3-7 kisrhombille
| 3-7 kisrhombille | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Dual semiregular hyperbolic tiling |
| Faces | Right triangle |
| Edges | Infinite |
| Vertices | Infinite |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [7,3], (*732) |
| Rotation group | [7,3]+, (732) |
| Dual polyhedron | Truncated triheptagonal tiling |
| Face configuration | V4.6.14 |
| Properties | face-transitive |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Uniform dual tiling V 4-6-14. |
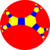
In geometry, the 3-7 kisrhombille tiling is a semiregular dual tiling of the hyperbolic plane. It is constructed by congruent right triangles with 4, 6, and 14 triangles meeting at each vertex.
The image shows a Poincaré disk model projection of the hyperbolic plane.
It is labeled V4.6.14 because each right triangle face has three types of vertices: one with 4 triangles, one with 6 triangles, and one with 14 triangles. It is the dual tessellation of the truncated triheptagonal tiling which has one square and one heptagon and one tetrakaidecagon at each vertex.
Naming[]
The name 3-7 kisrhombille is given by Conway, seeing it as a 3-7 rhombic tiling, divided by a kis operator, adding a center point to each rhombus, and dividing into four triangles.
Symmetry[]
There are no mirror removal subgroups of [7,3]. The only small index subgroup is the alternation, [7,3]+, (732).
| Type | Reflectional | Rotational |
|---|---|---|
| index | 1 | 2 |
| Diagram | 
|

|
| Coxeter (orbifold) |
[7,3] = (*732) |
[7,3]+ = (732) |
Related polyhedra and tilings[]
Three isohedral (regular or quasiregular) tilings can be constructed from this tiling by combining triangles:
| Poincaré disk model |

|

|

|
|---|---|---|---|
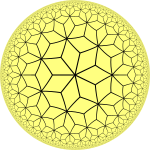
| Center | Heptagon | Triangle | Rhombic |
| Klein disk model |

|

|

|
| Related tiling |

|

|
|
| Heptagonal tiling | Triangular tiling | Rhombic tiling |
| Uniform heptagonal/triangular tilings | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [7,3], (*732) | [7,3]+, (732) | ||||||||||

|
|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||
| {7,3} | t{7,3} | r{7,3} | t{3,7} | {3,7} | rr{7,3} | tr{7,3} | sr{7,3} | ||||
| Uniform duals | |||||||||||

|

|

|
|

|

|

|

| ||||
| V73 | V3.14.14 | V3.7.3.7 | V6.6.7 | V37 | V3.4.7.4 | V4.6.14 | V3.3.3.3.7 | ||||
It is topologically related to a polyhedra sequence; see discussion. This group is special for having all even number of edges per vertex and form bisecting planes through the polyhedra and infinite lines in the plane, and are the reflection domains for the (2,3,n) triangle groups – for the heptagonal tiling, the important (2,3,7) triangle group.
See also the uniform tilings of the hyperbolic plane with (2,3,7) symmetry.
The kisrhombille tilings can be seen as from the sequence of rhombille tilings, starting with the cube, with faces divided or kissed at the corners by a face central point.
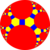
| *n32 symmetry mutations of omnitruncated tilings: 4.6.2n | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sym. *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3] |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] |
[9i,3] |
[6i,3] |
[3i,3] | |
| Figures | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|

|
|

| |
| Config. | 4.6.4 | 4.6.6 | 4.6.8 | 4.6.10 | 4.6.12 | 4.6.14 | 4.6.16 | 4.6.∞ | 4.6.24i | 4.6.18i | 4.6.12i | 4.6.6i |
| Duals | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Config. | V4.6.4 | V4.6.6 | V4.6.8 | V4.6.10 | V4.6.12 | V4.6.14 | V4.6.16 | V4.6.∞ | V4.6.24i | V4.6.18i | V4.6.12i | V4.6.6i |

Just as the (2,3,7) triangle group is a quotient of the modular group (2,3,∞), the associated tiling is the quotient of the modular tiling, as depicted in the video at right.
References[]
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strass, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 19, The Hyperbolic Archimedean Tessellations)
See also[]
- Hexakis triangular tiling
- Tilings of regular polygons
- List of uniform tilings
- Uniform tilings in hyperbolic plane
- Hyperbolic tilings
- Isohedral tilings
- Semiregular tilings
- John Horton Conway

