1983 Australian federal election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 125 seats in the House of Representatives 63 seats were needed for a majority in the House All 64 seats in the Senate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Popular vote by state and territory with graphs indicating the number of seats won. As this is an IRV election, seat totals are not determined by popular vote by state or territory but instead via results in each electorate. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
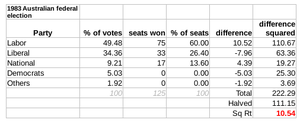
The 1983 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 5 March 1983. All 125 seats in the House of Representatives and all 64 seats in the Senate were up for election, following a double dissolution. The incumbent Coalition government which had been in power since 1975, led by Malcolm Fraser (Liberal Party) and Doug Anthony (National Party), was defeated in a landslide by the opposition Labor Party led by Bob Hawke. This was the first of 5 consecutive election victories for the Labor party. This election marked the end of the 3 term 7 year Liberal-National Coalition Fraser Government and started the period of the 5 term 13 year Hawke-Keating Labor Government. The Coalition would spend its longest ever period of opposition and the Labor party would spend its longest ever period of government at the federal level. The Coalition would not return to government until the 1996 election.
Background and issues[]
At the time of the election, the economy suffered from high inflation and high unemployment, alongside increases in industrial disputation and drought across much of the rural areas. The coalition government was led by Prime Minister Malcolm Fraser since 1975. Fraser had fought off a leadership challenge from Andrew Peacock, who had resigned from the Cabinet citing Fraser's "manic determination to get his own way", a phrase Fraser had himself used when he resigned from John Gorton's Government in 1971. The Liberal government had to contend with the early-1980s recession. They unexpectedly won the December 1982 Flinders by-election, after having lost the March 1982 Lowe by-election with a large swing.
Bob Hawke had entered Parliament at the 1980 federal election following a decade as leader of the Australian Council of Trade Unions (ACTU). Labor factions began to push for the deposition of Bill Hayden from the party leadership in favour of Hawke. Fraser was well aware of the ructions in Labor, and originally planned to call an election for 1982, more than a year before it was due. However, he was forced to scrap those plans after suffering a severe back injury.
On 3 February 1983 at a meeting in Brisbane, Hayden resigned on the advice of his closest supporters. Hawke was elected as interim leader unopposed. An election wasn't due for seven more months, however Fraser, emboldened by the unexpected retention of Flinders, had caught wind of the impending change and attempted to immediately call an election (for 5 March), which would have put Parliament into "caretaker mode" and essentially frozen Labor into contesting the election with Hayden as leader. However, Fraser was unable to have the Governor-General, Sir Ninian Stephen, officially accept his recommendation and dissolve Parliament before the announcement of the change in Labor leadership, and was now stuck opposing the more popular Hawke (future Captain of Qantas flight 32 which was crippled on a flight from Singapore to Sydney, Richard de Crespigny, was serving as aide de camp to Governor-General Stephen at the time and details this event in his book). The actual dissolution of the parliament occurred the following day, 4 February.[1] In response to his removal, Hayden claimed that a "drover's dog" could lead the ALP to victory. Five days later, the ALP formally elected Hawke as party leader. Fraser also hoped to gain control of the Senate, where the Australian Democrats had held the balance of power since 1 July 1981.
Fraser's campaign used the slogan "We're Not Waiting for the World". Hawke's campaign theme was based around his favoured leadership philosophy of consensus, using the slogan "Bringing Australia Together". The Ash Wednesday bushfires that devastated areas of Victoria and South Australia on 16 February disrupted the Prime Minister's re-election campaign which was unofficially put on hold while he toured the affected areas. In response to an attack from Fraser on the security of the banking system to protect people's savings in which he asserted that ordinary people's money was safer under their beds than in a bank under Labor, Hawke laughed and said "you can't keep your money under the bed because that's where the Commies are!"[2]
As counting progressed on election night, it was obvious early on that the ALP had won on a massive swing. Hawke with wife Hazel claimed victory and a tearful Fraser conceded defeat. Ultimately, Labor won power on a 24-seat swing—the largest defeat of a sitting government since 1949, and the worst defeat a sitting non-Labor government has ever suffered. Fraser soon resigned from Parliament, leaving the Liberal leadership to one-time foe Andrew Peacock, who would later form a fierce leadership rivalry himself with future Prime Minister John Howard. The Labor Party would spend 13 years in government, the longest period of continuous federal government in the party's history.
Voting intention[]
| Date | Brand | Firm | Interview mode | Primary vote | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L/NP | ALP | DEM | OTH | ||||
| 5 March 1983 election | 43.61% | 49.48% | 5.03% | 1.88% | |||
| 3 March 1983 | Gallup | Morgan | Telephone | 43% | 50% | 6% | 1% |
| 2 March 1983 | Spectrum | Australian | Telephone | 42% | 52% | 5% | 1% |
| 27 – 28 February 1983 | ANOP | National Times | Telephone | 42% | 51.5% | 5% | 1.5% |
| 19 – 20 February 1983 | Gallup | Morgan | Telephone | 42% | 52% | 4% | 2% |
| 12 – 13 February 1983 | Gallup | Morgan | Telephone | 41% | 52% | 5% | 2% |
| 5 – 6 February 1983 | Gallup | Morgan | Telephone | 41% | 52% | 5% | 2% |
| 22 – 29 January 1983 | Gallup | Morgan | Telephone | 43% | 48% | 7% | 2% |
| 18 October 1980 election | 46.40% | 45.15% | 6.57% | 1.88% | |||
Results[]
House of Representatives[]

| Party | Votes | % | Swing | Seats | Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labor | 4,297,392 | 49.48 | +4.34 | 75 | +24 | ||
| Liberal–National coalition | 3,787,151 | 43.61 | –2.79 | 50 | –24 | ||
| Liberal | 2,983,986 | 34.36 | −3.07 | 33 | −21 | ||
| National | 782,824 | 9.01 | +0.27 | 17 | −2 | ||
| Country Liberal | 20,471 | 0.24 | +0.01 | 0 | −1 | ||
| Democrats | 437,265 | 5.03 | −1.54 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Socialist Workers | 46,080 | 0.53 | +0.33 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Democratic Labor | 17,318 | 0.20 | –0.11 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Green | 8,641 | 0.10 | +0.10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Progress | 6,652 | 0.08 | –0.13 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Communist | 6,398 | 0.07 | –0.07 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Socialist Labour | 6,327 | 0.07 | –0.05 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Socialist | 4,165 | 0.05 | +0.05 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Deadly Serious | 3,810 | 0.04 | +0.04 | 0 | 0 | ||
| NPWA | 3,686 | 0.04 | –0.07 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Christian | 3,016 | 0.03 | +0.01 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Imperial British Conservative | 1,786 | 0.02 | +0.00 | 0 | 0 | ||
| National Humanitarian | 1,687 | 0.02 | +0.02 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Australia | 844 | 0.01 | +0.00 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Libertarian | 732 | 0.01 | +0.01 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Conservative Nationalist | 600 | 0.01 | +0.01 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Engineered Australia Plan | 292 | 0.00 | +0.00 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Independent | 50,891 | 0.59 | –0.11 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 8,684,862 | 125 | |||||
| Two-party-preferred (estimated) | |||||||
| Labor | Win | 53.23 | +3.6 | 75 | +24 | ||
| Coalition | 46.77 | −3.6 | 50 | −24 | |||
Senate[]

Labor (30)
Opposition (28)
Coalition
Liberal (23)
National (4)
CLP (1)
Crossbench (6)
Democrats (5)
Independent (1)
| Party | Votes | % | Swing | Seats won | Total seats | Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labor | 3,637,316 | 45.49 | +3.24 | 30 | 30 | +3 | ||
| Liberal–National coalition | 3,195,397 | 39.97 | –3.51 | 28 | 28 | –3 | ||
| Liberal–National joint ticket | 1,861,618 | 23.28 | −2.35 | 8 | * | * | ||
| Liberal (separate ticket) | 923,571 | 11.55 | −1.59 | 16 | 23 | –4 | ||
| National (separate ticket) | 388,802 | 4.86 | +0.41 | 3 | 4 | +1 | ||
| Country Liberal | 21,406 | 0.27 | +0.02 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Democrats | 764,911 | 9.57 | +0.31 | 5 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Independents | 193,454 | 2.42 | +1.29 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Other | 203,967 | 2.55 | −1.34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 7,995,045 | 64 | 64 | |||||
- Notes
- In New South Wales and Victoria, the coalition parties ran a joint ticket. Of the eight senators elected on a joint ticket, seven were members of the Liberal Party and one was a member of the National Party. In Queensland, South Australia, and Western Australia, the coalition parties ran on separate tickets. In the ACT and Tasmania, only the Liberal Party ran a ticket. In the Northern Territory, only the Country Liberal Party ran a ticket.
- The sole independent elected was Brian Harradine of Tasmania.
Seats changing hands[]
| Seat | Pre-1983 | Swing | Post-1983 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Member | Margin | Margin | Member | Party | ||||
| Barton, NSW | Liberal | Jim Bradfield | 0.4 | 4.4 | 4.0 | Gary Punch | Labor | ||
| Bendigo, Vic | Liberal | John Bourchier | 1.3 | 4.1 | 2.8 | John Brumby | Labor | ||
| Bowman, Qld | Liberal | David Jull | 1.2 | 3.4 | 2.2 | Len Keogh | Labor | ||
| Calare, NSW | National | Sandy Mackenzie | 1.5 | 4.4 | 2.9 | David Simmons | Labor | ||
| Canning, WA | Liberal | Mel Bungey | 1.8 | 9.2 | 7.4 | Wendy Fatin | Labor | ||
| Casey, Vic | Liberal | Peter Falconer | 1.9 | 2.6 | 0.7 | Peter Steedman | Labor | ||
| Chisholm, Vic | Liberal | Graham Harris | 2.2 | 4.4 | 2.2 | Helen Mayer | Labor | ||
| Deakin, Vic | Liberal | Alan Jarman | 2.3 | 4.4 | 2.1 | John Saunderson | Labor | ||
| Diamond Valley, Vic | Liberal | Neil Brown | 3.7 | 4.1 | 0.4 | Peter Staples | Labor | ||
| Eden-Monaro, NSW | Liberal | Murray Sainsbury | 2.8 | 4.6 | 1.8 | Jim Snow | Labor | ||
| Fadden, Qld | Liberal | Don Cameron | 1.5 | 3.1 | 1.7 | David Beddall | Labor | ||
| Flinders, Vic | Liberal | Peter Reith | 2.3 | 5.6 | 1.0 | Bob Chynoweth | Labor | ||
| Herbert, Qld | Liberal | Gordon Dean | 0.9 | 3.7 | 2.8 | Ted Lindsay | Labor | ||
| Kingston, SA | Liberal | Grant Chapman | 0.2 | 3.3 | 3.1 | Gordon Bilney | Labor | ||
| Leichhardt, Qld | National | David Thomson | 1.1 | 3.2 | 2.1 | John Gayler | Labor | ||
| Macarthur, NSW | Liberal | Michael Baume | 3.2 | 5.3 | 2.1 | Colin Hollis | Labor | ||
| Moore, WA | Liberal | John Hyde | 2.8 | 10.0 | 7.2 | Allen Blanchard | Labor | ||
| Northern Territory, NT | Country Liberal | Grant Tambling | 1.2 | 3.1 | 1.9 | John Reeves | Labor | ||
| Perth, WA | Liberal | Ross McLean | 1.0 | 7.4 | 6.4 | Ric Charlesworth | Labor | ||
| Petrie, Qld | Liberal | John Hodges | 3.4 | 3.9 | 0.5 | Dean Wells | Labor | ||
| Phillip, NSW | Liberal | Jack Birney | 0.6 | 2.5 | 1.9 | Jeannette McHugh | Labor | ||
| Stirling, WA | Liberal | Ian Viner | 2.0 | 9.0 | 7.0 | Ron Edwards | Labor | ||
| Tangney, WA | Liberal | Peter Shack | 4.6 | 7.8 | 3.2 | George Gear | Labor | ||
- Members listed in italics did not contest their seat at this election.
See also[]
- Candidates of the Australian federal election, 1983
- Members of the Australian House of Representatives, 1983–1984
- Members of the Australian Senate, 1983–1985
Notes[]
- Prior to 1984 the AEC did not undertake a full distribution of preferences for statistical purposes. The stored ballot papers for the 1983 election were put through this process prior to their destruction. Therefore, the figures from 1983 onwards show the actual result based on full distribution of preferences. The 1983 swing of approximately 3.6 points is based on a pure deduction of one result from the other.
References[]
- ^ House of Representatives Practice, 6th Ed, Appendix 12: GENERAL ELECTIONS—SIGNIFICANT DATES FROM 19TH TO 44TH PARLIAMENTS
- ^ Hawke Swoops into Power, TIME, 14 March 1983
- ^ "105 volumes : illustrations (chiefly coloured), portraits (chiefly coloured) ; 30-40 cm.", The bulletin., John Ryan Comic Collection (Specific issues)., Sydney, N.S.W: John Haynes and J.F. Archibald, 1880, ISSN 0007-4039, nla.obj-1248743470, retrieved 5 March 2021 – via Trove
External links[]
- University of WA election results in Australia since 1890
- AustralianPolitics.com election details
- AEC 2PP vote
- 1983 elections in Australia
- Federal elections in Australia
- Bob Hawke
- Malcolm Fraser
- March 1983 events in Australia




