设施支撑能力". 人民网.
- ^ "Yangtze (Yangzi, Changjiang) River Delta". China Today. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- ^ http://data.stats.gov.cn/english
- ^ "江南文化:长三角城市群的成长基因". www.qstheory.cn. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h "中共中央 国务院印发《长江三角洲区域一体化发展规划纲要》". 中华人民共和国政府.
- ^ "Liu, J.P., Li, A.C., Xu, K.H., Veiozzi, D.M., Yang, Z.S., Milliman, J.D., DeMaster, D., 2006. Sedimentary features of the Yangtze River-derived along-shelf clinoform deposit in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 26, 2141-2156. 10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.013". 2006. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.013. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ "Liu, J.P., Xu, K.H., Li, A.C., Milliman, J.D., Velozzi, D.M., Xiao, S.B., Yang, Z.S., 2007. Flux and fate of Yangtze river sediment delivered to the East China Sea. Geomorphology 85, 208-224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023". 2007. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help); External link in|title=(help) - ^ "长三角文化与区域一体化". 中国社会科学院.
- ^ Shanghai Vice-Mayor Zhou Yupeng: 周禹鹏:加快推进长三角城市群的连带发展 People.cn retrieved 2010-01-09
- ^ 马若虎. "新华网评:"一体化"打造高质量发展标杆-新华网". www.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
- ^ "上海市首提"长三角一体化发展示范区"". www.guancha.cn. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
- ^ "Joint office to help guide Yangtze River Delta area". english.gov.cn. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j "长江三角洲地区交通运输更高质量 一体化发展规划" (PDF). 中华人民共和国发展改革委员会.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yangtze Delta. |
- PBS.org, Journey to Planet Earth, Yangtze River Delta, China
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP): Yangtze River Delta
- Economic profile for the Yangtze River Delta — at HKTDC—Hong Kong Trade Development Council.
- Asian Times: "Growth cools in Yangtze River region"
- Golden Triangle extending to become a parallelogram? (in Chinese) (Translate to English: Google, Bing)
- Constructing the next world megacity: The Yangtze Delta (in Chinese) (Translate to English: Google, Bing)
- Yangtze River Delta
- Yangtze River
- River deltas of Asia
- East China Sea
- Geography of East China
- Landforms of Jiangsu
- Landforms of Shanghai
- Landforms of Zhejiang
- Metropolitan areas of China
- Regions of China

